Abstract
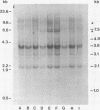
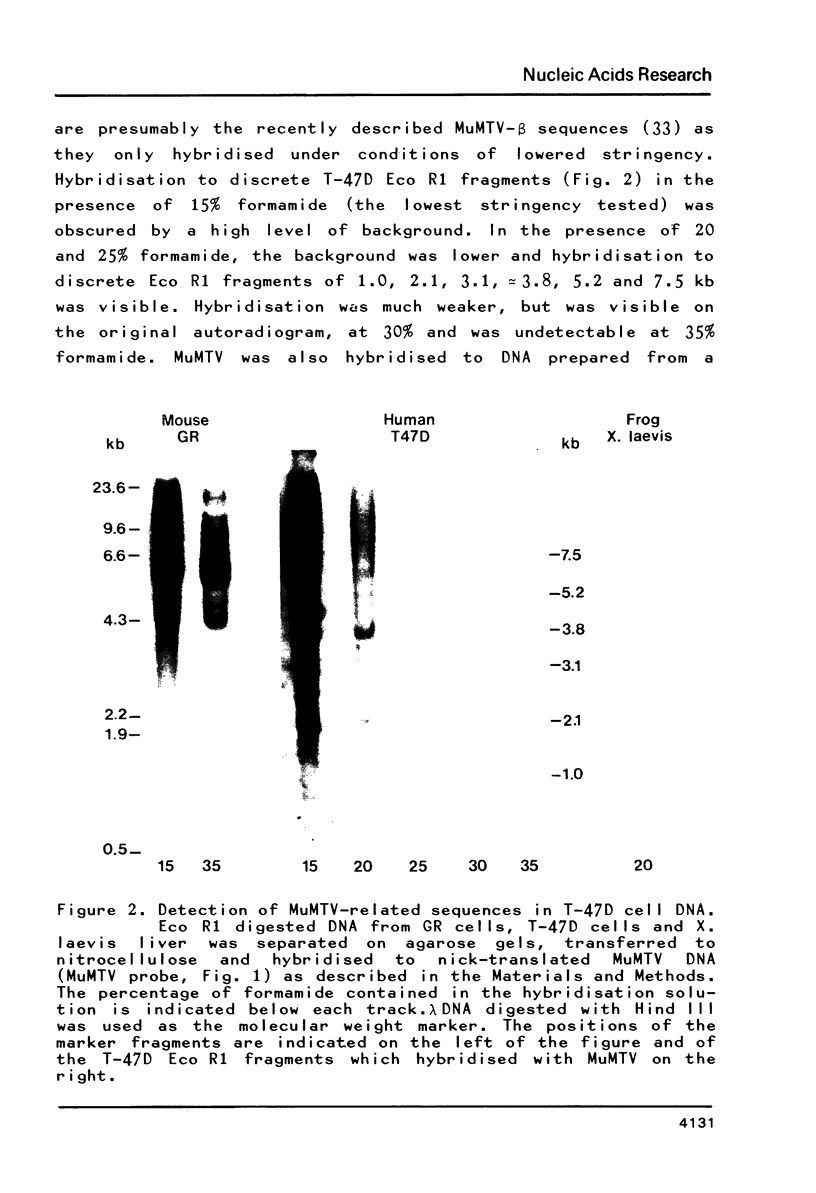
MuMTV-related sequences have been identified in the DNA of human breast cancer cells using the Southern transfer technique and hybridisation with cloned MuMTV DNA under conditions in which partially mismatched sequences form stable hybrids. Hybridisation with cloned fragments of the MuMTV genome showed that the gag-pol region shares the most homology (estimated to be greater than 80%) with the human MuMTV-related sequences, however, DNA fragments partially homologous to the MuMTV LTR, gag ad env regions were also detected. Analysis of several human DNA samples suggests that the majority of the human MuMTV-related sequences are genetically transmitted but additional Eco R1 fragments were detected in the DNA of one out of three breast cancer cell lines, MCF7. These sequences are potential probes for the human MuMTV-related retroviral sequences and will allow their possible role in human breast cancer to be evaluated.
Full text
PDF




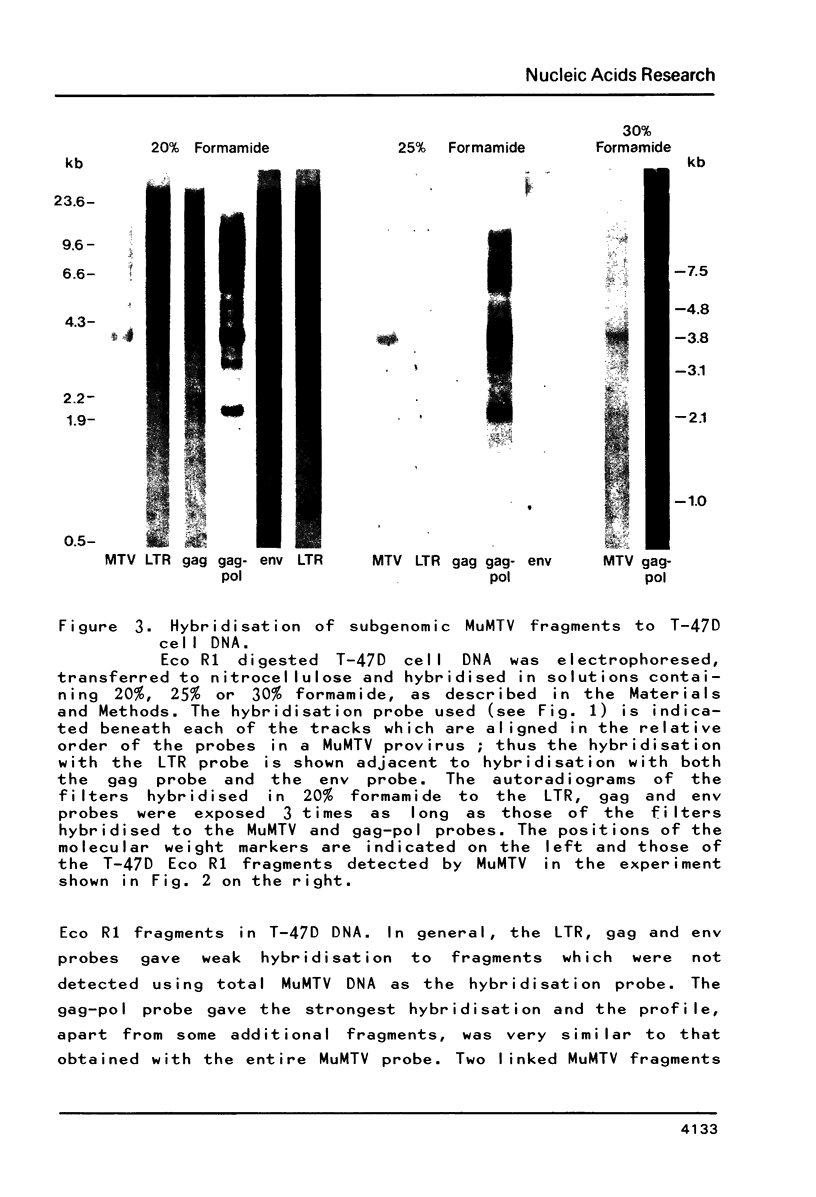






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axel R., Schlom J., Spiegelman S. Presence in human breast cancer of RNA homologous to mouse mammary tumour virus RNA. Nature. 1972 Jan 7;235(5332):32–36. doi: 10.1038/235032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., O'Connell C., Cohen M. Cloned endogenous retroviral sequences from human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4709–4713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breznik T., Cohen J. C. Altered methylation of endogenous viral promoter sequences during mammary carcinogenesis. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):255–257. doi: 10.1038/295255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E., Diggelmann H. Cloned mouse mammary tumor virus DNA is biologically active in transfected mouse cells and its expression is stimulated by glucocorticoid hormones. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):335–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calafat J., Hageman P. C. Remarks on virus-like particles in human breast cancer. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):260–262. doi: 10.1038/242260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan R., Drohan W., Gallahan D., D'Hoostelaere L., Potter M. Novel class of mouse mammary tumor virus-related DNA sequences found in all species of Mus, including mice lacking the virus proviral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4113–4117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan R., Drohan W., Tronick S., Schlom J. Detection and cloning of human DNA sequences related to the mouse mammary tumor virus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5503–5507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalbos D., Vignon F., Keydar I., Rochefort H. Estrogens stimulate cell proliferation and induce secretory proteins in a human breast cancer cell line (T47D). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Aug;55(2):276–283. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-2-276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. C., Shank P. R., Morris V. L., Cardiff R., Varmus H. E. Integration of the DNA of mouse mammary tumor virus in virus-infected normal and neoplastic tissue of the mouse. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):333–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das M. R., Mink M. M. Sequence homology of nucleic acids from human breast cancer cells and complementary DNA's from murine mammary tumor virus and Mason-Pfizer monkey virus. Cancer Res. 1979 Dec;39(12):5106–5113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel L. W., Young N. A., Tralka T. S., Lippman M. E., O'Brien S. J., Joyce M. J. Establishment and characterization of three new continuous cell lines derived from human breast carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1978 Oct;38(10):3352–3364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindan M. V., Spiess E., Majors J. Purified glucocorticoid receptor-hormone complex from rat liver cytosol binds specifically to cloned mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeats in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5157–5161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groner B., Buetti E., Diggelmann H., Hynes N. E. Characterization of endogenous and exogenous mouse mammary tumor virus proviral DNA with site-specific molecular clones. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):734–745. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.734-745.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keydar I., Chen L., Karby S., Weiss F. R., Delarea J., Radu M., Chaitcik S., Brenner H. J. Establishment and characterization of a cell line of human breast carcinoma origin. Eur J Cancer. 1979 May;15(5):659–670. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(79)90139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Kitamura A., Toyoshima K., Hirayama Y., Yoshida M. Avian sarcoma virus Y73 genome sequence and structural similarity of its transforming gene product to that of Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1982 May 20;297(5863):205–208. doi: 10.1038/297205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane M. A., Sainten A., Cooper G. M. Activation of related transforming genes in mouse and human mammary carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5185–5189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippman M. E., Bolan G. Oestrogen-responsive human breast cancer in long term tissue culture. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):592–593. doi: 10.1038/256592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. A., Bryan T., Rasheed S., Khan A. S. Identification and cloning of endogenous retroviral sequences present in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4892–4896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May F. E., Weber R., Westley B. R. Isolation and characterisation of the Xenopus laevis albumin genes: loss of 74K albumin gene sequences by library amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2791–2807. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConaughy B. L., Laird C. D., McCarthy B. J. Nucleic acid reassociation in formamide. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3289–3295. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath C. M., Grant P. M., Soule H. D., Glancy T., Rich M. A. Replication of oncornavirus-like particle in human breast carcinoma cell line, MCF-7. Nature. 1974 Nov 15;252(5480):247–250. doi: 10.1038/252247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesa-Tejada R., Keydar I., Ramanarayanan M., Ohno T., Fenoglio C., Spiegelman S. Detection in human breast carcinomas of an antigen immunologically related to a group-specific antigen of mouse mammary tumor virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1529–1533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalides R., van Nie R., Nusse R., Hynes N. E., Groner B. Mammary tumor induction loci in GR and DBAf mice contain one provirus of the mouse mammary tumor virus. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. H., Charney J., Kramarsky B., Lasfargues E. Y., Sarkar N. H., Brennan M. J., Burrows J. H., Sirsat S. M., Paymaster J. C., Vaidya A. B. Search for a human breast cancer virus. Nature. 1971 Feb 26;229(5287):611–614. doi: 10.1038/229611a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawata H., Bronzert D., Lippman M. E. Isolation and characterization of a tamoxifen-resistant cell line derived from MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5016–5021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., Varmus H. E. Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90409-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. S., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Multiple arrangements of viral DNA and an activated host oncogene in bursal lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):209–214. doi: 10.1038/295209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., Wrange O., Carlstedt-Duke J., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Purified glucocorticoid receptors bind selectively in vitro to a cloned DNA fragment whose transcription is regulated by glucocorticoids in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6628–6632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G. M. Glucocorticoid regulation of mouse mammary tumor virus gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 19;560(4):487–508. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(79)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlom J., Spiegelman S., Moore D. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity in virus-like particles isolated from human milk. Nature. 1971 May 14;231(5298):97–100. doi: 10.1038/231097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soule H. D., Vazguez J., Long A., Albert S., Brennan M. A human cell line from a pleural effusion derived from a breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Nov;51(5):1409–1416. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.5.1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tainsky M. A. Analysis of the virogenes related to the rhesus monkey endogenous type C retrovirus in monkeys and apes. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):922–930. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.922-930.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman J. S., McCarthy B. J. The relationship between mismatched base pairs and the thermal stability of DNA duplexes. II. Effects of deamination of cytosine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 4;294(1):416–424. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya A. B., Black M. M., Dion A. S., Moore D. H. Homology between human breast tumour RNA and mouse mammary tumour virus genome. Nature. 1974 Jun 7;249(457):565–567. doi: 10.1038/249565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E. Form and function of retroviral proviruses. Science. 1982 May 21;216(4548):812–820. doi: 10.1126/science.6177038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B., Wyler T., Jaggi R. B., Weber R., Ryffel G. U. Vitellogenin in Xenopus laevis is encoded in a small family of genes. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westley B., Rochefort H. A secreted glycoprotein induced by estrogen in human breast cancer cell lines. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90621-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westley B., Wyler T., Ryffel G., Weber R. Xenopus laevis serum albumins are encoded in two closely related genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3557–3574. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]