Abstract
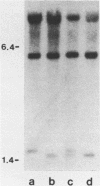
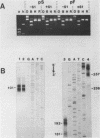
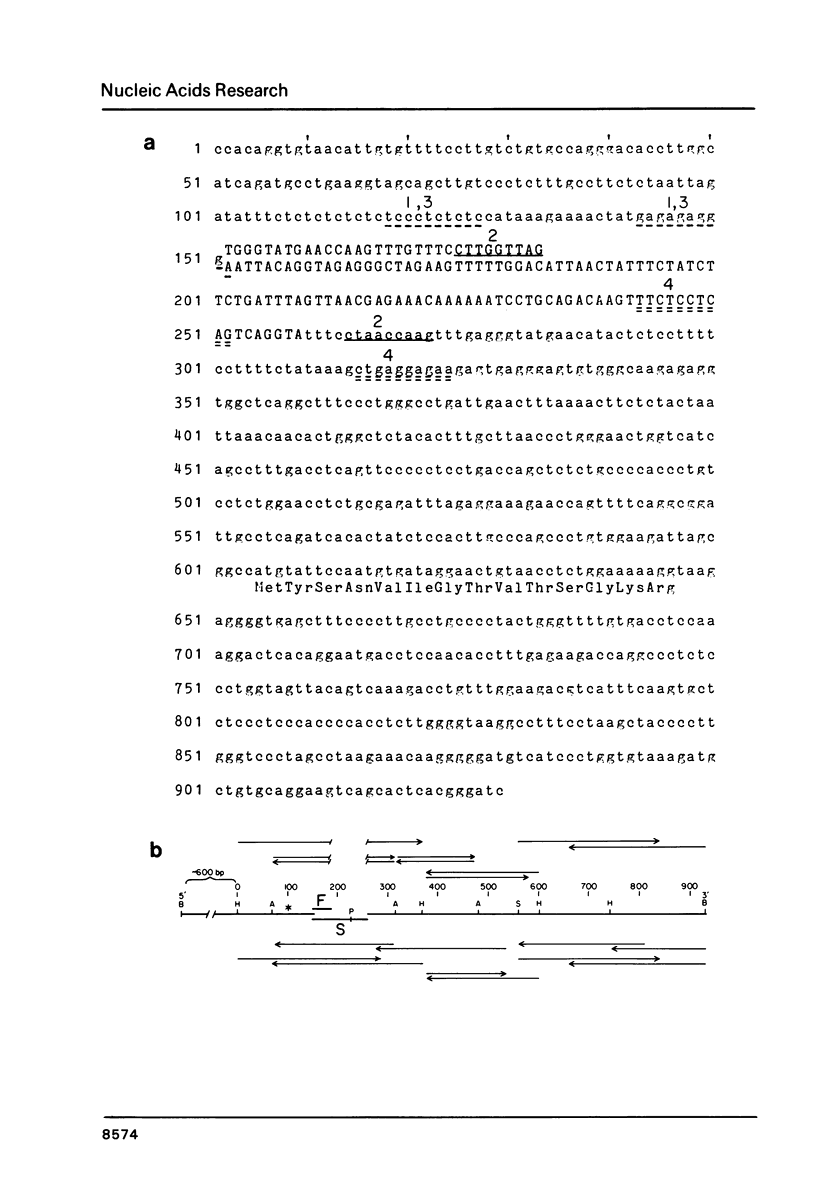
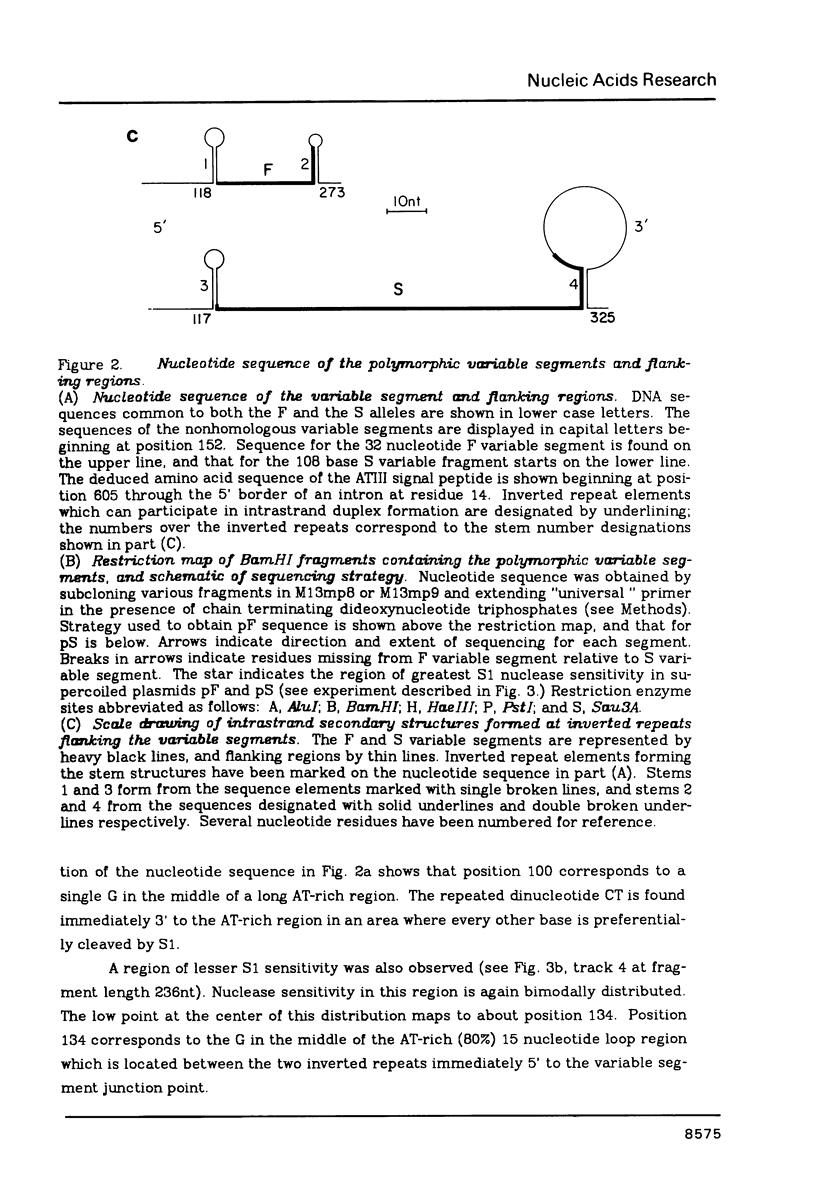
Nucleotide sequence analysis revealed that a DNA length polymorphism 5' to the human antithrombin III gene is due to the presence of 32bp or 108bp nonhomologous nucleotide sequences (variable segments) 345bp upstream from the translation initiation codon. Sequences at the 3' borders of both variable segments can form intrastrand inverted repeat structures with sequences further downstream. An inverted repeat is also found immediately 5' to the site where the variable segments are located. Thus, cruciform structures may form flanking the variable segments of both alleles of this DNA length polymorphism. DNA secondary structure may be detected with single strand specific nucleases. S1 nuclease sensitive sites were mapped in recombinant plasmids containing the cloned alleles of the ATIII length polymorphism. The site most sensitive to S1 is located upstream from the variable segments in an AT-rich segment flanked by 6bp direct repeats. A region of lesser nuclease sensitivity was also observed in the AT-rich loops formed between the inverted repeats 5' to the variable segments.
Full text
PDF




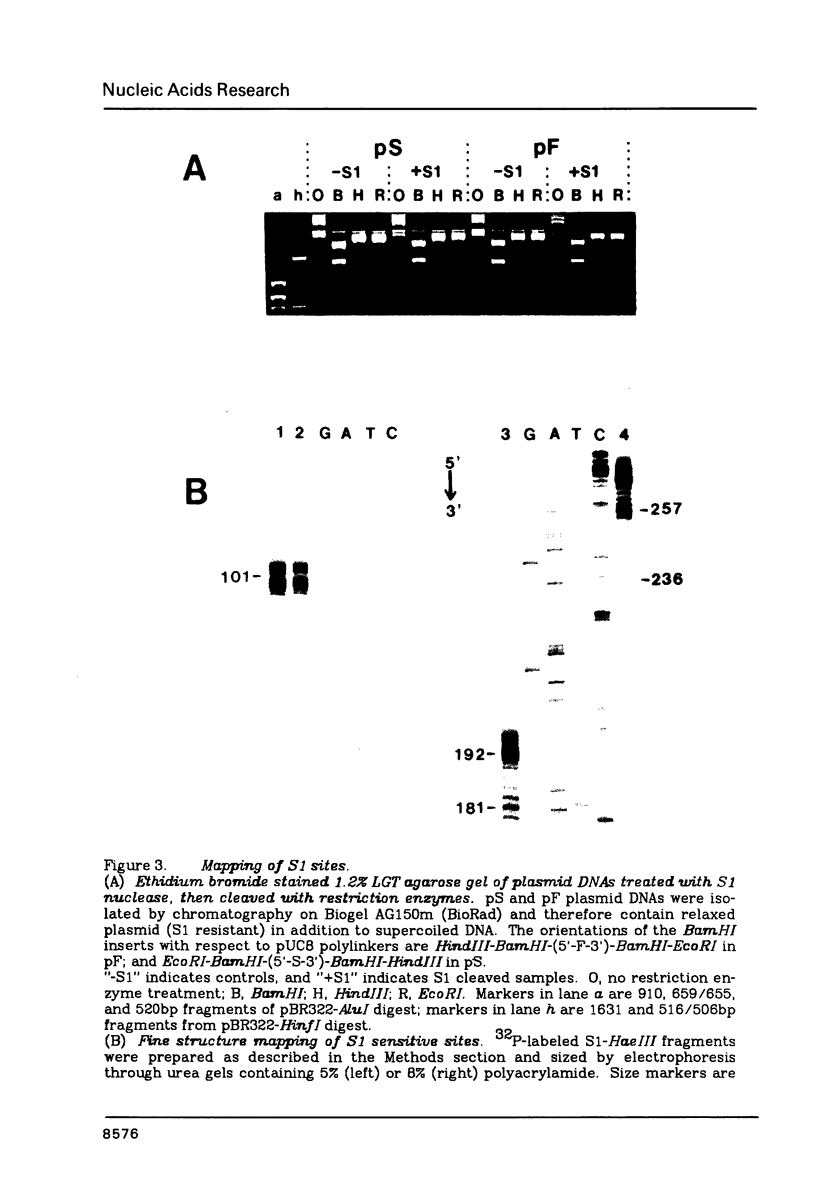
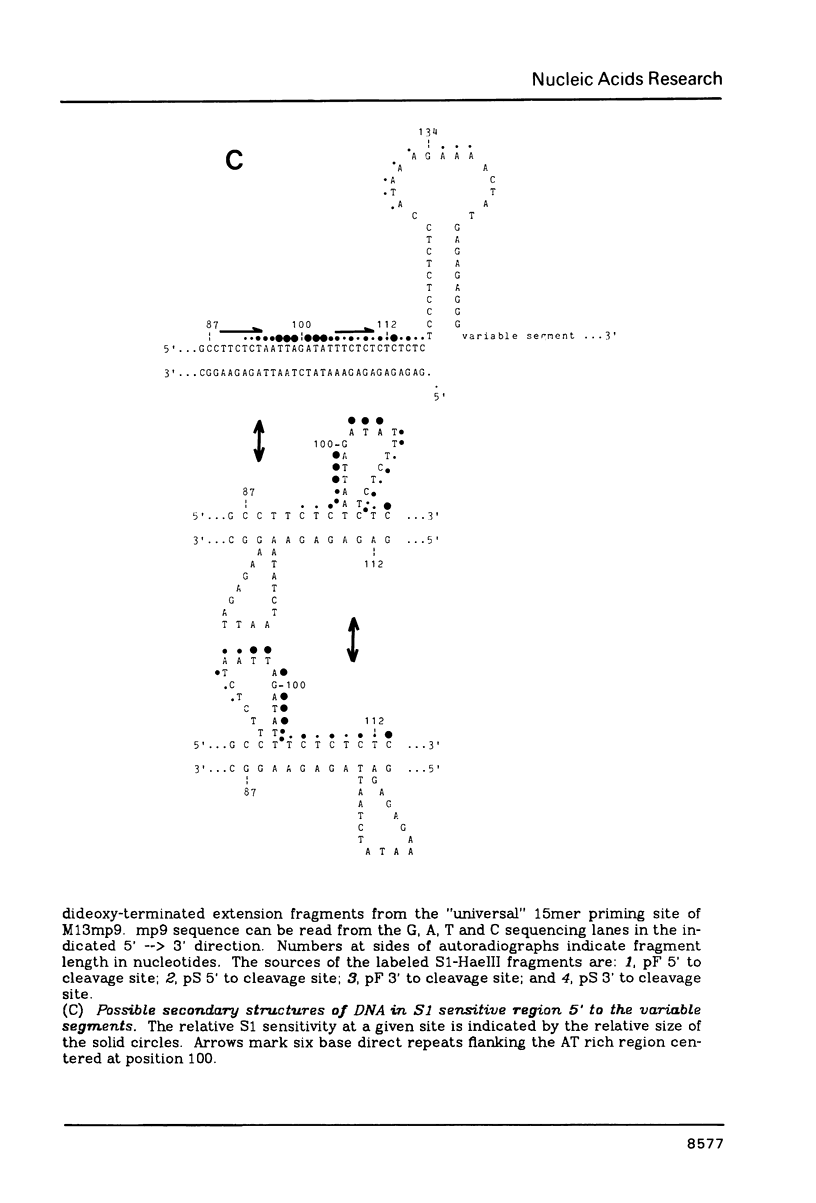





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Selby M. J., Rutter W. J. The highly polymorphic region near the human insulin gene is composed of simple tandemly repeating sequences. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):31–35. doi: 10.1038/295031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock S. C., Wion K. L., Vehar G. A., Lawn R. M. Cloning and expression of the cDNA for human antithrombin III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8113–8125. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnewell V., Fowler R. F., Skinner D. M. An inverted repeat borders a fivefold amplification in satellite DNA. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):862–865. doi: 10.1126/science.6879182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Warren R., Sarthy A., Palmiter R. D. Regulation of metallothionein--thymidine kinase fusion plasmids injected into mouse eggs. Nature. 1982 Mar 4;296(5852):39–42. doi: 10.1038/296039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding C. R., Russell W. C. S1 sensitive sites in adenovirus DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):21–36. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C. Homocopolymer sequences in the spacer of a sea urchin histone gene repeat are sensitive to S1 nuclease. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):714–716. doi: 10.1038/295714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong G. F. A systemic DNA sequencing strategy. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):539–549. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90213-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Richards R. I. Human metallothionein genes--primary structure of the metallothionein-II gene and a related processed gene. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):797–802. doi: 10.1038/299797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreitman M. Nucleotide polymorphism at the alcohol dehydrogenase locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):412–417. doi: 10.1038/304412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A., Ross W. Viral integration and excision: structure of the lambda att sites. Science. 1977 Sep 16;197(4309):1147–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.331474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Fritsch E. F., Parker R. C., Blake G., Maniatis T. The isolation and characterization of linked delta- and beta-globin genes from a cloned library of human DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1157–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie A. G., Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Ratliff R. L. Polymorphism of DNA double helices. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 15;143(1):49–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. Hairpin-loop formation by inverted repeats in supercoiled DNA is a local and transmissible property. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1271–1289. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. The inverted repeat as a recognizable structural feature in supercoiled DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6468–6472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace H. A., Pelham H. R., Travers A. A. Association of an S1 nuclease-sensitive structure with short direct repeats 5' of Drosophila heat shock genes. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):555–557. doi: 10.1038/304555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Wells R. D. Cruciform structures in supercoiled DNA. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):466–470. doi: 10.1038/289466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler L. A., Weber J. L., Gorski J. Polymorphism near the rat prolactin gene caused by insertion of an Alu-like element. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):159–160. doi: 10.1038/305159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeck R. E. A multicopy insertion sequence in the bovine genome with structural homology to the long terminal repeats of retroviruses. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):767–769. doi: 10.1038/298767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman A. R., White R. A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6754–6758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]