Abstract
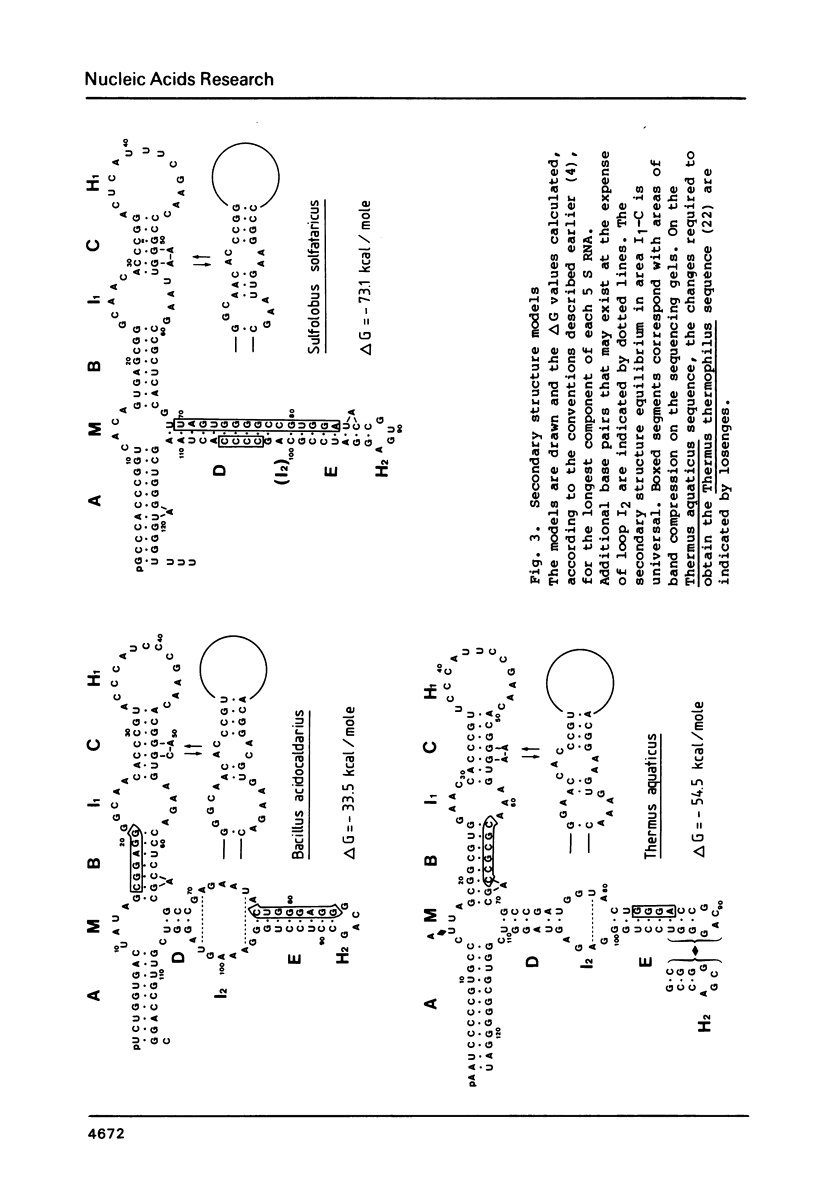
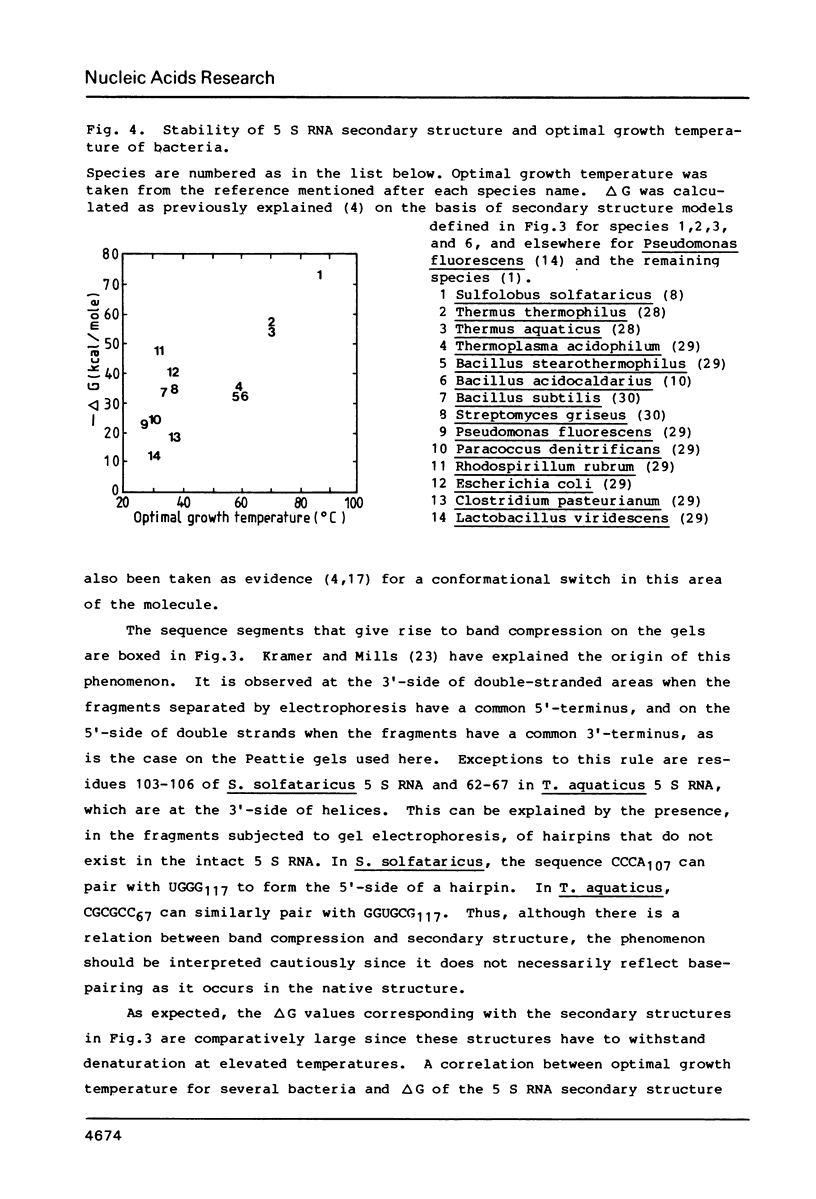
We have determined the nucleotide sequences of the 5 S rRNAs of three thermophilic bacteria: the archaebacterium Sulfolobus solfataricus, also named Caldariella acidophila, and the eubacteria Bacillus acidocaldarius and Thermus aquaticus. A 5 S RNA sequence for the latter species had already been published, but it looked suspect on the basis of its alignment with other 5 S RNA sequences and its base-pairing pattern. The corrected sequence aligns much better and fits in the universal five helix secondary structure model, as do the sequences for the two other examined species. The sequence found for Sulfolobus solfataricus is identical to that determined by others for Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. The secondary structure of its 5 S RNA shows a number of exceptional features which distinguish it not only from eubacterial and eukaryotic 5 S RNAs, but also from the limited number of archaebacterial 5 S RNA structures hitherto published. The free energy change of secondary structure formation is large in the three examined 5 S RNAs.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brierley C. L., Brierley J. A. A chemoautotrophic and thermophilic microorganism isolated from an acid hot spring. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Feb;19(2):183–188. doi: 10.1139/m73-028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D., Brock K. M., Belly R. T., Weiss R. L. Sulfolobus: a new genus of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria living at low pH and high temperature. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(1):54–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00408082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D., Freeze H. Thermus aquaticus gen. n. and sp. n., a nonsporulating extreme thermophile. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):289–297. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.289-297.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhm S., Fabian H., Welfle H. Universal structural features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomal 5S RNA derived from comparative analysis of their sequences. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1982;41(1):1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dams E., Vandenberghe A., De Wachter R. Sequences of the 5S rRNAs of Azotobacter vinelandii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas fluorescens with some notes on 5S RNA secondary structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1245–1252. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Rosa M., Gambacorta A., Bu'lock J. D. Effects of pH and temperature on the fatty acid composition of bacillus acidocaldarius. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):212–214. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.212-214.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wachter R., Chen M. W., Vandenberghe A. Conservation of secondary structure in 5 S ribosomal RNA: a uniform model for eukaryotic, eubacterial, archaebacterial and organelle sequences is energetically favourable. Biochimie. 1982 May;64(5):311–329. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delihas N., Andersen J. Generalized structures of the 5S ribosomal RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7323–7344. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBuy B., Weissman S. M. Nucleotide sequence of Pseudomonas fluorescens 5 S ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):747–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A., Huysmans E., Vandenberghe A., De Wachter R. Collection of published 5S and 5.8S ribosomal RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):r105–r133. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang B. L., De Baere R., Vandenberghe A., De Wachter R. Sequences of three molluscan 5 S ribosomal RNAs confirm the validity of a dynamic secondary structure model. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4679–4685. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huysmans E., Dams E., Vandenberghe A., De Wachter R. The nucleotide sequences of the 5S rRNAs of four mushrooms and their use in studying the phylogenetic position of basidiomycetes among the eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2871–2880. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komiya H., Kawakami M., Takemura S., Kumagai I., Erdmann V. A. Terminal heterogeneity and corrections of the nucleotide sequence of 5S rRNA from an extreme thermophile, Thermus thermophilus HB8. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 25;11(4):913–916. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.4.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer F. R., Mills D. R. RNA sequencing with radioactive chain-terminating ribonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5334–5338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland C. G. The requirements for specific sRNA binding by ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;18(1):90–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küntzel H., Piechulla B., Hahn U. Consensus structure and evolution of 5S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):893–900. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londei P., Teichner A., Cammarano P., De Rosa M., Gambacorta A. Particle weights and protein composition of the ribosomal subunits of the extremely thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Caldariella acidophila. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 1;209(2):461–470. doi: 10.1042/bj2090461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIRENBERG M. W., MATTHAEI J. H. The dependence of cell-free protein synthesis in E. coli upon naturally occurring or synthetic polyribonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct 15;47:1588–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazar R. N., Matheson A. T. Nucleotide sequence of Thermus aquaticus ribosomal 5 S ribonucleic acid. Sequence homologies in thermophilic organisms. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4256–4261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazar R. N., Wildeman A. G. Altered features in the secondary structure of Vicia faba 5.8s rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5345–5358. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl D. A., Luehrsen K. R., Woese C. R., Pace N. R. An unusual 5S rRNA, from Sulfolobus acidocaldarius, and its implications for a general 5S rRNA structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6129–6137. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studnicka G. M., Eiserling F. A., Lake J. A. A unique secondary folding pattern for 5S RNA corresponds to the lowest energy homologous secondary structure in 17 different prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1885–1904. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Rosa M., Gambacorta A., Bu'lock J. D. Extremely thermophilic acidophilic bacteria convergent with Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jan;86(1):156–164. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-1-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]