Abstract
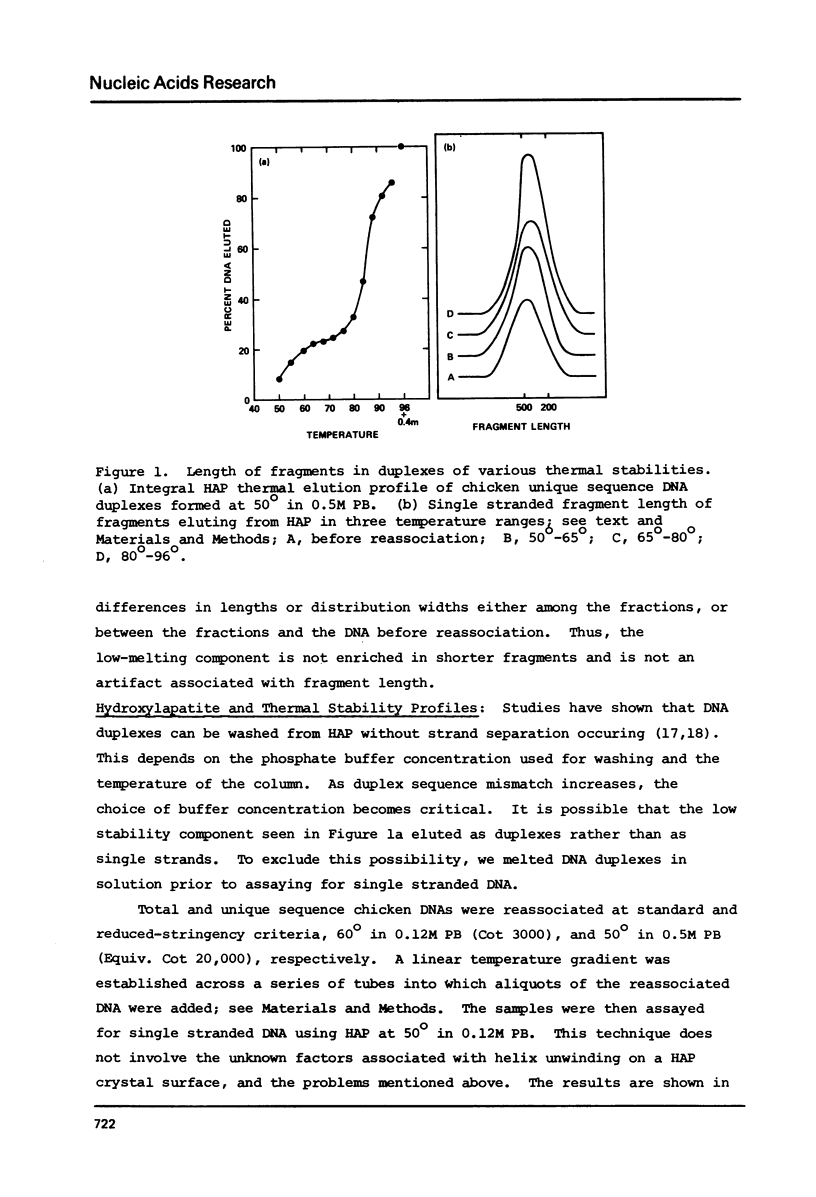
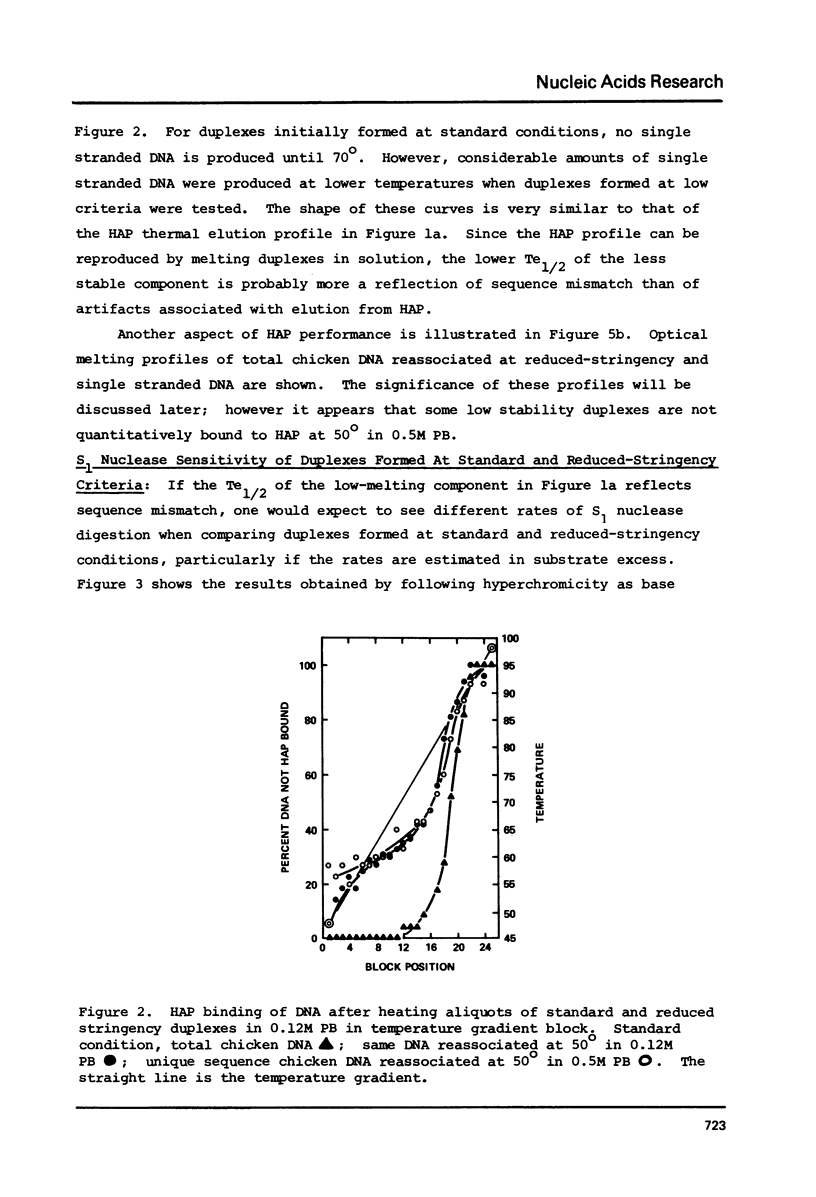
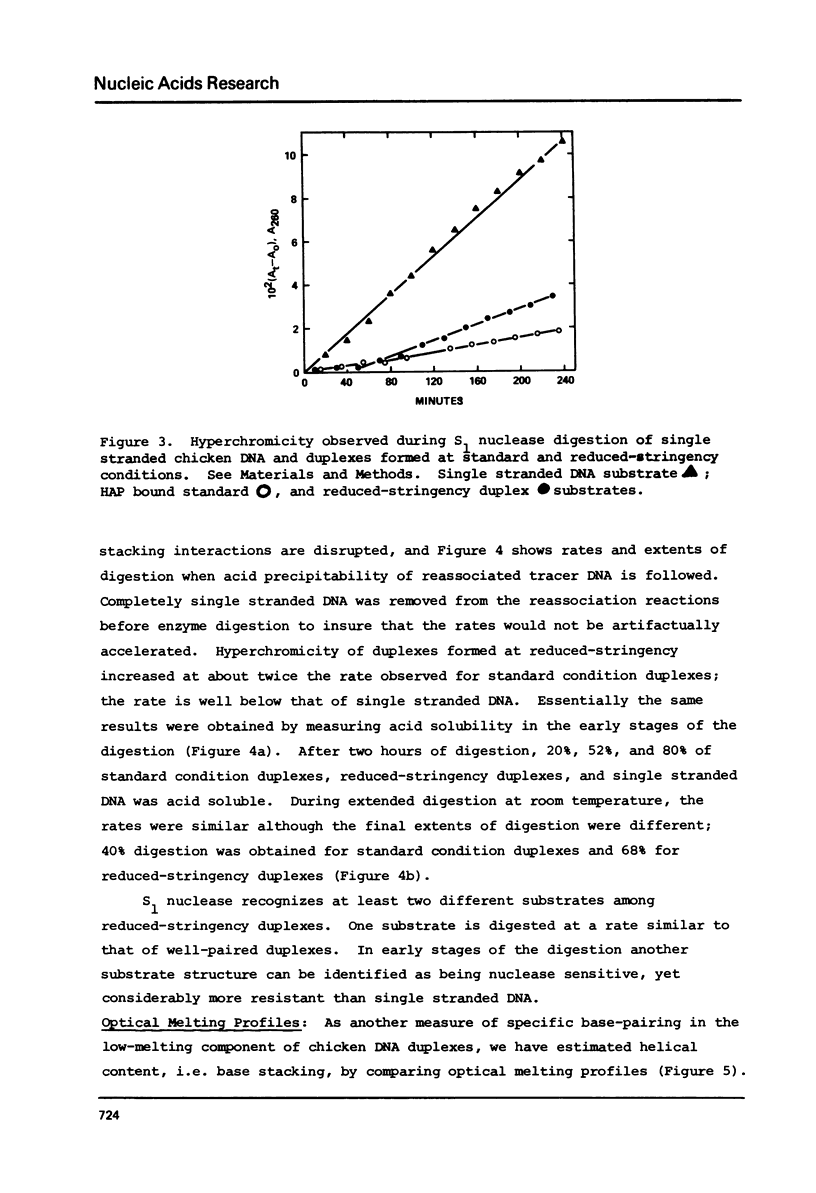
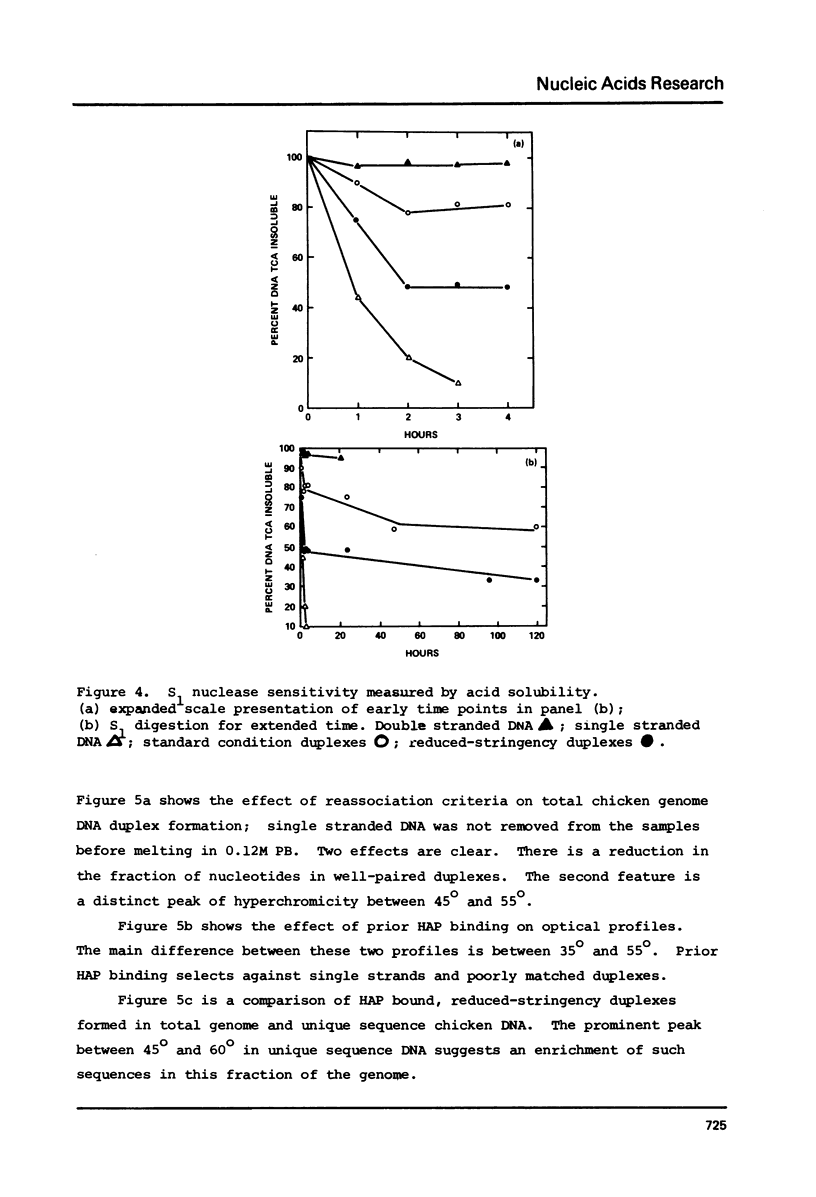
Reduced-stringency DNA reassociation conditions allow low stability duplexes to be detected in prokaryotic, plant, fish, avian, mammalian, and primate genomes. Highly diverged families of sequences can be detected in avian, mouse, and human unique sequence dNAs. Such a family has been described among twelve species of birds; based on species specific melting profiles and fractionation of sequences belonging to this family, it was concluded that permissive reassociation conditions did not artifactually produce low stability structures (1). We report S1 nuclease and optical melting experiments, and further fractionation of the diverged family to confirm sequence specific DNA reassociation at 50 degrees in 0.5 M phosphate buffer.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOLTON H. C., WEISS J. J. Hypochromism in the ultra-violet absorption of nucleic acids and related structures. Nature. 1962 Aug 18;195:666–668. doi: 10.1038/195666a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Brenner D. J., Neufeld B. R., Britten R. J. Reduction in the rate of DNA reassociation by sequence divergence. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 5;81(2):123–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Cetta A., Davidson E. H. The single-copy DNA sequence polymorphism of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1175–1186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Graham D. E., Eden F. C., Painchaud D. M., Davidson E. H. Evolutionary divergence and length of repetitive sequences in sea urchin DNA. J Mol Evol. 1976 Dec 31;9(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01796119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Graham D. E., Neufeld B. R. Analysis of repeating DNA sequences by reassociation. Methods Enzymol. 1974;29:363–418. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)29033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr H. E., Schimke R. T. Intragenomic DNA sequence homologies in the chicken and other members of the class Aves: DNA re-association under reduced stringency conditions. J Mol Evol. 1980 Aug;15(4):291–307. doi: 10.1007/BF01733136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROTHERS D. M., KALLENBACH N. R., ZIMM B. H. THE MELTING TRANSITION OF LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT DNA: THEORY AND EXPERIMENT. J Mol Biol. 1965 Apr;11:802–820. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Schmid C. W. A study of the evolution of repeated DNA sequences in primates and the existence of a new class of repetitive sequences in primates. J Mol Biol. 1979 Feb 5;127(4):437–460. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. M., Schmid C. W. Related single copy sequences in the human genome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 17;609(3):349–363. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. M., Umeda J., Lee R. K., Schmid C. W. A phase diagram of the binding of mismatched duplex DNAs to hydroxyapatite. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 17;609(3):364–371. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall T. J., Grula J. W., Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Evolution of sea urchin non-repetitive DNA. J Mol Evol. 1980 Dec;16(2):95–110. doi: 10.1007/BF01731580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes F. N., Lilly E. H., Ratliff R. L., Smith D. A., Williams D. L. Thermal transitions in mixtures of polydeoxyribodinucleotides. Biopolymers. 1970;9(9):1105–1117. doi: 10.1002/bip.1970.360090911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov I. G., Markov G. G. Heterogeneity of mouse unique deoxyribonucleic acid. FEBS Lett. 1974 Oct 15;47(2):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov I. G., Markov G. G. On the heterogeneity of the slow reassociating ("unique") DNA. Mol Cell Biochem. 1978 Jun 28;20(2):111–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00241389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein W. H., Thomas T. L., Lai C., Scheller R. H., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Characteristics of individual repetitive sequence families in the sea urchin genome studied with cloned repeats. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):889–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPSETT M. N., HEPPEP L. A., BRADLEY D. F. Complex formation between oligonucleotides and polymers. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:857–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird C. D., McConaughy B. L., McCarthy B. J. Rate of fixation of nucleotide substitutions in evolution. Nature. 1969 Oct 11;224(5215):149–154. doi: 10.1038/224149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHELSON A. M. Hypochromicity of oligo- and polynucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jun 11;55:841–848. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90897-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinson H. G. The nucleic acid-hydroxylapatite interaction. II. Phase transitions in the deoxyribonucleic acid-hydroxylapatite system. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):145–150. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy B. J., McConaughy B. L. Related base sequences in the DNA of simple and complex organisms. I. DNA-DNA duplex formation and the incidence of partially related base sequences in DNA. Biochem Genet. 1968 Jun;2(1):37–53. doi: 10.1007/BF01458450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConaughy B. L., McCarthy B. J. Related base sequences in the DNA of simple and complex organisms. VI. The extent of base sequence divergence among the DNAs of various rodents. Biochem Genet. 1970 Jun;4(3):425–446. doi: 10.1007/BF00485758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConaughy B. L., McCarthy B. J. The interaction of oligodeoxynucleotides with denatured DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 21;149(1):180–189. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90700-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. P., Scheller R. H., Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Evolutionary change in the repetition frequency of sea urchin DNA sequences. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):649–660. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young B. D., Paul J. Absence from the mouse genome of DNA sequences related to the globin gene family. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 25;96(4):783–789. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90153-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


