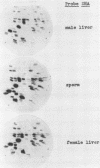
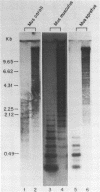
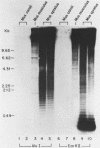
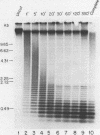
Abstract
We report the construction of a small library of recombinant plasmids containing Mus musculus repetitive DNA inserts. The repetitive cloned fraction was derived from denatured genomic DNA by reassociation to a Cot value at which repetitive, but not unique, sequences have reannealed followed by exhaustive S1 nuclease treatment to degrade single stranded DNA. Initial characterizations of this library by colony filter hybridizations have led to the identification of a previously undetected M. musculus minor satellite as well as to clones containing M. musculus major satellite sequences. This new satellite is repeated 10-20 times less than the major satellite in the M. musculus genome. It has a repeat length of 130 nucleotides compared with the M. musculus major satellite with a repeat length of 234 nucleotides. Sequence analysis of the minor satellite has shown that it has a 29 base pair region with extensive homology to one of the major satellite repeating subunits. We also show by in situ hybridization that this minor satellite sequence is located at the centromeres and possibly the arms of at least half the M musculus chromosomes. Sequences related to the minor satellite have been found in the DNA of a related Mus species, Mus spretus, and may represent the major satellite of that species.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. M., Scheller R. H., Posakony J. W., McAllister L. B., Trabert S. G., Beall C., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Repetitive sequences of the sea urchin genome. Distribution of members of specific repetitive families. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 5;145(1):5–28. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth R. K., Gross K. W., Gremke L. C., Hastie N. D. Developmentally regulated mRNAs in mouse liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):500–504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
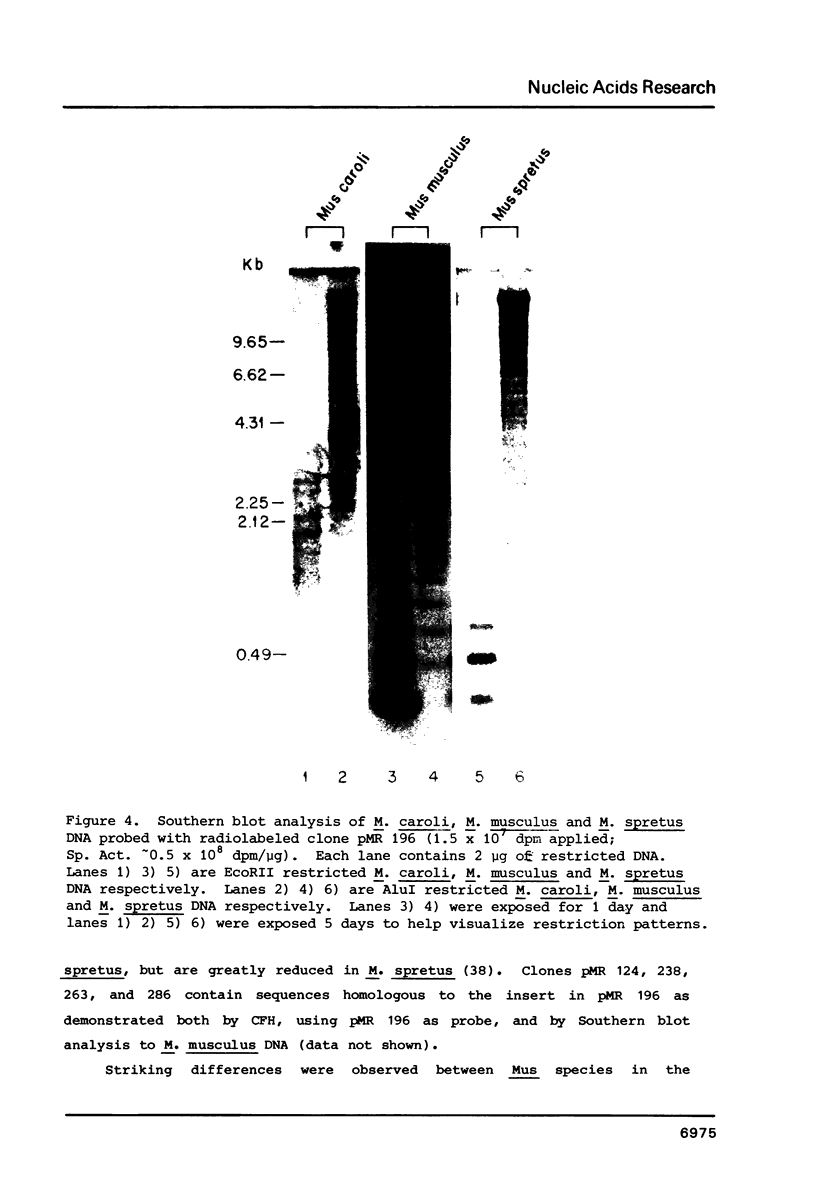
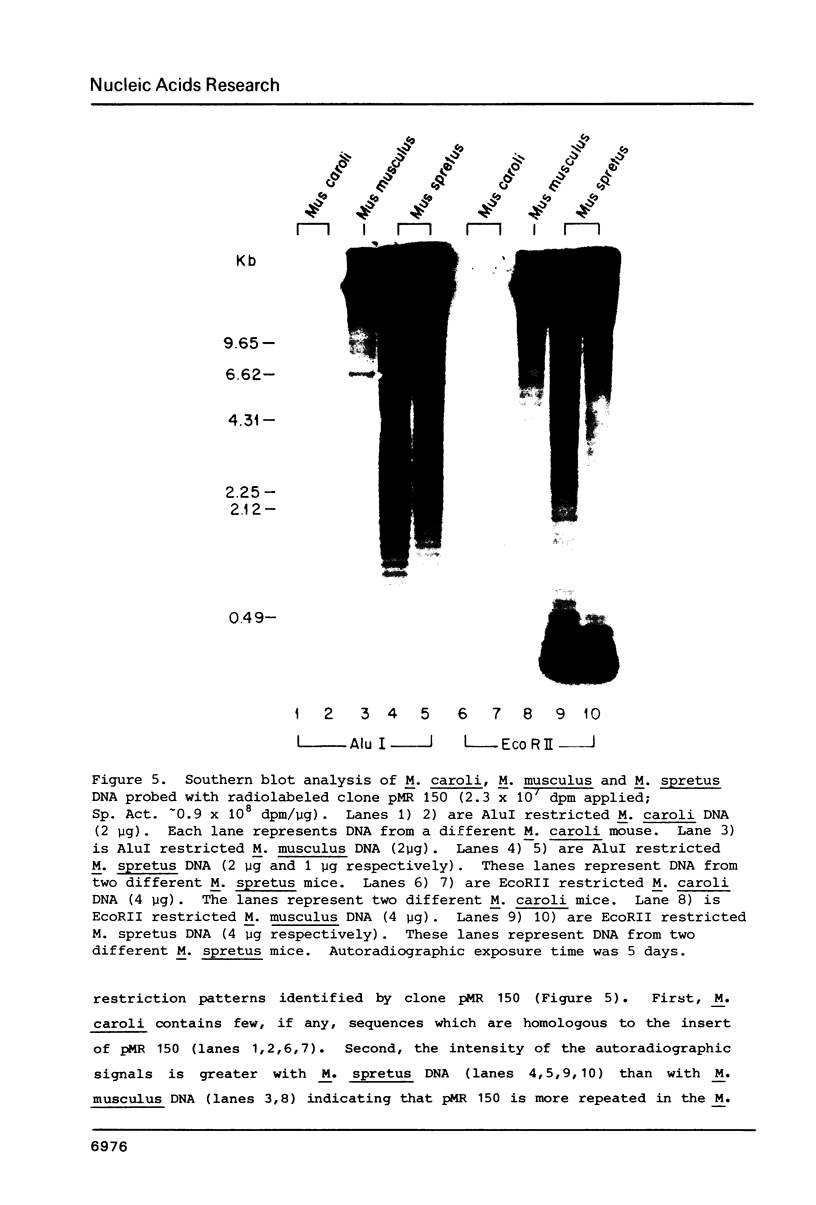
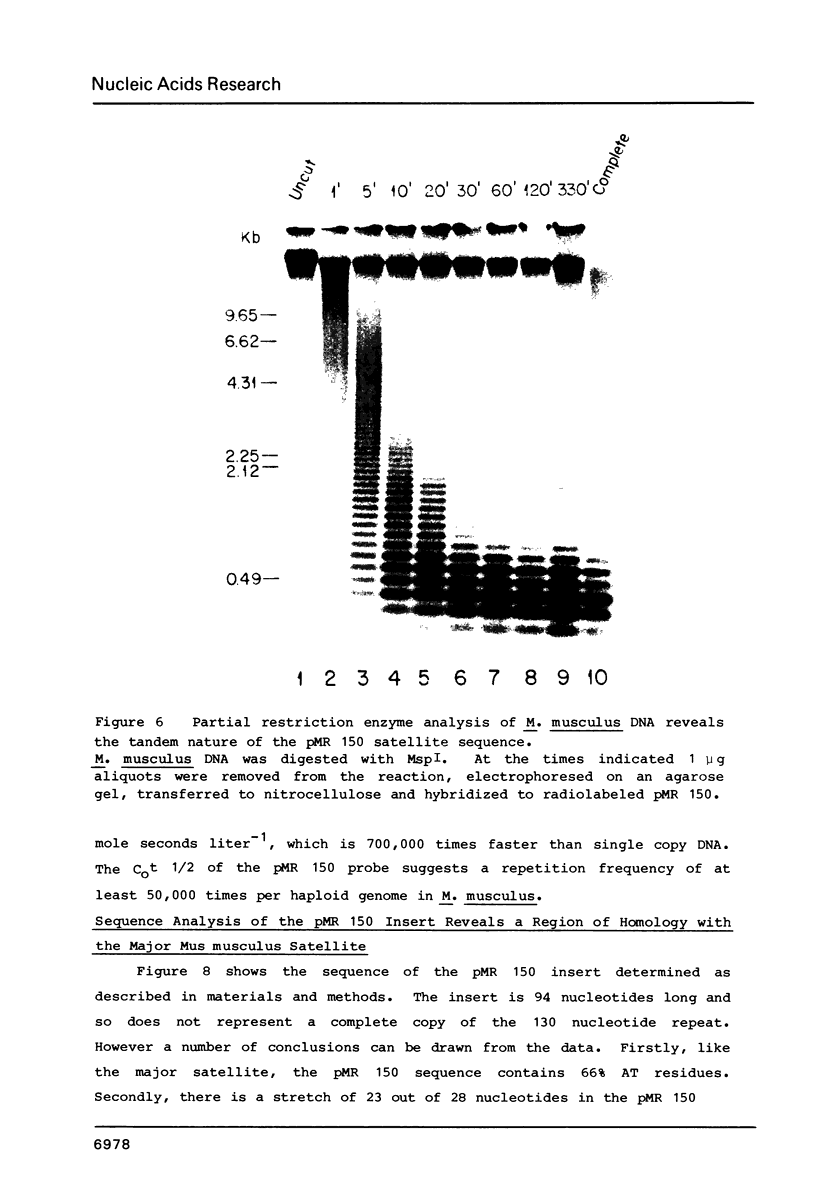
- Brown S. D., Dover G. A. Conservation of segmental variants of satellite DNA of Mus musculus in a related species: Mus spretus. Nature. 1980 May 1;285(5759):47–49. doi: 10.1038/285047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L. Molecular arrangement and evolution of heterochromatic DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:121–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campo M. S., Bishop J. O. Two classes of messenger RNA in cultured rat cells: repetitive sequence transcripts and unique sequence transcripts. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 25;90(4):649–663. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90530-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantini F. D., Scheller R. H., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Repetitive sequence transcripts in the mature sea urchin oocyte. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):173–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Galau G. A., Angerer R. C., Britten R. J. Comparative aspects of DNA organization in Metazoa. Chromosoma. 1975 Jul 21;51(3):253–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00284818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhard W., Meitinger T., Höchtl J., Zachau H. G. A new family of interspersed repetitive DNA sequences in the mouse genome. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 25;157(3):453–471. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90471-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Altenburger W. Nucleotide sequence of mouse satellite DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):683–696. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Characterization of distinct segments in mouse satellite DNA by restriction nucleases. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 1;73(2):383–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11329.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. W. Chromosomal and nuclear location of mouse satellite DNA in individual cells. Nature. 1970 Mar 7;225(5236):912–915. doi: 10.1038/225912a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein W. H., Thomas T. L., Lai C., Scheller R. H., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Characteristics of individual repetitive sequence families in the sea urchin genome studied with cloned repeats. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):889–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacic R. T., van Holde K. E. Sedimentation of homogeneous double-strand DNA molecules. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 5;16(7):1490–1498. doi: 10.1021/bi00626a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramerov D. A., Grigoryan A. A., Ryskov A. P., Georgiev G. P. Long double-stranded sequences (dsRNA-B) of nuclear pre-mRNA consist of a few highly abundant classes of sequences: evidence from DNA cloning experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Feb;6(2):697–713. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.2.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krayev A. S., Markusheva T. V., Kramerov D. A., Ryskov A. P., Skryabin K. G., Bayev A. A., Georgiev G. P. Ubiquitous transposon-like repeats B1 and B2 of the mouse genome: B2 sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7461–7475. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIYAZAWA Y., THOMAS C. A., Jr NUCLEOTIDE COMPOSITION OF SHORT SEGMENTS OF DNA MOLECULES. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:223–237. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. P., Costantini F. D., Posakony J. W., Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Evolutionary conservation of repetitive sequence expression in sea urchin egg RNA's. Science. 1980 May 30;208(4447):1046–1048. doi: 10.1126/science.6154974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. P., Scheller R. H., Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Evolutionary change in the repetition frequency of sea urchin DNA sequences. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):649–660. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardue M. L., Gall J. G. Chromosomal localization of mouse satellite DNA. Science. 1970 Jun 12;168(3937):1356–1358. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3937.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posakony J. W., Scheller R. H., Anderson D. M., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Repetitive sequences of the sea urchin genome. III. Nucleotide sequences of cloned repeat elements. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 15;149(1):41–67. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Straus N. A. Relatedness of mouse satellite deoxyribonucleic acid to deoxyribonucleic acid of various Mus species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3546–3550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossant J., Vijh M., Siracusa L. D., Chapman V. M. Identification of embryonic cell lineages in histological sections of M. musculus in-equilibrium M. caroli chimaeras. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1983 Feb;73:179–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Jay E., Wu R. Terminal labeling and addition of homopolymer tracts to duplex DNA fragments by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jan;3(1):101–116. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheller R. H., Anderson D. M., Posakony J. W., McAllister L. B., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Repetitive sequences of the sea urchin genome. II. Subfamily structure and evolutionary conservation. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 15;149(1):15–39. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90258-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheller R. H., Costantini F. D., Kozlowski M. R., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Specific representation of cloned repetitive DNA sequences in sea urchin RNAs. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):189–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheller R. H., Thomas T. L., Lee A. S., Klein W. H., Niles W. D., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Clones of individual repetitive sequences from sea urchin DNA constructed with synthetic Eco RI sites. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):197–200. doi: 10.1126/science.847467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiurba R., Nandi S. Isolation and characterization of germ line DNA from mouse sperm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3947–3951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;76:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61789-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. SINEs and LINEs: highly repeated short and long interspersed sequences in mammalian genomes. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):433–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siracusa L. D., Chapman V. M., Bennett K. L., Hastie N. D., Pietras D. F., Rossant J. Use of repetitive DNA sequences to distinguish Mus musculus and Mus caroli cells by in situ hybridization. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1983 Feb;73:163–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Long range periodicities in mouse satellite DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 5;94(1):51–69. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90404-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton W. D., McCallum M. Related satellite DNA's in the genus Mus. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):633–652. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Komaroff L., Efstratiadis A., Broome S., Lomedico P., Tizard R., Naber S. P., Chick W. L., Gilbert W. A bacterial clone synthesizing proinsulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3727–3731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth-Gutai M. Recombination in SV40-infected cells: nucleotide sequences at viral-viral recombinant joints in naturally arising variants. Virology. 1981 Mar;109(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90505-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]