Abstract
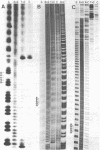
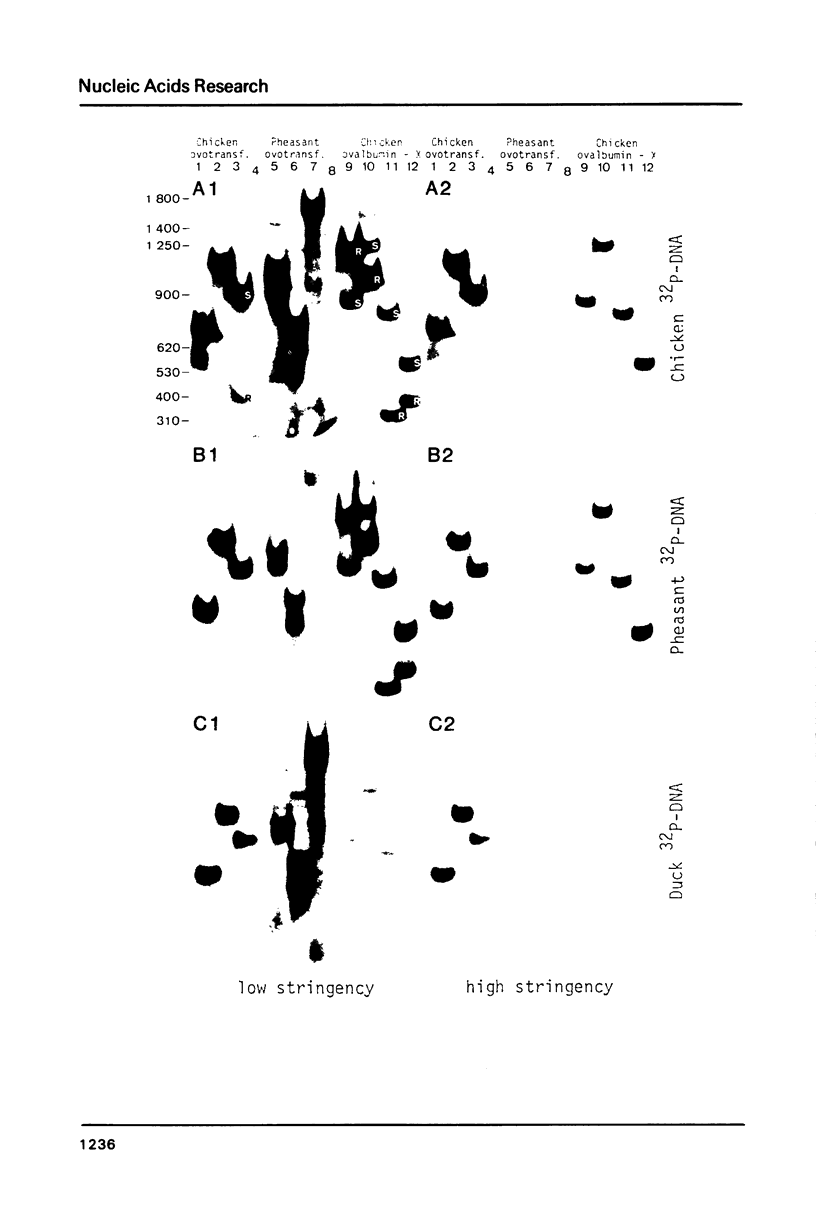
Peculiar DNA sequences made up by the tandem repetition of a 5 bp unit have been identified within or upstream from three avian protein-coding genes. One sequence is located within an intron of the chicken "ovalbumin-X" gene with 5'-TCTCC-3' as basic repeat unit (36 repeats). Another sequence made of 27 repeats of a 5'-GGAAG-3' basic unit is found 2500 base pairs upstream from the promoter of the chicken ovotransferrin (conalbumin) gene. A related but different sequence is present in the corresponding region of the ovotransferrin gene in the pheasant, with 5'-GGAAA-3' as the basic unit (55 repeats). These three satellite-like elements are thus characterized by a total assymetry in base distribution, with purines restricted to one strand, and pyrimidines to the other. Two of the basic repeat units can be derived from the third one (GGAAA) by a single base pair change. These related sequences are found repeated in three avian genomes, at degrees which vary both with the sequence type and the genome type. Evolution of tandemly repeated sequences (including satellites) is in general studied by analysing randomly picked elements. The presence of conserved protein-coding regions neighbouring satellite-like sequences allow to follow their evolution at a single locus, as exemplified by the striking comparison of the pheasant and chicken sequences upstream from the ovotransferrin gene.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldacci P., Royal A., Brégégère F., Abastado J. P., Cami B., Daniel F., Kourilsky P. DNA organisation in the chicken lysozyme gene region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3575–3588. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Selby M. J., Rutter W. J. The highly polymorphic region near the human insulin gene is composed of simple tandemly repeating sequences. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):31–35. doi: 10.1038/295031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellard M., Dretzen G., Bellard F., Oudet P., Chambon P. Disruption of the typical chromatin structure in a 2500 base-pair region at the 5' end of the actively transcribed ovalbumin gene. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):223–230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellard M., Kuo M. T., Dretzen G., Chambon P. Differential nuclease sensitivity of the ovalbumin and beta-globin chromatin regions in erythrocytes and oviduct cells of laying hen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2737–2750. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L. Molecular arrangement and evolution of heterochromatic DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:121–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabretta B., Robberson D. L., Barrera-Saldaña H. A., Lambrou T. P., Saunders G. F. Genome instability in a region of human DNA enriched in Alu repeat sequences. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):219–225. doi: 10.1038/296219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet M., Gannon F., Hen R., Maroteaux L., Perrin F., Chambon P. Organization and sequence studies of the 17-piece chicken conalbumin gene. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):567–574. doi: 10.1038/282567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Effron K., Rechavi G., Ben-Neriah Y., Zakut R., Givol D. Simple DNA sequences in homologous flanking regions near immunoglobulin VH genes: a role in gene interaction? Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 11;10(11):3353–3370. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.11.3353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortadas J., Olofsson B., Meunier-Rotival M., Macaya G., Bernardi G. THE DNA components of the chicken genome. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 15;99(1):179–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling S. M., Crampton J. M., Williamson R. Organization of a family of highly repetitive sequences within the human genome. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 5;154(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90416-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Regulation of gene expression: possible role of repetitive sequences. Science. 1979 Jun 8;204(4397):1052–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.451548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Kim S. K., Hood L. E. DNA sequences mediating class switching in alpha-immunoglobulins. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1360–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.6774415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Segni G., Carrara G., Tocchini-Valentini G. R., Shoulders C. C., Baralle F. E. Selective in vitro transcription of one of the two Alu family repeats present in the 5' flanking region of the human epsilon-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6709–6722. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epplen J. T., McCarrey J. R., Sutou S., Ohno S. Base sequence of a cloned snake W-chromosome DNA fragment and identification of a male-specific putative mRNA in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3798–3802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Kakunaga T. Potential Z-DNA forming sequences are highly dispersed in the human genome. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):396–398. doi: 10.1038/298396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Petrino M. G., Kakunaga T. A novel repeated element with Z-DNA-forming potential is widely found in evolutionarily diverse eukaryotic genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6465–6469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilig R., Muraskowsky R., Kloepfer C., Mandel J. L. The ovalbumin gene family: complete sequence and structure of the Y gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 24;10(14):4363–4382. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.14.4363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilig R., Muraskowsky R., Mandel J. L. The ovalbumin gene family. The 5' end region of the X and Y genes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 25;156(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90455-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilig R., Perrin F., Gannon F., Mandel J. L., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene family: structure of the X gene and evolution of duplicated split genes. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):625–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90309-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd V. J., Saunders G. F. Linkage arrangement of human placental lactogen and growth hormone genes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10673–10680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Davis M., Sinn E., Patten P., Hood L. Antibody diversity: somatic hypermutation of rearranged VH genes. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):573–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90399-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson G. M., Knoll B. J., March C. J., Woo S. L., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Definition of 5' and 3' structural boundaries of the chromatin domain containing the ovalbumin multigene family. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1501–1507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie A. G., Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Ratliff R. L. Polymorphism of DNA double helices. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 15;143(1):49–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Leder P. Organization and complete sequence of identical embryonic and plasmacytoma kappa V-region genes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3691–3694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prager E. M., Wilson A. C. Slow evolutionary loss of the potential for interspecific hybridization in birds: a manifestation of slow regulatory evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):200–204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza C., Doolittle W. F. Unusual physical organization of the Halobacterium genome. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):384–389. doi: 10.1038/295384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sures I., Lowry J., Kedes L. H. The DNA sequence of sea urchin (S. purpuratus) H2A, H2B and H3 histone coding and spacer regions. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1033–1044. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varley J. M., Macgregor H. C., Erba H. P. Satellite DNA is transcribed on lampbrush chromosomes. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):686–688. doi: 10.1038/283686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo S. L., Beattie W. G., Catterall J. F., Dugaiczyk A., Staden R., Brownlee G. G., O'Malley B. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of the chicken chromosomal ovalbumin gene and its biological significance. Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 27;20(22):6437–6446. doi: 10.1021/bi00525a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J., Hanahan D., Tate V., Boedtker H., Doty P. Structure of the pro alpha 2 (I) collagen gene. Nature. 1981 Nov 12;294(5837):129–135. doi: 10.1038/294129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]