Abstract
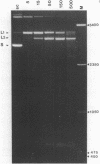
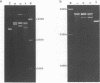
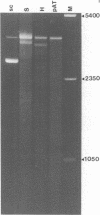
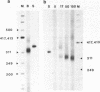
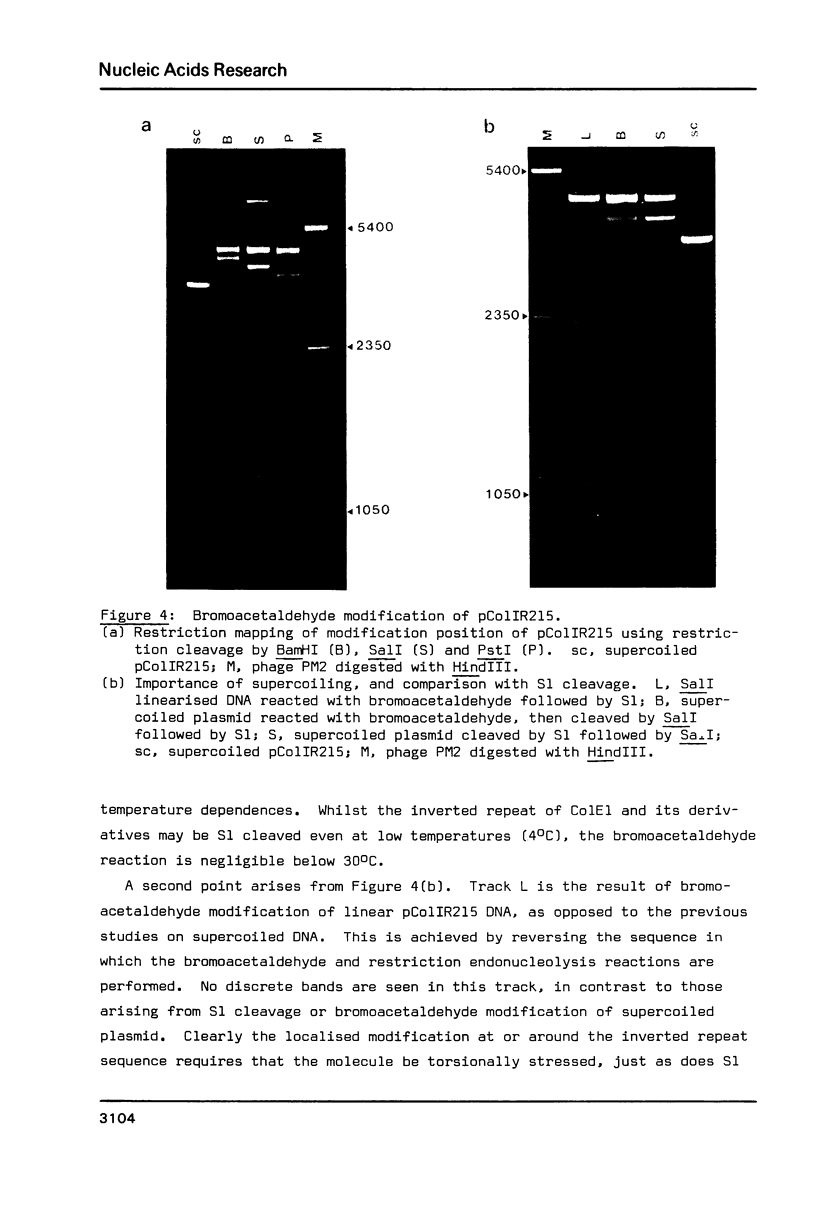
Bromoacetaldehyde, a reagent which modifies unpaired adenine residues, selectively modifies supercoiled DNA in the region of inverted repeats which are known targets for single-strand-specific nucleases. The reaction is dependent upon the topological state of the molecule, and the absolute importance of the inverted repeat has been demonstrated. Finer mapping of the distribution of the modification pattern reveals significant and interesting differences from the S1 nuclease target positions. Bromoacetaldehyde modification is distributed over a wider region covering the whole inverted repeat, with greatest extent of reaction in the regions which flank the inverted repeat. It is suggested that an altered conformation may be propagated into these sequences. These results further support the contention that inverted repeats adopt an altered conformation when negatively supercoiled, for which the principal suggestion remains the cruciform structure.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beard P., Morrow J. F., Berg P. Cleavage of circular, superhelical simian virus 40 DNA to a linear duplex by S1 nuclease. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1303–1313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1303-1313.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beerman T. A., Lebowitz J. Further analysis of the altered secondary structure of superhelical DNA. Sensitivity to methylmercuric hydroxide a chemical probe for unpaired bases. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 25;79(3):451–470. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. J. Stable cruciform formation at inverted repeat sequences in supercoiled DNA. Biopolymers. 1982 Mar;21(3):679–696. doi: 10.1002/bip.360210314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkner K. L., Folk W. R. Polynucleotide kinase exchange reaction: quantitave assay for restriction endonuclease-generated 5'-phosphoroyl termini in DNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3176–3184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. Instability of palindromic DNA in Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):409–416. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. II. Influence of base sequence on helix structure. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):761–786. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Lomonossoff G. P., Laskey R. A. High sequence specificity of micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2659–2673. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Ohmori H., Tomizawa J. DNA gyrase and DNA supercoiling. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):35–40. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagan C. E., Warren G. J. Lethality of palindromic DNA and its use in selection of recombinant plasmids. Gene. 1982 Jul-Aug;19(1):147–151. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90199-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz J., Chaudhuri A. K., Gonenne A., Kitos G. Carbodiimide modification of superhelical PM2 DNA: considerations regarding reaction at unpaired bases and the unwinding of superhelical DNA with chemical probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jun;4(6):1695–1711. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.6.1695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. Dynamic, sequence-dependent DNA structure as exemplified by cruciform extrusion from inverted repeats in negatively supercoiled DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):101–112. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. Hairpin-loop formation by inverted repeats in supercoiled DNA is a local and transmissible property. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1271–1289. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. In vivo consequences of plasmid topology. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):380–382. doi: 10.1038/292380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. The inverted repeat as a recognizable structural feature in supercoiled DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6468–6472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Kemper B., Hays J., Weisberg R. A. T4 endonuclease VII cleaves holliday structures. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Mizuuchi M., Gellert M. Cruciform structures in palindromic DNA are favored by DNA supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 5;156(2):229–243. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka A., Nomura N., Morita M., Sugisaki H., Sugimoto K., Takanami M. Nucleotide sequence of small ColE1 derivatives: structure of the regions essential for autonomous replication and colicin E1 immunity. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 May 4;172(2):151–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00268276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Wells R. D. Cruciform structures in supercoiled DNA. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):466–470. doi: 10.1038/289466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Nordheim A., Rich A., Wang J. C. Flipping of cloned d(pCpG)n.d(pCpG)n DNA sequences from right- to left-handed helical structure by salt, Co(III), or negative supercoiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4560–4564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Sequence dependence of the helical repeat of DNA in solution. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):375–378. doi: 10.1038/292375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt J. R. POSSIBLE SEPARATION OF INTERTWINED NUCLEIC ACID CHAINS BY TRANSFER-TWIST. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1955 Mar 15;41(3):181–183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.41.3.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. Helical periodicity of DNA determined by enzyme digestion. Nature. 1980 Aug 7;286(5773):573–578. doi: 10.1038/286573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. Sequence-dependent helical periodicity of DNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):378–380. doi: 10.1038/292378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P. Initiation of transcription by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase from supercoiled and non-supercoiled bacteriophage PM2 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 5;91(4):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90274-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secrist J. A., 3rd, Barrio J. R., Leonard N. J., Villar-Palasi C., Gilman A. G. Fluorescent modification of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate: spectroscopic properties and activity in enzyme systems. Science. 1972 Jul 21;177(4045):279–280. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4045.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Braverman B., Louis J. B., Servis R. E. Nucleic acid reactivity and conformation. II. Reaction of cytosine and uracil with sodium bisulfite. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):4060–4064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton C. K., Klysik J., Stirdivant S. M., Wells R. D. Left-handed Z-DNA is induced by supercoiling in physiological ionic conditions. Nature. 1982 Sep 23;299(5881):312–316. doi: 10.1038/299312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton C. K., Wells R. D. Relationship between superhelical density and cruciform formation in plasmid pVH51. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6292–6295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinograd J., Lebowitz J., Watson R. Early and late helix-coil transitions in closed circular DNA. The number of superhelical turns in polyoma DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):173–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M. Purification and further properties of single-strand-specific nuclease from Aspergillus oryzae. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):192–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vologodskii A. V., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Theoretical study of cruciform states in superhelical DNAs. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jul 5;143(2):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Fujii S., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G. A., van Boeckel S. A., Rich A. Molecular structure of r(GCG)d(TATACGC): a DNA--RNA hybrid helix joined to double helical DNA. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):601–604. doi: 10.1038/299601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., Crawford J. L., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Rich A. Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):680–686. doi: 10.1038/282680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Interactions between twisted DNAs and enzymes: the effects of superhelical turns. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 25;87(4):797–816. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90085-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth-Gutai M., Lebowitz J. Introduction of interrupted secondary structure in supercoiled DNA as a function of superhelix density: consideration of hairpin structures in superhelical DNA. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):195–204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.195-204.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]