Abstract
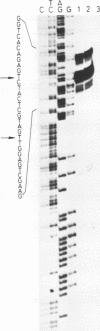
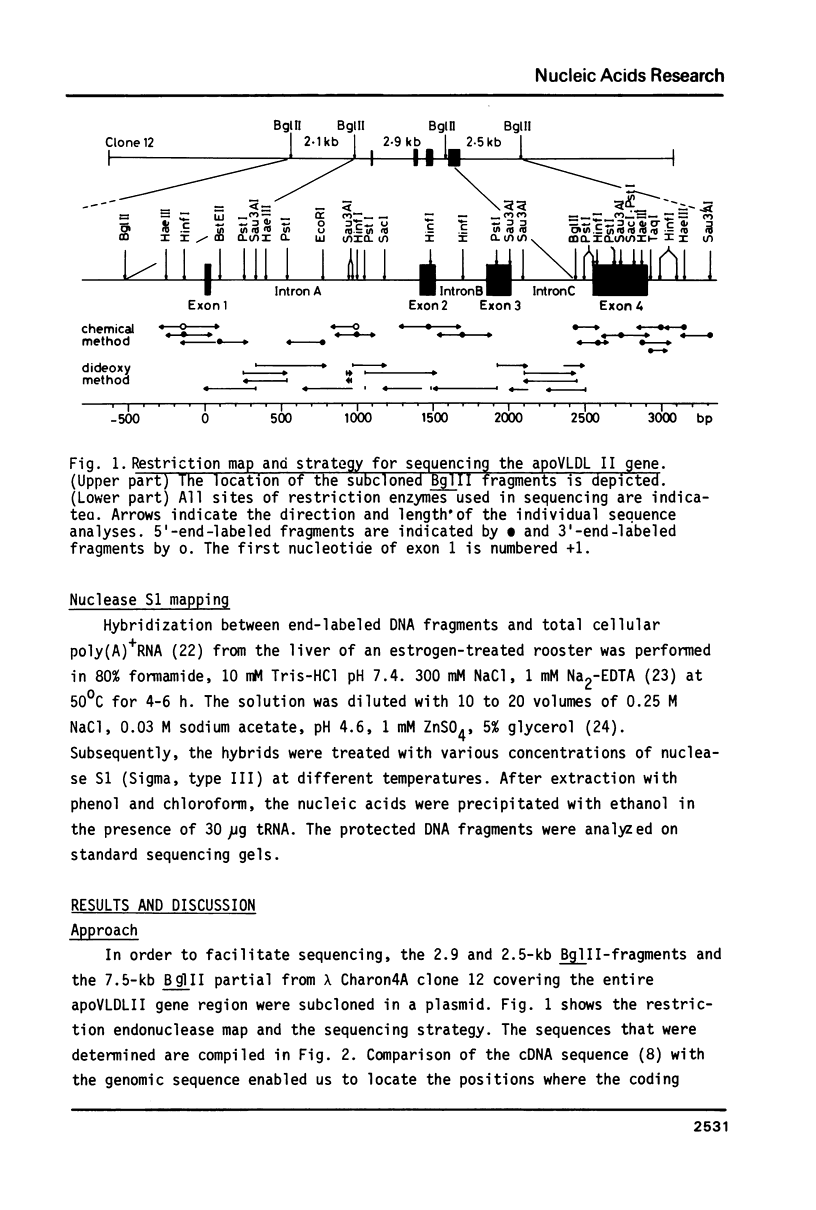
The nucleotide sequence of the chicken apo Very Low Density Lipoprotein II (apoVLDL II) gene and the regions immediately flanking the gene was determined. Nuclease S1 mapping showed that transcription is initiated at two sites, about 11 bp apart, of which the one lying downstream is used preferentially. Comparison of the 2918-base pair gene sequence with the earlier determined cDNA sequence [Wieringa et al. (1981) Nucleic Acids Research 9, 489-501] enabled us to identify the four exons which are 38 (or 49), 100, 160 and 358 bp long. One of the intron-exon junctions has an unusual sequence. In the 5' flanking region several palindromic sequences are observed. Sequences near the 5' and 3' ends show homologies with the ovalbumin gene.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L., Bradley W. A., Means A. R. Amino acid sequence of the signal peptide of apoVLDL-II, a major apoprotein in avian very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10060–10063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L., Means A. R., O'Malley B. W. Steroid hormone regulation of specific gene expression. Vitam Horm. 1978;36:259–295. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60986-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet M., Gannon F., Hen R., Maroteaux L., Perrin F., Chambon P. Organization and sequence studies of the 17-piece chicken conalbumin gene. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):567–574. doi: 10.1038/282567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J., Brüning H. J. Plasmids useable as gene-cloning vectors in an in vitro packaging by coliphage lambda: "cosmids". Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):85–107. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. Split genes and RNA splicing. Science. 1979 Apr 20;204(4390):264–271. doi: 10.1126/science.373120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faye G., Leung D. W., Tatchell K., Hall B. D., Smith M. Deletion mapping of sequences essential for in vivo transcription of the iso-1-cytochrome c gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlinger P., Krust A., LeMeur M., Perrin F., Cochet M., Gannon F., Dupret D., Chambon P. Multiple initiation and polyadenylation sites for the chicken ovomucoid transcription unit. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 5;162(2):345–364. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90531-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girvitz S. C., Bacchetti S., Rainbow A. J., Graham F. L. A rapid and efficient procedure for the purification of DNA from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Aug;106(2):492–496. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90553-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grez M., Land H., Giesecke K., Schütz G., Jung A., Sippel A. E. Multiple mRNAs are generated from the chicken lysozyme gene. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):743–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilig R., Muraskowsky R., Mandel J. L. The ovalbumin gene family. The 5' end region of the X and Y genes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 25;156(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90455-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Lin H. Y., Chan L., Means A. R. Amino acid sequence of a major apoprotein from hen plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):250–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Jat P., Treisman R., Favaloro J., Folk W. R. 5' termini of polyoma virus early region transcripts synthesized in vivo by wild-type virus and viable deletion mutants. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 5;159(2):189–224. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90493-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll B. J., Woo S. L., Beattie W., O'Malley B. W. Identification and sequence analysis of the 5' domain of the X and Y pseudo-ovalbumin genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7949–7953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E. C., Roop D. R., Tsai M. J., Woo S. L., O'Malley B. W. Heterogeneous initiation regions for transcription of the chicken ovomucoid gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 25;10(18):5553–5567. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.18.5553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malek L. T., Eschenfeldt W. H., Munns T. W., Rhoads R. E. Heterogeneity of the 5' terminus of hen ovalbumin messenger ribonucleic acid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1657–1673. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijlink F. C., van het Schip A. D., Arnberg A. C., Wieringa B., Ab G., Gruber M. Structure of the chicken apo very low density lipoprotein II gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9668–9671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. I., Shine J., Ullrich A., Wells J. R., Goodman H. M. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of adult chicken betal globin cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1137–1146. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Calvo J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the E coli gene coding for dihydrofolate reductase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2255–2274. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberon X., Covarrubias L., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. IV. Deletion derivatives of pBR322 and pBR325. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90328-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabak H. F., Flavell R. A. A method for the recovery of DNA from agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2321–2332. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogeli G., Ohkubo H., Sobel M. E., Yamada Y., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Structure of the promoter for chicken alpha 2 type I collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5334–5338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Ab G., Gruber M. The nucleotide sequence of the very low density lipoprotein II mRNA from chicken. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):489–501. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Roskam W., Arnberg A., van der Zwaag-Gerritsen J., Ab G., Gruber M. Purification of the mRNA for chicken very low density lipoproteinII and molecular cloning of its full-length double-stranded cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2147–2163. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. L. Apoproteins of avian very low density lipoprotein: demonstration of a single high molecular weight apoprotein. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 20;18(6):1056–1063. doi: 10.1021/bi00573a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskocil R., Bensky P., Dower W., Goldberger R. F., Gordon J. I., Deeley R. G. Coordinate regulation of two estrogen-dependent genes in avian liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskocil R., Goldman P., Deeley R. G. Cloning and structural characterization of an estrogen-dependent apolipoprotein gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9662–9667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Hagenbüchle O., Schibler U. A single mouse alpha-amylase gene specifies two different tissue-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]