Abstract
Few biopharmaceutical preparations developed from biologicals are available for tissue regeneration and scar management. When developing biological treatments with cellular therapy, selection of cell types and establishment of consistent cell banks are crucial steps in whole-cell bioprocessing. Various cell types have been used in treatment of wounds to reduce scar to date including autolog and allogenic skin cells, platelets, placenta, and amniotic extracts. Experience with fetal cells show that they may provide an interesting cell choice due to facility of outscaling and known properties for wound healing without scar. Differential gene profiling has helped to point to potential indicators of repair which include cell adhesion, extracellular matrix, cytokines, growth factors, and development. Safety has been evidenced in Phase I and II clinical fetal cell use for burn and wound treatments with different cell delivery systems. We present herein that fetal cells present technical and therapeutic advantages compared to other cell types for effective cell-based therapy for wound and scar management.
1. Introduction
Cell-based therapies are penetrating gently into routine medical care and especially for wound management of skin. They offer the promise of repairing and/or replacing damaged tissue and restoring lost functionality, because ideally, they provide all of the factors necessary for wound healing. Several cell types and tissues have been proposed as starting material including autologous cells, adult stem cells including those derived from bone marrow, and adipose tissue, fetal cells, embryonic stem cells, platelets, and tissues from placental and amniotic fluid. These cell types are used for biological preparations in processing vaccines and medicinal, veterinary, and tissue engineering products [1–41]. As the literature and information is vast on cell-based therapies, this paper will concentrate on fetal cells as the choice in wound and scar management. Firstly, we will define differences between stem, and mesenchymal and fetal cells, as the literature is confusing with these terminologies, followed by a short review of fetal wound healing and associated processes. Importantly, cell choice and the technical specifications to outscale, stability, safety, and delivery are the major hurdles for development of biologicals for better wound treatments and scar management. Fetal skin cells present biological, technical, and therapeutic advantages lending towards possible routine cellular-based therapy for wound and scar management. All of these aspects will be addressed in the description of how dedicated fetal skin cell banks can be developed, potential delivery systems, and cellular mechanisms of repair with gene profile differences between fetal and young skin cells to illustrate biological families implicated in wound healing. Finally, the capacity of this cell type in wound and scar management is illustrated and summarized from Phase I and II clinical safety studies in humans.
1.1. Cellular Sources as Therapeutic Agents: Terminology Clarification, Technical Requirements, and Cell Banking
There is some confusion between the terminology and potential of embryonic, fetal, and adult stem cells. These cells are referred to in the literature as embryonic stem cells, fetal cells, and mesenchymal stem cells, respectively. However, more frequently, all of these cell types are referred to as simply stem cells, neglecting all of the legal and technical aspects associated with each specific cell type. To illustrate these differences, Figure 1 lists the major cell sources used in developing therapeutic applications showing that some cell choices are more adaptable to cellular therapy in patients. This adaptability is highly associated with technical facility of expanding and selecting cell populations needed. Tissue choices from animal and human at all ages of development can be evaluated with advantages and disadvantages for each final cell type (Figure 1). In legal aspects, the term “embryo” denotes the earliest stages following fertilization of an ovum by a sperm. Zygote would include early stage cleavage embryos produced by cell division up to 50–60 cell stage (each cell which is a blastomere) and the blastocyte for the 60 cell stage to the point of implantation at about 2 weeks after-fertilization. “Embryonic stem cells” (ES) are developed from preimplantation embryos from the inner-cell mass before the first 2 weeks of development. These cells are frequently obtained from extra embryos developed by “in vitro” fertilization techniques to aid couples for fertility purposes. Because these particular cells have created quite an ethical debate, other researchers have begun using “fetal embryonic cells” derived from voluntary interruption of pregnancy between 5 and 8 weeks. Cell lines are normally developed from the genital ridge of the fetus. As this tissue is considered as an organ donation in most countries, it bypasses the major problems that have been raised by embryonic stem cells. Most fetal cell research is developed from specific tissues such as skin, muscle bone, or cartilage at the latter end of the first trimester (11–14 weeks) following voluntary interruption of pregnancies. Cell lines at this stage are tissue specific, and therefore, “fetal cells” are differentiated with specific functions. Fetal cells are derived from a legal organ donation when the mother donor ensures informed consent, provided that the tissue is a donation and not paid for and that there is no change in timing or method of pregnancy interruption for the sake of research. As fetal cells are from organ donations and under transplantation medicine, they are also routinely included in the terminology as adult stem cells.
Figure 1.
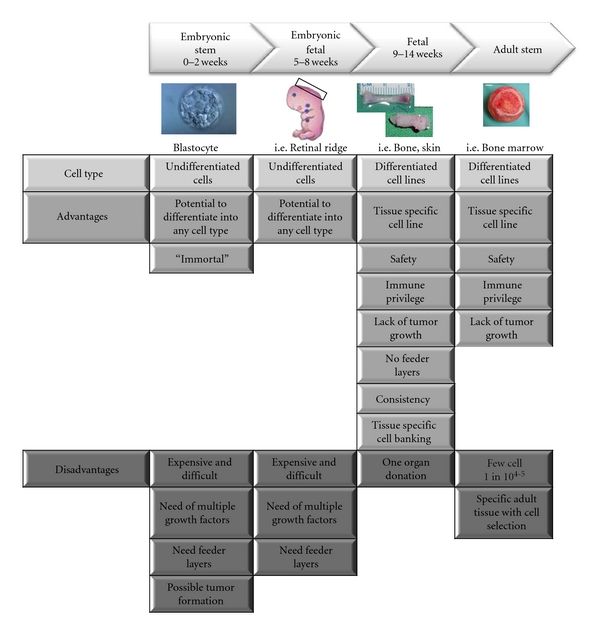
Cellular source and development stage with advantages and disadvantages.
Adult stem cells can be established from most tissues of the body, and the most frequently isolated ones come from bone marrow and adipose tissues of young and adult individuals and are referred to as “mesenchymal stem cells” (MSCs).
Each of the cell types mentioned in Figure 1 have different technical requirements for producing appropriate cells that could be used as therapeutic agents.
Embryonic stem cells that are isolated from early-stage embryo present the particularity of being pluripotent and have an advantage over those cells from adult mesenchymal stem cells, which can differentiate only into a restricted number of cell lineages. However, cultures of these stem cell types are technically very demanding, because the amount of tissue to begin is very low for embryonic stem cells and the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from the tissue mass is difficult (only 1 stem cell for every 104-5 cells in total adult tissue). Maintenance and expansion of stem cells in an undifferentiated state require the addition of many specific growth factors [28, 29], and so far, culture of embryonic stem cells and some mesenchymal stem cells are not possible without feeder layers which is in some part responsible for the inconsistent colony cell growth [29]. The necessity to use many exogenous growth factors as well as feeder layers to differentiate into specific cellular lineages are limiting factors for the scaleup of stem cell cultures for clinical applications. There are other major issues with these stem cell types for security as the cells can dedifferentiate once placed into an in vivo environment and even develop into tumors. Many techniques involving cell cloning or encapsulation would be necessary for assuring delivery of correct cell populations.
Unlike stem cells, fetal cells are differentiated cells with high expansion, regeneration, and low immunogenic properties [10, 12]. As the fetal cells are already differentiated and do not need to be directed or altered, the vast number of additional growth factors normally necessary are not needed for cell culture and expansion, and these cells are not known to dedifferentiate once placed into the in vivo environment [7–9, 12].
Establishment of cell banks is a crucial step in the process of many vaccines, medicinal products, or tissue-engineering products, and therefore, the choice of cell type is extremely important for technical and security reasons. A “cell bank” is the stocked product of consistent cell cultures that are frozen into small vials that withstand long-term freezing in liquid nitrogen (−165°C). The initial cell bank is frequently termed the master cell bank (MCB) from which each vial can derive a working cell bank (WCB). Whole cell bioprocessing and adaptable procedures to good manufacturing processes (GMPs) make it possible to develop extensive MCB and WCB to facilitate thorough testing of the cells. Once MCBs are accomplished, WCB can be produced to establish individual batches of treatments for high numbers of patients. Further, these cell banks can be tested completely for safety regarding sterility, pathogens and adventitious agents, and tumorigenicity.
Historically, fetal cells have been used in cell banking procedures for medicinal products for many years already. Already in the 1930s, medical doctors and scientists have used tissue from voluntary pregnancy interruptions not only for understanding cell biology but also an important entity in the development of vaccines by using defined tissue-derived cell lines. The Nobel Prize for Medicine in 1954 was awarded to American immunologists who developed the polio vaccine based on cultures of human fetal cells. Since this time, many other necessary vaccines (rubella, chicken pox, hepatitis A, etc.) have been developed with the use of fetal cell lines including two primary human diploid cell lines which were originally prepared in the 1960s. The first cell line, WI-38 (Wistar Institute 38), was developed by Leonard Hayfleck in 1964 from fetal tissue from a voluntary pregnancy interruption and later given the ATCC (American Type Culture Collection) number of CCL-75. This cell line was used for the historical production of vaccine RA 27/3 against Rubella.
1.2. Fetal Wound Healing
Considerable interest and research have been dedicated to the understanding of wound healing and the associated process. Whereas adult cutaneous wounds heal more slowly and with scar formation to restore tissue integrity, fetal skin, in utero, is observed to have rapid and scarless tissue repair characterized by regeneration of an organized dermis with normal appendages and by a relative lack of inflammation [42–45]. Fundamental differences between fetal and adult skin and the fetal and adult skin wound environment may be important in inducing efficient tissue repair.
Molecular analysis of wound healing has largely been devoted to cytokines and most particularly those of the transforming growth factor (TGF) family and their role in manipulating cutaneous wound healing and scar formation [46]. It has been suggested that scarless wound healing in fetal skin at early gestation is a result of the unique cytokine or growth factor profile [3, 45]. Of these, transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) has been most widely studied as it is implicated in the transition between scarless healing and repair with scar formation [47].
Three highly homologous TGF-β isoforms are known in humans: β1, β2, and β3 [46]. Each form has been found by immunohistochemistry in unwounded fetal skin. However, low levels of TGF-β1 and high levels of TGF-β3 are expressed at gestational ages associated with scarless repair [3, 45].
Exogenous application of TGF-β1 to normally scarless fetal wounds resulted in scar formation with an adult-like inflammatory response observed [47]. The profibrotic nature of TGF-β1, and possibly TGF-β2, was confirmed in wounds of adult rats, since neutralizing TGF-β1 and β2 with antibodies partially reduced the amount of scarring [48]. However, antifibrotic properties can be seen with the isoform TGF-β3 as injection, or application of this isoform showed reduced scarring and inflammation in adult wounds [48, 49]. When using a rabbit hypertrophic scar model, TGF-β3 was confirmed to show increased properties in wound healing but not scar reduction [50]. It has been suggested that the relative proportion of TGF-β isoforms, and not the absolute concentration of any one isoform determines the wound repair outcome [3, 45–47].
TGF-β2 has been shown to be significantly higher in fetal skin dermal fibroblasts than in foreskin tissue fibroblasts but no major differences with TGF-β1 and TGF-β3 [11]. When looking at expression of the three isoforms in five different fetal skin cell lines, it was observed that TGF-β1 gene expression is much higher than that of TGF-β3. Importantly, variability between fetal donors for the TGF-β isoforms was very small which is generally the opposite for that of skin from young and old donors. Importance has been given to the TGF-β3 isoform by a company in England, Renovo Ltd., who have used human recombinant TGF-β3 (Juvista) in clinical trials showing 70% response rate for scar reduction to date.
However, TGF-β1 and β2 neutralizing antibodies do not entirely prevent scarring in the adult, and other studies question the efficacy of TGF-β3 in wound healing [50].
More recently, inhibition of TGFbRII-mediated signaling was demonstrated with a gene-therapy approach in a rabbit hypertrophic scarring model showing some reduction biologically. Lack of complete reduction could either be due to the technical difficulties suggested by the authors for low transduction efficiency, or it may suggest that factors other than TGF-β may also be important in scarless repair. As TGF-β's particular importance in wound healing is also due to their ability to modulate ECM formation, two genes have previously been shown in wound healing in fetal skin (laminin b1, LAMb1) and in hypertrophic scar (dermatopontin, DPT) [51]. Dermatopontin and laminins have important roles in cell-matrix interactions and matrix assembly, and dermatopontin has been shown to be decreased in hypertrophic scar and systemic sclerosis skin fibroblasts [52].
As wound healing is very complex, there are certainly many other molecules within the TGF-β superfamily which could have a role. For instance, bone morphogenic protein (BMP) family of genes and their receptors are among those in the TGF-β superfamily genes and have also been strongly associated with cutaneous wound healing and scarless wound healing in the fetus. Overexpression of BMP-6 was shown to delay re-epitheliazation and promote scar formation in a transgenic mouse model [53]. BMP-6 is important for maintaining skin homeostasis and is 3.8 times higher expressed in fetal dermal fibroblasts than in newborn foreskin fibroblasts. More recent studies have shown evidence for the importance of angiogenesis and nerve involvement in wound repair [54, 55]. Pleiotrophin (PTN), a cytokine inducing heparin-binding/differentiation, is certain to have a major role in angiogenesis in wound healing. Midkine (MDK) and PTN, which have 50% amino acid sequence identity and striking domain homology, are the two members of the Ptn/Mdk developmental gene family [55]. Interestingly, PTN has been recently shown to induce functional neovasculature in vivo [55]. As fetal tissue heals with no inflammatory response, lower MDK and PTN expression is perhaps preferable, as they could have an important role in angiogenesis.
In the past, gene profiling differences have been shown for fetal cells compared to adult cells [9], and therefore, it was also of interest to determine gene expression alterations in banked fetal dermal skin cells (used in tissue engineering for burns and wounds to date) and young dermal skin cells that have been banked in the same manner to have a listing of potential gene families from fetal banked cells to compare to young skin cells and other gene profiling studies. Young skin was, therefore, obtained from behind the ears of a 12 year old boy (12 yOS) following a surgical ear alignment and with the approval of the Hospital Ethics Committee to use this discarded material for research with parent and child oral and written approval. To identify differentially expressed genes in banked fetal dermal skin cells, we used cDNA microarray containing approximately 12,500 sequences (U95A human genome chip, Affymetrix UK, High Wycombe). Three arrays were hybridized for banked fetal skin cells (14 wFS) and banked young skin cells each (12 yOS). Briefly, RNA was isolated from cultured cells at passage one for each of the three cell banks. The statistical analyses were performed with a classical analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the global error assessment (GEA). Genes were selected by this method at α level 0.001. Significant genes, with at least a 1.5 fold change, were classified according to the gene ontology following the criteria of the DAVID (database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery) as described previously [9].
When comparing banked fetal dermal skin cells to banked young fibroblasts with our conditions, 167 genes changed by 1.5 fold or more. Between those genes, 74 were upregulated in fetal cells and 93 were downregulated (Table 1). Gene ontology of important differentially expressed genes was annotated following the criteria of the DAVID database (http://david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov/) for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery) [56, 57]. As many of the genes analyzed could be involved in multiple biological processes, they have been placed in a category for their best representation (Figure 2).
Table 1.
Regulated genes in fetal banked cells compared to young banked cells.
| Enter gene ID | Gene symbol | Gene name | Fold increase (expressed in log2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3205 | HOXA9 | Homeobox A9 | 4.103 |
| 2890 | GRIA1 | Glutamate receptor, ionotropic, AMPA 1 | 4.050 |
| 3223 | HOXC6 | Homeobox C6 | 3.255 |
| 3202 | HOXA5 | Homeobox A5 | 3.243 |
| 2861 | GPR37 | G protein-coupled receptor 37 (Endothelin receptor type B-LIKE) | 3.221 |
| 5789 | PTPRS | Protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, D | 3.171 |
| 3206 | HOXA10 | Homeobox A10 | 3.084 |
| 2321 | FLT1 | FMS-related tyrosine kinase 1 | 3.060 |
| 9452 | ITM2A | Integral membrane protein 2A | 3.030 |
| 862 | RUNX1T1 | RUNT-related transcription factor 1; translocated TO, 1 (cyclin D-related) | 2.985 |
| 1047 | CLGN | Calmegin | 2.916 |
| 744 | MPPED2 | Metallophosphoesterase domain containing 2 | 2.844 |
| 9056 | SLC7A7 | Solute carrier family 7, Member 7 | 2.806 |
| 1948 | EFNB2 | Ephrin-B2 | 2.770 |
| 23266 | LPHN2 | Latrophilin 2 | 2.714 |
| 9865 | KIAA0644 | KIAA0644 gene product | 2.689 |
| 23705 | CADM1 | Immunoglobulin superfamily, member 4 | 2.607 |
| 1016 | CDH18 | Cadherin 18, type 2 | 2.553 |
| 2294 | FOXF1 | Forkhead box F1 | 2.543 |
| 140462 | ASB9 | DKFZP564L0862 protein | 2.452 |
| 5947 | RBP1 | Retinol binding protein 1, cellular | 2.394 |
| 83939 | EIF2A | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2A, 65 KDA | 2.276 |
| 5918 | RARRES1 | Retinoic acid receptor responder (tazarotene induced) 1 | 2.256 |
| 3306 | HSPA2 | Heat shock 70 KDA protein 2 | 2.211 |
| 5880 | RAC2 | RAS-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 2 (RHO family, small GTP binding protein RAC2) | 2.175 |
| 151230 | KLHL23 | Kelch-like 23 | 2.171 |
| 284 | ANGPT1 | Angiopoietin 1 | 2.171 |
| 2201 | FBN2 | Fibrillin 2 (congenital contractural arachnodactyly) | 2.164 |
| 3880 | KRT19 | Keratin 19 | 2.163 |
| 57157 | PHTF2 | Putative homeodomain transcription factor 2 | 2.147 |
| 154796 | AMOT | Angiomotin | 2.121 |
| 1012 | CDH13 | Cadherin 13, H-cadherin (heart) | 2.086 |
| 5507 | PPP1R3C | Protein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 3C | 2.042 |
| 1908 | EDN3 | Endothelin 3 | 2.032 |
| 6319 | SCD | Stearoyl-coa desaturase (delta-9-desaturase) | 2.022 |
| 5307 | PITX1 | Paired-like homeodomain transcription factor 1 | 2.008 |
| 6899 | TBX1 | T-box 1 | 1.957 |
| 5099 | PCDH7 | BH-protocadherin (brain-heart) | 1.939 |
| 3215 | HOXB5 | Homeobox B5 | 1.880 |
| 6664 | SOX11 | Sry (sex determining region Y)-box 11 | 1.862 |
| 4004 | LMO1 | Lim domain only 1 (rhombotin 1) | 1.830 |
| 10924 | SMPDL3A | Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase, acid-like 3A | 1.810 |
| 3233 | HOXD4 | Homeobox D4 | 1.810 |
| 3232 | HOXD3 | Homeobox D3 | 1.809 |
| 1305 | COL13A1 | Collagen, type XIII, alpha 1 | 1.772 |
| 444 | ASPH | Aspartate beta-hydroxylase | 1.767 |
| 5781 | PTPN11 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 11 (noonan syndrome 1) | 1.749 |
| 4908 | NTF3 | Neurotrophin 3 | 1.741 |
| 7046 | TGFBR1 | Transforming growth factor, beta receptor I (activin a receptor type II-like kinase, 53 KDA) | 1.722 |
| 5743 | PTGS2 | Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase) | 1.708 |
| 23475 | QPRT | Quinolinate phosphoribosyltransferase | 1.704 |
| 934 | CD24 | CD24 antigen | 1.698 |
| 10773 | ZBTB6 | Zinc finger protein 482 | 1.685 |
| 2048 | EPHB2 | EPH receptor B2 | 1.624 |
| 23089 | PEG10 | Paternally expressed 10 | 1.617 |
| 26013 | L3MBTL | Lethal (3) malignant brain tumor L(3)MBT protein (drosophila) homolog | 1.614 |
| 3434 | IFIT1 | Interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 1 | 1.613 |
| 5156 | PDGFRA | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor, alpha polypeptide | 1.610 |
| 382 | ARF6 | ADP-ribosylation factor 6 | 1.610 |
| 2028 | ENPEP | Glutamyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase A) | 1.607 |
| 10643 | IGF2BP3 | Insulin-like growth factor 2 MRNA binding protein 3 | 1.604 |
| 8091 | HMGA2 | High mobility group at-hook 2 | 1.580 |
| 900 | CCNG1 | Cyclin G1 | 1.579 |
| 4192 | MDK | Midkine (neurite growth-promoting factor 2) | 1.577 |
| 552889 | LOC552889 | Hypothetical LOC552889 | 1.576 |
| 540 | ATP7B | Atpase, CU++ transporting, beta polypeptide | 1.565 |
| 2289 | FKBP5 | FK506 binding protein 5 | 1.543 |
| 4194 | MDM4 | MDM4, transformed 3t3 cell double minute 4 | 1.538 |
| 5764 | PTN | Pleiotrophin | 1.533 |
| 8935 | SKAP2 | SRC family associated phosphoprotein 2 | 1.528 |
| 273 | AMPH | Amphiphysin | 1.527 |
| 2799 | GNS | Glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase (sanfilippo disease IIID) | 1.519 |
| 5311 | PKD2 | Polycystic kidney disease 2 (autosomal dominant) | 1.518 |
| 10402 | ST3GAL6 | ST3 beta-galactoside alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase 6 | 1.501 |
| 3764 | KCNJ8 | Potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 8 | −1.501 |
| 6347 | CCL2 | Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 | −1.509 |
| 2030 | SLC29A1 | Solute carrier family 29 | −1.517 |
| 2919 | CXCL1 | Chemokine (C-X-C MOTIF) ligand 1 | −1.519 |
| 1839 | HBEGF | Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor | −1.522 |
| 3488 | IGFBP5 | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 | −1.539 |
| 5678 | PSG9 | Pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 9 | −1.557 |
| 3643 | INSR | Insulin receptor | −1.569 |
| 10974 | C10ORF116 | Chromosome 10 open reading frame 116 | −1.580 |
| 4071 | TM4SF1 | Transmembrane 4 L six family member 1 | −1.580 |
| 1832 | DSP | Desmoplakin | −1.590 |
| 4487 | MSX1 | MSH homeobox homolog 1 | −1.613 |
| 27295 | PDLIM3 | PDZ and LIM domain 3 | −1.615 |
| 1294 | COL7A1 | Collagen, type VII, alpha 1 | −1.617 |
| 182 | JAG1 | Jagged 1 (alagille syndrome) | −1.617 |
| 22891 | ZNF365 | Zinc finger protein 365 | −1.619 |
| 4223 | MEOX2 | Mesenchyme homeobox 2 | −1.660 |
| 8076 | MFAP5 | Microfibrillar associated protein 5 | −1.665 |
| 51363 | GALNAC4S-6ST | KIAA0598 gene product | −1.676 |
| 5354 | PLP1 | Proteolipid protein 1 | −1.694 |
| 1410 | CRYAB | Crystallin, alpha B | −1.699 |
| 4854 | NOTCH3 | Notch homolog 3 | −1.743 |
| 116039 | OSR2 | ODD-skipped related 2 | −1.753 |
| 10873 | ME3 | Malic enzyme 3, NADP(+)-dependent, mitochondrial | −1.760 |
| 5865 | RAB3B | RAB3B, member RAS oncogene family | −1.764 |
| 10391 | CORO2B | Coronin, actin binding protein, 2B | −1.770 |
| 22809 | ATF5 | Activating transcription factor 5 | −1.782 |
| 6356 | CCL11 | Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 11 | −1.783 |
| 7869 | SEMA3B | Semaphorin 3B | −1.802 |
| 8404 | SPARCL1 | SPARC-like 1 (MAST9, HEVIN) | −1.813 |
| 1004 | CDH6 | Cadherin 6, type 2, K-cadherin (fetal kidney) | −1.823 |
| 131578 | LRRC15 | Leucine rich repeat containing 15 | −1.836 |
| 3855 | KRT7 | Keratin 7 | −1.846 |
| 11145 | HRASLS3 | HRAS-like suppressor 3 | −1.853 |
| 5919 | RARRES2 | Retinoic acid receptor responder | −1.862 |
| 5493 | PPL | Periplakin | −1.882 |
| 27063 | ANKRD1 | Ankyrin repeat domain 1 (cardiac muscle) | −1.891 |
| 684 | BST2 | Bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2 | −1.918 |
| 8190 | MIA | Melanoma inhibitory activity | −1.932 |
| 7042 | TGFB2 | Transforming growth factor, beta 2 | −1.950 |
| 6004 | RGS16 | Regulator of G-protein signalling 16 | −1.969 |
| 7020 | TFAP2A | Transcription factor AP-2 alpha | −2.008 |
| 3589 | IL11 | Interleukin 11 | −2.022 |
| 8549 | LGR5 | Leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 | −2.027 |
| 2277 | FIGF | C-FOS induced growth factor | −2.029 |
| 4958 | OMD | Osteomodulin | −2.047 |
| 10351 | ABCA8 | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A (ABC1), member 8 | −2.051 |
| 2065 | ERBB3 | V-ERB-B2 erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene | −2.073 |
| 5649 | RELN | Reelin | −2.130 |
| 6663 | SOX10 | SRY (sex determining region Y)-BOX 10 | −2.172 |
| 2878 | GPX3 | Glutathione peroxidase 3 (plasma) | −2.183 |
| 1620 | DBC1 | Deleted in bladder cancer 1 | −2.208 |
| 4629 | MYH11 | Myosin, heavy polypeptide 11, smooth muscle | −2.221 |
| 4046 | LSP1 | Lymphocyte-specific protein 1 | −2.224 |
| 5730 | PTGDS | Prostaglandin D2 synthase 21 KDA (BRAIN) | −2.252 |
| 6781 | STC1 | Stanniocalcin 1 | −2.290 |
| 1675 | CFD | Complement factor D (ADIPSIN) | −2.298 |
| 3490 | IGFBP7 | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 | −2.317 |
| 10439 | OLFM1 | Olfactomedin 1 | −2.341 |
| 23090 | ZNF423 | Zinc finger protein 423 | −2.372 |
| 1842 | ECM2 | Extracellular matrix protein 2 | −2.426 |
| 11098 | PRSS23 | Protease, serine, 23 | −2.431 |
| 7857 | SCG2 | SECRETOGRANIN II (CHROMOGRANIN C) | −2.448 |
| 2628 | GATM | Glycine amidinotransferase | −2.463 |
| 358 | AQP1 | Aquaporin 1 | −2.507 |
| 8418 | CMAH | Cytidine monophosphate-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase | −2.533 |
| 2006 | ELN | Elastin (supravalvular aortic stenosis, williams-beuren syndrome) | −2.589 |
| 3481 | IGF2 | Insulin-like growth factor 2 (somatomedin A) | −2.592 |
| 4804 | NGFR | Nerve growth factor receptor (tnfr superfamily, member 16) | −2.625 |
| 2675 | GFRA2 | GDNF family receptor alpha 2 | −2.646 |
| 249 | ALPL | Alkaline phosphatase, liver/bone/kidney | −2.671 |
| 2596 | GAP43 | Growth associated protein 43 | −2.678 |
| 11075 | STMN2 | Stathmin-like 2 | −2.695 |
| 5803 | PTPRZ1 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor-type, Z polypeptide 1 | −2.695 |
| 8744 | TNFSF9 | Tumor necrosis factor superfamily, member 9 | −2.723 |
| 8644 | AKR1C3 | Aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C3 | −2.837 |
| 8839 | WISP2 | WNT1 inducible signaling pathway protein 2 | −2.910 |
| 124 | ADH1C | Alcohol dehydrogenase 1A (CLASS I) | −2.927 |
| 1734 | DIO2 | Deiodinase, iodothyronine, type II | −2.947 |
| 1116 | CHI3L1 | Chitinase 3-like 1 (cartilage glycoprotein-39) | −3.329 |
| 5320 | PLA2G2A | Phospholipase A2, group IIA (platelets, synovial fluid) | −3.355 |
| 3123 | HLA-DRB6 | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 1 | −3.415 |
| 3128 | HLA-DRB5 | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 6 | −3.415 |
| 4915 | NTRK2 | Neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type 2 | −3.552 |
| 3479 | IGF1 | Insulin-like growth factor 1 (somatomedin C) | −3.682 |
| 3897 | L1CAM | L1 cell adhesion molecule | −3.706 |
| 347 | APOD | Apolipoprotein D | −3.749 |
| 50486 | G0S2 | G0/G1switch 2 | −3.913 |
| 2824 | GPM6B | Glycoprotein M6B | −4.029 |
| 1299 | COL9A3 | Collagen, type IX, alpha 3 | −4.076 |
| 9244 | CRLF1 | Cytokine receptor-like factor 1 | −4.463 |
| 2662 | GDF10 | Growth differentiation factor 10 | −4.813 |
| 1311 | COMP | Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein | −4.840 |
Figure 2.
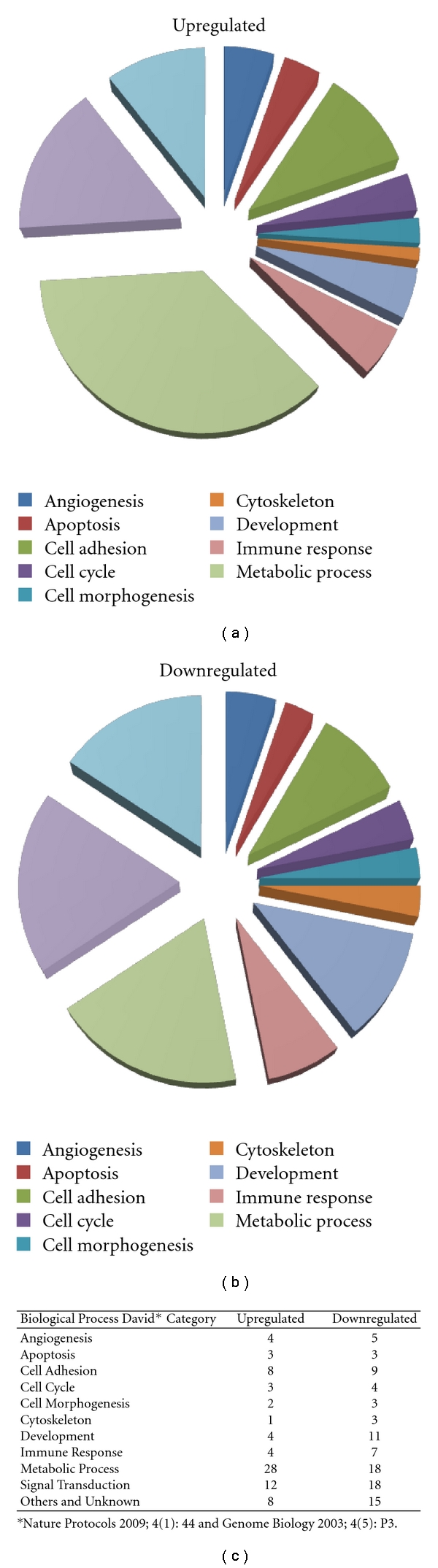
Gene profiling and biological processes of fetal versus young skin cells. A cDNA microarray containing approximately 12,500 sequences (U95A human genome chip, Affymetrix UK, High Wycombe) was used to identify differentially expressed genes in banked fetal dermal skin cells compared to young skin cells. Three arrays were hybridised for each separate cell bank, and gene ontology of important differentially expressed genes was annotated following the criteria of the DAVID database (http://david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov/) for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Biological processes of gene ontology is reported in the pie graphs for both up- and down-regulated genes (category for their best representation).
Although individual growth factors (TGF-β2, TGF-β3, IL-10, and PDGF) have been shown in the clinic to help in different aspects of overall wound healing, it is indeed a very complex process [3, 45]. Most likely, many factors taken together are necessary for complete wound closure which could indeed be offered by a cell-based therapy for which many factors could be different in fetal cells such as those found in Table 1.
Indeed, it has been shown that efficient repair could be obtained in 2nd and 3rd degree burns in children [7], acute wounds [8], and in chronic wounds [9] to date, and the whole-cell bioprocessing and age of the cells were very important aspects [10, 12].
2. Fetal Tissue Collection, Culture, and Cell Bank Requirements
One of the major challenges for assuring that more patients will benefit from cell-based therapies in the future will be the optimisation of the choice of cell type as well as their isolation and proliferation. The development of master cell banks from the cell choice provides a major advantage for the creation of a therapeutic biological agent. Careful selection of donors and extensive screening of both the donor and cultured cells avoids transmissible viral, fungal, or bacterial disease and, therefore, can provide a safe and secure utilization of cells for therapeutic purposes.
Fetal cells have the advantage of being an organ donation, and only very small biopsies are necessary for developing extensive, consistent master cell banks for many tissues. Thorough safety testing of mother donor for infectious diseases (status of the donor for HIV, HBV, and HCV) at the time of tissue donation and again 3 months after to ensure negative sero-conversion can be ensured. During the informed consent of the patient, an interview for overall health is recorded to evaluate eligibility into an organ donation program. For the tissue, information concerning the age of the fetus, date, time, and place of acquirement need to be obtained along with types and amounts of tissue received. The transfer containers can be labelled with the identification code to assure an anonymous organ donation. All culture products used for the transfer of tissue and cell culture need to be of clinical grade quality. Cell banking and testing criteria need to be accomplished under cGMP conditions such as required for human diploid cells used for vaccine production and for cell substrates used for biotechnological products. Testing routinely accomplished on cell banks includes tests for viruses, virus-like particles, mycoplasmas, fungi, yeasts, and bacteria with both in vitro and in vivo testing. Donor source is identified by isoenzyme testing, and in vitro testing of picornavirus, orthomyxovirus, pramyxovirus, herpesvirus, adenovirus, and reovirus is routinely accomplished with several control cell lines when the tissue is human source (Q-PCR for HepB, HepC, HIV-1, HIV-2, HTLV-1, HTLV-2, HHV-6, HHV-7, HHV-8, EBV, hCMV, SV40, and B19 parvovirus). In vivo virus testing using suckling mice, adult mice, guinea pigs and embryonated eggs is routinely employed.
It is important to note that until now, there have been no reported biopharmaceuticals derived from continuous cell cultures that have been implicated in the transmission of infectious agents to humans. Most sources of contamination are adventitious, which means that the contamination is introduced from an external source such as the culture products.
3. Cellular Delivery Systems: Collagen Matrix, Cream, and Hydrogel
Once safety can be assured, efficient cell presentation with biocompatible delivery systems can be assessed for specific tissues. For delivery systems, biocompatible biomaterials need to be available in order to provide an extracellular matrix environment for cell differentiation, delivery, and release. To be admitted for clinical use, it is more rapid to use approved medical device quality material. Cell and materials need to be tested together to assure not only biocompatibility but also their interactions, cellular stability, possible degraded by-products of combination, and degradation or absorption. Ease of applicability of the final product will be of importance for clinical use.
Preparations from biologicals, and particularly from live cells and their delivery to the patient are a major complication for treatment, and the shelf life is very limited with such preparations. Many products for skin repair have applied alternatives such as freeze-dried, frozen, and refrigerator stocking [18–23]. Stability and bioequivalence will have to meet the exigent and stringent technical aspects for development of therapeutic products.
Cellular therapies can be delivered as three-dimensional constructs (tissue-engineered live cell constructs) that can be placed topically over wound and scar surfaces or in solutions composed of creams or biogels. For large-surface wounds and areas that are difficult to apply overlying bandages, cream and biogel preparations permit an advantage for multiple daily applications with either live (hydrogel) or inactivated (cream) cells (Figure 3). Final preparations need to be consistent with equivalent “dosage” of cellular products delivered such as a cell density or by protein content.
Figure 3.
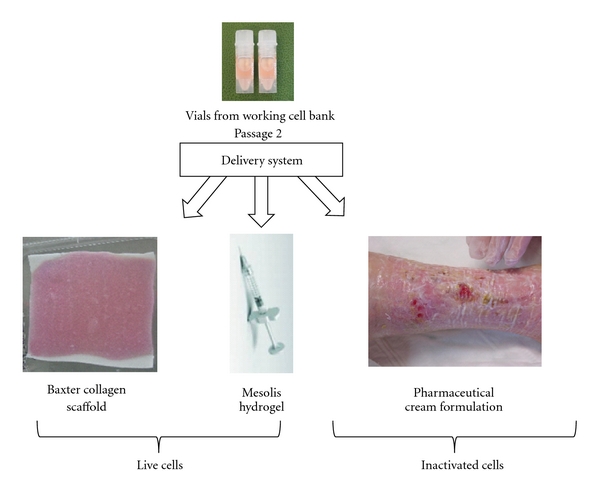
Cell delivery by “biological bandage”, hydrogel, and pharmaceutical cream formulation. Each identical ampoule of fetal skin cells (working cell bank) can be seeded directly into biocompatible collagen (Tissue Fleece, Baxter, Switzerland), hydrogels (Mesolis, Anties, Plan-les-Ouates, Switzerland), or into pharmaceutical cream formulations (oil-in-water emulsion base was prepared under GLP, Good Laboratory Practices) that assure biological stability.
4. Assessment of Fetal Cell Therapy in Wound and Scar Management
Management of wounds using fetal cell therapy have been intended for both acute and chronic wounds and for burns. In the first clinical studies reported using continuous fetal skin cell lines [7, 8], they were designed to prepare wound beds with fetal cells before autografting of patients who were programmed for secondary surgery for wound closure. This fetal cell preparative step was accomplished with the intention of having both a better “take” for the autograft and enhanced quality of treated skin. For pediatric burn patients, the pretreatment with fetal cells showed to be very efficient in wound closure to the point, where all 8 patients included in the study did not have to have the planned autografts for continued treatment [7, 8]. Treated skin showed complete closure rapidly with little hypertrophy of new skin and no retraction seen.
In studies reported using fetal cells for chronic leg ulcers, patients were selected on the basis of a history of having refractory chronic leg ulcers, which did not heal using traditional therapies, such as compression (active and passive), hydrocolloids, and autografts [9]. Ulcers such as illustrated in Figure 4 (female patient 1, with a history of painful postthrombotic ulcer for 14 years, consecutive to deep venous system and short saphenous vein insufficiency) portray the use of several delivery systems of live and inactivated fetal skin cells. For this particular patient, previous autografts and different compression therapies including 4 layers bandages were not successful. Immediately following the first fetal skin construct, edema diminished, pain was relieved, and fibrin production elimination was evident. Applications of fetal skin constructs one time per week were capable of gradual but rapid closure of this large, deep, and painful ulcer. At 11 weeks, the larger portion of the ulcer was healed. Healed ulcer and surrounding skin was treated with pharmaceutical cream preparation with inactivated fetal skin cells until full closure. At one year followup, the patient shows skin that is still atrophic but with no presence of scar tissue (Figure 4). Although etiologies of ulcer patients are varied, similar observations were reported using fetal skin cells for treatment in 8 patients representing 13 ulcers included in the clinical safety studies [9]. Examples of rapid evolution of acute wounds and burns treated in the same manner with fetal cell preparations are portrayed in Figure 5. These patients were selected to represent the early repair processes noted and associated anti-inflammatory effects. Regardless of wound etiology (Patient 2 presented with an incision from a glass wound, Patient 3 with an intense soder burn, and Patient 4 with an acid burn), it can be generally observed that rapid epitheliazation of skin was initiated.
Figure 4.
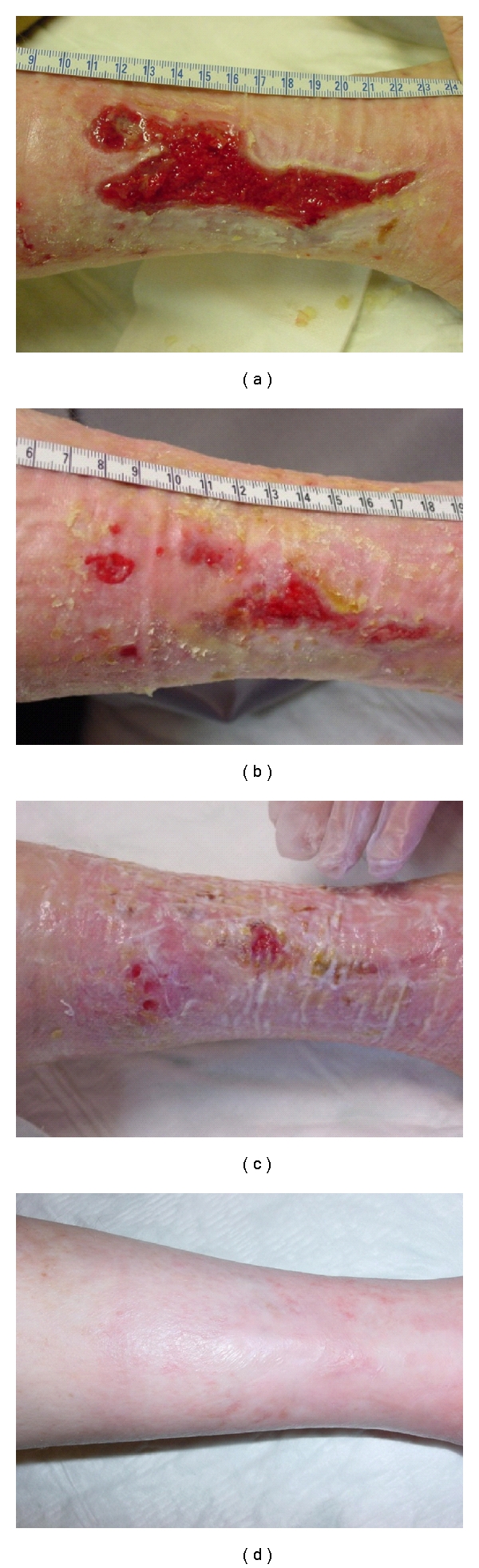
Fetal cell therapy of chronic wounds. Patient 1 (female 64 years old) with a history of painful postthrombotic ulcer for 14 years, consecutive to deep venous system, and short saphenous vein insufficiency (a). Evolution of the large, deep, and painful ulcer with applications of fetal skin constructs one time per week at 1 month (b) and two months (c). Following the majority of closure at 2 months, surrounding skin was treated with pharmaceutical cream preparation with inactivated fetal skin cells until full closure at 11 weeks (d). At one year followup, the patient shows skin that is still atrophic but no presence of scar tissue. “Biological bandage” preparations: fetal cells (seeding density of 5 × 103 cells/cm2 with cells from the WCB at passages 3-4) were placed in culture media and seeded on the collagen sheet and placed into a 37°C incubator at 95% relative humidity and 10% CO2. Final products were employed for the patients in clinical Phase I and II studies for burns and wounds. Cream preparation: the cream was prepared under controlled, clean-room conditions in an automated pharmaceutical machine (Moltomat, Krieger AG, Basel, Switzerland). Its composition contained hydrogenated vegetable oil, glycerine, propylene glycol, cetearyl, ethyhexanoate, decyl oleate, ceteanyl alcohol, cetyl palmitate, glucose, ascorbyl palmitate, tocopheryl acetate, propylparaben, methylparaben, potassium chloride, magnesium chloride, sodium cetearyl sulphate, and simethicone. Samples were tested for quality control with respect to microbiological and physicochemical (viscosity, pH, conductivity, mass volume, colorimetry, and microscopy). Cell concentrations of 5 × 103/mL were used on deteriorated skin of patients surrounding chronic ulcers and following wound closure of wound burn patients (Figure 5).
Figure 5.
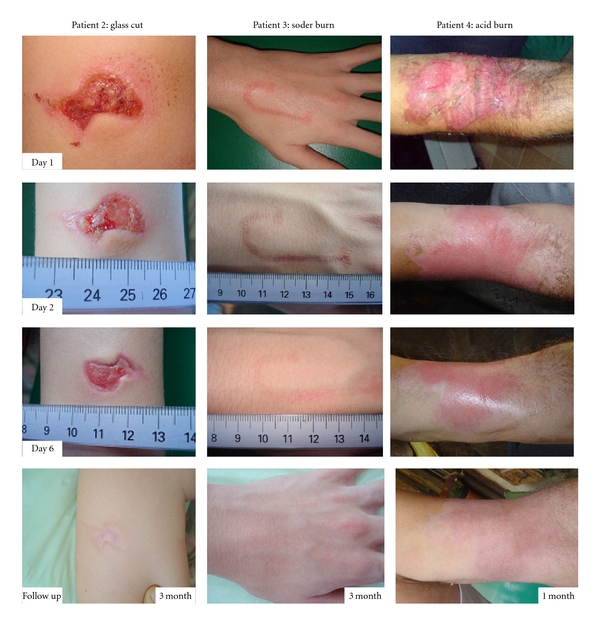
Patients with various forms of acute wounds (Patient 2) glass incision (Patient 3) soder burn, and (Patient 4) acid burn treated with fetal cell preparations as described for Figure 4. Evolution of wounds early in treatment with bandage changes every 2 days illustrates rapid wound repair with low associated inflammation.
5. Discussion
Biologicals for wound and scar management have predominantly been developed with neonatal or young foreskin tissue cell culture to date (companies including, Smith and Nephew, XCELLentis, Organogenesis, Ortec, and DFB Pharmaceuticals) [13–15, 17, 18]. Differences of expression in wound healing gene families between fetal cells and foreskin cells used in biological preparations could be responsible for more efficient repair processes seen in the clinic and particularly for the rapidity in the treatment of acute wounds and burns [11]. Fetal skin represents the ideal paradigm of all tissue repair due to its inherent ability to repair through regeneration rather than scar. Even though fetal wound repair is a tightly regulated process involving many cellular mediators, the precise mechanisms of efficient wound healing without scar formation remain unknown despite the great increase in knowledge gained over the past decades. Chen et al. [58] have proposed that understanding the “blueprint of fetal skin repair” might allow the manipulation of adult wound healing in order to decrease scarring and fibrosis. There are indeed many genes that are significantly different in the “fetal skin blueprint” when compared to both younger and older skin that have been elucidated in previous work [9] and in this paper with banked fetal and young skin cells accomplished with the same cell banking techniques. Herein, we show that expression profiling of banked fetal cells compared to young skin has provided biological grouping of important gene families implicated in the mechanism of wound repair (such as cell adhesion, angiogenesis, and development; see pie graphs Figure 2, Table 1).
Indeed, individual growth factors (TGF-β2, TGF-β3, IL-10, and PDGF) have been shown in the clinic to help in different aspects of overall wound healing, but it is a very complex process. Most likely, many factors taken together are necessary for complete wound closure which could indeed be offered by a cell-based therapy for wound management. In making parallels with currently used medicines, it is now becoming more and more of a problem for single growth factors in wound and tissue repair. As milligram quantities are necessary for treatment of wounds such as that with platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF, Regranex), the long-term use is showing some safety concern. The use of this growth factor for the treatment of chronic leg ulcers has now been limited to short treatment regimens due to increased cancer in the patients (Ortho-McNeil-Janssen Pharmaceuticals; Important Drug Warning insert of medication). When only one growth factor or cytokine is used, the dosage accumulations are very high. Cellular therapies (or total cellular products) could provide the more correct balance for dosages of individual proteins or factors. The pmol/nmol quantities of individual proteins (when delivered all together are ~2-3 μg) have been shown to be effective without the secondary effects on long term [7–9].
New biologicals may be of high interest if the safety and simplicity can be assured and if the overall cost can be limited.
Regarding the use of the cells for preclinical trials, it will be particularly important to ensure consistency of growth of the cells and consistency of the harvest obtained. High consistency in fetal cell banking can be achieved due to the minimum requirements of fetal cell cultures. In contrast with MSC, fetal cells do not require feeder layers for growth nor growth factors for differentiation. Fetal cells show qualities required for the establishment of GMP cell banks to be used for medicinal and tissue-engineering products. The lifespan and the proliferation rate of the fetal cells can allow master cell banks of 100–300 ampoules containing 5–10 millions cells each from 2 cm2 of tissue at very early passaging (Passage 1 and 2). MCB and WCB have been prepared from fetal skin tissue in short periods of time compared to other primary cells [8, 10].
Regulation of final products and the simplicity will be mandatory milestones for biological development. Until 2007, Phase I and II safety studies with fetal cells were regulated in Switzerland (where the clinical trials were held) by the Department of Public Health (OFSP) under Transplantation Law (for living cell transplants) and by “hospital preparations in small quantities” by the state chemist (for inactivated cells). For comparison in the United States by the FDA, other cell types (i.e., foreskin) were regulated, in the majority, as medical devices or cosmetic products. New regulatory requirements issued in recent years (2007) will assure better safety, but cost will be largely affected. All cellular products must be in compliance with guidelines of good manufacturing practice (GMP) with respect to medicinal products and investigational medicinal products for human use. The European Union (EU) regulation on advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs) was adopted in all European Member States on Dec. 30, 2008, and the FDA recently also proposed regulations on human cells, tissues, as well as for cellular and tissue-based products. The main scope of the regulations is to establish clear classification criteria for many new cell-based medicinal products. For the EU, it makes reference to the 2004/23/EC directive on donation, procurement, and testing of human cells and tissues and also with directive 2002/98/EC on human blood and blood components. All together, these directives dictate that human cells have to be in compliance with the quality requirements therein described and that all ATMP have to be prepared under GMP conditions. Key elements including identity, purity, sterility, stability, safety, and efficacy are recommended for cellular-based products. In all, these new regulations impose strict criteria for the production and the environment used for the production of cell-based products to be used in clinical trials and treatments [59–69]. Evolution of advanced cellular therapeutics worldwide and how they are regulated will have a major impact on availability to patients. Clear regulatory affairs of cellular use, whether they are delivered living or inactivated, will be necessary to help researchers and clinicians in future therapies.
Cell therapies and tissue engineering are beginning to show great promise in wound and scar management. The cell choice is, therefore, an important factor for simplifying the overall technique and bringing therapy rapidly to the patient.
Thus, fetal cells with their high expansion, simple culture conditions (do not require feeder layers or extensive growth factors for expansion which is a major reason for their consistency in scaling out), and low immunogenicity properties [10, 12] are ideal conditions for whole-cell bioprocessing destined for cell therapy, tissue-engineering, and medicinal products. Additionally, they have already been used in safety clinical Phase I and II studies showing rapid and efficient tissue repair with minimal scarring [7–9, 12].
Delivery systems to afford better stocking and stability will be important milestones for biological products, and topical preparations that show biological activity would be a great benefit. Overall, the advantage of cellular preparations is that there is no need for a chemical “active ingredient” for wound healing and scar management.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Foundations SANTE and the Sandoz Family for financial aid in our Fetal Cell Transplantation Program of Switzerland.
References
- 1.Limat A, Mauri D, Hunziker T. Successful treatment of chronic leg ulcers with epidermal equivalents generated from cultured autologous outer root sheath cells. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 1996;107(1):128–135. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12298415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bianco P, Robey PG. Stem cells in tissue engineering. Nature. 2001;414(6859):118–121. doi: 10.1038/35102181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bullard KM, Longaker MT, Lorenz HP. Fetal wound healing: current biology. World Journal of Surgery. 2003;27(1):54–61. doi: 10.1007/s00268-002-6737-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kaviani A, Perry TE, Dzakovic A, Jennings RW, Ziegler MM, Fauza DO. The amniotic fluid as a source of cells for fetal tissue engineering. Journal of Pediatric Surgery. 2001;36(11):1662–1665. doi: 10.1053/jpsu.2001.27945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kaviani A, Perry TE, Barnes CM, et al. The placenta as a cell source in fetal tissue engineering. Journal of Pediatric Surgery. 2002;37(7):995–999. doi: 10.1053/jpsu.2002.33828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wu CH, Chang GY, Chang WC, Hsu CT, Chen RS. Wound healing effects of porcine placental extracts on rats with thermal injury. British Journal of Dermatology. 2003;148(2):236–245. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hohlfeld J, De Buys Roessingh A, Hirt-Burri N, et al. Tissue engineered fetal skin constructs for paediatric burns. The Lancet. 2005;366(9488):840–842. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.de Buys Roessingh AS, Hohlfeld J, Scaletta C, et al. Development, characterization, and use of a fetal skin cell bank for tissue engineering in wound healing. Cell Transplantation. 2006;15(8-9):823–834. doi: 10.3727/000000006783981459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ramelet AA, Hirt-Burri N, Raffoul W, et al. Chronic wound healing by fetal cell therapy may be explained by differential gene profiling observed in fetal versus old skin cells. Experimental Gerontology. 2009;44(3):208–218. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2008.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Quintin A, Hirt-Burri N, Scaletta C, Schizas C, Pioletti DP, Laurent-Applegate LA. Consistency and safety of cell banks for research and clinical use: preliminary analysis of fetal skin banks. Cell Transplantation. 2007;16(7):675–684. doi: 10.3727/000000007783465127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hirt-Burri N, Scaletta C, Gerber S, Pioletti DP, Applegate LA. Wound-healing gene family expression differences between fetal and foreskin cells used for bioengineered skin substitutes. Artificial Organs. 2008;32(7):509–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1594.2008.00578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Applegate LA, Scaletta C, Hirt-Burri N, Raffoul W, Pioletti D. Whole-cell bioprocessing of human fetal cells for tissue engineering of skin. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology. 2009;22(2):63–73. doi: 10.1159/000178865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Curran MP, Plosker GL. Bilayered bioengineered skin substitute (Apligraf®): a review of its use in the treatment of venous leg ulcers and diabetic foot ulcers. BioDrugs. 2002;16(6):439–455. doi: 10.2165/00063030-200216060-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kuroyanagi Y, Yamada N, Yamashita R, Uchinuma E. Tissue-engineered product: allogeneic cultured dermal substitute composed of spongy collagen with fibroblasts. Artificial Organs. 2001;25(3):180–186. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1594.2001.025003180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fimiani M, Pianigiani E, Di Simplicio FC, et al. Other uses of homologous skin grafts and skin bank bioproducts. Clinics in Dermatology. 2005;23(4):396–402. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2004.07.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ng KW, Khor HL, Hutmacher DW. In vitro characterization of natural and synthetic dermal matrices cultured with human dermal fibroblasts. Biomaterials. 2004;25(14):2807–2818. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.09.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Falanga V, Margolis D, Alvarez O, et al. Rapid healing of venous ulcers and lack of clinical rejection with an allogeneic cultured human skin equivalent. Archives of Dermatology. 1998;134(3):293–300. doi: 10.1001/archderm.134.3.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Waymack P, Duff RG, Sabolinski M. The effect of a tissue engineered bilayered living skin analog, over meshed split-thickness autografts on the healing of excised burn wounds. Burns. 2000;26(7):609–619. doi: 10.1016/s0305-4179(00)00017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Coulomb B, Lebreton C, Dubertret L. Influence of human dermal fibroblasts on epidermalization. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 1989;92(1):122–125. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep13071335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Coulomb B, Friteau L, Baruch J, et al. Advantage of the presence of living dermal fibroblasts within in vitro reconstructed skin for grafting in humans. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 1998;101(7):1891–1903. doi: 10.1097/00006534-199806000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rakhorst HA, Posthumus-Van Sluijs SJ, Tra WMW, et al. Fibroblasts accelerate culturing of mucosal substitutes. Tissue Engineering. 2006;12(8):2321–2331. doi: 10.1089/ten.2006.12.2321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hansbrough JF, Mozingo DW, Kealey GP, Davis M, Gidner A, Gentzkow GD. Clinical trials of a biosynthetic temporary skin replacement, dermagraft-transitional covering, compared with cryopreserved human cadaver skin for temporary coverage of excised burn wounds. Journal of Burn Care and Rehabilitation. 1997;18(1):43–51. doi: 10.1097/00004630-199701000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wainwright DJ. Use of an acellular allograft dermal matrix (AlloDerm) in the management of full-thickness burns. Burns. 1995;21(4):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0305-4179(95)93866-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Snyder RJ. Treatment of nonhealing ulcers with allografts. Clinics in Dermatology. 2005;23(4):388–395. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2004.07.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Badiavas EV, Paquette D, Carson P, Falanga V. Human chronic wounds treated with bioengineered skin: histologic evidence of host-graft interactions. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 2002;46(4):524–530. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2002.120534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sheridan RL, Choucair RJ. Acellular allogenic dermis does not hinder initial engraftment in burn wound resurfacing and reconstruction. Journal of Burn Care and Rehabilitation. 1997;18(6):496–499. doi: 10.1097/00004630-199711000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ichioka S, Kouraba S, Sekiya N, Ohura N, Nakatsuka T. Bone marrow-impregnated collagen matrix for wound healing: experimental evaluation in a microcirculatory model of angiogenesis, and clinical experience. British Journal of Plastic Surgery. 2005;58(8):1124–1130. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2005.04.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Atala A. Recent developments in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Current Opinion in Pediatrics. 2006;18(2):167–171. doi: 10.1097/01.mop.0000193294.94646.be. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.De Coppi P, Bartsch G, Siddiqui MM, et al. Isolation of amniotic stem cell lines with potential for therapy. Nature Biotechnology. 2007;25(1):100–106. doi: 10.1038/nbt1274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jones I, Currie L, Martin R. A guide to biological skin substitutes. British Journal of Plastic Surgery. 2002;55(3):185–193. doi: 10.1054/bjps.2002.3800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Osswald SS, Elston DM, Vogel PS. Giant right plantar keloid treated with excision and tissue-engineered allograft. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 2003;48(1):131–134. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2003.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hasegawa T, Suga Y, Mizoguchi M, et al. Clinical trial of allogeneic cultured dermal substitute for the treatment of intractable skin ulcers in 3 patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 2004;50(5):803–804. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2003.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Fimiani M, Pianigiani E, Di Simplicio FC, et al. Other uses of homologous skin grafts and skin bank bioproducts. Clinics in Dermatology. 2005;23(4):396–402. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2004.07.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mostow EN, Haraway GD, Dalsing M, Hodde JP, King D. Effectiveness of an extracellular matrix graft (OASIS Wound Matrix) in the treatment of chronic leg ulcers: a randomized clinical trial. Journal of Vascular Surgery. 2005;41(5):837–843. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2005.01.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Eaglstein WH, Iriondo M, Laszlo K. A composite skin substitute (graftskin) for surgical wounds: a clinical experience. Dermatologic Surgery. 1995;21(10):839–843. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4725.1995.tb00709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gallico GG, O’Connor NE, Compton CC, Remensnyder JP, Kehinde O, Green H. Cultured epithelial autografts for giant congenital nevi. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 1989;84(1):1–9. doi: 10.1097/00006534-198907000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Carter DM, Lin AN, Varghese MC. Treatment of junctional epidermolysis bullosa with epidermal autografts. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 1987;17(2):246–250. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(87)70199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Shakespeare PG. The role of skin substitutes in the treatment of burn injuries. Clinics in Dermatology. 2005;23(4):413–418. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2004.07.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kashiwa N, Ito O, Ueda T, Kubo K, Matsui H, Kuroyanagi Y. Treatment of full-thickness skin defect with concomitant grafting of 6-fold extended mesh auto-skin and allogeneic cultured dermal substitute. Artificial Organs. 2004;28(5):444–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1594.2004.00009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Still J, Glat P, Silverstein P, Griswold J, Mozingo D. The use of a collagen sponge/living cell composite material to treat donor sites in burn patients. Burns. 2003;29(8):837–841. doi: 10.1016/s0305-4179(03)00164-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chan ESY, Lam PK, Liew CT, Lau HCH, Yen RSC, King WWK. A new technique to resurface wounds with composite biocompatible epidermal graft and artificial skin. Journal of Trauma. 2001;50(2):358–362. doi: 10.1097/00005373-200102000-00028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Beanes SR, Hu FY, Soo C, et al. Confocal microscopic analysis of scarless repair in the fetal rat: defining the transition. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2002;109(1):160–170. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200201000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Cass DL, Meuli M, Adzick NS. Scar wars: implications of fetal wound healing for the pediatric burn patient. Pediatric Surgery International. 1997;12(7):484–489. doi: 10.1007/BF01258707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Armstrong JR, Ferguson MWJ. Ontogeny of the skin and the transition from scar-free to scarring phenotype during wound healing in the pouch young of a marsupial, Monodelphis domestica. Developmental Biology. 1995;169(1):242–260. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Dang C, Ting K, Soo C, Longaker MT, Lorenz HP. Fetal wound healing current perspectives. Clinics in Plastic Surgery. 2003;30(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/s0094-1298(02)00067-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Beanes SR, Dang C, Soo C, Ting K. Skin repair and scar formation: the central role of TGF-beta. Expert reviews in molecular medicine. 2003;5(8):1–22. doi: 10.1017/S1462399403005817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lin RY, Adzick NS. The role of the fetal fibroblast and transforming growth factor-β in a model of human fetal wound repair. Seminars in Pediatric Surgery. 1996;5(3):165–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Shah M, Foreman DM, Ferguson MWJ. Neutralisation of TGF-β and TGF-β or exogenous addition of TGF-β to cutaneous rat wounds reduces scarring. Journal of Cell Science. 1995;108(3):985–1002. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.3.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Shah M, Foreman DM, Ferguson MWJ. Control of scarring in adult wounds by neutralising antibody to transforming growth factor β . The Lancet. 1992;339(8787):213–214. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90009-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Wu L, Siddiqui A, Morris DE, Cox DA, Roth SI, Mustoe TA. Transforming growth factor β3 (TGFβ3) accelerates wound healing without alteration of scar prominence: histologic and competitive reverse- transcription-polymerase chain reaction studies. Archives of Surgery. 1997;132(7):753–760. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1997.01430310067014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Okamoto O, Fujiwara S, Abe M, Sato Y. Dermatopontin interacts with transforming growth factor β and enhances its biological activity. Biochemical Journal. 1999;337(3):537–541. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kuroda K, Okamoto O, Shinkai H. Dermatopontin expression is decreased in hypertrophic scar and systemic sclerosis skin fibroblasts and is regulated by transforming growth factor- β1, interleukin-4, and matrix collagen. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 1999;112(5):706–710. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.1999.00563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kaiser S, Schirmacher P, Philipp A, et al. Induction of bone morphogenetic protein-6 in skin wounds. Delayed reepitheliazation and scar formation in BMP-6 overexpressing transgenic mice. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 1998;111(6):1145–1152. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.1998.00407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Stelnicki EJ, Doolabh V, Lee S, et al. Nerve dependency in scarless fetal wound healing. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2000;105(1):140–147. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200001000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Christman KL, Fang Q, Kim AJ, et al. Pleiotrophin induces formation of functional neovasculature in vivo. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2005;332(4):1146–1152. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.04.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nature Protocols. 2009;4(1):44–57. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Dennis G, Jr., Sherman BT, Hosack DA, et al. DAVID: database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biology. 2003;4(5):p. P3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Chen W, Fu X, Ge S, et al. Profiling of genes differentially expressed in a rat of early and later gestational ages with high-density oligonucleotide DNA array. Wound Repair and Regeneration. 2007;15(1):147–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-475X.2006.00195.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.EU. Advanced therapy medicinal products amending Directive 2001/83/EC and Regulation (EC) no. 726/2004. In: Parliament, editor. Regulation (EC) no. 1394/2007, 2007.
- 60.EU. Advanced therapy medicinal products amending Directive 2001/83/EC and Regulation (EC) no. 726/2004. In: Parliament, editor. Regulation (EC) no. 1394/2007, 2007.
- 61.EU. Community code relating to medicinal products for hum use. In: Parliament E, editor. Directive 2001/83/EC, 2001.
- 62.EU. Setting standards of quality and safety for the donation, procurement, testing, processing, preservation, storage and distribution of human tissues and cells. In: Parliament E, editor. Directive 2004/23/EC, 2004.
- 63.EU. Implementing Directive 2004/23/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards certain technical requirements for the donation, procurement and testing of human tissues and cells. In: Parliament E, editor. Directive 2006/17/EC, 2006.
- 64.EU. Implementing Directive 2004/23/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards traceability requirements, notification of serious adverse reactions and events and certain technical requirements for the coding, processing, preservation, storage and distribution of human tissues and cells. In: Parliament E, editor. Directive 2006/86/EC, 2006.
- 65.FDA. Human cells, tissues, and cellular and tissue-based products. 21 CFR 1271, 2006.
- 66.Heinonen M, Oila O, Nordström K. Current issues in the regulation of human tissue-engineering products in the European Union. Tissue Engineering. 2005;11(11-12):1905–1911. doi: 10.1089/ten.2005.11.1905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Trommelmans L, Selling J, Dierickx K. A critical assessment of the directive on tissue engineering of the European Union. Tissue Engineering. 2007;13(4):667–672. doi: 10.1089/ten.2006.0089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.SwissMedics. Swiss Federal Council Transplantation Law. TxL; SR 81021, 2007.
- 69.PMP/ICH. Note for guidance on quality of biotechnological products: derivation and characterisation of cell substrates used for production of biotechnological/biological products. CPMP/ICH/294/95, 2001. [PubMed]


