Abstract
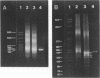
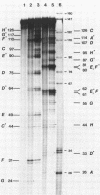
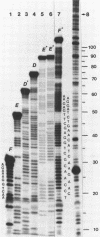
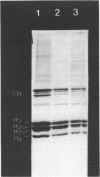
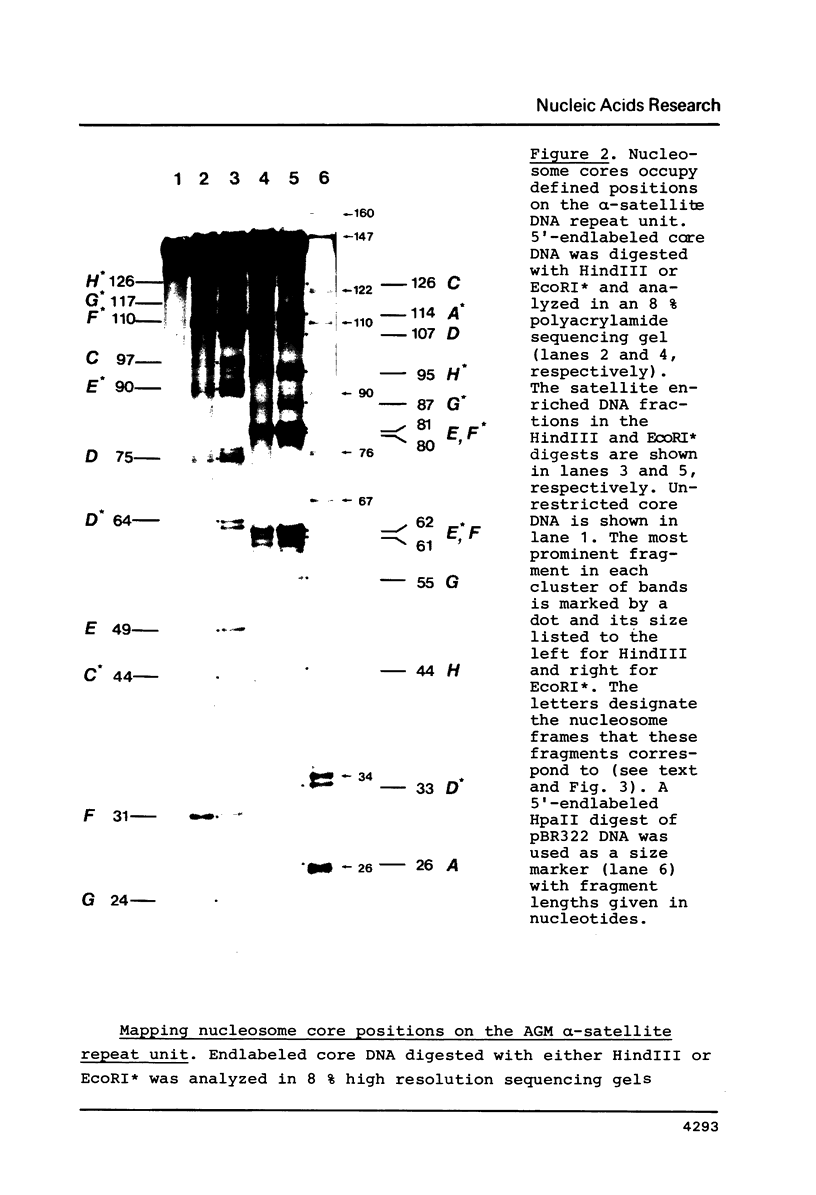
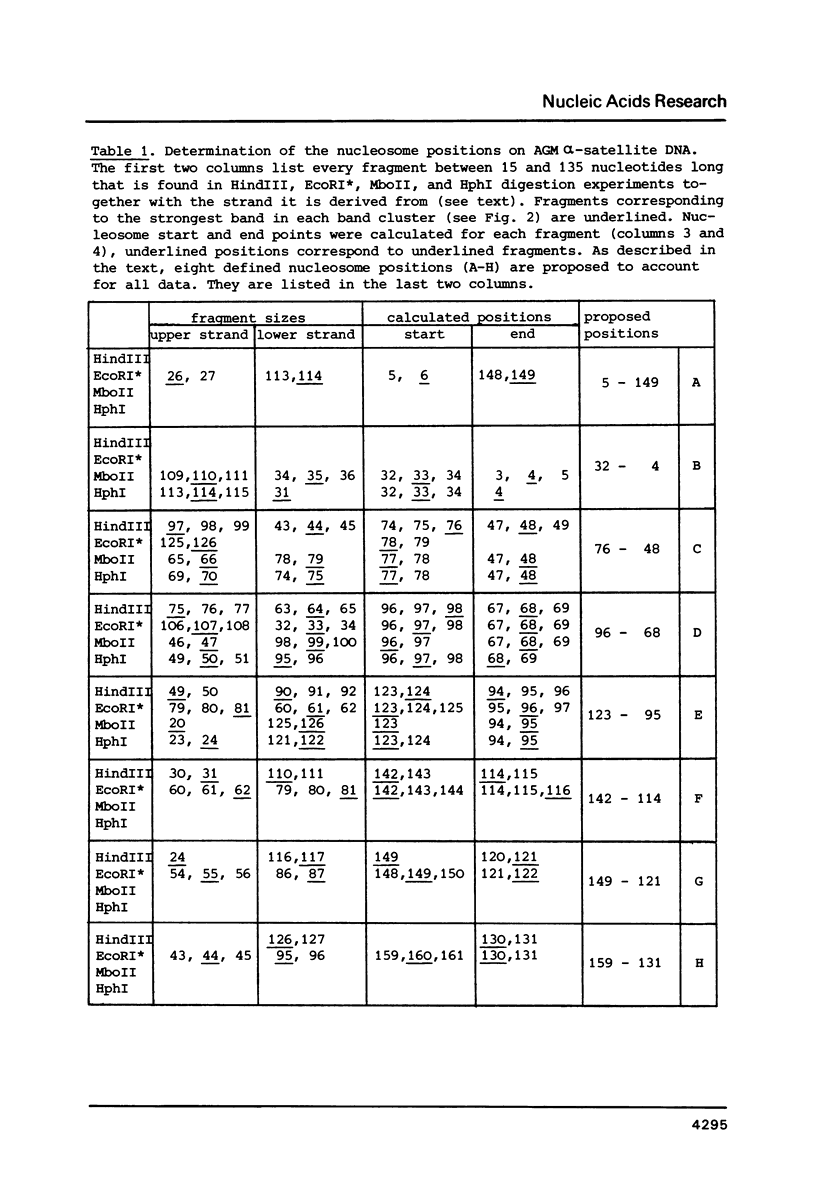
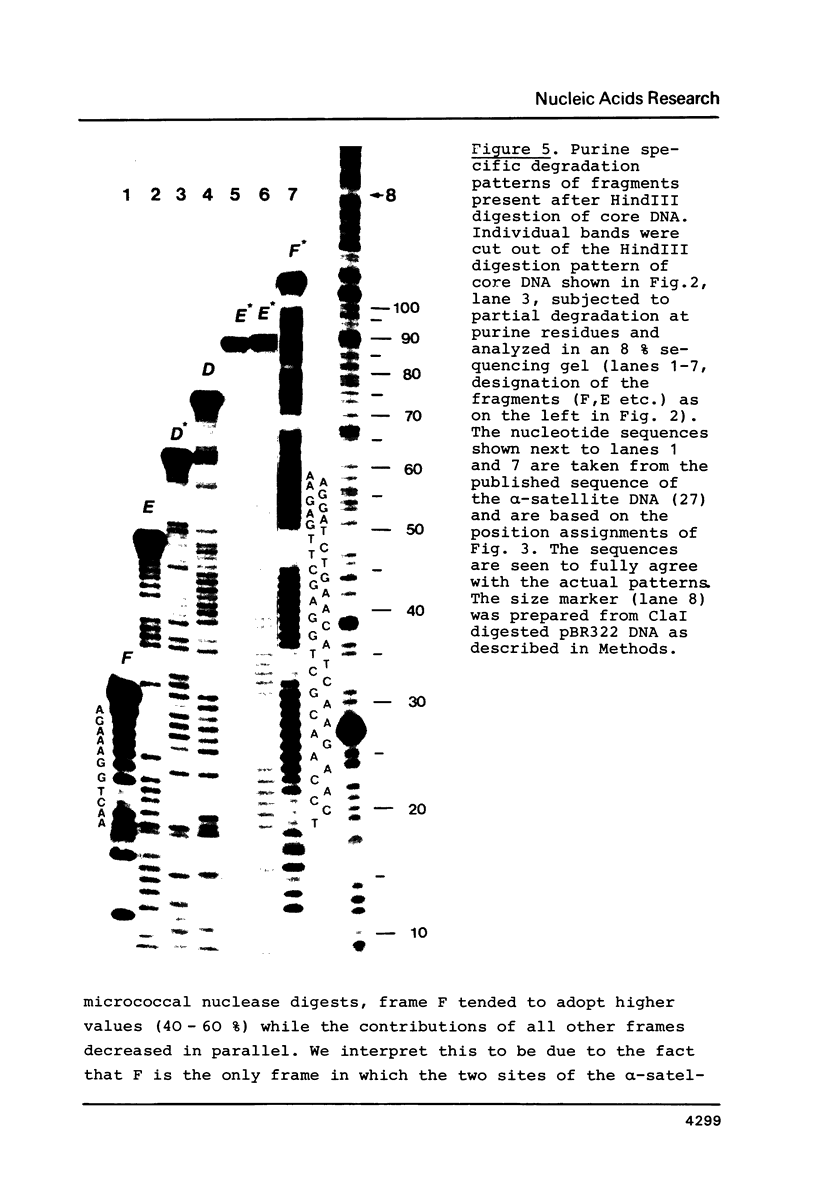
The question of nucleosome phasing on African Green Monkey (AGM) alpha-satellite DNA has been addressed by employing a new approach. Nucleosome cores were prepared from AGM nuclei with micrococcal nuclease, exonuclease III and nuclease S1. The core DNA population derived from alpha-satellite DNA containing chromatin was purified from total core DNA by denaturation of the DNA, reassociation to a low Cot value, and hydroxyapatite chromatography to separate the renatured satellite fraction. After end-labeling the termini of the alpha-satellite containing core DNA fragments were mapped by high resolution gel electrophoresis relative to known restriction sites along the 172 bp repeat unit of the satellite DNA. The results show that nucleosomes occupy eight strictly defined positions on the alpha-satellite DNA which could be determined with an accuracy of +/- 1 base pair. Approximately 35% of all nucleosomes are organized in one of these frames while the other seven registers contribute about 10% each.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown F. L., Musich P. R., Maio J. J. The repetitive sequence structure of component alpha DNA and its relationship to the nucleosomes of the African green monkey. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 15;131(4):777–799. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90201-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L. Molecular arrangement and evolution of heterochromatic DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:121–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright I. L., Abmayr S. M., Fleischmann G., Lowenhaupt K., Elgin S. C., Keene M. A., Howard G. C. Chromatin structure and gene activity: the role of nonhistone chromosomal proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982;13(1):1–86. doi: 10.3109/10409238209108709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Lomonossoff G. P., Laskey R. A. High sequence specificity of micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2659–2673. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fittler F., Zachau H. G. Subunit structure of alpha-satellite DNA containing chromatin from African green monkey cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 11;7(1):1–13. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray C. P., Sommer R., Polke C., Beck E., Schaller H. Structure of the orgin of DNA replication of bacteriophage fd. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):50–53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene P. J., Heyneker H. L., Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Betlach M. C., Covarrubias A. A., Backman K., Russel D. J., Tait R., Boyer H. W. A general method for the purification of restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2373–2380. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewish D. R., Burgoyne L. A. Chromatin sub-structure. The digestion of chromatin DNA at regularly spaced sites by a nuclear deoxyribonuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):504–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90740-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Altenburger W. Sequence specific cleavage of DNA by micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2643–2658. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Deoxyribonuclease II as a probe for chromatin structure. I. Location of cleavage sites. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 15;144(3):305–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90093-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo-Kemenes T., Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:89–121. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo-Kemenes T., Omori A., Zachau H. G. Non-random arrangement of nucleosomes in satellite I containing chromatin of rat liver. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 25;8(22):5377–5390. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.22.5377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. W. The isolation and purification of histones. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;16:183–203. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss A., Sain B., Csordás-Tòth E., Venetianer P. A new sequence-specific endonuclease (Bsp) from Bacillus sphaericus. Gene. 1977 Jul;1(5-6):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. The location of nucleosomes in chromatin: specific or statistical. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):579–580. doi: 10.1038/292579a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linxweiler W., Hörz W. Sequence specificity of exonuclease III from E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):4845–4859. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.4845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Another potential artifact in the study of nucleosome phasing by chromatin digestion with micrococcal nuclease. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musich P. R., Brown F. L., Maio J. J. Nucleosome phasing and micrococcal nuclease cleavage of African green monkey component alpha DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):118–122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musich P. R., Maio J. J., Brown F. L. Subunit structure of chromatin and the organization of eukaryotic highly repetitive DNA: indications of a phase relation between restriction sites and chromatin subunits in African green monkey and calf nuclei. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 15;117(3):657–677. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omori A., Igo-Kemenes T., Zachau H. G. Different repeat lengths in rat satellite I DNA containing chromatin and bulk chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 25;8(22):5363–5375. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.22.5363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polisky B., Greene P., Garfin D. E., McCarthy B. J., Goodman H. M., Boyer H. W. Specificity of substrate recognition by the EcoRI restriction endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3310–3314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Singer M., Rosenberg M. Highly reiterated sequences of SIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIAN. Science. 1978 Apr 28;200(4340):394–402. doi: 10.1126/science.205944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer D. S. Arrangement of a highly repeated DNA sequence in the genome and chromatin of the African green monkey. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5506–5514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;76:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61789-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachau H. G., Igo-Kemenes T. Face to phase with nucleosomes. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):597–598. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Hörz W. Analysis of highly purified satellite DNA containing chromatin from the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1481–1494. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]