Abstract
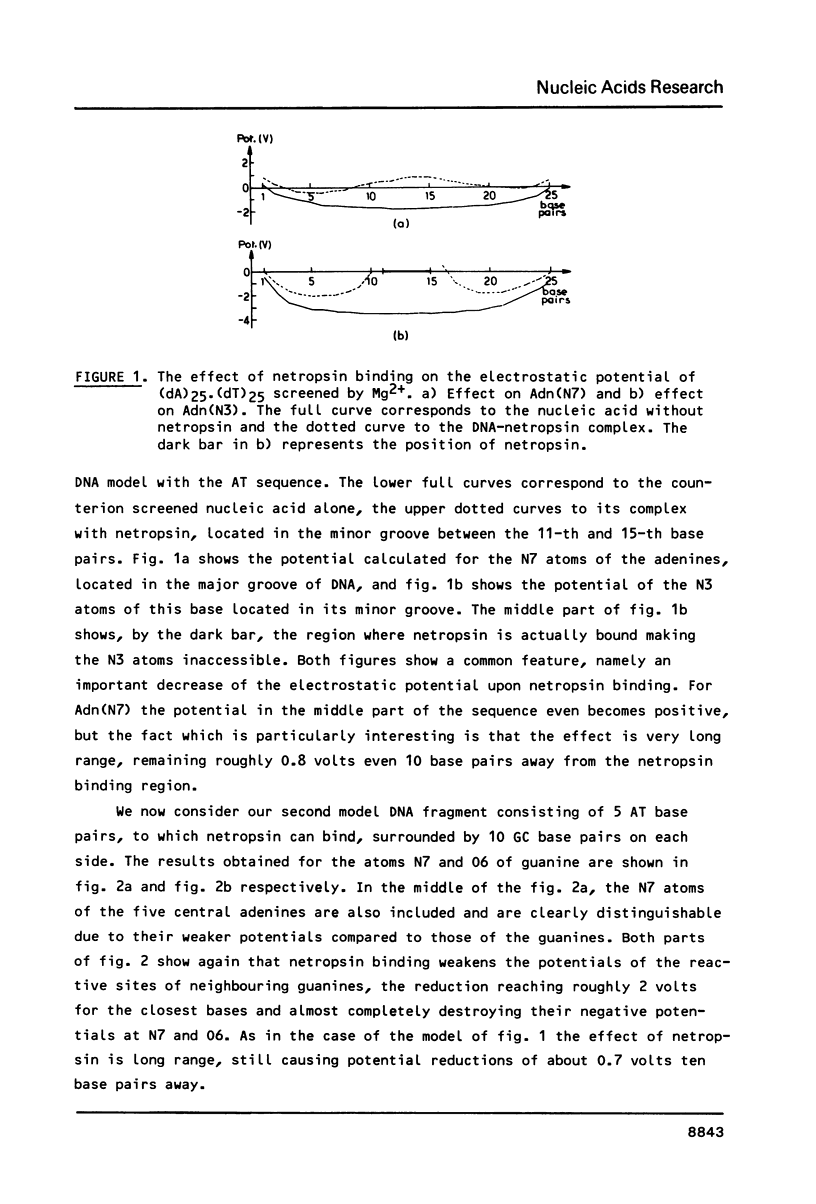
The effect of netropsin binding on the electrostatic potential of DNA reactive sites is presented. Calculations are performed for atoms N7 and O6 of guanine, N3 and N7 of adenine of model, 25 base pair long, DNA-netropsin complexes. An important weakening of the potential is found spreading along all the oligonucleotide chain studied. The results are discussed in connection with the inhibitory effect of a related ligand, distamycin A, on DNA methylation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Birdsall D. L., Leslie A. G., Ratliff R. L. Left-handed DNA helices. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):743–745. doi: 10.1038/283743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullman A., Pullman B. Molecular electrostatic potential of the nucleic acids. Q Rev Biophys. 1981 Aug;14(3):289–380. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B., Kuśmierek J. T. Chemical mutagenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:655–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B. The chemical effects of nucleic acid alkylation and their relation to mutagenesis and carcinogenesis. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1975;15(0):219–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer C., Marck C., Guschlbauer W. Z-DNA and other non-B-DNA structures are reversed to B-DNA by interaction with netropsin. FEBS Lett. 1983 Apr 5;154(1):156–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80894-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



