Abstract
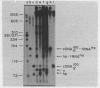
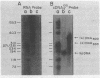
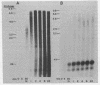
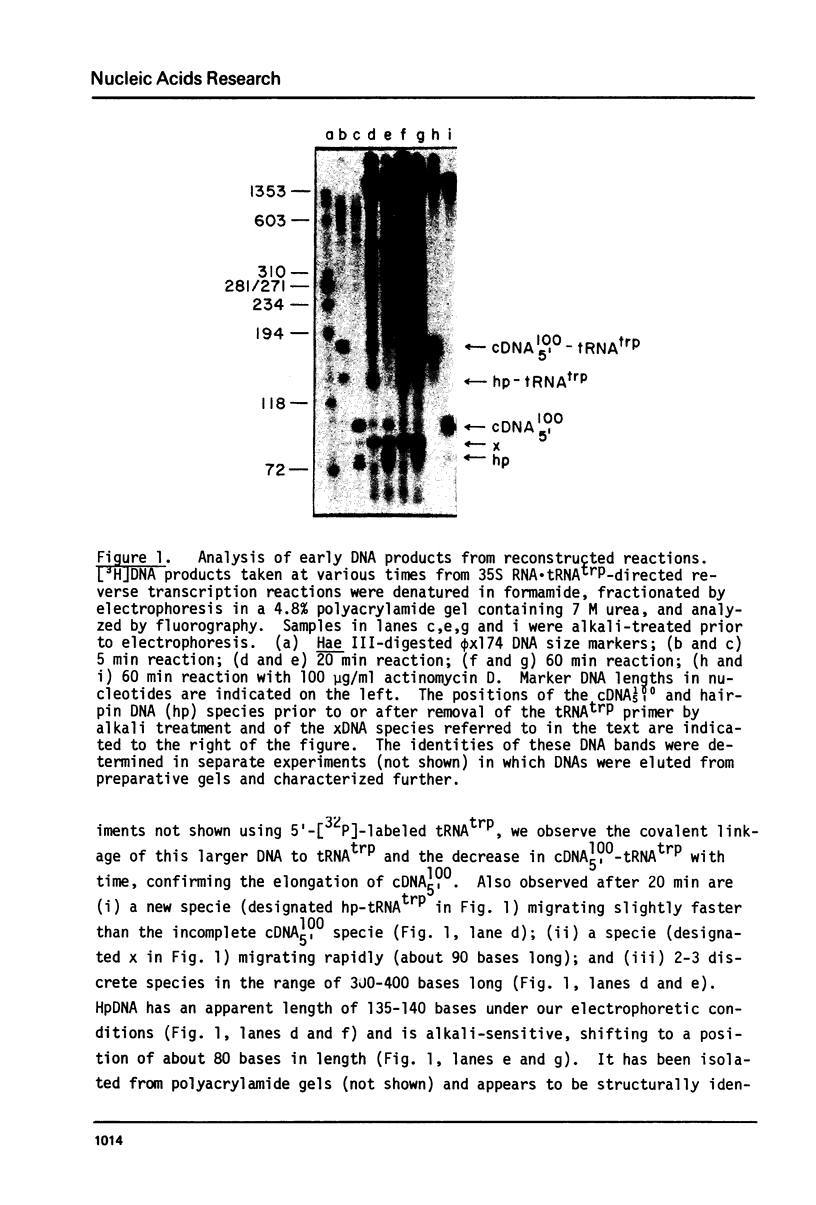
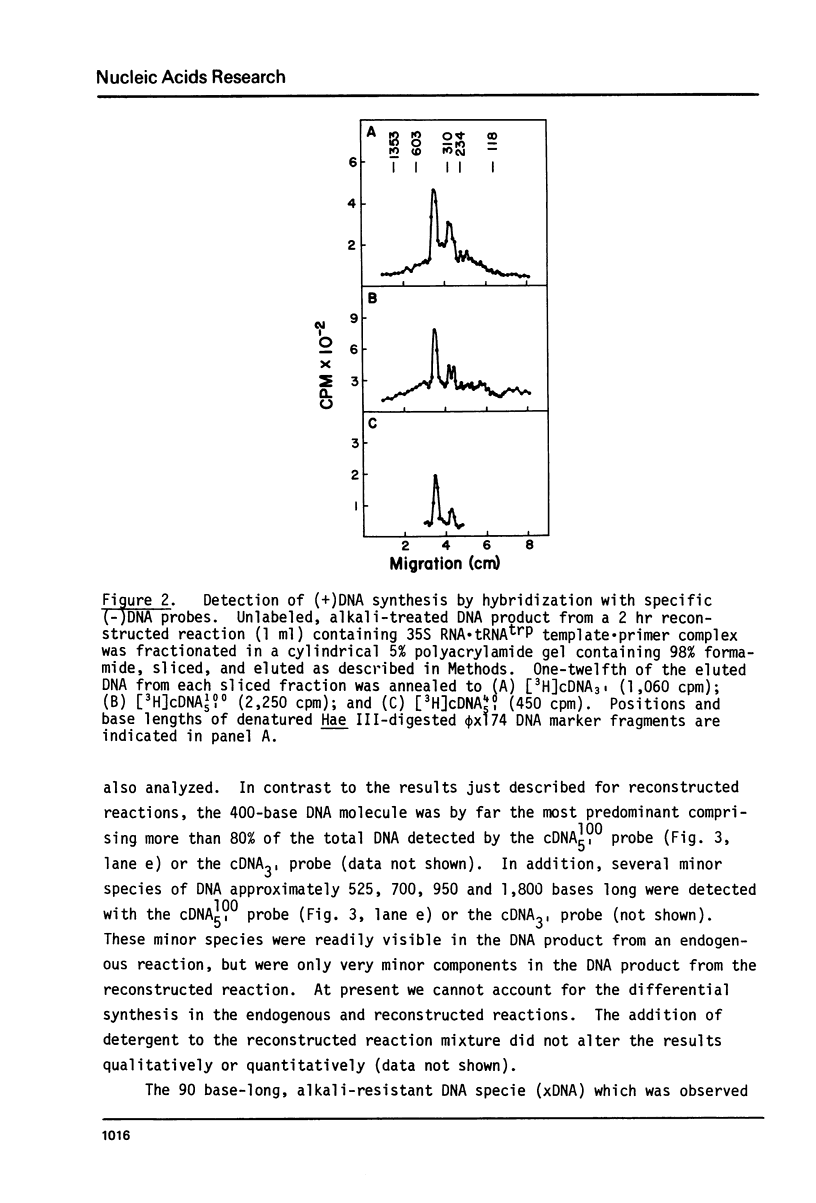
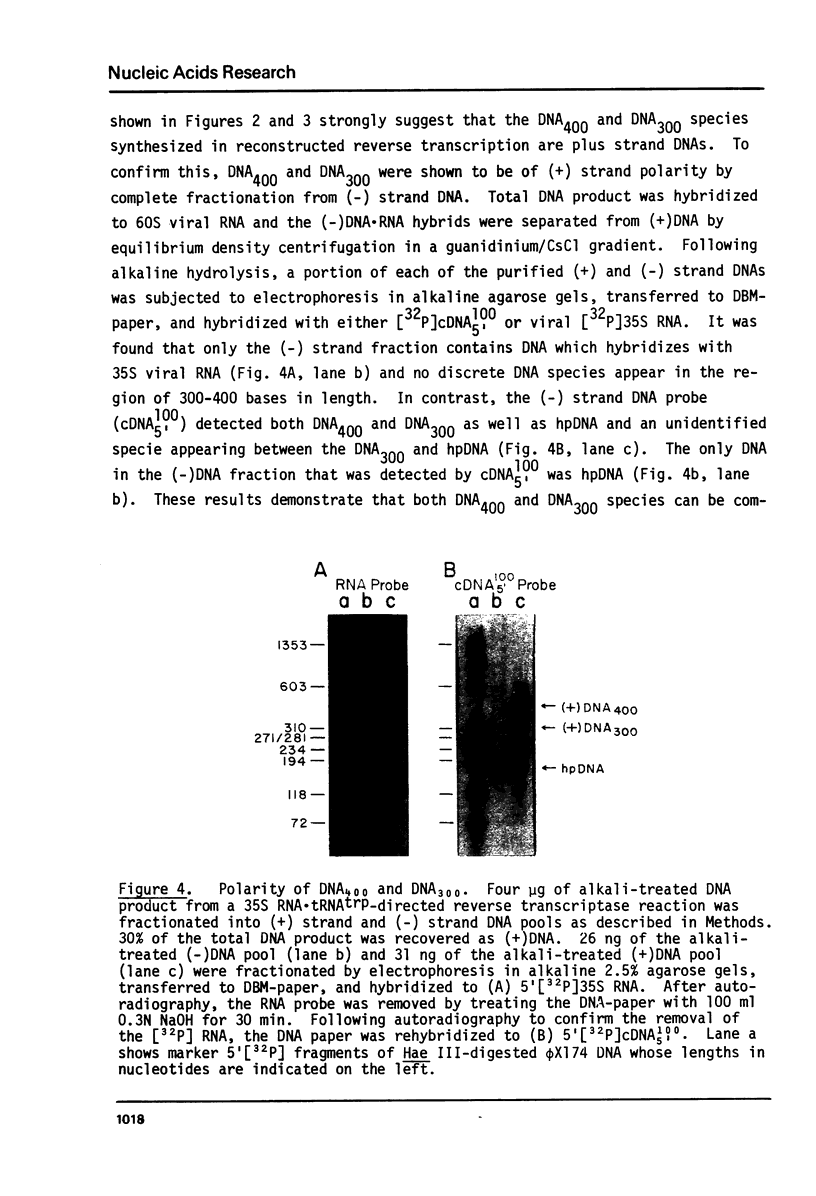
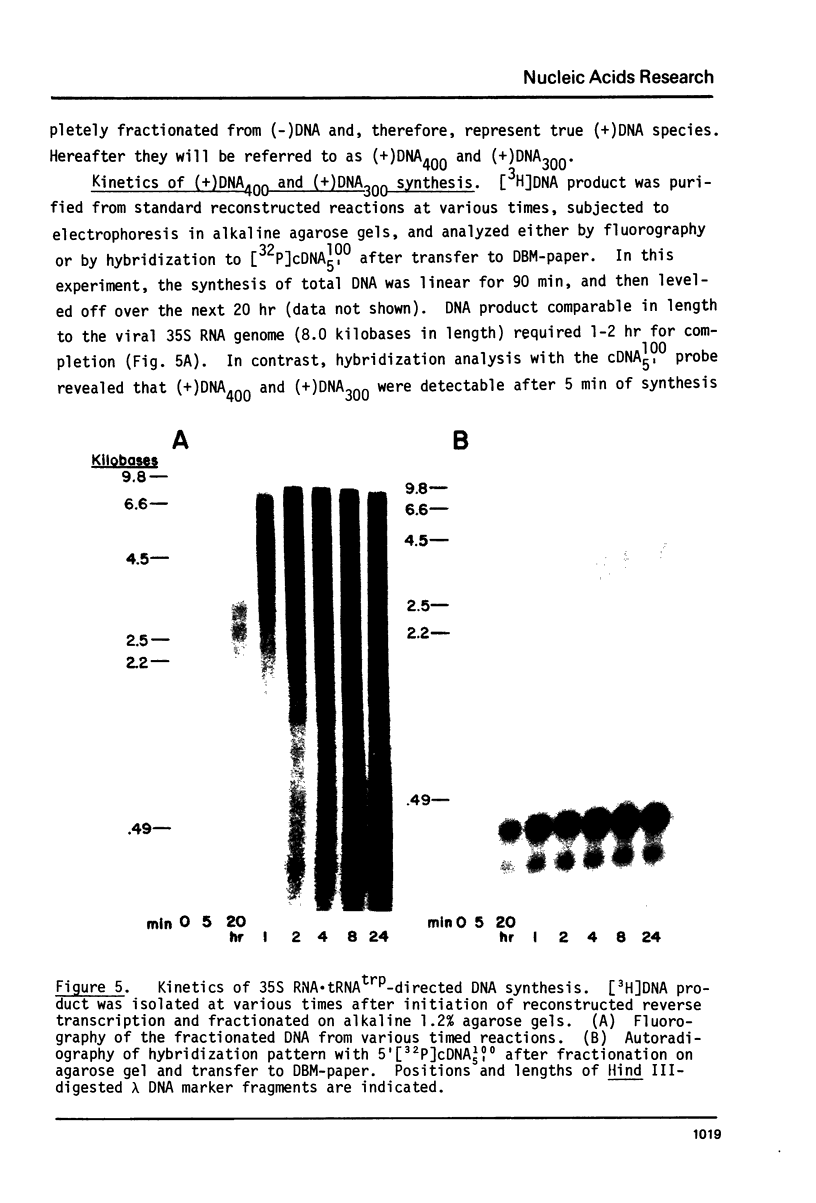
The early DNa products of reverse transcription have been analyzed from reconstructed reactions containing avian myeloblastosis virus 35S RNA . tRNAtrp complex and highly purified reverse transcriptase. We describe conditions for the synthesis of genome-length complementary DNA and two discrete species of plus strand DNA (the same chemical polarity as the viral RNA genome) about 300 and 400 nucleotides in length. Plus DNA400 and plus DNA300 were detected by molecular hybridization with DNA probes complementary to sequences from both the 3'- and 5'-ends of the viral RNA. Both species appear to be copied from the 5'-end of minus strand DNA by their hybridization properties and their early synthesis when only the 5'-end of minus strand DNA is available as template. Restriction endonuclease mapping of plus DNA400 and plus DNA300 rules out a precursor-product relationship between the two. Rather the results suggest a unique initiation site for both species, with plus DNA400 containing internal sequences not present in plus DNA300. Plus DNA400 and plus DNA300 appear to be analogous to early plus DNA species detected in cells early after retrovirus infection. Thus, purified reverse transcriptase appears to be enzymatically sufficient for synthesis of genome-length complementary DNA and initiation and synthesis of early plus strand DNA as observed in infected cells.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1209–1211. doi: 10.1038/2261209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bantle J. A., Maxwell I. H., Hahn W. E. Specificity of oligo (dT)-cellulose chromatography in the isolation of polyadenylated RNA. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:413–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90549-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz E. W., Jr, Dina D. Moloney murine sarcoma virions synthesize full-genome-length double-stranded DNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3294–3298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann D. G., Souza L. M., Baluda M. A. Characterization of avian myeloblastosis-associated virus DNA intermediates. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):366–372. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.366-372.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone L. R., Skalka A. M. Viral DNA synthesized in vitro by avian retrovirus particles permeabilized with melittin. I. Kinetics of synthesis and size of minus- and plus-strand transcripts. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):109–116. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.109-116.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone L. R., Skalka A. M. Viral DNA synthesized in vitro by avian retrovirus particles permeabilized with melittin. II. Evidence for a strand displacement mechanism in plus-strand synthesis. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):117–126. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.117-126.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. The isolation of messenger RNA from mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:605–612. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunte T., Novak U., Friedrich R., Moelling K. Effect of actinomycin D on nucleic acid hybridization: the cause of erroneous DNA elongation during DNA synthesis of RNA tumor viruses in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 11;610(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaconas G., van de Sande J. H. 5'-32P labeling of RNA and DNA restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Faras A. J. Avian retrovirus RNA-directed DNA synthesis: transcription at the 5' terminus of the viral genome and the functional role for the viral terminal redundancy. Virology. 1978 May 15;86(2):297–311. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg J. E., Sawyer R. C., Taylor J. M., Faras A. J., Levinson W. E., Goodman H. M., Bishop J. M. Transcription of DNA from the 70S RNA of Rous sarcoma virus. I. Identification of a specific 4S RNA which serves as primer. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1126–1133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1126-1133.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dina D., Benz E. W., Jr Structure of murine sarcoma virus DNA replicative intermediates synthesized in vitro. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):377–389. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.377-389.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Bister K., Moscovici C. Genetic structure of avian myeloblastosis virus, released from transformed myeloblasts as a defective virus particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5120–5124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. P., Soll L., Yarus M. The purification and sequence of a temperature-sensitive tryptophan tRNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5562–5566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enea V., Zinder N. D. Guanidinium-CsCl density gradients for isopycnic analysis of nucleic acids. Science. 1975 Nov 7;190(4214):584–586. doi: 10.1126/science.1188358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich R., Kung H. J., Baker B., Varmus H. E., Goodman H. M., Bishop J. M. Characterization of DNA complementary to nucleotide sequences at the 5'-terminus of the avian sarcoma virus genome. Virology. 1977 Jun 1;79(1):198–215. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90345-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilboa E., Goff S., Shields A., Yoshimura F., Mitra S., Baltimore D. In vitro synthesis of a 9 kbp terminally redundant DNA carrying the infectivity of Moloney murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):863–874. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Bovey R., Young R. A. Tissue-specific expression of mouse-alpha-amylase genes: nucleotide sequence of isoenzyme mRNAs from pancreas and salivary gland. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada F., Sawyer R. C., Dahlberg J. E. A primer ribonucleic acid for initiation of in vitro Rous sarcarcoma virus deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3487–3497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Rous sarcoma virus genome is terminally redundant: the 5' sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):989–993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu T. W., Sabran J. L., Mark G. E., Guntaka R. V., Taylor J. M. Analysis of unintegrated avian RNA tumor virus double-stranded DNA intermediates. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):810–818. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.810-818.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacian D. L., Watson K. F., Burny A., Spiegelman S. Purification of the DNA polymerase of avian myeloblastosis virus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 24;246(3):365–383. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90773-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung H. J., Fung Y. K., Majors J. E., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Synthesis of plus strands of retroviral DNA in cells infected with avian sarcoma virus and mouse mammary tumor virus. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):127–138. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.127-138.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J. P. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity of RNA tumor virus. VI. Processive mode of action of avian myeloblastosis virus polymerase. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):932–939. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.932-939.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., van deSande H. Chain length determination of small double- and single-stranded DNA molecules by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3787–3794. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manly K. F., Smoler D. F., Bromfeld E., Baltimore D. Forms of deoxyribonucleic acid produced by virions of the ribonucleic acid tumor viruses. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):106–111. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.106-111.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell J. P., Garapin A. C., Levinson W. E., Quintrell N., Fanshier L., Bishop J. M. DNA polymerases of Rous sarcoma virus: delineation of two reactions with actinomycin. Nature. 1970 Oct 31;228(5270):433–435. doi: 10.1038/228433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra S. W., Goff S., Gilboa E., Baltimore D. Synthesis of a 600-nucleotide-long plus-strand DNA by virions of Moloney murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4355–4359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak U., Friedrich R., Moelling K. Elongation of DNA complementary to the 5' end of the avian sarcoma virus genome by the virion-associated RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):438–452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.438-452.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyes B. E., Stark G. R. Nucleic acid hybridization using DNA covalently coupled to cellulose. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen J. C., Watson K. F. Avian retrovirus RNA-directed DNA synthesis by purified reverse transcriptase. Covalent linkage of RNA to plus strand DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 31;97(4):1376–1383. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Dahlberg J. E. RNA-directed DNA synthesis in Moloney murine leukemia virus: interaction between the primer tRNA and the genome RNA. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):398–407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.398-407.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosok M. J., Watson K. F. Fractionation of two protein kinases from avian myeloblastosis virus and characterization of the protein kinase activity preferring basic phosphoacceptor proteins. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):872–880. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.872-880.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer R. C., Dahlberg J. E. Small RNAs of Rous sarcoma virus: characterization by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and fingerprint analysis. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1226–1237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1226-1237.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Zamecnik P. C., Weith H. L. Rous sarcoma virus genome is terminally redundant: the 3' sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):994–998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shank P. R., Hughes S. H., Kung H. J., Majors J. E., Quintrell N., Guntaka R. V., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Mapping unintegrated avian sarcoma virus DNA: termini of linear DNA bear 300 nucleotides present once or twice in two species of circular DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1383–1395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staskus K. A., Collett M. S., Faras A. J. Initiation of DNA synthesis by the avian oncornavirus RNA-directed DNA polymerase: structural and functional localization of the major species of primer RNA on the oncornavirus genome. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):162–168. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll E., Billeter M. A., Palmenberg A., Weissmann C. Avian myeloblastosis virus RNA is terminally redundant: implications for the mechanism of retrovirus replication. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):57–72. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90185-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. The terminal redundancy of the retrovirus genome facilitates chain elongation by reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1115–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tal J., Kung H. J., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Characterization of DNA complementary to nucleotide sequences adjacent to poly(A) at the 3'-terminus of the avian sarcoma virus genome. Virology. 1977 Jun 1;79(1):183–197. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90344-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M. An analysis of the role of tRNA species as primers for the transcription into DNA of RNA tumor virus genomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 21;473(1):57–71. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(77)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Hsu T. W. Reverse transcription of avian sarcoma virus RNA into DNA might involve copying of the tRNA primer. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):531–534. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.531-534.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Illmensee R. Site on the RNA of an avian sarcoma virus at which primer is bound. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):553–558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.553-558.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Illmensee R., Summers J. Efficeint transcription of RNA into DNA by avian sarcoma virus polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 6;442(3):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Mizutani S. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1211–1213. doi: 10.1038/2261211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Heasley S., Kung H. J., Oppermann H., Smith V. C., Bishop J. M., Shank P. R. Kinetics of synthesis, structure and purification of avian sarcoma virus-specific DNA made in the cytoplasm of acutely infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):55–82. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90295-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M. The reverse transcriptase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 21;473(1):1–38. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(77)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M. Purification and further properties of single-strand-specific nuclease from Aspergillus oryzae. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):192–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson K. F., Schendel P. L., Rosok M. J., Ramsey L. R. Model RNA-directed DNA synthesis by avian myeloblastosis virus DNA polymerase and its associated RNase H. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3210–3219. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]