Abstract
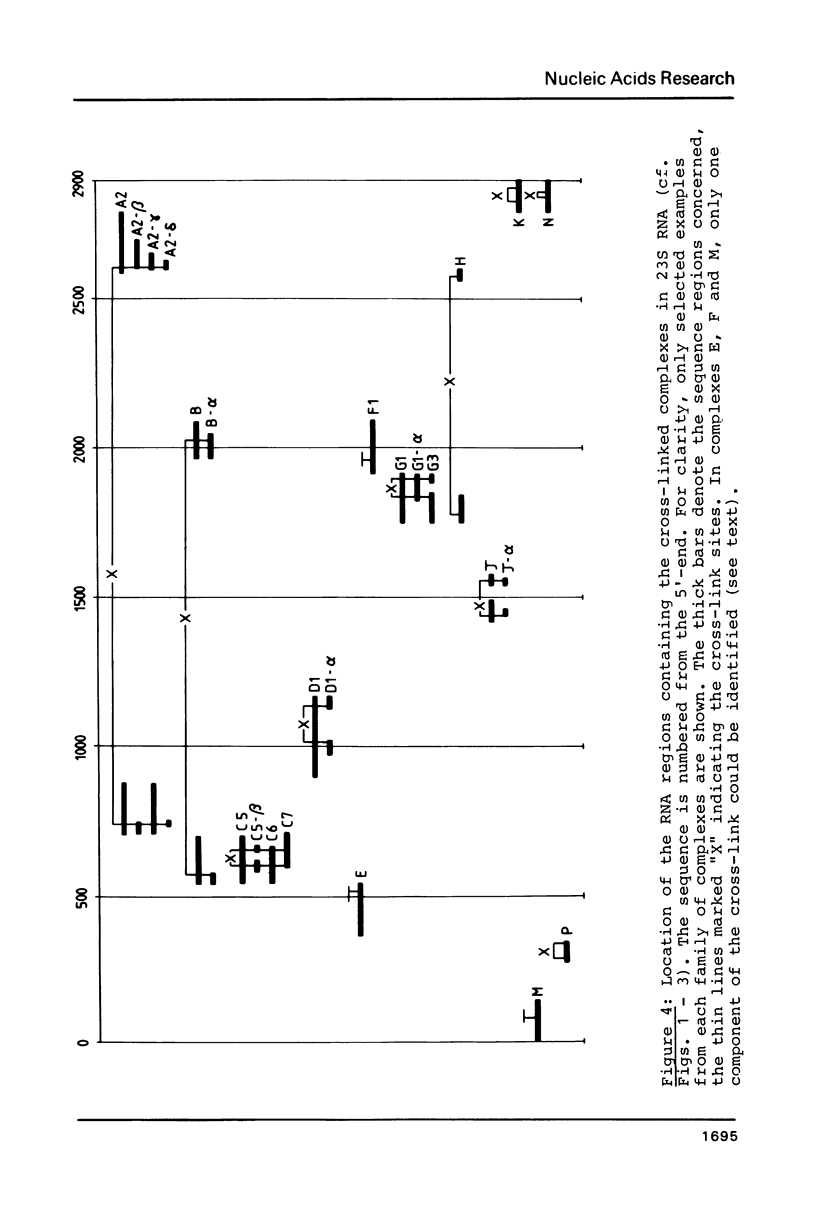
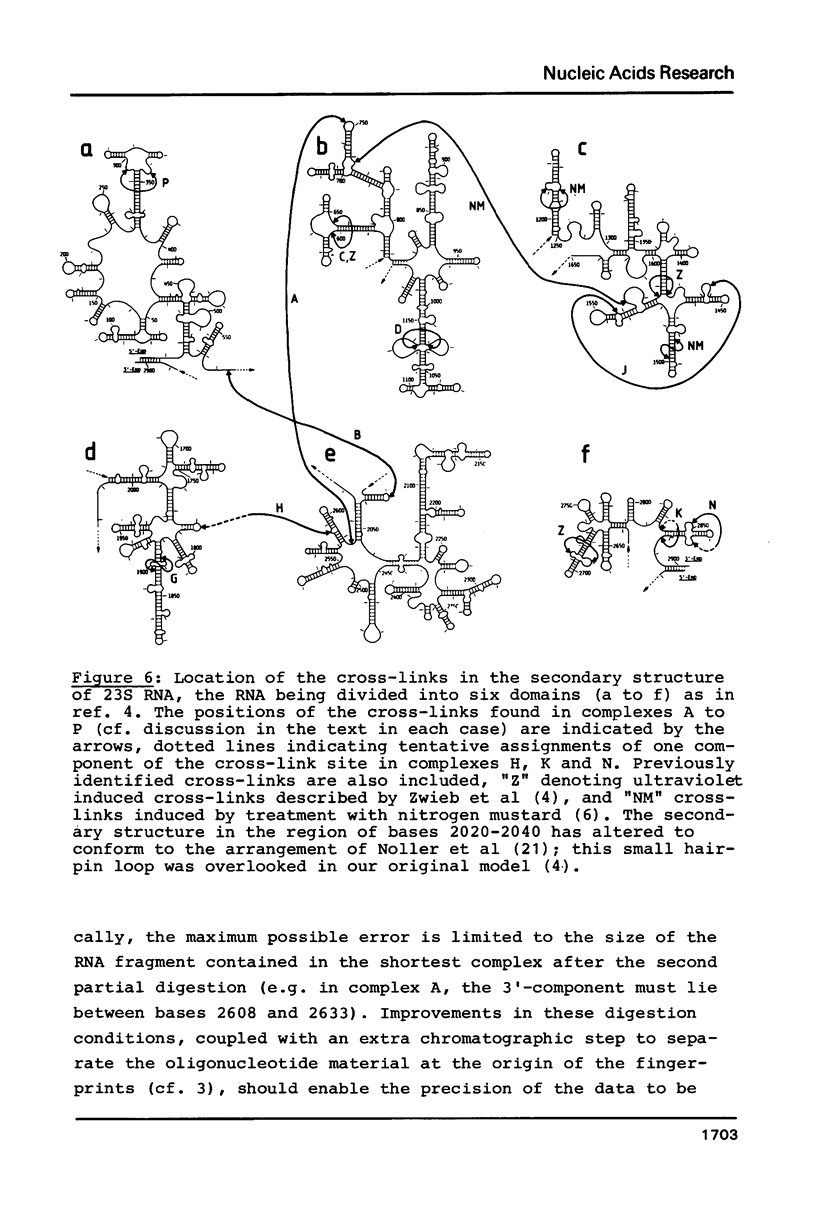
Intra-RNA cross-links were introduced into E. coli 50S ribosomal subunits by mild ultraviolet irradiation. The subunits were partially digested with cobra venom nuclease, and the cross-linked RNA complexes were isolated by two-dimensional electrophoresis. Many of the complexes were submitted to a second partial digestion procedure. Oligonucleotide analysis of the RNA fragments obtained in this manner enabled cross-links between the following ribonuclease T1 oligonucleotides in the 23S RNA to be established: positions 292-296 and 339-350; 601-604 and 652-656; 1018-1022 and 1140-1149; 1433-1435 and 1556-1560; 1836-1839 and 1898-1903; 2832-2834 (tentative) and 2878-2885; 2849-2852 and 2865-2867 (tentative); 739-748 and 2609-2618; 571-577 and 2030-2032; 1777-1792 (tentative) and 2584-2588. The first seven of these cross-links lie within the secondary structure of the 23S RNA, whereas the last three are tertiary structural cross-links. The degree of precision of the individual determinations was variable, depending on the nucleotide sequence in the vicinity of the cross-link site concerned.
Full text
PDF

















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backendorf C., Ravensbergen C. J., Van der Plas J., van Boom J. H., Veeneman G., Van Duin J. Basepairing potential of the 3' terminus of 16S RNA: dependence on the functional state of the 30S subunit and the presence of protein S21. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1425–1444. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi A. A fast method of analysis of the 5' terminal nucleotides of deoxyribooligonucleotides. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jun;59(2):501–507. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90303-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Machatt M. A., Pouyet J., Ebel J. P., Edwards K., Kössel H. Primary and secondary structures of Escherichia coli MRE 600 23S ribosomal RNA. Comparison with models of secondary structure for maize chloroplast 23S rRNA and for large portions of mouse and human 16S mitochondrial rRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4303–4324. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 23S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):201–204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlix J. L. Stimultaneous purification of Escherichia coli termination factor rho, RNAase III and RNAase H. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Feb 21;51(2):369–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H. Site specific enzymatic cleavage of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 11;7(1):179–192. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotz C., Zwieb C., Brimacombe R., Edwards K., Kössel H. Secondary structure of the large subunit ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli, Zea mays chloroplast, and human and mouse mitochondrial ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3287–3306. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon R. M., Parish J. H. Fractions of RNA and ribonucleoprotein from bacterial polysomes. II. Reactions with sulphur mustard. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 24;246(3):542–552. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90791-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankin A. S., Skripkin E. A., Chichkova N. V., Kopylov A. M., Bogdanov A. A. An enzymatic approach for localization of oligodeoxyribonucleotide binding sites on RNA. Application to studying rRNA topography. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 31;131(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80378-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller K., Brimacombe R. Specific cross-linking of proteins S7 and L4 to ribosomal RNA, by UV irradiation of Escherichia coli ribosomal subunits. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Dec 9;141(4):343–355. doi: 10.1007/BF00331455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Kop J., Wheaton V., Brosius J., Gutell R. R., Kopylov A. M., Dohme F., Herr W., Stahl D. A., Gupta R. Secondary structure model for 23S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6167–6189. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinke J., Meinke M., Brimacombe R., Fink G., Rommel W., Fasold H. The use of azidoarylimidoesters in RNA-protein cross-linking studies with Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1980 Mar 5;137(3):301–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90318-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiege W., Zwieb C., Brimacombe R. Precise localisation of three intra-RNA cross-links in 23S RNA and one in 5S RNA, induced by treatment of Escherichia coli 50S ribosomal subunits with bis-(2-chloroethyl)-methylamine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7211–7229. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner S., Thompson J. F., Hearst J. E., Noller H. F. Identification of a site of psoralen crosslinking in E. coli 16S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2839–2849. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilenko S. K., Ryte V. C. [Isolation of highly purified ribonuclease from cobra (Naja oxiana) venom]. Biokhimiia. 1975 May-Jun;40(3):578–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volckaert G., Fiers W. Micro thin-layer techniques for rapid sequence analysis of 32P-labeled RNA: double digestion and pancreatic ribonuclease analyses. Anal Biochem. 1977 Nov;83(1):228–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90531-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuki A., Brimacombe R. Nucleotide sequences of Escherichia coli 16-S RNA associated with ribosomal proteins S7, S9, S10, S14 and S19. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):23–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C., Brimacombe R. Localisation of a series of intra-RNA cross-links in 16S RNA, induced by ultraviolet irradiation of Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunits. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 11;8(11):2397–2411. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.11.2397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C., Brimacombe R. Max-Planck-Institut für Molekulare Genetik, Abteilung Wittmann, Berlin-Dahlem, GFR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;6(5):1775–1790. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.5.1775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C., Ross A., Rinke J., Meinke M., Brimacombe R. Evidence for RNA-RNA cross-link formation in Escherichia coli ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Aug;5(8):2705–2720. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.8.2705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]