Abstract
Lytic infection with polyoma virus leads in Go-arrested primary mouse kidney cell cultures to a mitotic host response. In the present work we focused our attention on cellular RNA synthesis shortly after onset of polyoma T-antigen synthesis. Onset of polyoma-induced stimulation of 45S pre-rRNA synthesis was determined by hybridization of total cellular RNA with a plasmid (pMrSalB) containing the 5'-end of the mouse ribosomal gene and of the other cellular RNA species by standard biochemical analysis of cellular fractions. The results showed that polyoma-induced stimulation of cellular hnRNA (hnRNP) synthesis, the earliest presently known host cell reaction, preceded onset of stimulated 45S pre-rRNA synthesis and that the latter was paralleled by polyoma-induced stimulation of 5S RNA, tRNA and overall protein synthesis. The polyoma-induced mitotic response is similar to that triggered by simian virus 40 and by certain nonviral mitogens.
Full text
PDF






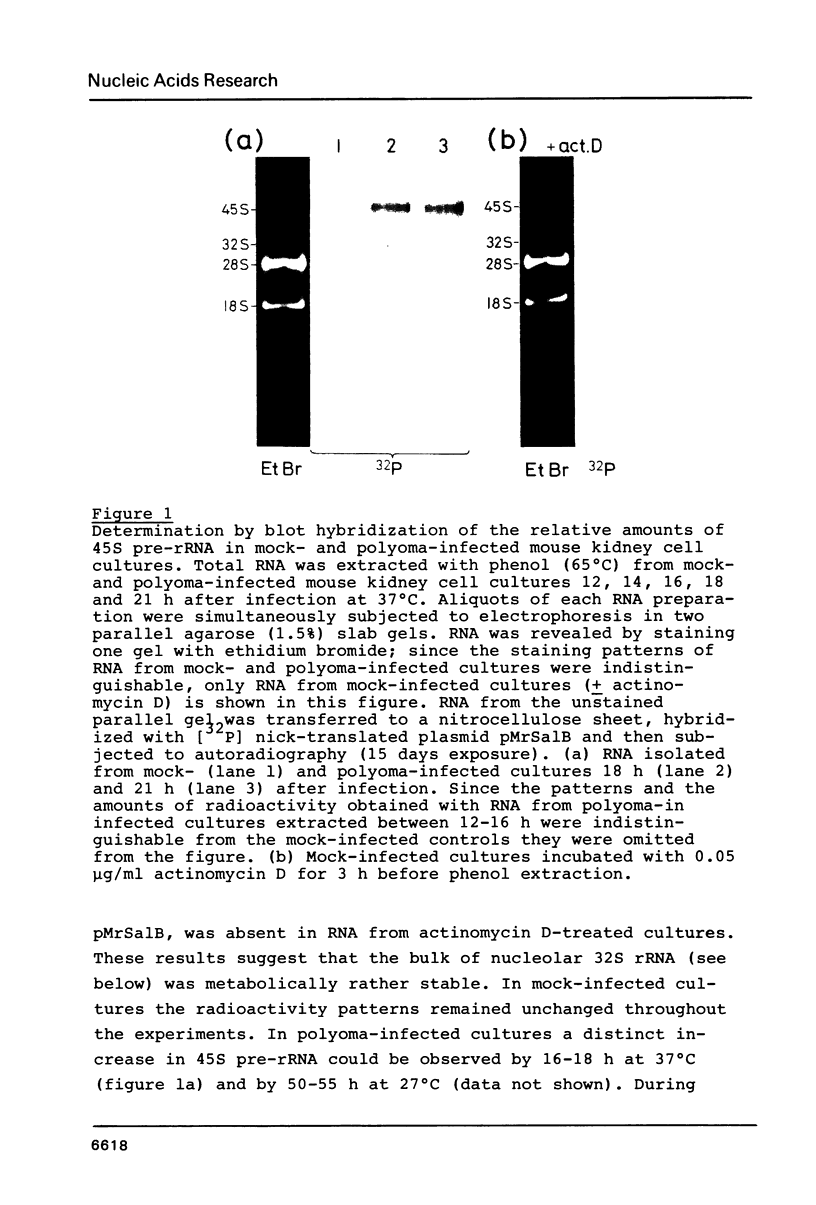



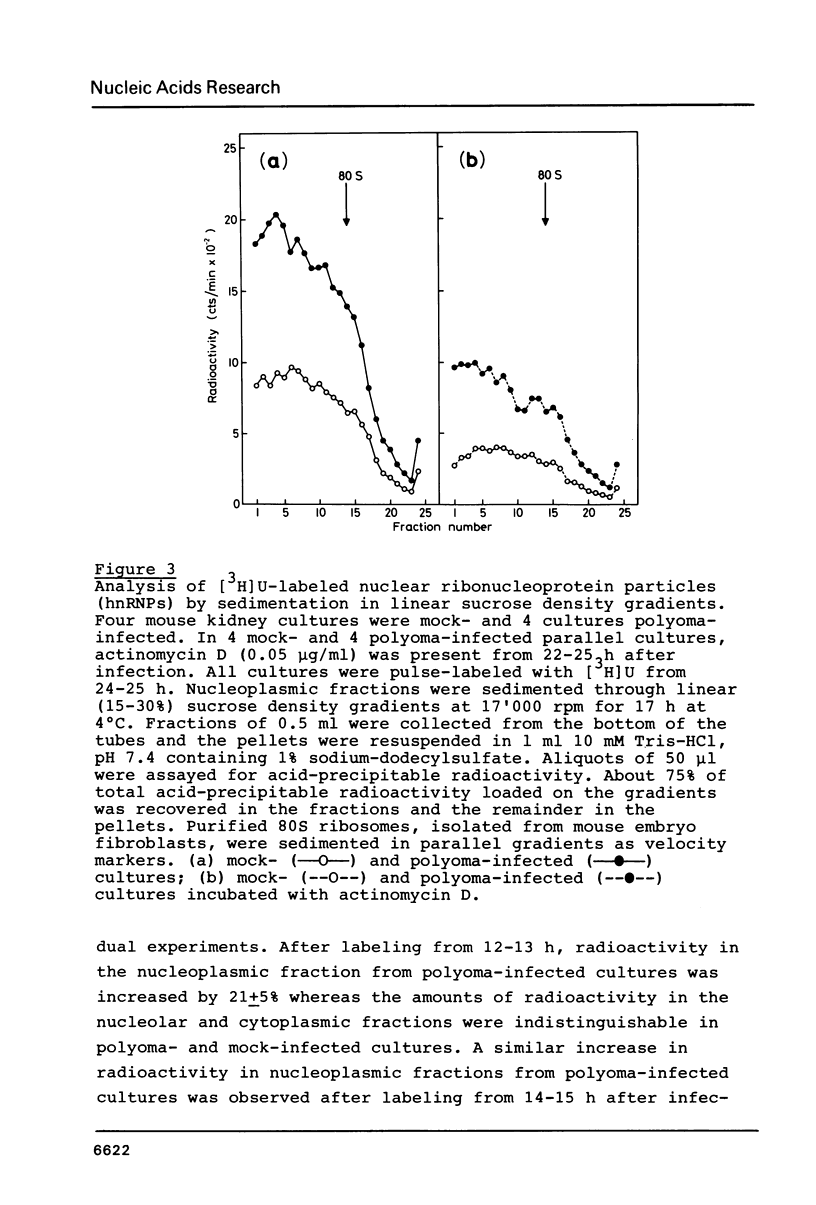






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheim N. Characterization of mouse ribosomal gene fragments purified by molecular cloning. Gene. 1979 Oct;7(2):83–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga R., Ide T., Whelly S. Stimulation of ribosomal RNA synthesis in isolated nuclei and nucleoli by partially purified preparations of SV40 T antigen. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):685–691. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R., Lane D. P., Tjian R. Use of monoclonal antibodies as probes of simian virus 40 T antigen ATPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11854–11858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R., Peden K., Pipas J. M., Nathans D., Tjian R. Biochemical activities of T-antigen proteins encoded by simian virus 40 A gene deletion mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):220–228. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Smith A. E. Polyoma virus transforming protein associates with the product of the c-src cellular gene. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):435–439. doi: 10.1038/303435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacherio D., Hager L. P. A poly(dT)-stimulated ATPase activity associated with simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8113–8116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann M., Graessman A. "Early" simian-virus-40-specific RNA contains information for tumor antigen formation and chromatin replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):366–370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Gross H. J. Structural organization of mouse rDNA: comparison of transcribed and non-transcribed regions. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Jan;177(2):223–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00267433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Mapping of a mouse ribosomal DNA promoter by in vitro transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6093–6102. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Specific transcription of mouse ribosomal DNA in a cell-free system that mimics control in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Vogt M., Dulbecco R. Induction of cellular DNA synthesis by polyoma virus. II. Increase in the rate of enzyme synthesis after infection with polyoma virus in mouse kidney cells. Virology. 1965 Nov;27(3):262–272. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashinakagawa T., Muramatsu M. Ribosome precursor particles in the nucleolus of rat liver. Easily extractable nucleolar 60-S ribonucleoprotein particles and their relation to cytoplasmic large ribosomal subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Feb 15;42(1):245–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiscott J. B., Defendi V. Simian virus 40 gene A regulation of cellular DNA synthesis. II. In nonpermissive cells. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):802–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.802-812.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellems R. E., Morhenn V. B., Pfendt E. A., Alt F. W., Schimke R. T. Polyoma virus and cyclic AMP-mediated control of dihydrofolate reductase mRNA abundance in methotrexate-resistant mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):309–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandjian E. W., Loche M., Darlix J. L., Cramer R., Türler H., Weil R. Simian virus 40 large tumor antigen: a "RNA binding protein"? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1139–1143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandjian E. W., Matter J. M., Léonard N., Weil R. Simian virus 40 and polyoma virus stimulate overall cellular RNA and protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1476–1480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress M., May E., Cassingena R., May P. Simian virus 40-transformed cells express new species of proteins precipitable by anti-simian virus 40 tumor serum. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):472–483. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.472-483.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kára J., Weil R. Specific activation of the DNA-synthesizing apparatus in contact-inhibited mouse kidney cells by polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jan;57(1):63–70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Smale S. T., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. Regulation of human ribosomal RNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3558–3562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter J. M., Khandjian E. W., Weil R. Polyoma-induced stimulation of nucleoplasmic transcription is paralleled by development of resistance against actinomycin D. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 25;11(4):1039–1058. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.4.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter J. M., Weil R. The relation between polyoma T-antigen and increased 5S RNA synthesis in cell-free extracts from polyoma-infected mouse kidney cell cultures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7643–7655. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May E., May P., Weil R. "Early" virus-specific RNA may contain information necessary for chromosome replication and mitosis induced by Simian Virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1654–1658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May P., May E., Bordé J. Stimulation of cellular RNA synthesis in mouse-kidney cell cultures infected with SV40 virus. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jul;100(2):433–436. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: in vitro and in vivo initiation and processing sites. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirault M. E., Scherrer K. Isolation of preribosomes from HeLa cells and their characterization by electrophoresis on uniform and exponential-gradient-polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Nov 11;23(2):372–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M., Onishi T. Rapid isolation of nucleoli from detergent-purified nuclei of tumor and tissue culture cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;15:221–234. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Rio D. C., Robbins A. K., Tjian R. SV40 gene expression is modulated by the cooperative binding of T antigen to DNA. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Molecular weight estimation and separation of ribonucleic acid by electrophoresis in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):668–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson T. Proteins associated with heterogeneous nuclear RNA in eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 25;83(2):163–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90386-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., La Torre J., Kelley D. E., Greenberg J. R. On the lability of poly(A) sequences during extraction of messenger RNA from polyribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P. RNA processing comes of age. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 2):28s–38s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.28s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persico-DiLauro M., Martin R. G., Livingston D. M. Interaction of Simian Virus 40 chromatin with Simian Virus 40 T-antigen. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):451–460. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.451-460.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipas J. M., Peden K. W., Nathans D. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 T antigen: isolation and characterization of mutants with deletions in the T-antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):203–213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt S. C., Grainger R. M. A mosaicism in the higher order structure of Xenopus oocyte nucleolar chromatin prior to and during ribosomal gene transcription. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):711–720. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90434-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pétursson G., Weil R. A study on the mechanism of polyoma-induced activation of the cellular DNA-synthesizing apparatus. Synchronization by FUdR of virus-induced DNA synthesis. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1968;24(1):1–29. doi: 10.1007/BF01242898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöckl E., Wintersberger E. Increased rate of RNA synthesis: early reaction of primary mouse kidney cells to infection with polyoma virus of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.8-19.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Stark G. R., Alwine J. C. Autoregulation of simian virus 40 gene A by T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon C., Türler H., Weil R. Polyoma-induced stimulation of cellular RNA synthesis is paralleled by changed expression of the viral genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1483–1503. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samarina O. P., Lukanidin E. M., Molnar J., Georgiev G. P. Structural organization of nuclear complexes containing DNA-like RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):251–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90292-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherrer K., Imaizumi-Scherrer M. T., Reynaud C. A., Therwath A. On pre-messenger RNA and transcriptions. A review. Mol Biol Rep. 1979 May 31;5(1-2):5–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00777484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutzbank T., Robinson R., Oren M., Levine A. J. SV40 large tumor antigen can regulate some cellular transcripts in a positive fashion. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):481–490. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90245-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Smith R., Griffin B., Fried M. Protein kinase activity associated with polyoma virus middle T antigen in vitro. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90204-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soprano K. J., Galanti N., Jonak G. J., McKercher S., Pipas J. M., Peden K. W., Baserga R. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 T antigen: stimulation of cellular DNA synthesis and activation of rRNA genes by mutants with deletions in the T-antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):214–219. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Ozer H. L. Temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40: infection of permissive cells. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):516–524. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.516-524.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiercy J. M., Weil R. Serum-induced stimulation of nucleoplasmic and nucleolar transcription in mouse 3T3 fibroblasts revisited. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 1;131(1):47–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Türler H. The tumor antigens and the early functions of polyoma virus. Mol Cell Biochem. 1980 Sep 15;32(2):63–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00227801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINOCOUR E. Purification of polyoma virus. Virology. 1963 Feb;19:158–168. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil R., Kára J. Polyoma "tumor antigen": an activator of chromosome replication? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):1011–1017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil R., Salomon E., May E., May P. A simplifying concept in tumor virology: virus-specific "pleiotropic effectors". Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):381–395. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil R. Viral 'tumor antigens': A novel type of mammalian regulator protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 17;516(3):301–388. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]