Abstract
Hybrid prokaryotic/eukaryotic expression vectors have been used to introduce Drosophila histone genes into CV-1 African green monkey tissue culture cells. Transfection of CV-1 cells with Drosophila genes under the control of insect DNA promoter sequences results in low level expression of histone genes. On the other hand, when the Drosophila H2a gene is juxtaposed downstream from the long terminal repeat sequence of Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) expression of the insect gene is considerably more efficient; both 3' polyadenylated insect histone messenger RNA and putative Drosophila H2a histone protein can be readily detected in the transduced cells. Using this RSV/H2a vector, we have been able to demonstrate the presence of Drosophila H2a histone in monomer nucleosome preparations isolated from transfected CV-1 cells. These results suggest the feasibility of 'remodeling' cellular chromatin in vivo in precisely defined ways. The techniques described may be generally applicable to other genes coding for chromosomal proteins.
Full text
PDF


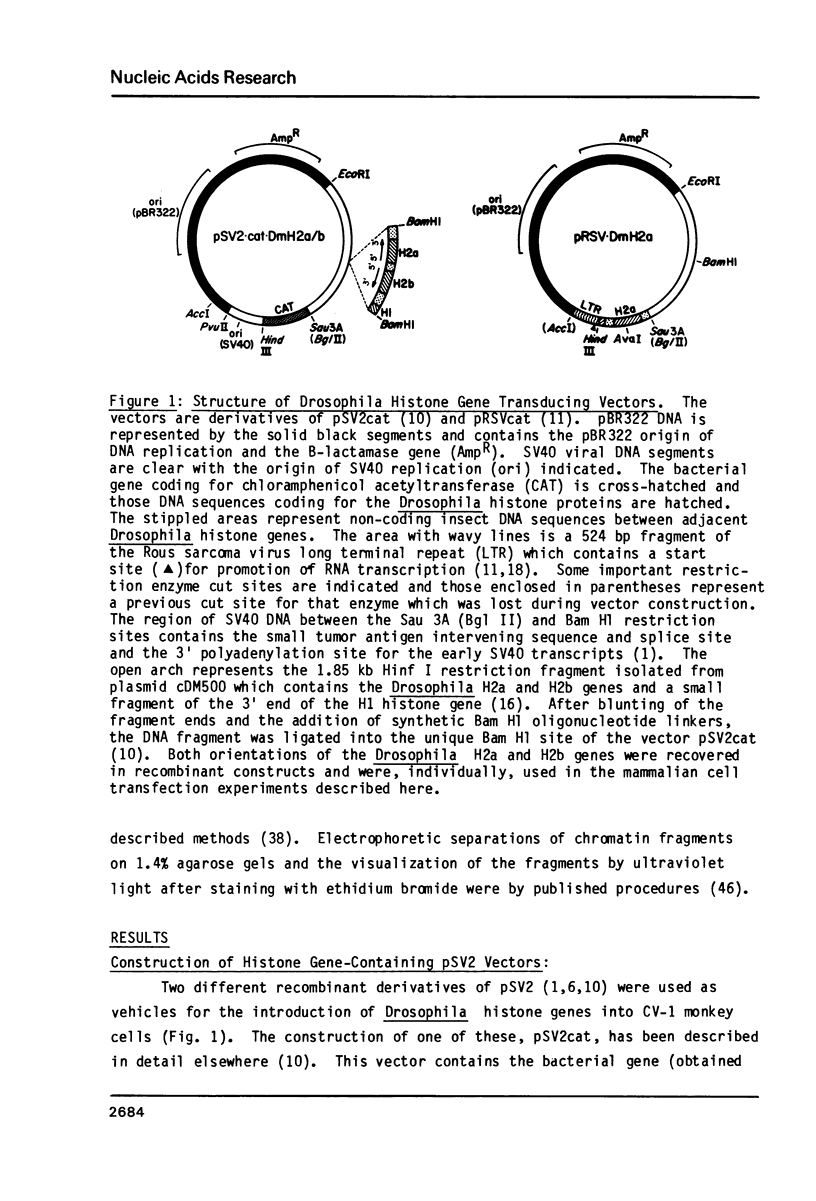











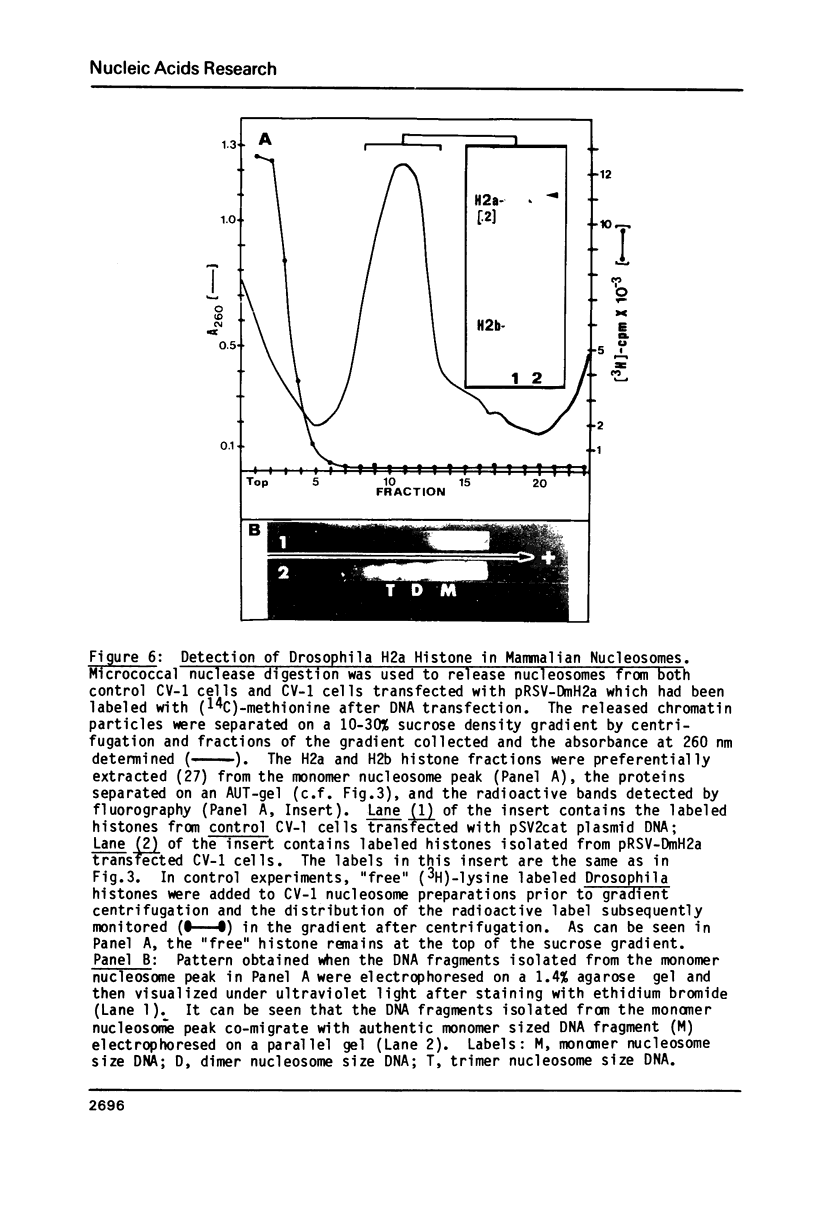




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfageme C. R., Zweidler A., Mahowald A., Cohen L. H. Histones of Drosophila embryos. Electrophoretic isolation and structural studies. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3729–3736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Parker B. A., Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:220–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. V., Lengyel J. A. Changing rates of histone mRNA synthesis and turnover in Drosophila embryos. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):717–727. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90435-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg P. Dissections and reconstructions of genes and chromosomes. Science. 1981 Jul 17;213(4505):296–303. doi: 10.1126/science.6264595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., West M. H., Stedman J. D. Two-dimensional gel analysis of histones in acid extracts of nuclei, cells, and tissues. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(1):17–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani D., Berg P. Regulated expression of human interferon beta 1 gene after transduction into cultured mouse and rabbit cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5166–5170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbère-Garapin F., Horodniceanu F., Kourilsky P., Garapin A. C. A new dominant hybrid selective marker for higher eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M., Mertz J. E. Coupled transcription-translation of DNA injected into Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Delimitation of far upstream sequences required for maximal in vitro transcription of an H2A histone gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):297–301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Dhar R., Khoury G. Simian virus 40 tandem repeated sequences as an element of the early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huez G., Marbaix G., Gallwitz D., Weinberg E., Devos R., Hubert E., Cleuter Y. Functional stabilisation of HeLa cell histone messenger RNAs injected into Xenopus oocytes by 3'-OH polyadenylation. Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):572–573. doi: 10.1038/271572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo-Kemenes T., Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:89–121. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg I. Histones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:159–191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H. Histone genes and histone messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:837–870. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifton R. P., Goldberg M. L., Karp R. W., Hogness D. S. The organization of the histone genes in Drosophila melanogaster: functional and evolutionary implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1047–1051. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlino G. T., Tyagi J. S., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Transcription of the chicken alpha 2 (Type I) collagen gene by homologous cell-free extracts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7254–7261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Gurdon J. B. Purified DNAs are transcribed after microinjection into Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1502–1506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Expression of a bacterial gene in mammalian cells. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1422–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.6251549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Howard B. H., Berg P. Synthesis of rabbit beta-globin in cultured monkey kidney cells following infection with a SV40 beta-globin recombinant genome. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):108–114. doi: 10.1038/277108a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlenbusch H. H., Olivera B. M., Tuan D., Davidson N. Selective dissociation of histones from calf thymus nucleoprotein. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):299–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A., Hereford L. M. Yeast histone genes show dosage compensation. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellicer A., Wigler M., Axel R., Silverstein S. The transfer and stable integration of the HSV thymidine kinase gene into mouse cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90308-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R., Chang D., Chung S. C. Carbohydrate modifications of the high mobility group proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6704–6708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R., Jones A. Genomic transcriptional activity and the structure of chromatin. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):495–500. doi: 10.1038/260495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schümperli D., Howard B. H., Rosenberg M. Efficient expression of Escherichia coli galactokinase gene in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):257–261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Howard B. H., Berg P. Construction and characterization of SV40 recombinants with beta-globin cDNA substitutions in their early regions. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(3):177–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramani S., Mulligan R., Berg P. Expression of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase complementary deoxyribonucleic acid in simian virus 40 vectors. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;1(9):854–864. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.9.854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M. H., Bonner W. M. Histone 2A, a heteromorphous family of eight protein species. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 8;19(14):3238–3245. doi: 10.1021/bi00555a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodland H. R. Histone synthesis during the development of Xenopus. FEBS Lett. 1980 Nov 17;121(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81252-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Identification of a functional promoter in the long terminal repeat of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90555-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







