Abstract
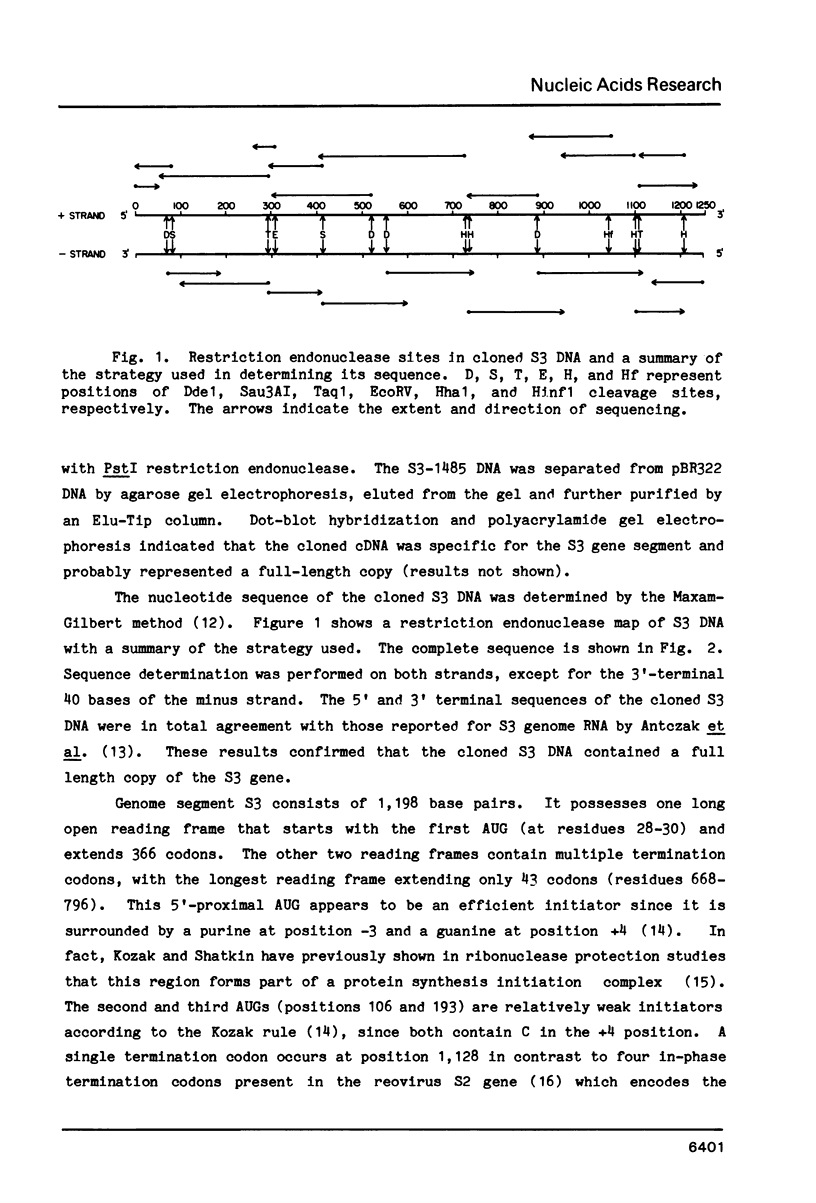
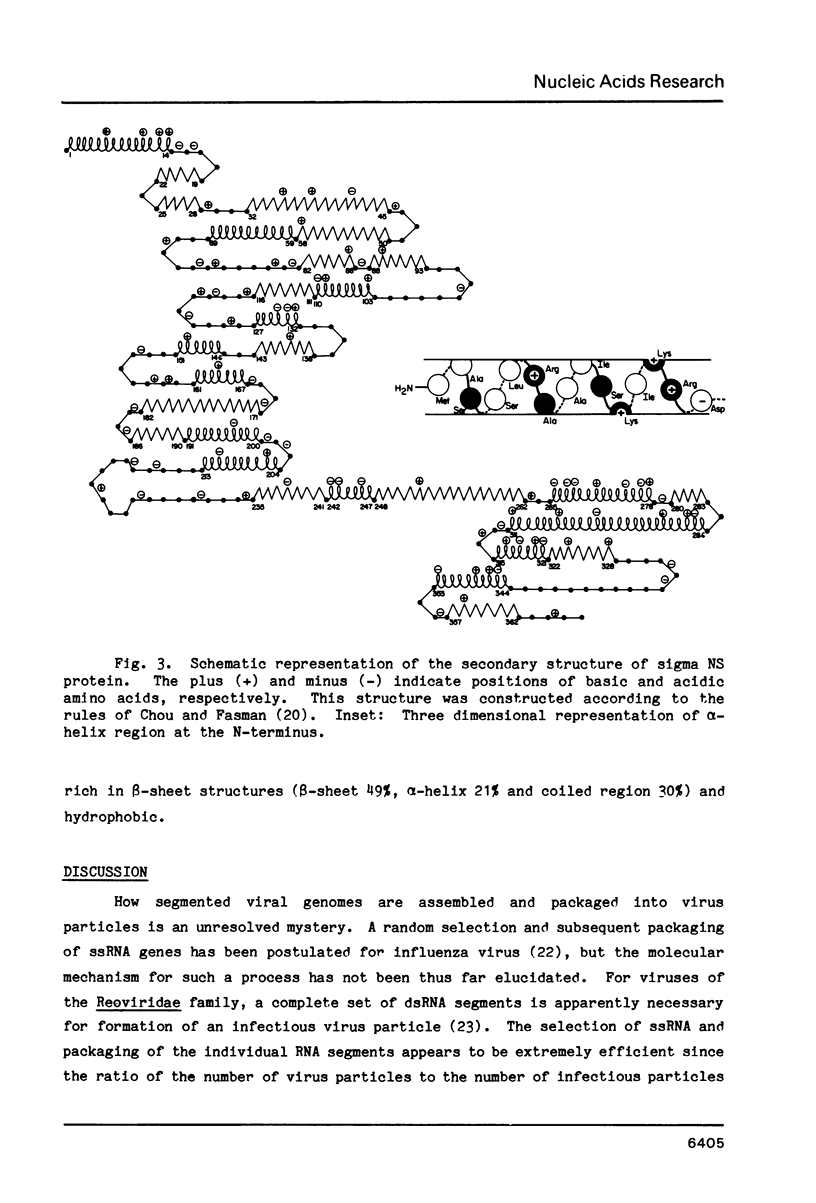
This report describes the complete nucleotide sequence of human reovirus (Dearing strain) genome segment S3. Previous studies indicated that this RNA encodes the major non-structural viral polypeptide sigma NS, a protein that binds ssRNAs (Huisman & Joklik, Virology 70, 411-424, 1976) and has a poly(C)-dependent poly(G) polymerase activity (Gomatos et al., J. Virol. 39, 115-124, 1981). The genome segment consists of 1,198 nucleotides and possesses an open reading frame that extends 366 codons from the first AUG triplet (residues 28-30). There is no significant sequence homology between the plus strand of genome segment S3 and that of genome segment S2 determined previously (Cashdollar et al., PNAS 79, 7644-7648, 1982). However, S3 RNA has significant dyad symmetry and regions that can potentially hybridize (delta G = -26 KCal/mole) with S2 RNA. From the predicted amino acid sequence a possible secondary structure for sigma NS protein was determined. Structural features of reovirus RNA and sigma NS are discussed in relation to their role(s) in viral genome assembly.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antczak J. B., Chmelo R., Pickup D. J., Joklik W. K. Sequence at both termini of the 10 genes of reovirus serotype 3 (strain Dearing). Virology. 1982 Sep;121(2):307–319. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Bellamy A. R., Street J. E., Siegman L. J. A general strategy for cloning double-stranded RNA: nucleotide sequence of the Simian-11 rotavirus gene 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7075–7088. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashdollar L. W., Esparza J., Hudson G. R., Chmelo R., Lee P. W., Joklik W. K. Cloning the double-stranded RNA genes of reovirus: sequence of the cloned S2 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7644–7648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzynkiewicz E., Shatkin A. J. Assignment of reovirus mRNA ribosome binding sites to virion genome segments by nucleotide sequence analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):337–350. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., Morgan M., Muthukrishnan S., Shatkin A. J. Reovirus messenger RNA contains a methylated, blocked 5'-terminal structure: m-7G(5')ppp(5')G-MpCp-. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):362–366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomatos P. J., Prakash O., Stamatos N. M. Small reovirus particle composed solely of sigma NS with specificity for binding different nucleic acids. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):115–124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.115-124.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomatos P. J., Stamatos N. M., Sarkar N. H. Small reovirus-specific particle with polycytidylate-dependent RNA polymerase activity. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):556–565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.556-565.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huddleston J. A., Brownlee G. G. The sequence of the nucleoprotein gene of human influenza A virus, strain A/NT/60/68. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):1029–1038. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huismans H., Joklik W. K. Reovirus-coded polypeptides in infected cells: isolation of two native monomeric polypeptides with affinity for single-stranded and double-stranded RNA, respectively. Virology. 1976 Apr;70(2):411–424. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Richardson M. A., Ikegami N., Shatkin A. J., Furuichi Y. Molecular cloning of double-stranded RNA virus genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):373–377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Joklik W. K. Temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. I. Patterns of gene expression by mutants of groups C, D, and E. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90359-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joklik W. K. Structure and function of the reovirus genome. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Dec;45(4):483–501. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.4.483-501.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M., Shatkin A. J. Characterization of ribosome-protected fragments from reovirus messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4259–4266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae M. A., Joklik W. K. The nature of the polypeptide encoded by each of the 10 double-stranded RNA segments of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):578–593. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama M., Graham A. F. Appearance of defective virions in clones of reovirus. J Virol. 1970 Nov;6(5):693–694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.5.693-694.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuerch A. R., Joklik W. K. Temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. IV. Evidence that anomalous electrophoretic migration behavior of certain double-stranded RNA hybrid species is mutant group-specific. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):218–229. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90301-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Christman J. K., Acs G. The reovirus replicative cycle. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:375–408. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spendlove R. S., McClain M. E., Lennette E. H. Enhancement of reovirus infectivity by extracellular removal or alteration of the virus capsid by proteolytic enzymes. J Gen Virol. 1970 Aug;8(2):83–94. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-8-2-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrington R. C., Hayward C., Kapuler A. M. Conformational studies of reovirus single-stranded RNAs synethesized in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 7;331(2):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90436-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



