Full text
PDF


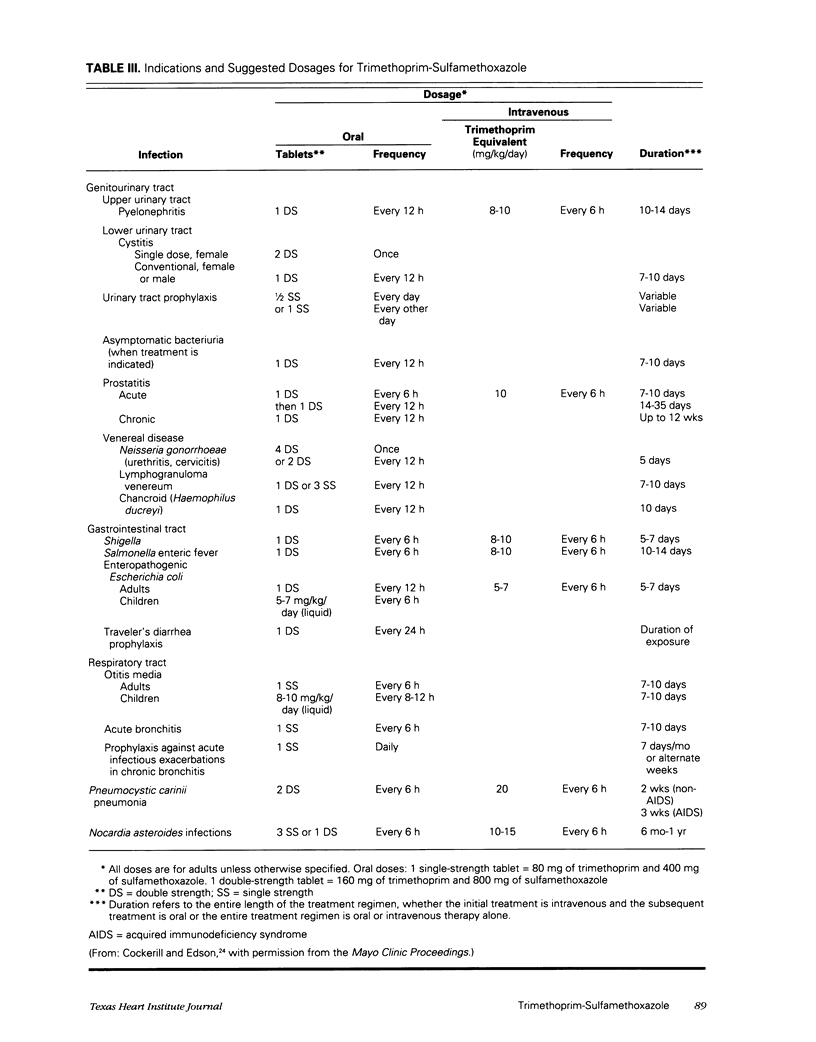




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthonisen N. R., Manfreda J., Warren C. P., Hershfield E. S., Harding G. K., Nelson N. A. Antibiotic therapy in exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Feb;106(2):196–204. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-2-196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apuzzio J. J., Ganesh V. V., Dispensiere B. R., Miller A. M., Louria D. B. Prophylaxis with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in abdominal, pelvic, and prostatic surgery. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Mar-Apr;9 (Suppl 2):S211–S217. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_2.s211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjapongs W., Sadudi N., Noeypatimanond S. Trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole combination in the treatment of falciparum malaria. J Med Assoc Thai. 1970 Dec;53(12):849–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berglund F., Killander J., Pompeius R. Effect of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole on the renal excretion of creatinine in man. J Urol. 1975 Dec;114(6):802–808. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)67149-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomstedt G. C. Results of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole prophylaxis in ventriculostomy and shunting procedures. A double-blind randomized trial. J Neurosurg. 1985 May;62(5):694–697. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.62.5.0694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Grose W. E., Keating M. J. Use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for treatment of infections in patients with cancer. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):579–585. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunham R. C., Kuo C., Stevens C. E., Holmes K. K. Treatment of concomitant Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis infections in women: comparison of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole with ampicillin-probenecid. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):491–499. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchall J. J., Elwell L. P., Fling M. E. Molecular mechanisms of resistance to trimethoprim. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):246–254. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchall J. J., Hitchings G. H. Inhibitor binding analysis of dihydrofolate reductases from various species. Mol Pharmacol. 1965 Sep;1(2):126–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushby S. R., Hitchings G. H. Trimethoprim, a sulphonamide potentiator. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 May;33(1):72–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T., Rumans L., Arnold K. Response of typhoid fever caused by chloramphenicol-susceptible and chloramphenicol-resistant strains of Salmonella typhi to treatment with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):551–561. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M. S., Ronfeld R. A. Pharmacokinetic data and drug monitoring: I. Antibiotics and antiarrhythmics. J Clin Pharmacol. 1975 May-Jun;15(5-6):405–418. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1975.tb02362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill F. R., 3rd, Edson R. S. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Mayo Clin Proc. 1987 Oct;62(10):921–929. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)65049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig W. A., Kunin C. M. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole: pharmacodynamic effects of urinary pH and impaired renal function. Studies in humans. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Apr;78(4):491–497. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-78-4-491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crider S. R., Colby S. D. Susceptibility of enterococci to trimethoprim and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):71–75. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley M. N., Levitz R. E., Quintiliani R., Hickingbotham J. M., Nightingale C. H. Pharmacokinetics of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of adult patients with normal meninges. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):811–814. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson C. D., DuPont H. L., Mathewson J. J., West M. S., Johnson P. C., Bitsura J. A. Treatment of traveler's diarrhea with sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim and loperamide. JAMA. 1990 Jan 12;263(2):257–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson C. D., Johnson P. C., Dupont H. L., Morgan D. R., Bitsura J. A., de la Cabada F. J. Ciprofloxacin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole as initial therapy for travelers' diarrhea. A placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Feb;106(2):216–220. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-2-216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischl M. A., Dickinson G. M., La Voie L. Safety and efficacy of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim chemoprophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in AIDS. JAMA. 1988 Feb 26;259(8):1185–1189. doi: 10.1001/jama.259.8.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman L. J., Trenholme G. M., Kaplan R. L., Segreti J., Hines D., Petrak R., Nelson J. A., Mayer K. W., Landau W., Parkhurst G. W. Empiric antimicrobial therapy of domestically acquired acute diarrhea in urban adults. Arch Intern Med. 1990 Mar;150(3):541–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordin F. M., Simon G. L., Wofsy C. B., Mills J. Adverse reactions to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Apr;100(4):495–499. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-4-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey D., Hamilton-Miller J. M., Brumfitt W. Incidence and mechanisms of resistance to trimethoprim in clinically isolated gram-negative bacteria. Chemotherapy. 1979;25(3):147–156. doi: 10.1159/000237834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose W. E., Bodey G. P., Loo T. L. Clinical pharmacology of intravenously administered trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Mar;15(3):447–451. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.3.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurwith M., Truog K., Hinthorn D., Liu C. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim alone for prophylaxis of infection in granulocytopenic patients. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):593–601. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschlag M. R. Activity of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole against Chlamydia trachomatis in vitro. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):500–505. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding G. K., Ronald A. R., Nicolle L. E., Thomson M. J., Gray G. J. Long-term antimicrobial prophylaxis for recurrent urinary tract infection in women. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):438–443. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan A., Erian M. M., Farid Z., Hathout S. D., Sorensen K. Trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole in acute brucellosis. Br Med J. 1971 Jul 17;3(5767):159–160. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5767.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverkos H. W. Assessment of therapy for toxoplasma encephalitis. The TE Study Group. Am J Med. 1987 May;82(5):907–914. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90151-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchings G. H. Biochemical background of trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole. Med J Aust. 1973 Jun 30;1(2 Suppl):5–9. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1973.tb111178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Rivera G. K., Schell M. J., Thornton D., Lott L. Successful intermittent chemoprophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jun 25;316(26):1627–1632. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198706253162604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson-York G. L., Gump B. B., Gump D. W. Activity of trimethoprim (TMP), sulphamethoxazole (SMX) and the combination against Bacteroides fragilis group isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Nov;12(5):515–518. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.5.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jick H. Adverse reactions to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in hospitalized patients. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):426–428. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalowski S., Nanra R. S., Mathew T. H., Kincaid-Smith P. Deterioration in renal function in association with co-trimoxazole therapy. Lancet. 1973 Feb 24;1(7800):394–397. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90251-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandil E. Treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole combination. Dermatologica. 1973;146(5):303–309. doi: 10.1159/000251981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz Z., Lancet M., Seligson-Singer S., Reznik R. [Asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women]. Harefuah. 1974 Nov 1;87(9):390–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer I., Ritz R., Brunner F. Aseptic meningitis as an adverse effect of co-trimoxazole. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jun 16;308(24):1481–1481. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198306163082415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremers P., Duvivier J., Heusghem C. Pharmacokinetic studies of co-trimoxazole in man after single and repeated doses. J Clin Pharmacol. 1974 Feb-Mar;14(2):112–117. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1974.tb02300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz R. E., Quintiliani R. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for bacterial meningitis. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Jun;100(6):881–890. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-6-881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz N., Saravolatz L. D. Use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in a glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-deficient population. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Mar-Apr;9 (Suppl 2):S218–S229. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_2.s218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meares E. M., Jr Prostatitis: review of pharmacokinetics and therapy. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):475–483. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. D., Kusmiesz H., Jackson L. H., Woodman E. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole therapy for shigellosis. JAMA. 1976 Mar 22;235(12):1239–1243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. F., Acar J. F., Altmann G., Blackburn B. O., Chao L., Courtieu A. L., Evans D. A., Guzman M., Holmes M., Jacobs M. R. Laboratory surveillance of synergy between and resistance to trimethoprim and sulfonamides. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):351–357. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R. B., Welling P. G. Clinical pharmacokinetics of co-trimoxazole (trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole). Clin Pharmacokinet. 1980 Sep-Oct;5(5):405–423. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198005050-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavillard E. R. Treatment of nocardial infection with trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole. Med J Aust. 1973 Jun 30;1(2 Suppl):65–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintiliani R., Levitz R. E., Nightingale C. H. Potential role of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in the treatment of serious hospital-acquired bacterial infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Mar-Apr;9 (Suppl 2):S160–S167. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_2.s160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H., Rodriguez W. J., Khan W. N., Mann R., Barsanti R. G., Ross S. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in the treatment of otitis media caused by ampicillin-resistant strains of Haemophilus influenzae. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):514–516. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siber G. R., Gorham C. C., Ericson J. F., Smith A. L. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in children and adults with normal and impaired renal function. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):566–578. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiera H., Lawson W., Weinrauch H. Wegener's granulomatosis treated with sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim. Report of a case. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Sep;148(9):2065–2066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolkoff-Rubin N. E., Weber D., Fang L. S., Kelly M., Wilkinson R., Rubin R. H. Single-dose therapy with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for urinary tract infection in women. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):444–448. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Rozenberg-Arska M., Dekker A. Prevention of infection in the neutropenic patient. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Nov-Dec;11 (Suppl 7):S1545–S1550. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_7.s1545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. C., de Jongh C. A., Newman K. A., Crowley J., Wiernik P. H., Schimpff S. C. Selective antimicrobial modulation as prophylaxis against infection during granulocytopenia: trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole vs. nalidixic acid. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):624–634. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Wiss K., Bushby M. B., Hollowell D. C. In vitro activity of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole against the nontuberculous mycobacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):326–331. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells C. L., Podzorski R. P., Peterson P. K., Ramsay N. K., Simmons R. L., Rhame F. S. Incidence of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole-resistant enterobacteriaceae among transplant recipients. J Infect Dis. 1984 Nov;150(5):699–706. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.5.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton J. M., Coleman D. L., Wofsy C. B., Luce J. M., Blumenfeld W., Hadley W. K., Ingram-Drake L., Volberding P. A., Hopewell P. C. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or pentamidine for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. A prospective randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Jul;105(1):37–44. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., Lau W. K., Gale R. P., Young L. S. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for the treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jun;92(6):762–769. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-6-762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormser G. P., Keusch G. T. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Sep;91(3):420–429. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-3-420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



