Fig. 3.
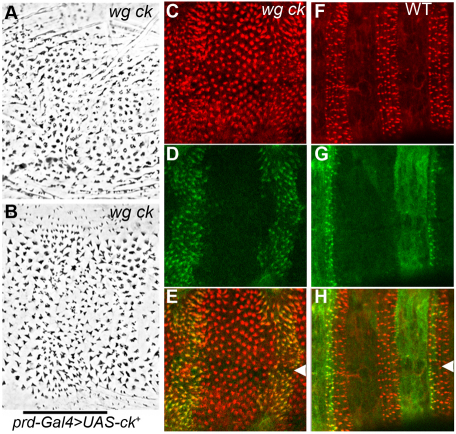
Denticle shape can be rescued by providing ectopic ck. (A,B) wgCX4ckKT9 double mutants secrete a uniform lawn of rounded denticles that are rescued to a pointed, hooked appearance (B) when prd-Gal4 drives ectopic expression of a wild-type ck transgene in odd-numbered segments, marked by bar. (C) Rhodamine phalloidin staining in 14-hour AEL wgCX4ckKT9 double mutants also detects rescued elongation and shaping of actin bundles in the domains expressing UAS-ck.(D,E) The GFP-tagged ck product accumulates strongly in incipient denticles of these wgCX4ckKT9 mutants (merge, E) and this distribution coincides perfectly with those denticles that are rescued. (F) Wild-type siblings show no structural alteration of denticles where ck is overexpressed. (G) Much of the prd expression domain in a wild-type embryo underlies naked cuticle, showing that GFP-tagged ck remains cytoplasmic in non-denticle-secreting cells and is recruited to the denticles in denticle-secreting cells (merge, H). Arrowheads mark the ventral midline.