Abstract
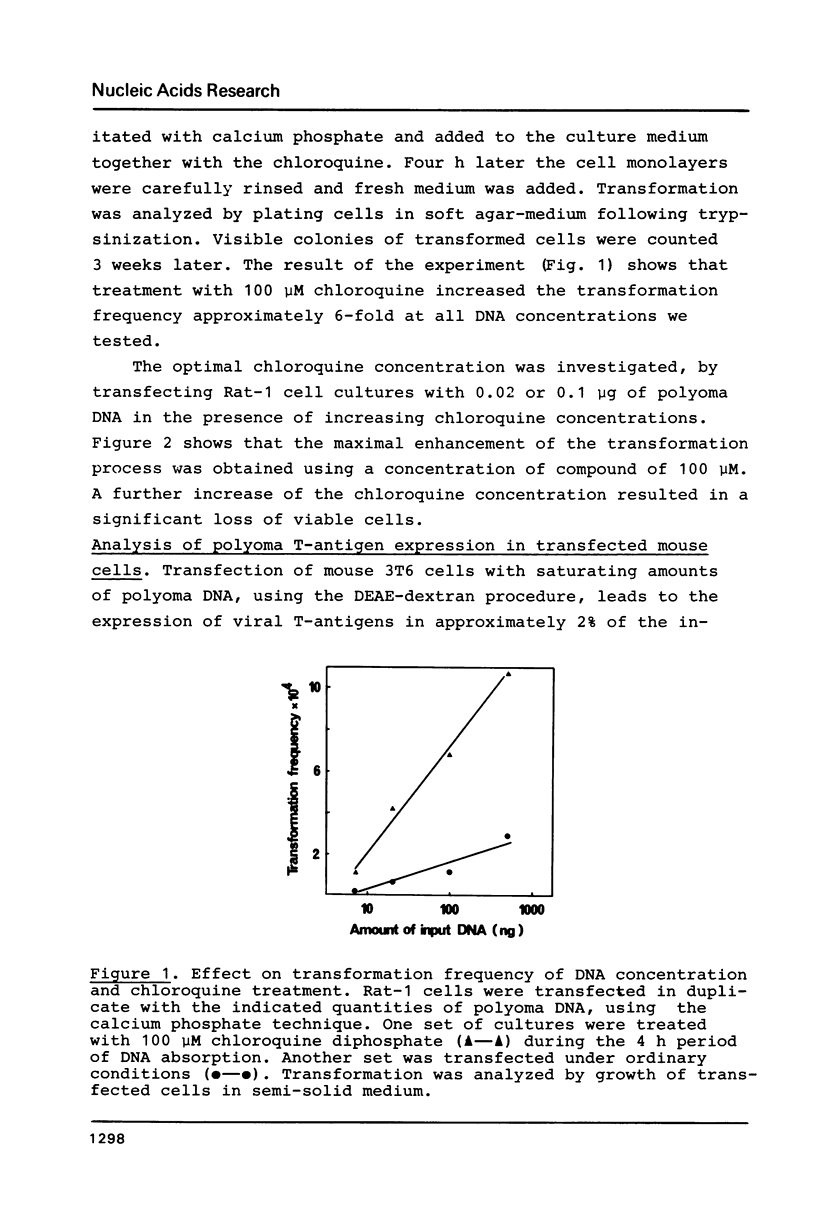
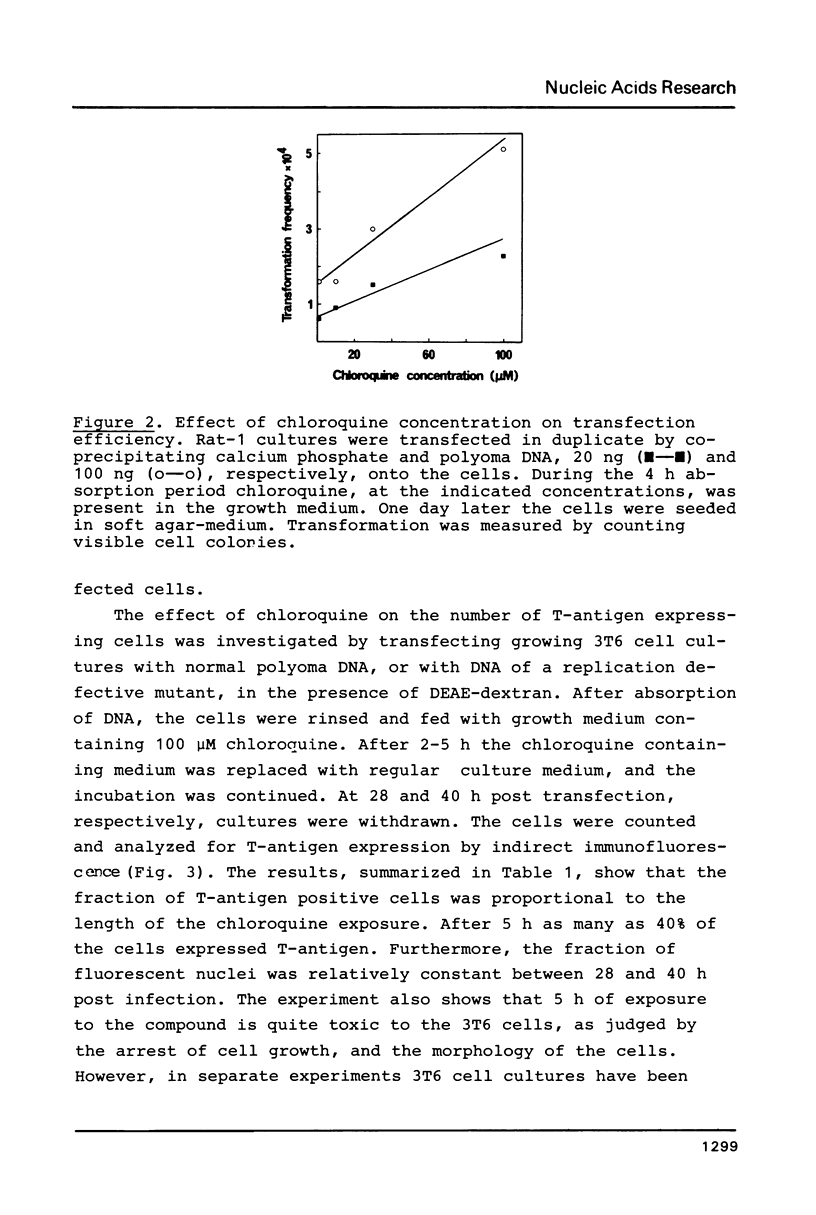
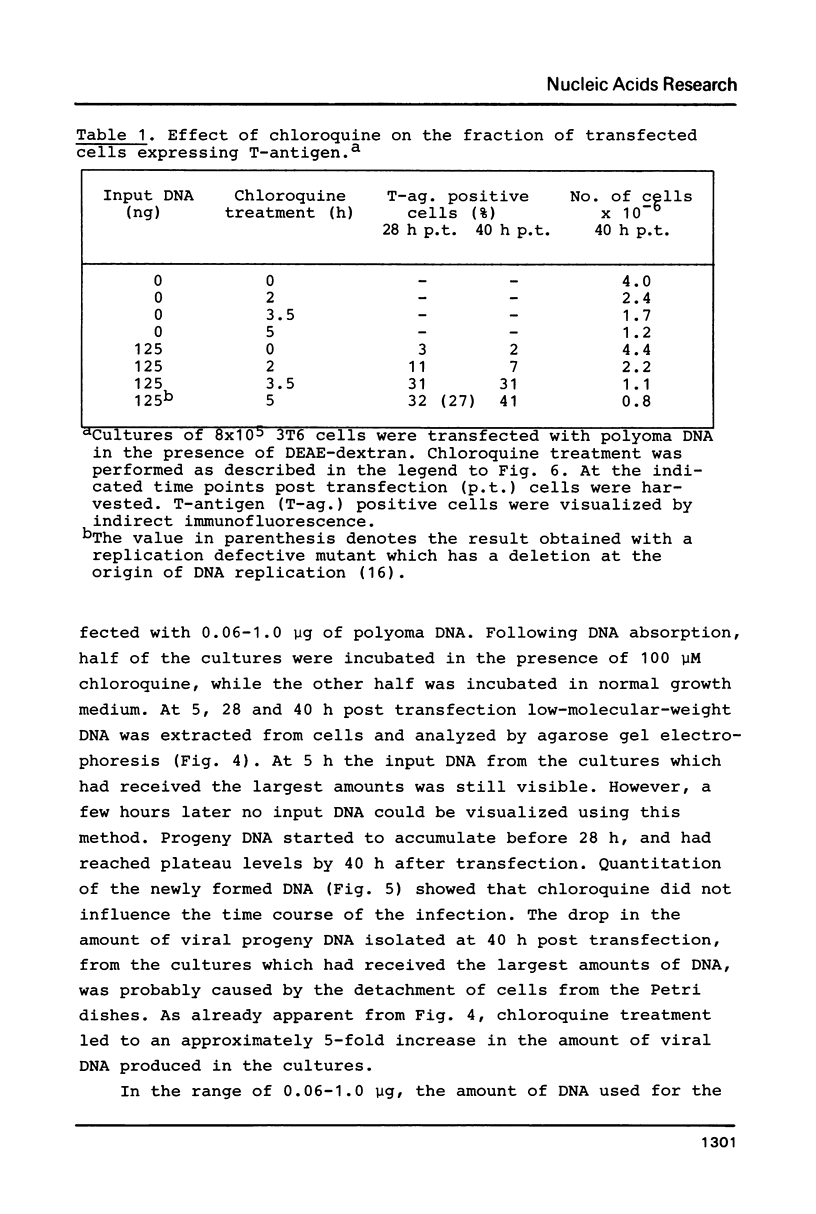
Chloroquine treatment of rodent cells during the first hours of polyoma DNA transfection increase the fraction of cells expressing viral functions. The effect has been observed after DNA absorption using both the DEAE-dextran and calcium phosphate coprecipitation methods. Exposure to chloroquine increased the proportion of transfected mouse cells to approximately 40%. From a culture of one million such cells, microgram quantities of newly synthesized viral DNA could be isolated. Similarly, the transformation frequency of rat cells following polyoma DNA transfection was approximately 6-fold increased by chloroquine treatment. The effect of the compound was even more pronounced in transfections with linear forms of polyoma DNA, suggesting that chloroquine inhibits degradation of DNA absorbed by the cells.
Full text
PDF








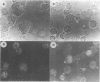
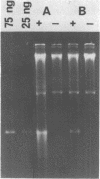
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COHEN S. N., YIELDING K. L. SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC STUDIES OF THE INTERACTION OF CHLOROQUINE WITH DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jul;240:3123–3131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon J., Shenk T. E., Berg P. Biochemical procedure for production of small deletions in simian virus 40 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1392–1396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Sharp P. A. SV40 DNA transfection of cells in suspension: analysis of efficiency of transcription and translation of T-antigen. Gene. 1981 Mar;13(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimayorca G. A., Eddy B. E., Stewart S. E., Hunter W. S., Friend C., Bendich A. ISOLATION OF INFECTIOUS DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID FROM SE POLYOMA-INFECTED TISSUE CULTURES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Dec;45(12):1805–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.12.1805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhart W. Complementation and transformation by temperature-sensitive mutants of polyoma virus. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):120–125. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90133-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost E., Williams J. Mapping temperature-sensitive and host-range mutations of adenovirus type 5 by marker rescue. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann M., Graessmann A. Regulation mechanism of simian virus 40 late gene expression in primary kidney cells and simian virus 40 transformed 3T3 cells. Virology. 1975 Jun;65(2):591–594. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin B. E., Fried M., Cowie A. Polyoma DNA: a physical map. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2077–2081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. V., Estes M. K., Pagano J. S. The uptake of SV40 DNA by nonpermissive cells in the presence of DEAE-dextran. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 1;228(1):105–116. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90550-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loyter A., Scangos G. A., Ruddle F. H. Mechanisms of DNA uptake by mammalian cells: fate of exogenously added DNA monitored by the use of fluorescent dyes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):422–426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Nilsson M. G., Magnusson G. Non-contiguous segments of the polyoma genome required in cis for DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1982 Nov 15;161(4):533–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90406-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael R. O., Williams G. M. Chloroquine inhibition of repair of DNA damage induced in mammalian cells by methyl methanesulfonate. Mutat Res. 1974 Dec;25(3):391–396. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(74)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson S. V., Magnusson G. Sealing of gaps in duplex DNA by T4 DNA ligase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1425–1437. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Poole B. Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3327–3331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassoulzadegan M., Binetruy B., Cuzin F. High frequency of gene transfer after fusion between bacteria and eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):257–259. doi: 10.1038/295257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W. Direct transfer of cloned genes from bacteria to mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2163–2167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Walsh J. E., Griffin B. E. Coding potential and regulatory signals of the polyoma virus genome. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):445–453. doi: 10.1038/283445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L. M., Danna K. J. Efficient infection of monkey cells with DNA of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7575–7578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Wilkie N. M. An improved technique for obtaining enhanced infectivity with herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):447–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIL R. A quantitative assay for a subviral infective agent related to polyoma virus. Virology. 1961 May;14:46–53. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warden D., Thorne H. V. The infectivity of polyoma virus DNA for mouse embryo cells in the presence of diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Gen Virol. 1968 Dec;3(3):371–377. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-3-371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whichard L. P., Washington M. E., Holbrook D. J., Jr The inhibition in vitro of bacterial DNA polymerases and RNA polymerase by antimalarial 8-aminoquinolines and by chloroquine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 16;287(1):52–67. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wibo M., Poole B. Protein degradation in cultured cells. II. The uptake of chloroquine by rat fibroblasts and the inhibition of cellular protein degradation and cathepsin B1. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):430–440. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]