Abstract
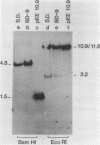
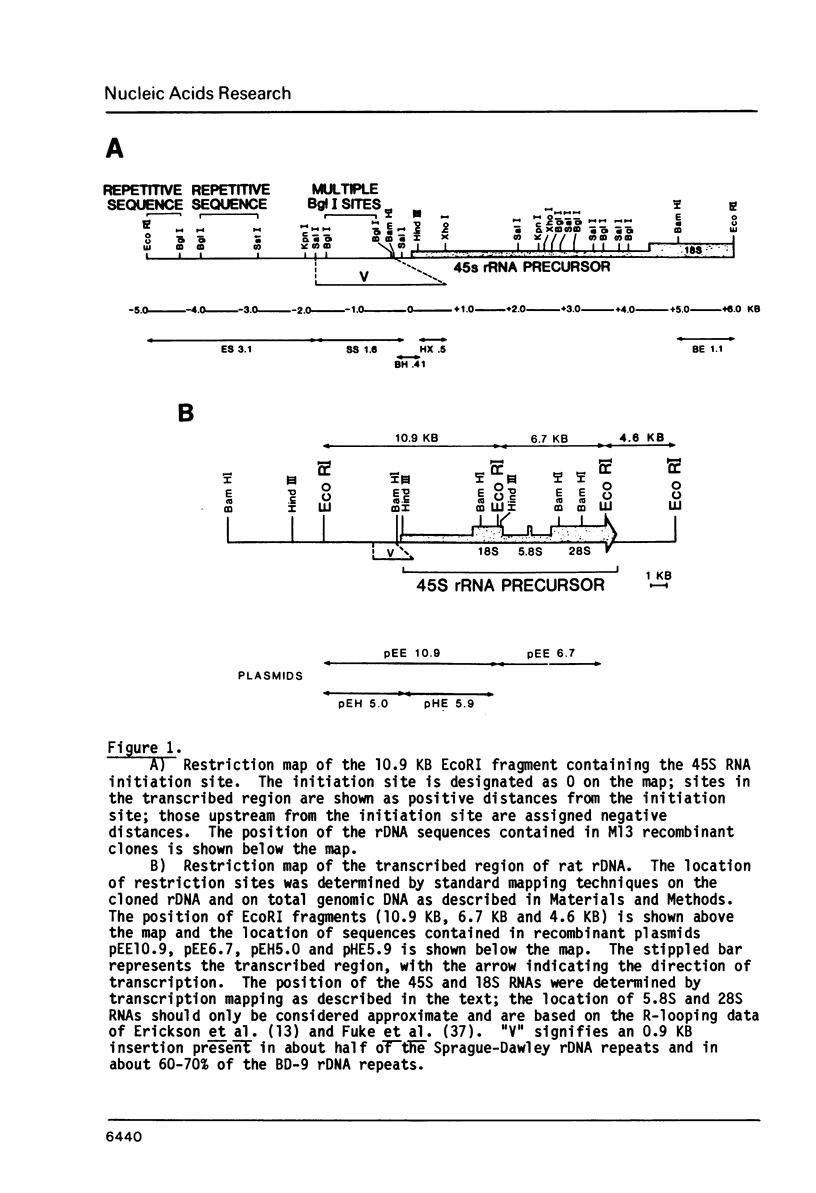
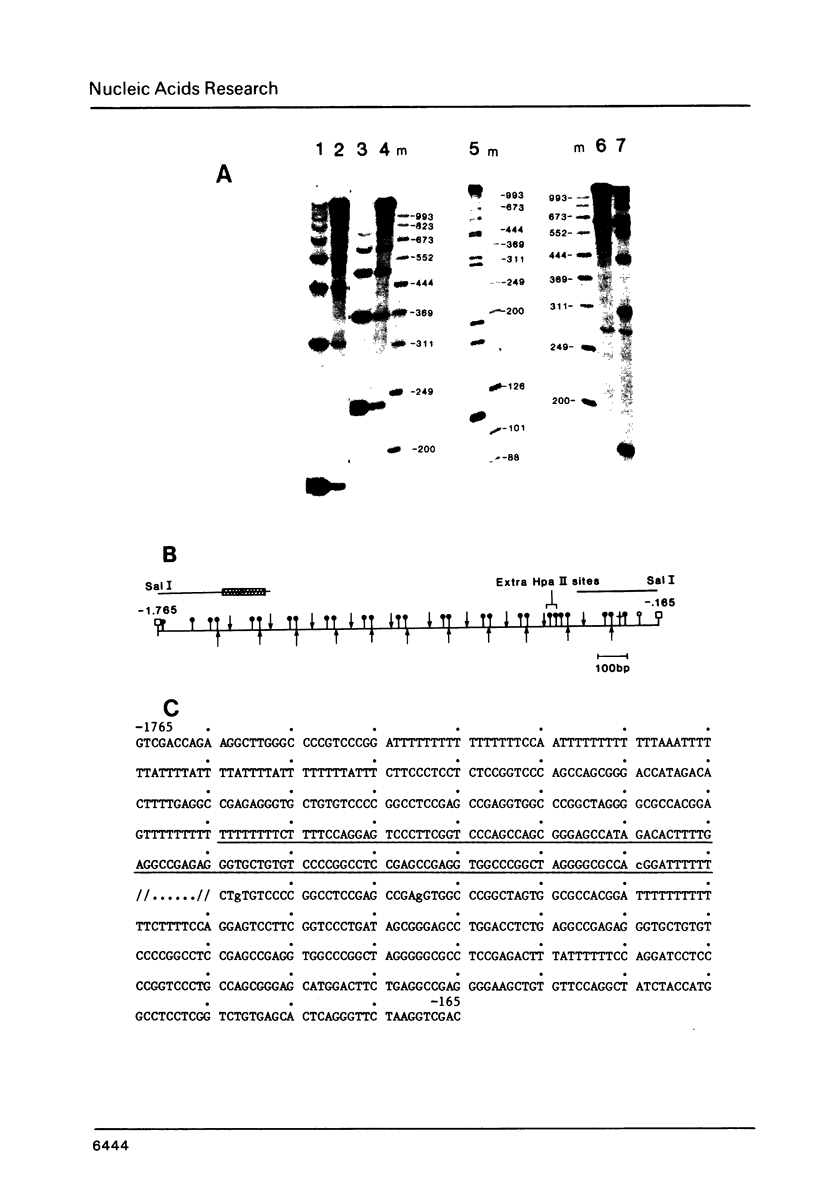
A detailed restriction map was determined for a 10.9 KB region that contains the initiation site for 45S pre-rRNA and the first 1.7 KB of the 18S rRNA coding region. When the restriction pattern of the cloned rDNA was compared with that of total rat DNA, the rDNA regions of both Sprague-Dawley and BD-9 rats were identical to each other and to that of the cloned rDNA. However, both strains exhibit a major polymorphism consisting of an insertion of 0.9 KB of DNA in the nontranscribed spacer between 0.29 KB and 1.8 KB upstream from the 45S RNA initiation site. This region consists of tandem repeats approximately 130 base pairs in length. These repeats contain large poly T tracts and are similar in sequence to analogous elements 5' to the origin of mouse rRNA transcription. Regions containing highly repetitious DNA sequences were located at sites 2.8 KB and 4.3 KB upstream from the initiation site. The repetitive sequence at 2.8 KB from the initiation site anneal to a known Alu-equivalent type 2 sequence derived from the second intron of the rat growth hormone gene.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnheim N. Characterization of mouse ribosomal gene fragments purified by molecular cloning. Gene. 1979 Oct;7(2):83–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheim N., Krystal M., Schmickel R., Wilson G., Ryder O., Zimmer E. Molecular evidence for genetic exchanges among ribosomal genes on nonhomologous chromosomes in man and apes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7323–7327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheim N., Kuehn M. The genetic behaviour of a cloned mouse ribosomal DNA segment mimics mouse ribosomal gene evolution. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):743–763. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90483-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheim N., Seperack P., Banerji J., Lang R. B., Miesfeld R., Marcu K. B. Mouse rDNA nontranscribed spacer sequences are found flanking immunoglobulin CH genes and elsewhere throughout the genome. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheim N., Southern E. M. Heterogeneity of the ribosomal genes in mice and men. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boseley P., Moss T., Mächler M., Portmann R., Birnstiel M. Sequence organization of the spacer DNA in a ribosomal gene unit of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braga E. A., Yussifov T. N., Nosikov V. V. Structural organization of rat ribosomal genes restriction endonuclease analysis of genomic and cloned ribosomal DNAs. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(2):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buongiorno-Nardelli M., Amaldi F., Beccari E., Junakovic N. Size of ribosomal DNA repeating units in Xenopus laevis: limited individual heterogeneity and extensive population polymorphism. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):105–117. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen E. S., Dover G. A. Multiple Pol I initiation sequences in rDNA spacers of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):7017–7026. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.7017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Krauter K., Walling L., Weinberger C., Ray M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in the production of liver-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. M., Rushford C. L., Dorney D. J., Wilson G. N., Schmickel R. D. Structure and variation of human ribosomal DNA: molecular analysis of cloned fragments. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Financsek I., Mizumoto K., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. Human ribosomal RNA gene: nucleotide sequence of the transcription initiation region and comparison of three mammalian genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuke M., Dennis K. J., Busch H. Characterization of cloned rat ribosomal DNA fragments. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(1):25–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00422762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Soellner C., Scholz I. Characterization of a cloned ribosomal fragment from mouse which contains the 18S coding region and adjacent spacer sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1351–1369. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada F., Kato N. Nucleotide sequences of 4.5S RNAs associated with poly(A)-containing RNAs of mouse and hamster cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1273–1285. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington C. A., Chikaraishi D. M. Identification and sequence of the initiation site for rat 45S ribosomal RNA synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3317–3332. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes S. R., Jelinek W. R. Low molecular weight RNAs transcribed in vitro by RNA polymerase III from Alu-type dispersed repeats in Chinese hamster DNA are also found in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6130–6134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes S. R., Toomey T. P., Leinwand L., Jelinek W. R. The Chinese hamster Alu-equivalent sequence: a conserved highly repetitious, interspersed deoxyribonucleic acid sequence in mammals has a structure suggestive of a transposable element. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;1(7):573–583. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.7.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Stang H. D., Browne J. K., Martin M. O., Huot M., Lipeles J., Salser W. Human ribosomal RNA gene spacer sequences are found interspersed elsewhere in the genome. Gene. 1981 Nov;15(2-3):177–186. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeeswaran P., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. Short interspersed repetitive DNA elements in eucaryotes: transposable DNA elements generated by reverse transcription of RNA pol III transcripts? Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):141–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90296-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. The rabbit beta-globin gene contains a large large insert in the coding sequence. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1097–1108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90172-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R. Inverted repeated DNA from Chinese hamster ovary cells studied with cloned DNA fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W., Evans R., Wilson M., Salditt-Georgieff M., Darnell J. E. Oligonucleotides in heterogeneous nuclear RNA: similarity of inverted repeats and RNA from repetitious DNA sites. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 11;17(14):2776–2783. doi: 10.1021/bi00607a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao F. T., Hartz J. A., Law M. L., Davidson J. N. Isolation and chromosomal localization of unique DNA sequences from a human genomic library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):865–869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Rae P. M. Nontranscribed spacer sequences promote in vitro transcription of Drosophila ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6879–6886. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami R., Urano Y., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. Organization of ribosomal RNA gene repeats of the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3219–3233. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal M., Arnheim N. Length heterogeneity in a region of the human ribosomal gene spacer is not accompanied by extensive population polymorphism. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 25;126(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90281-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal M., D'Eustachio P., Ruddle F. H., Arnheim N. Human nucleolus organizers on nonhomologous chromosomes can share the same ribosomal gene variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5744–5748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn M., Arnheim N. Nucleotide sequence of the genetically labile repeated elements 5' to the origin of mouse rRNA transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):211–224. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melli M., Whitfield C., Rao K. V., Richardson M., Bishop J. O. DNA-RNA hybridization in vast DNA excess. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 5;231(18):8–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page G. S., Smith S., Goodman H. M. DNA sequence of the rat growth hormone gene: location of the 5' terminus of the growth hormone mRNA and identification of an internal transposon-like element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 11;9(9):2087–2104. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.9.2087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. D., Dickson E., Jelinek W. Determination of nucleotide sequences from double-stranded regions of HeLa cell nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 5;115(4):571–589. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblum L. I., Parker D. L., Cassidy B. Isolation and characterization of rat ribosomal DNA clones. Gene. 1982 Jan;17(1):75–77. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90102-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblum L. I., Reddy R., Cassidy B. Transcription initiation site of rat ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7345–7362. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Wu J. R., Sala-Trepat J. M., Wallace R. B., Reyes A. A., Bonner J. The rat serum albumin gene: analysis of cloned sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3256–3260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumph W. E., Wu J. R., Bonner J. Determination of the size of rat ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid repeating units by electron microscopy. Biochemistry. 1979 Jun 26;18(13):2864–2871. doi: 10.1021/bi00580a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tantravahi U., Guntaka R. V., Erlanger B. F., Miller O. J. Amplified ribosomal RNA genes in a rat hepatoma cell line are enriched in 5-methylcytosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):489–493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullu E., Murphy S., Melli M. Human 7SL RNA consists of a 140 nucleotide middle-repetitive sequence inserted in an alu sequence. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Arsdell S. W., Denison R. A., Bernstein L. B., Weiner A. M., Manser T., Gesteland R. F. Direct repeats flank three small nuclear RNA pseudogenes in the human genome. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B., Brown D. D., Reeder R. H. The molecular basis for length heterogeneity in ribosomal DNA from Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Aug 25;105(4):461–486. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Isolation and sequence organization of human ribosomal DNA. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 5;128(3):289–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90089-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]