Abstract
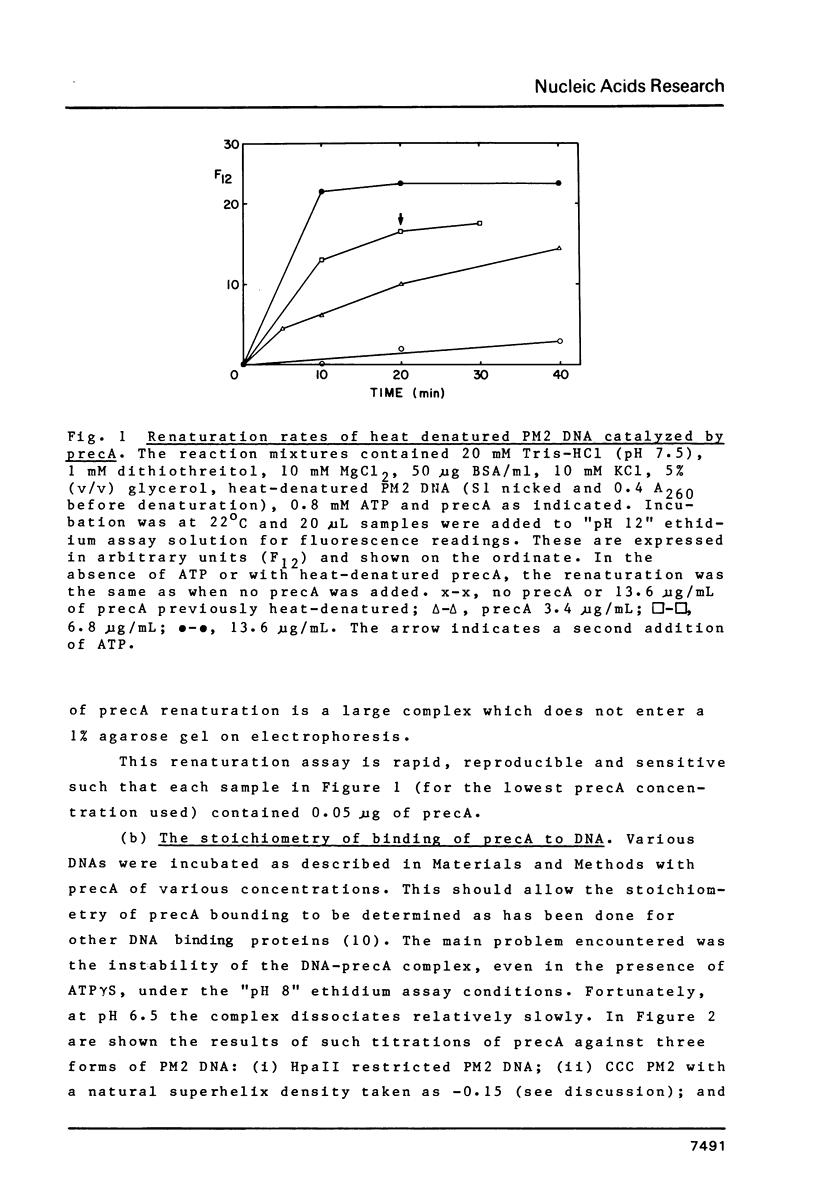
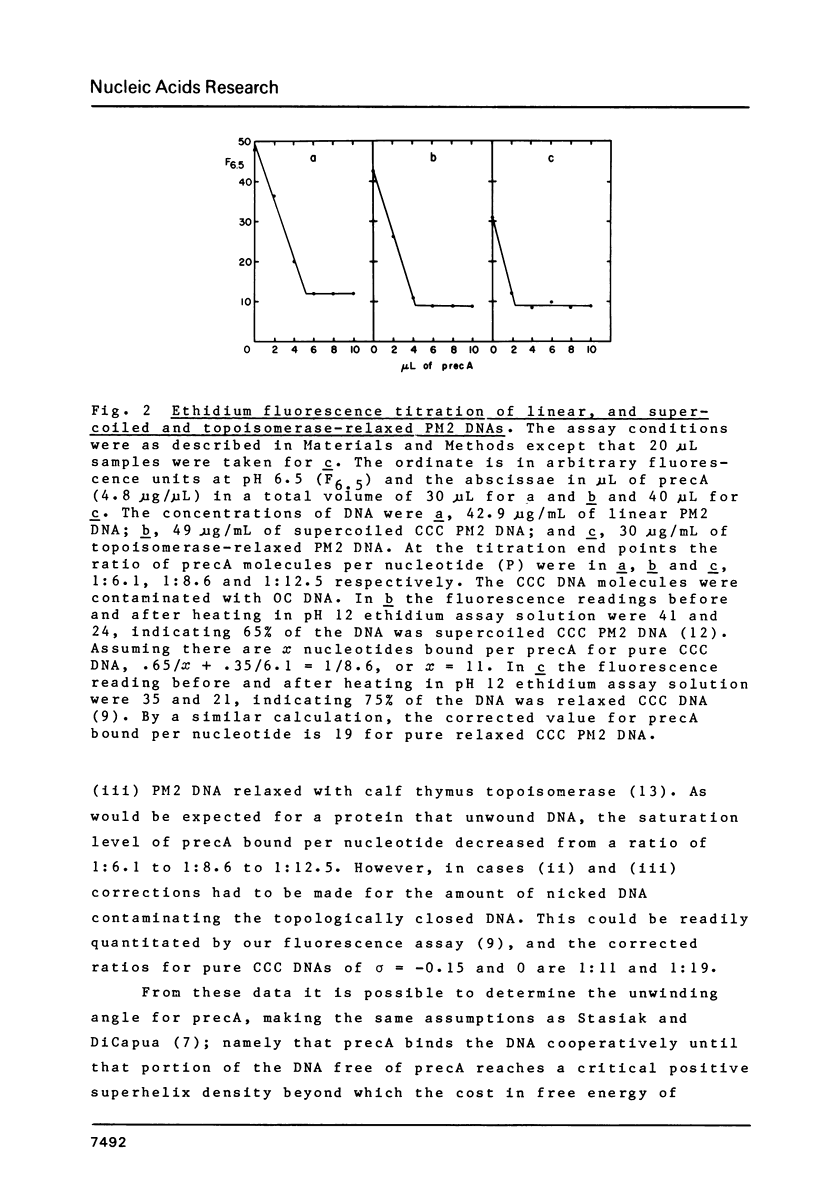
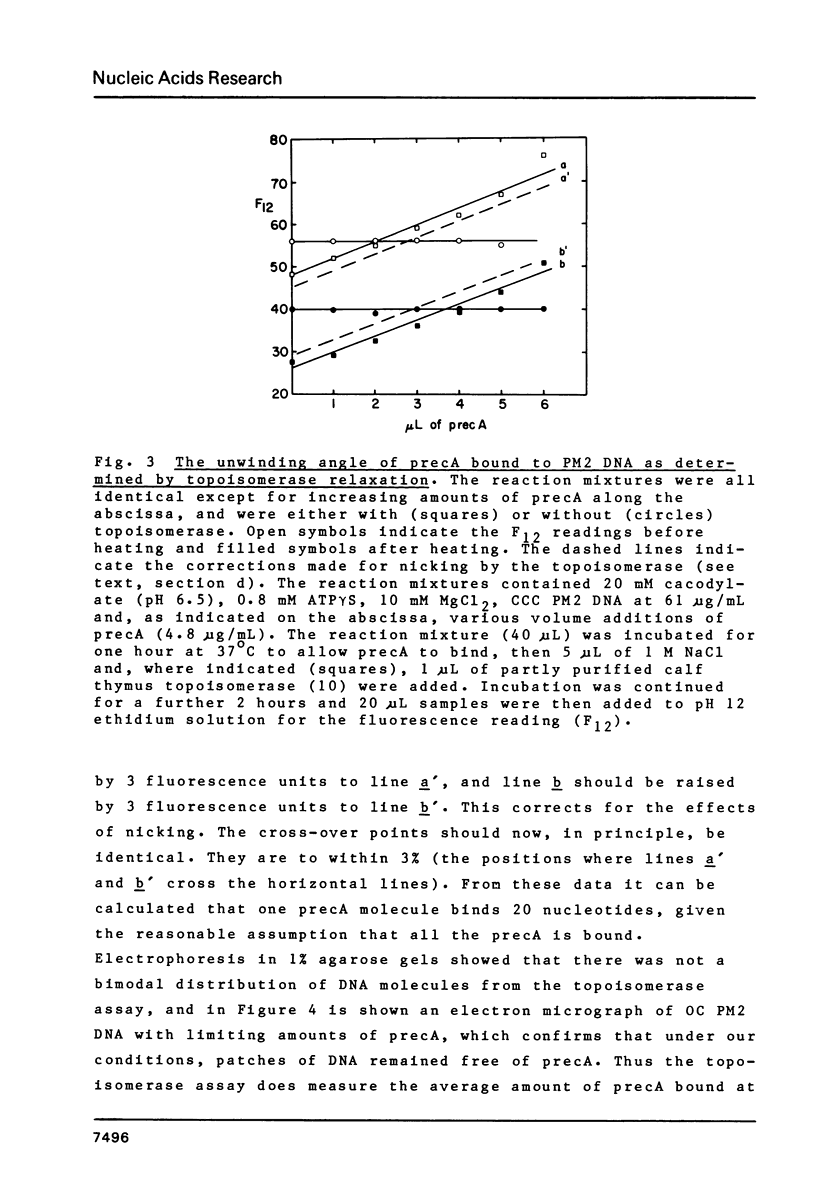
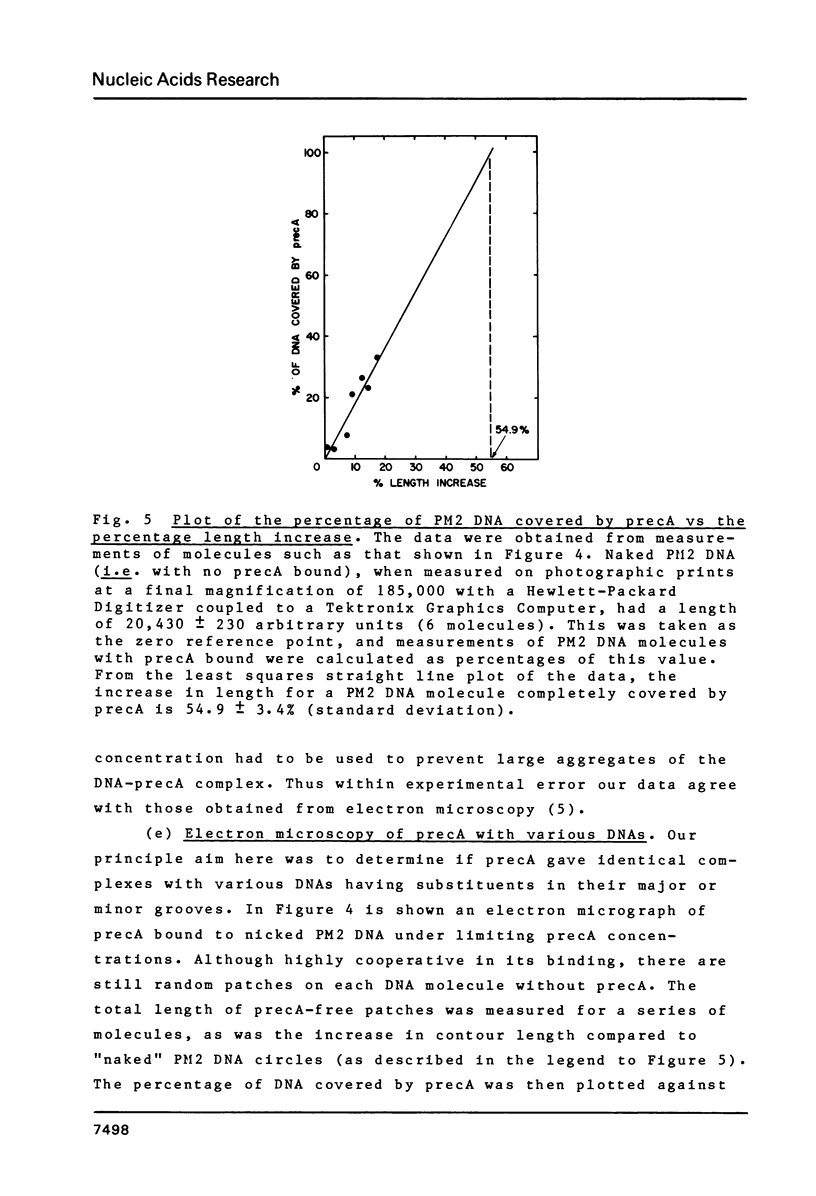
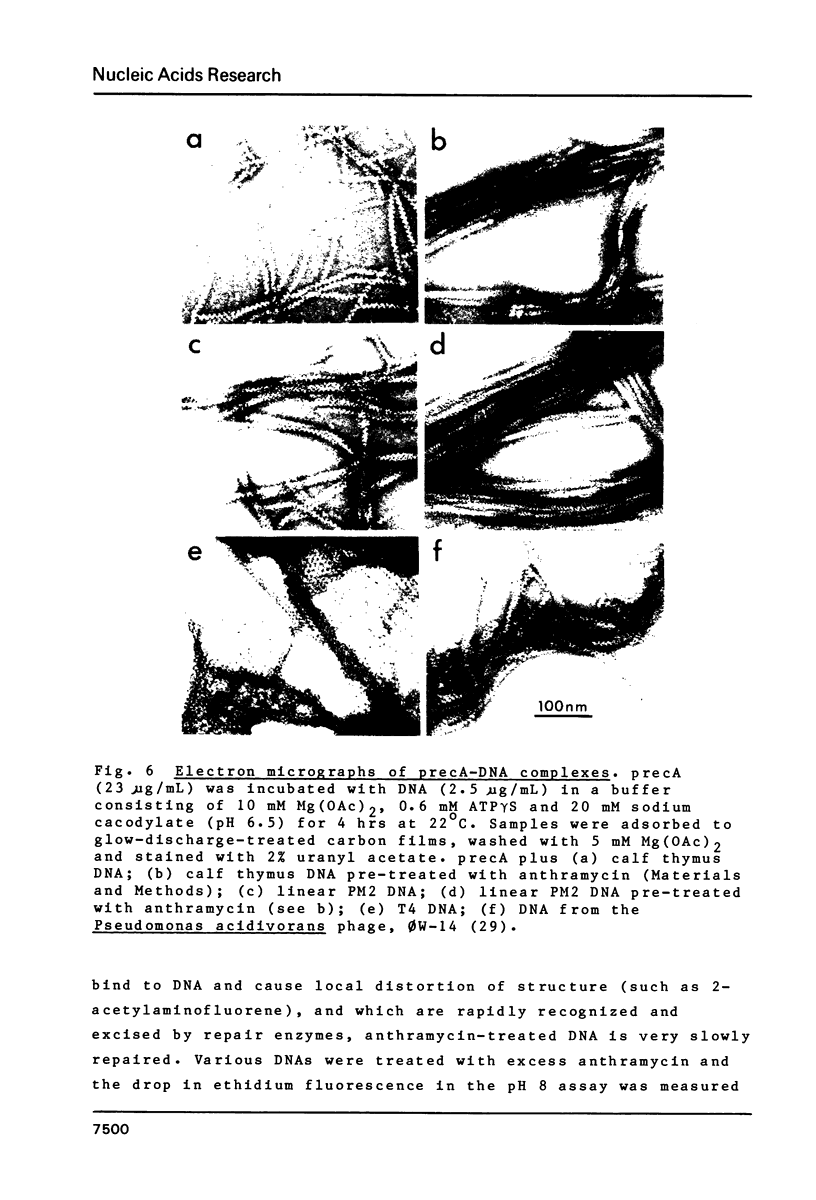
Ethidium fluorescence assays were adapted for the rapid and sensitive detection of precA; in addition, fluorescence measurements on binding precA to linear, OC and CCC PM2 DNAs have enabled the stoichiometry of precA binding as well as the precA-induced unwinding angle of DNA to be determined. The stoichiometry of binding was independently confirmed by sedimentation analysis to be one precA molecule per 3 bp. The unwinding angle was also independently confirmed by measurements of fluorescence changes induced by the binding of precA to CCC DNA which was relaxed by topoisomerase to give a precA-induced unwinding angle of 51 degrees. Electron microscopy of OC DNA molecules which bound nonsaturating amounts of precA revealed that the length increase in DNA due to precA was approximately 55%. Finally, examination of negatively stained precA complexes with a variety of linear DNAs showed that the minor groove is the primary site of interaction for this protein.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cassuto E., West S. C., Mursalim J., Conlon S., Howard-Flanders P. Initiation of genetic recombination: homologous pairing between duplex DNA molecules promoted by recA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3962–3966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassuto E., West S. C., Podell J., Howard-Flanders P. Genetic recombination: recA protein promotes homologous pairing between duplex DNA molecules without strand unwinding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):4201–4210. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.4201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciarrocchi G., Pedrini A. M. Determination of pyrimidine dimer unwinding angle by measurement of DNA electrophoretic mobility. J Mol Biol. 1982 Feb 25;155(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90445-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. M., McEntee K., Lehman I. R. A simple and rapid procedure for the large scale purification of the recA protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4676–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Capua E., Engel A., Stasiak A., Koller T. Characterization of complexes between recA protein and duplex DNA by electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):87–103. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90514-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn K., Chrysogelos S., Griffith J. Electron microscopic visualization of recA-DNA filaments: evidence for a cyclic extension of duplex DNA. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):757–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Bose R. J., Warren R. A. 5-(4-Aminobutylaminomethyl)uracil, an unusual pyrimidine from the deoxyribonucleic acid of bacteriophage phiW-14. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):151–157. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Morgan A. R. A rapid method for the measurement of the unwinding angle of intercalating agents and the superhelix density of circular DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2425–2439. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGavin S. A model for the specific pairing of homologous double-stranded nucleic acid molecules during genetic recombination. Heredity (Edinb) 1977 Aug;39(1):15–25. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1977.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGavin S. Models of specifically paired like (homologous) nucleic acid structures. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jan 28;55(2):293–298. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. R., Evans D. H., Lee J. S., Pulleyblank D. E. Review: ethidium fluorescence assay. Part II. Enzymatic studies and DNA-protein interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 10;7(3):571–594. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. R., Lee J. S., Pulleyblank D. E., Murray N. L., Evans D. H. Review: ethidium fluorescence assays. Part 1. Physicochemical studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 10;7(3):547–569. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.3.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrusek R. L., Anderson G. L., Garner T. F., Fannin Q. L., Kaplan D. J., Zimmer S. G., Hurley L. H. Pyrrol[1,4]benzodiazepine antibiotics. Proposed structures and characteristics of the in vitro deoxyribonucleic acid adducts of anthramycin, tomaymycin, sibiromycin, and neothramycins A and B. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1111–1119. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Morgan A. R. The sense of naturally occurring superhelices and the unwinding angle of intercalated ethidium. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 5;91(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90368-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Homologous pairing and strand exchange in genetic recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:405–437. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Recombination activities of E. coli recA protein. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90224-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. Helical periodicity of DNA determined by enzyme digestion. Nature. 1980 Aug 7;286(5773):573–578. doi: 10.1038/286573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Stachelek C., Konigsberg W., Rupp W. D. Sequences of the recA gene and protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2611–2615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Stachelek C., Konigsberg W., Rupp W. D. Sequences of the recA gene and protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2611–2615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scraba D. G., Bradley R. D., Leyritz-Wills M., Warren R. A. Bacteriophage phi W-14: the contribution of covalently bound putrescine to DNA packing in the phage head. Virology. 1983 Jan 15;124(1):152–160. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90298-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stasiak A., Di Capua E., Koller T. Elongation of duplex DNA by recA protein. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):557–564. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stasiak A., Di Capua E. The helicity of DNA in complexes with recA protein. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):185–186. doi: 10.1038/299185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volodin A. A., Shepelev V. A., Kosaganov Y. N. Stoichiometry and kinetics of complex formation by the recA protein and a double-stranded DNA. FEBS Lett. 1982 Aug 16;145(1):53–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Helical repeat of DNA in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):200–203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. The degree of unwinding of the DNA helix by ethidium. I. Titration of twisted PM2 DNA molecules in alkaline cesium chloride density gradients. J Mol Biol. 1974 Nov 15;89(4):783–801. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock G. M., McEntee K., Lehman I. R. ATP-dependent renaturation of DNA catalyzed by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):126–130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock G. M., McEntee K., Lehman I. R. Hydrolysis of nucleoside triphosphates catalyzed by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Characterization of ATP hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8829–8834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C. Use of polylysine for adsorption of nuclei acids and enzymes to electron microscope specimen films. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2311–2315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]