Abstract
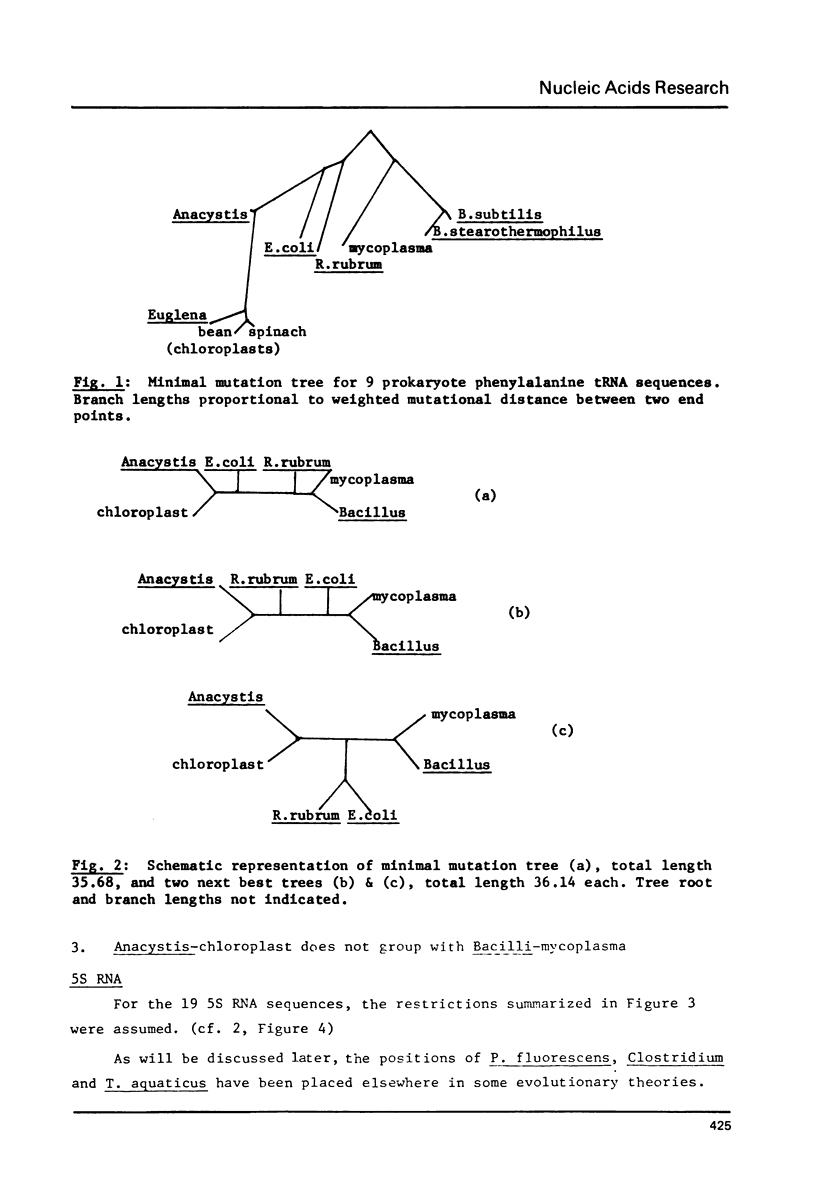
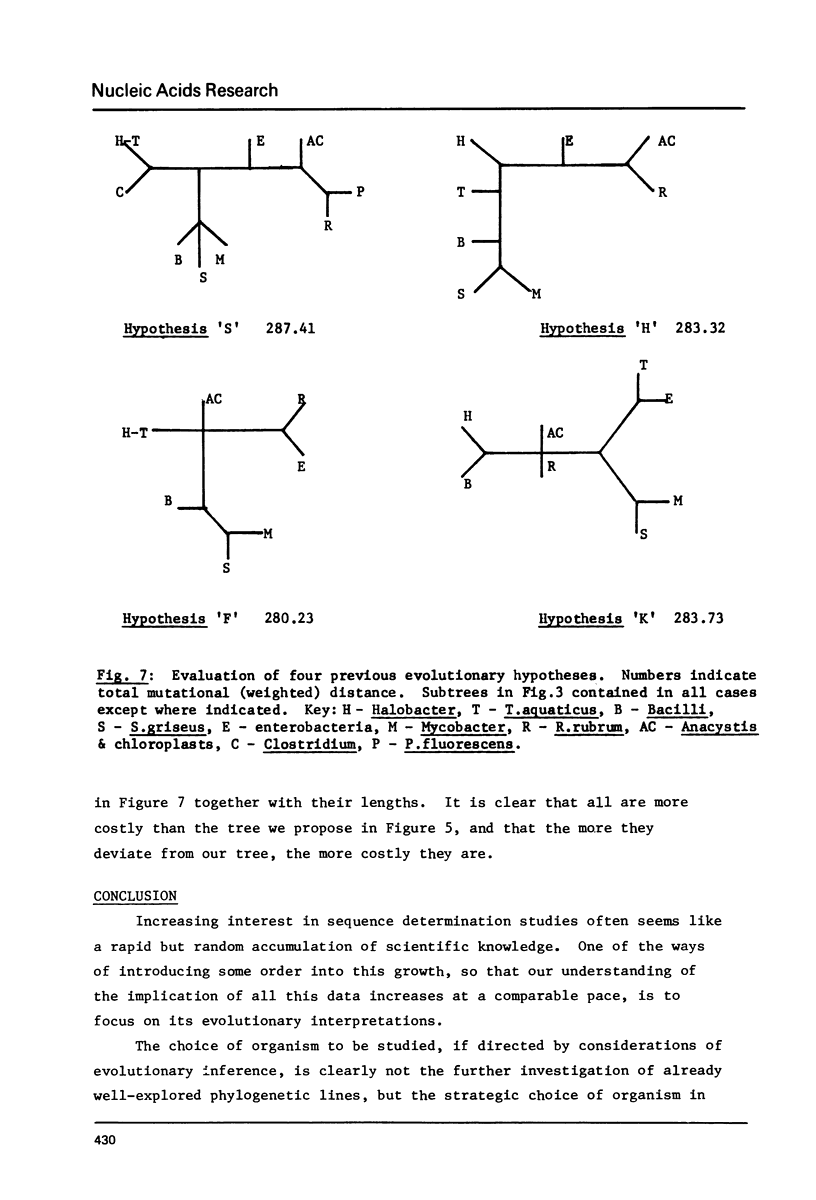
Minimal mutation trees, and almost minimal trees, are constructed from two data sets, one of phenylalanine tRNA sequences, and the other of 5S RNA sequences, from a diverse range of organisms. The two sets of results are mutually consistent. Trees representing previous evolutionary hypotheses are compared using a total weighted mutational distance criterion. The importance of sequence data from relatively little-studed phylogenetic lines is stressed. A procedure is illustrated which circumvents the computational difficulty of evaluating the astronomically large number of possible trees, without resorting to suboptimal methods.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cedergren R. J., Sankoff D., LaRue B., Grosjean H. The evolving tRNA molecule. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1981;11(1):35–104. doi: 10.3109/10409238109108699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A. Collection of published 5S and 5.8S RNA sequences and their precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):r25–r42. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.213-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori H., Osawa S. Evolutionary change in 5S RNA secondary structure and a phylogenic tree of 54 5S RNA species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küntzel H., Heidrich M., Piechulla B. Phylogenetic tree derived from bacterial, cytosol and organelle 5S rRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1451–1461. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larue B., Cedergren R. J., Sankoff D., Grosjean H. Evolution of methionine initiator and phenylalanine transfer RNAs. J Mol Evol. 1979 Dec;14(4):287–300. doi: 10.1007/BF01732496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankoff D., Cedergren R. J., Lapalme G. Frequency of insertion-deletion, transversion, and transition in the evolution of 5S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Evol. 1976 Mar 29;7(2):133–149. doi: 10.1007/BF01732471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. M., Dayhoff M. O. Origins of prokaryotes, eukaryotes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. Science. 1978 Jan 27;199(4327):395–403. doi: 10.1126/science.202030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoncsits A. 3' Terminal labelling of RNA of RNA with beta-32P-pyrophosphate group and its application to the sequence analysis of 5S RNA from Streptomyces griseus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4111–4124. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



