Abstract
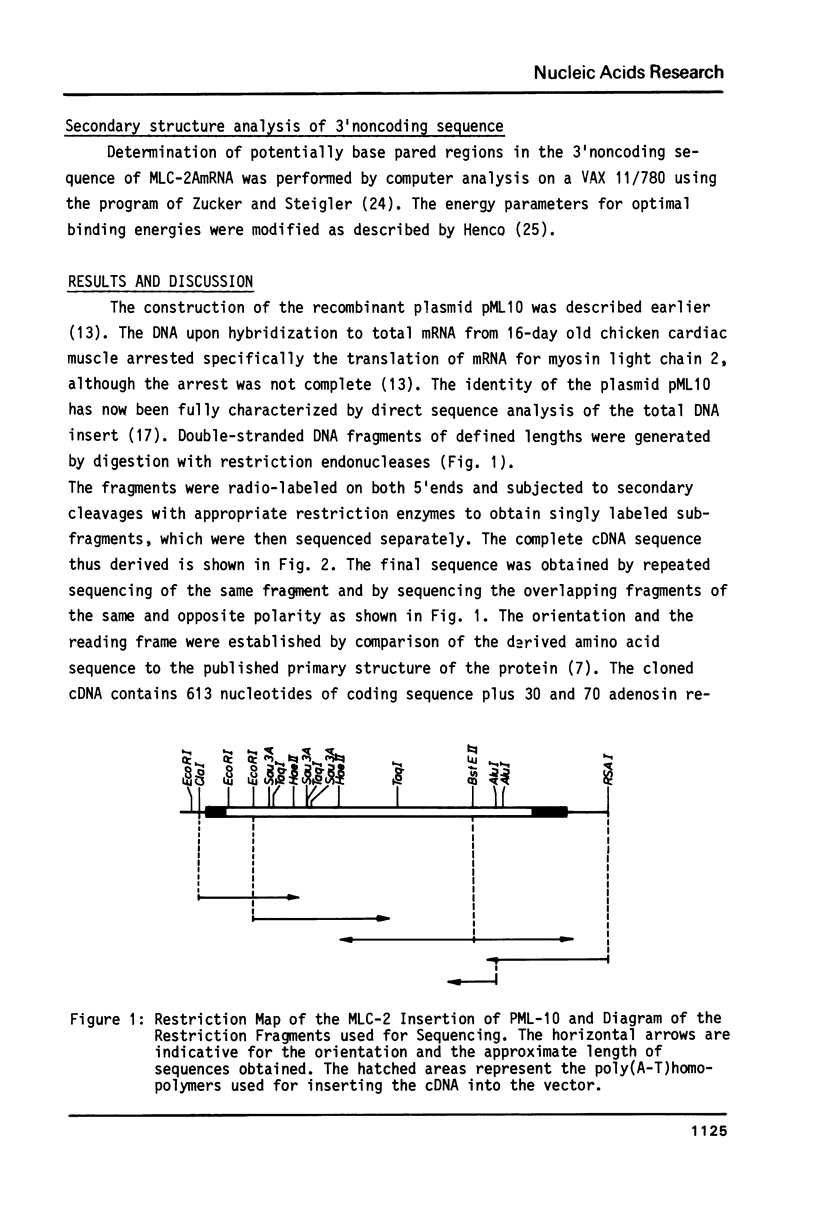
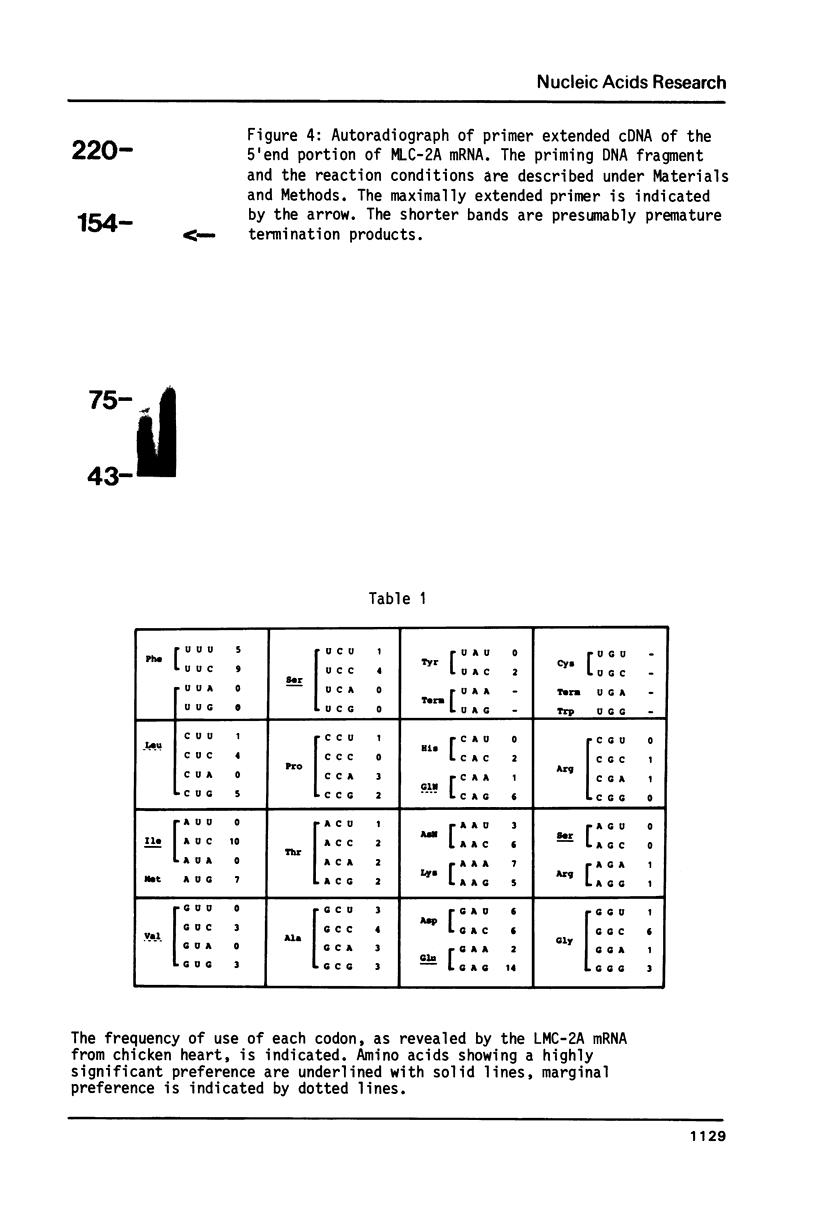
The nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone (pML10) for chicken cardiac myosin light chain is described. The cDNA insert contains 613 nucleotides representing the entire coding sequence, with the exception of nine NH2-terminal amino acids, and the full 3'-non-coding region of 146 nucleotides. The missing 5' terminus of the mRNA, not represented in the clone pML10, was obtained by extension of the cDNA using a 43 nucleotide long internal EcoR1 fragment as a primer. The non-coding region contains several direct and inverted repeated sequences and the polyadenylation signal sequence AATAAA. The coding portion exhibits non-random usage of synonymous codons with a strong bias for codons ending in G and C.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold H. H., Siddiqui M. A. Cloning of synthetic deoxyribonucleic acid that codes for embryonic cardiac myosin light-chain polypeptide. Biochemistry. 1979 Dec 11;18(25):5641–5647. doi: 10.1021/bi00592a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazaral M., Helinski D. R. Circular DNA forms of colicinogenic factors E1, E2 and E3 from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 14;36(2):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90374-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deacon N. J., Shine J., Naora H. Complete nucleotide sequence of a cloned chicken alpha-globin cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1187–1199. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C., Maniatis T. The primary structure of rabbit beta-globin mRNA as determined from cloned DNA. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):571–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Duerinck F., Haegeman G., Iserentant D., Merregaert J., Min Jou W., Molemans F., Raeymaekers A., Van den Berghe A. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage MS2 RNA: primary and secondary structure of the replicase gene. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):500–507. doi: 10.1038/260500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katcoff D., Nudel U., Zevin-Sonkin D., Carmon Y., Shani M., Lehrach H., Frischauf A. M., Yaffe D. Construction of recombinant plasmids containing rat muscle actin and myosin light chain DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):960–964. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller L. R., Emerson C. P., Jr Synthesis of adult myosin light chains by embryonic muscle cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1020–1024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick-Jones J. The subunit structure of gizzard myosin. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Mar 15;265(867):183–189. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1973.0021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. L., Jukes T. H. Non-Darwinian evolution. Science. 1969 May 16;164(3881):788–798. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3881.788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maita T., Umegane T., Kato Y., Matsuda G. Amino-acid sequence of the L-1 light chain of chicken cardiac-muscle myosin. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):565–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda G., Maita T., Kato Y., Chen J. I., Umegane T. Amino acid sequences of the cardiac L-2A, L-2B and gizzard 17 000-Mr light chains of chicken muscle myosin. FEBS Lett. 1981 Dec 7;135(2):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80789-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrie W. T., Perry S. V. An electrophoretic study of the low-molecular-weight components of myosin. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;119(1):31–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1190031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani M., Nudel U., Zevin-Sonkin D., Zakut R., Givol D., Katcoff D., Carmon Y., Reiter J., Frischauf A. M., Yaffe D. Skeletal muscle actin mRNA. Characterization of the 3' untranslated region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):579–589. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik-David H., Hay N., Aloni Y. Site of premature termination of late transcription of simian virus 40 DNA: enhancement by 5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2743–2747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockdale F. E., Raman N., Baden H. Myosin light chains and the developmental origin of fast muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):931–935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroynowski I., Yanofsky C. Transcript secondary structures regulate transcription termination at the attenuator of S. marcescens tryptophan operon. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):34–38. doi: 10.1038/298034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Brown D. D. Isolation and identification of the messenger RNA for silk fibroin from Bombyx mori. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 14;63(3):409–429. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90437-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Butler-Browne G. S., Gros F. Identification of a novel form of myosin light chain present in embryonic muscle tissue and cultured muscle cells. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):415–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



