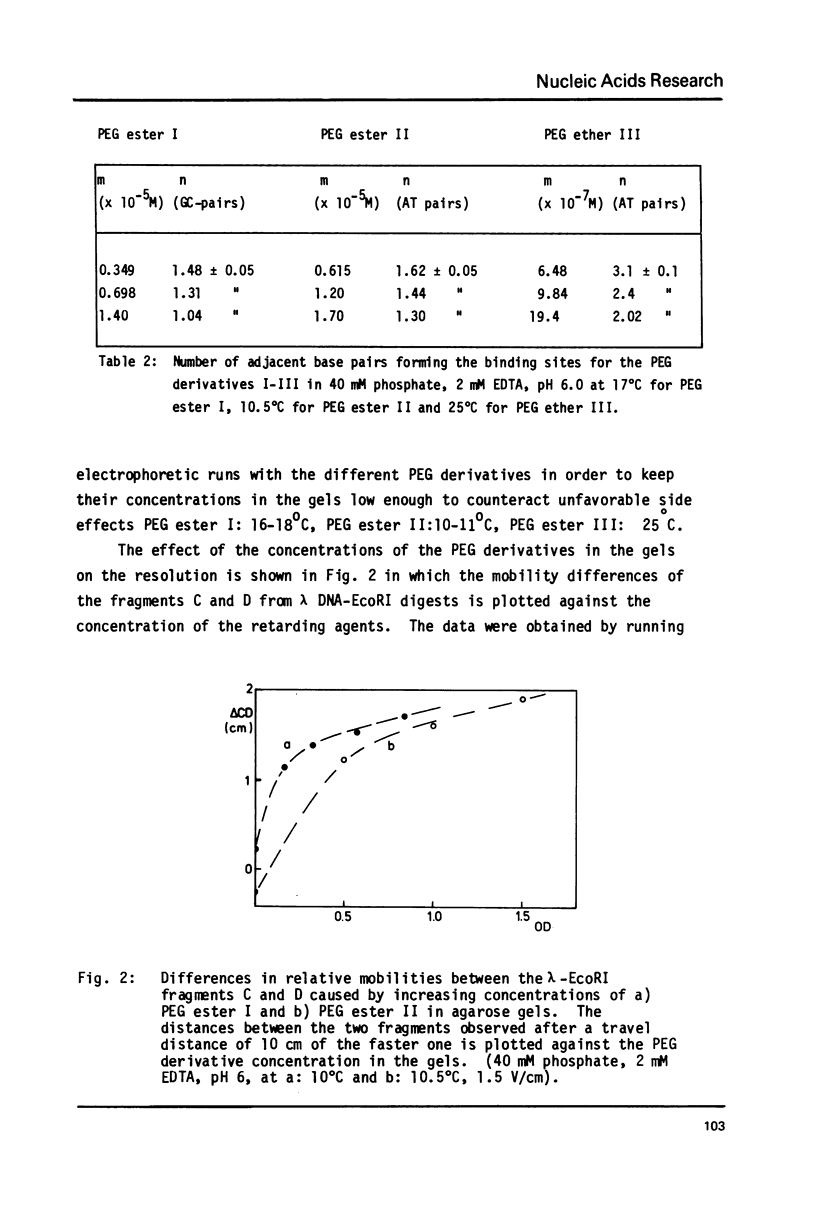
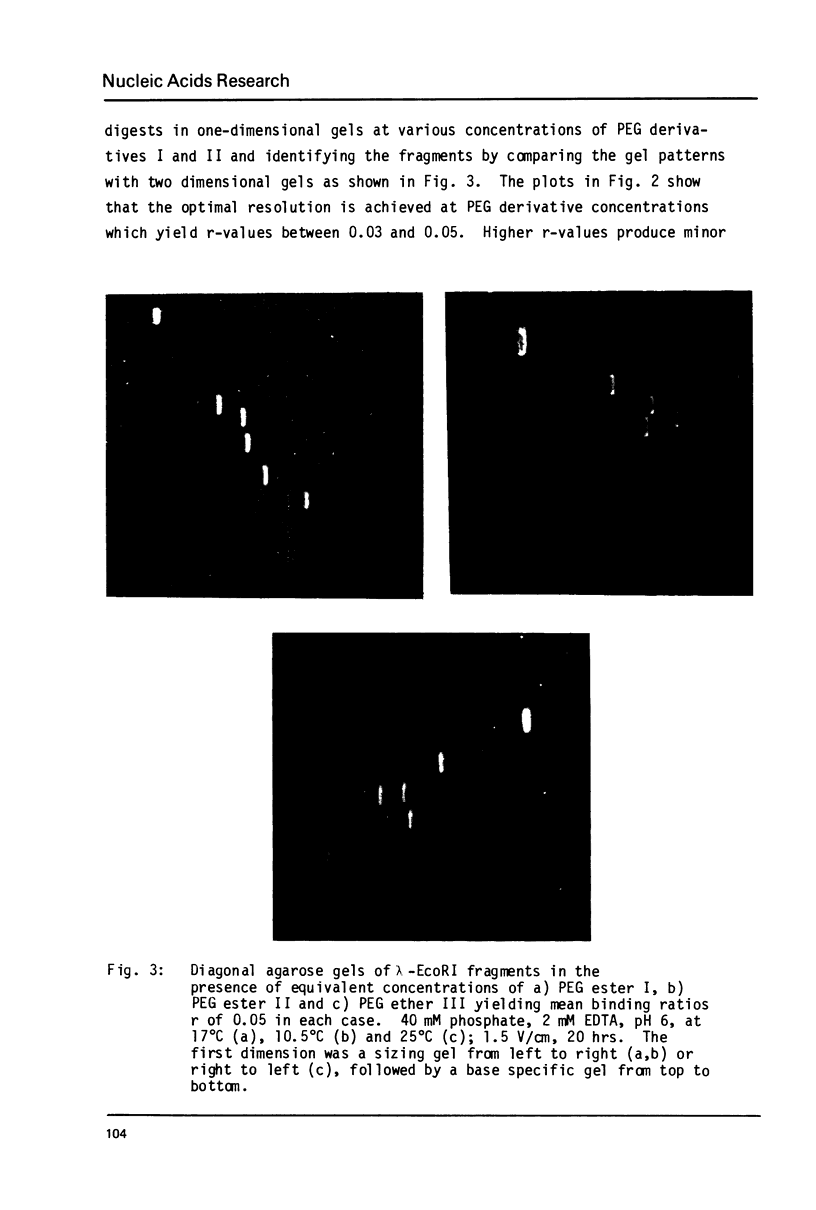
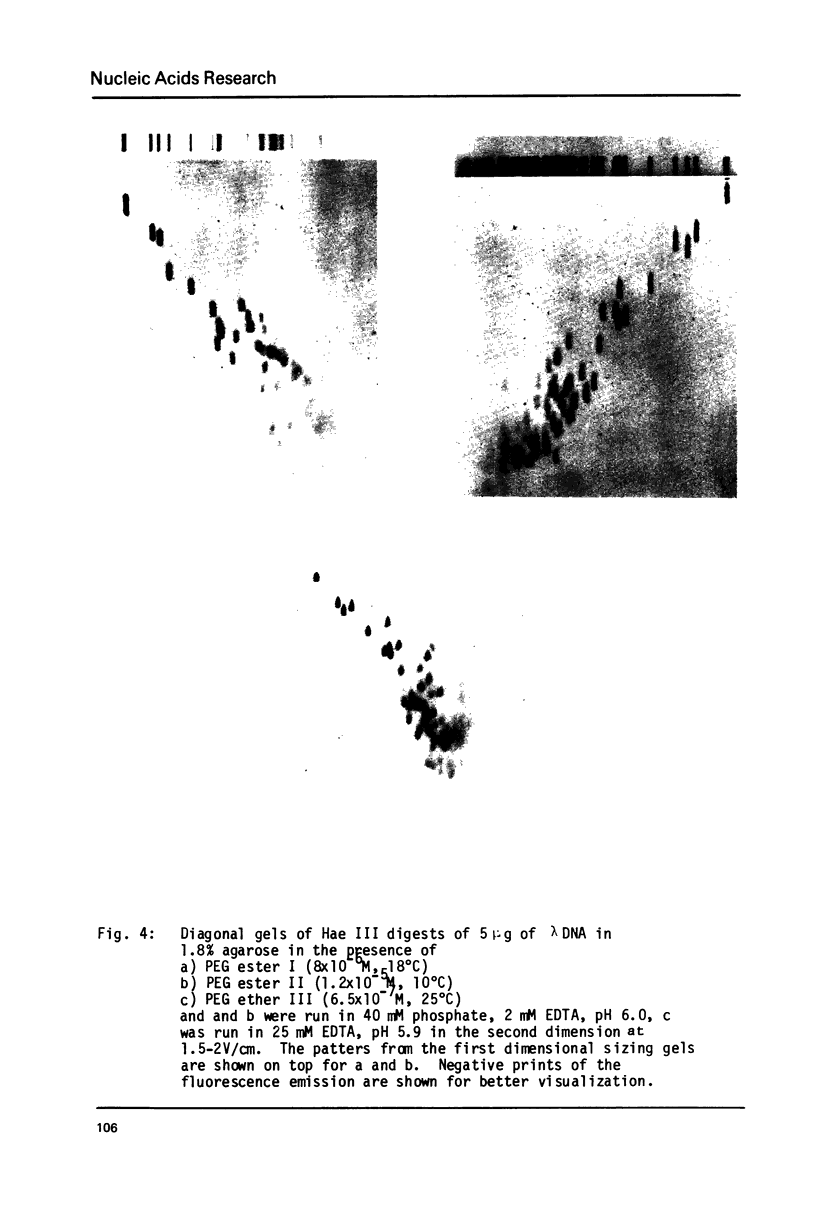
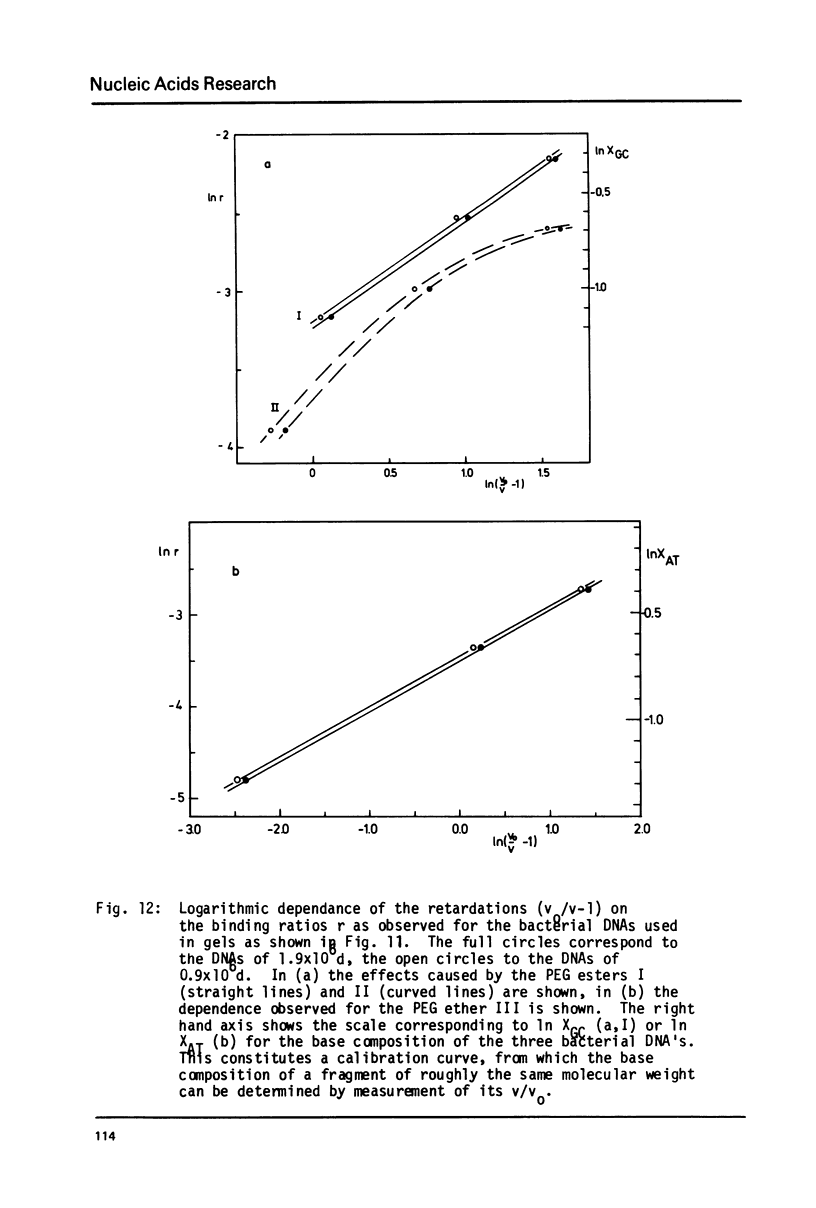
Abstract
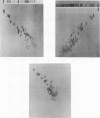
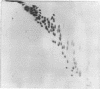
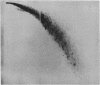
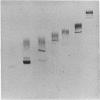
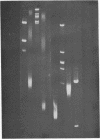
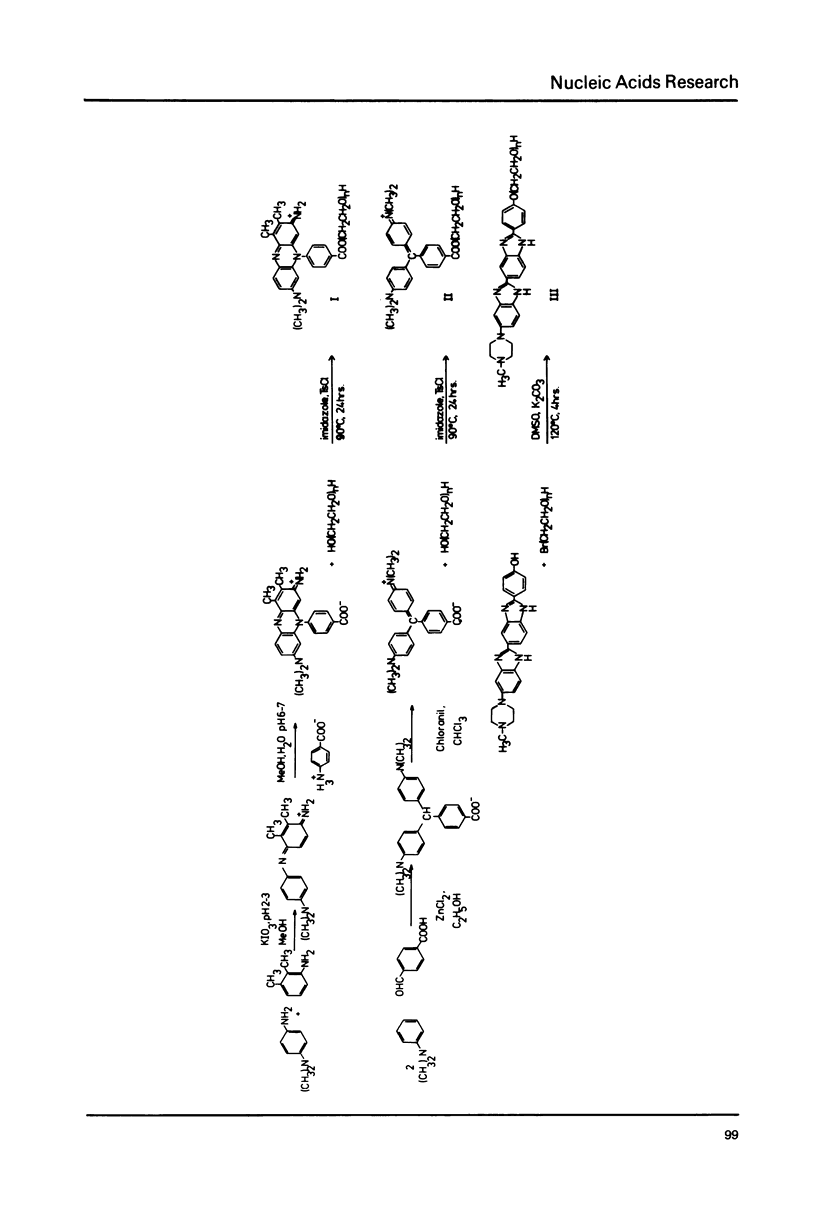
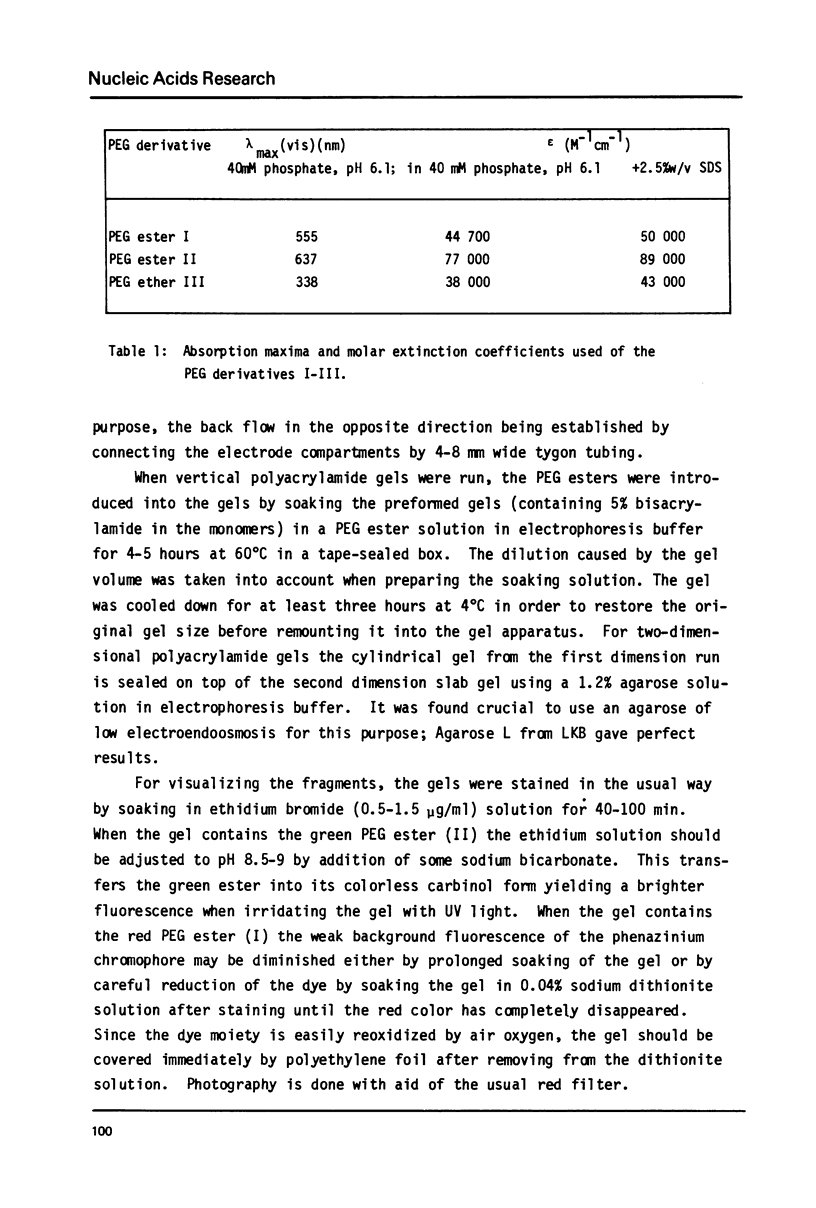
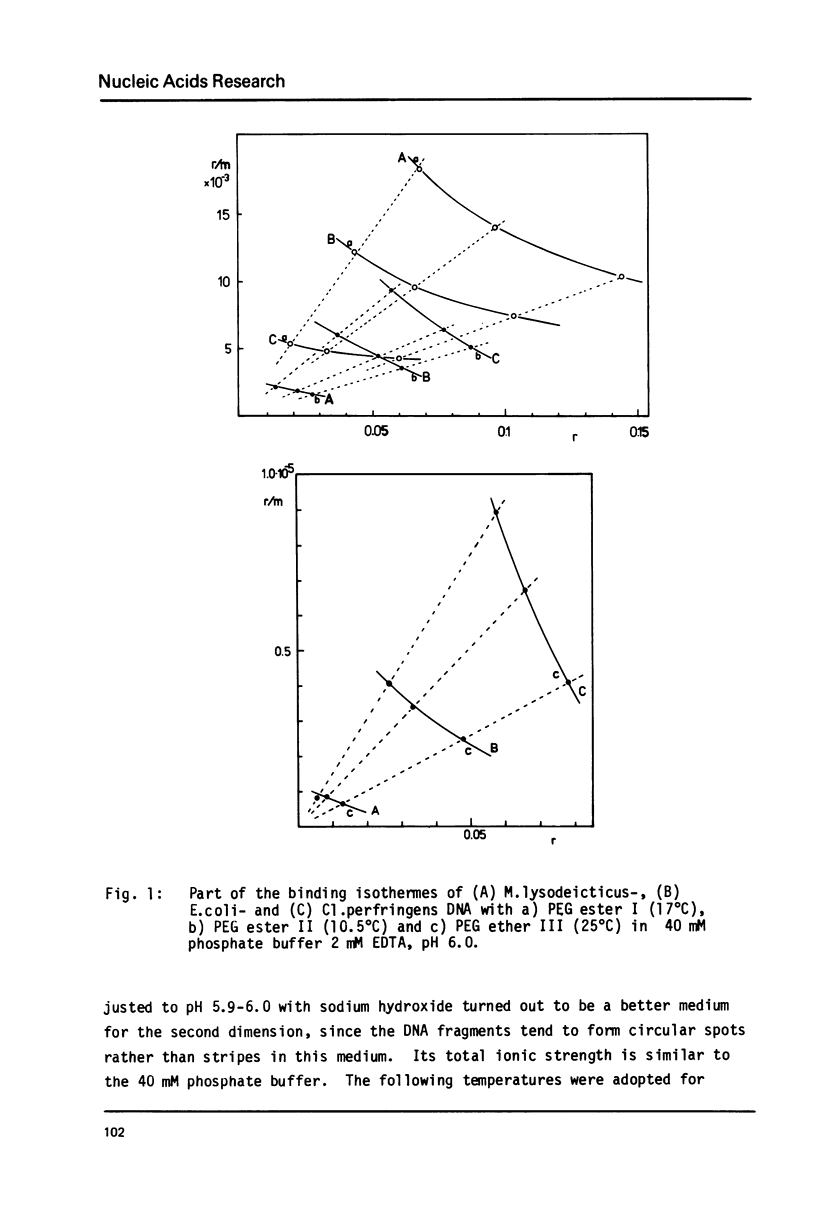
Various base pair specific DNA ligands comprising a phenyl phenazinium dye, a triphenylmethan dye and Hoechst 33258 were covalently bound to polyethylene glycol (PEG) via ester or ether bonds. The DNA interactions of the PEG derivatives formed were shown to exhibit the same base pair specificity as the parent compounds. Since the PEG chains thus bound to the DNA could be expected to increase drastically the frictional coefficient of the DNA, the PEG derivatives were used for base specific DNA separations in agarose and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The procedures, which do not require any special techniques, are described in detail. The resolution observed in agarose gels allows one to separate equally sized DNA fragments differing as little as 1% in base composition at mean travel distances of about 10 cm. Examples of gels showing the base compositional heterogeneity of restriction fragments obtained from lambda DNA, E. coli DNA and calf thymus DNA are given.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bunemann H., Muller W. Basenspezifische Affinitätschromatographie von Nucleinsäuren. Naturwissenschaften. 1977 Dec;64(12):632–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Fiers W. A two-dimensional electrophoretic procedure for the separation of DNA restriction fragments. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 25;110(2):387–404. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer S. G., Lerman L. S. Length-independent separation of DNA restriction fragments in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90200-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs C., Rosenvold E. C., Honigman A., Szybalski W. A simple method for identifying the palindromic sequences recognized by restriction endonucleases: the nucleotide sequence of the AvaII site. Gene. 1978 Sep;4(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL J. P., DREYER W. J. Measurement of protein-binding phenomena by gel filtration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 8;63:530–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loucks E., Chaconas G., Blakesley R. W., Wells R. D., van de Sande J. H. Antibiotic induced electrophoretic mobility shifts of DNA restriction fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;6(5):1869–1879. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.5.1869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Bünemann H., Dattagupta N. Interactions of heteroaromatic compounds with nucleic acids. 2. Influence of substituents on the base and sequence specificity of intercalating ligands. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May;54(1):279–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakroppa W., Müller W. Fractionation of DNA on hydroxyapatite with a base-specific complexing agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):699–703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Friedmann T., Air G. M., Barrell B. G., Brown N. L., Fiddes J. C., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Slocombe P. M., Smith M. The nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage phiX174. J Mol Biol. 1978 Oct 25;125(2):225–246. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90346-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger R. S., Salomon R., Peacock A. C. Isolation of mouse satellite deoxyribonucleic acid by composite polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov;10(23):4219–4223. doi: 10.1021/bi00799a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]