Abstract
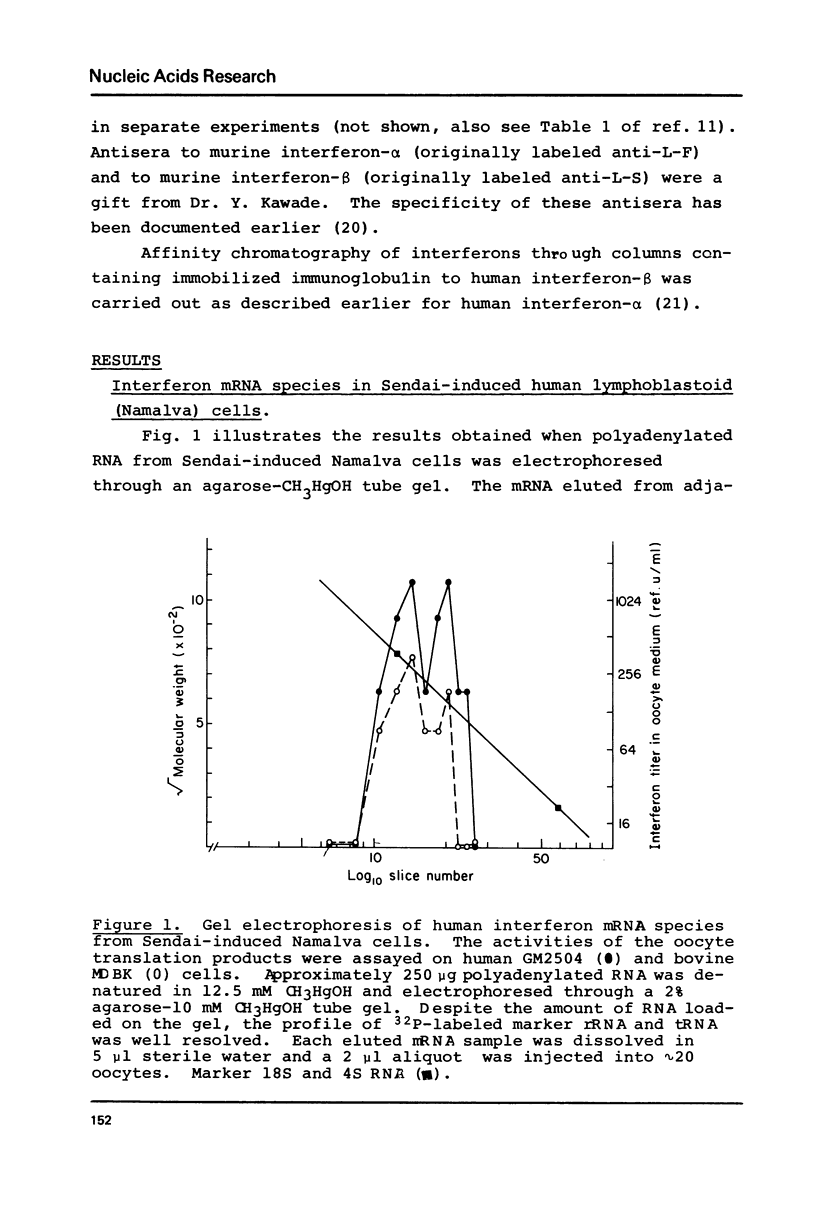
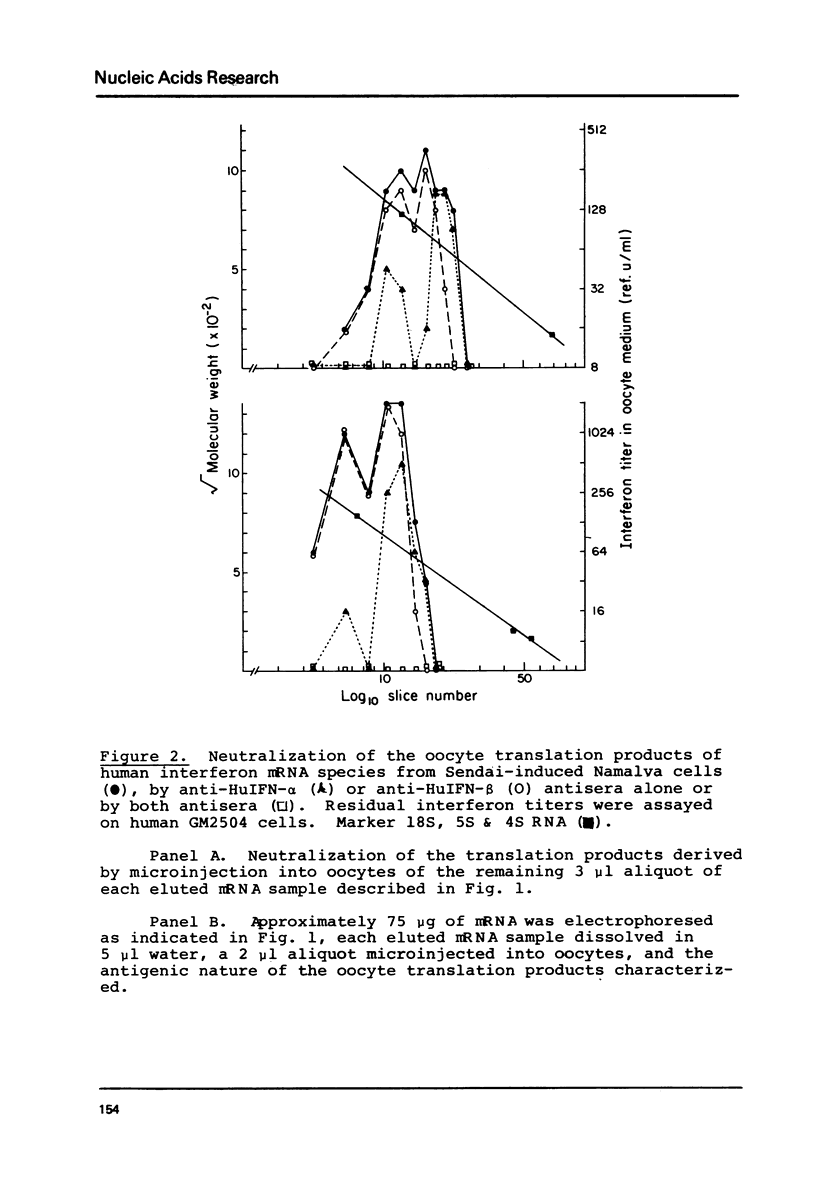
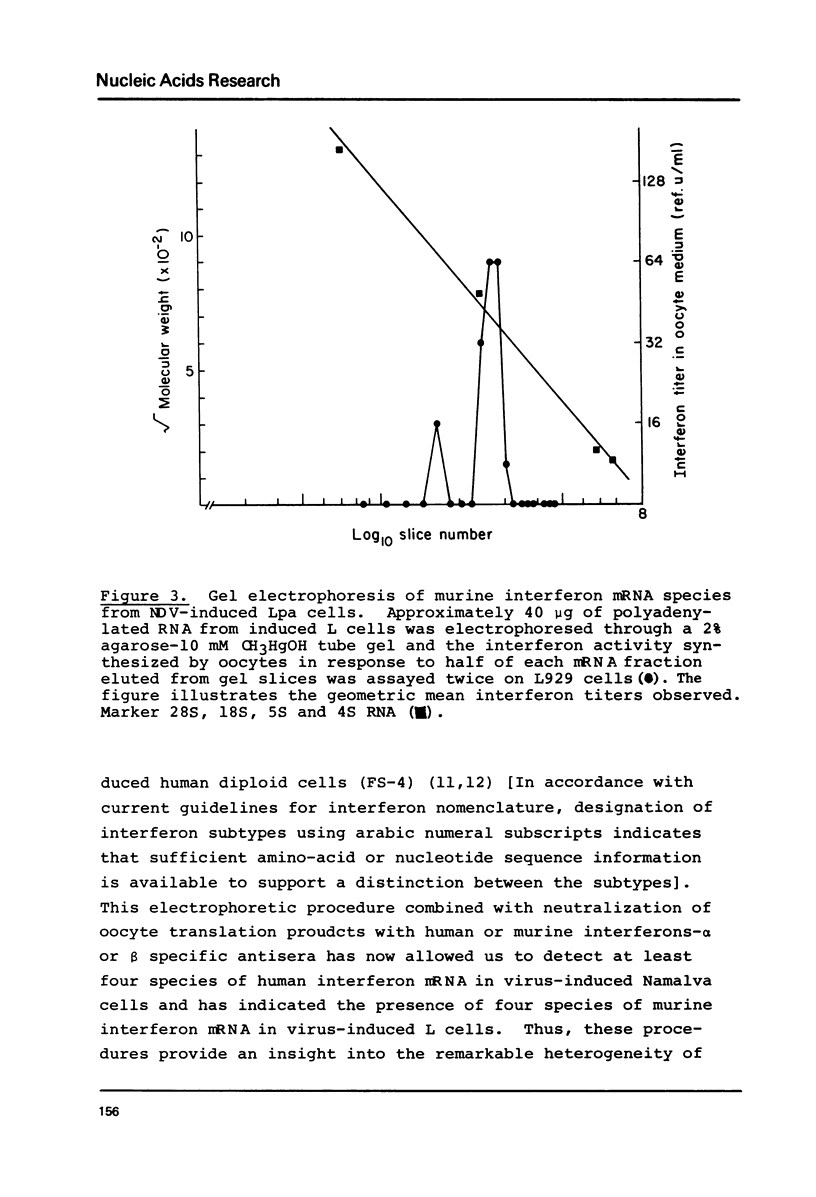
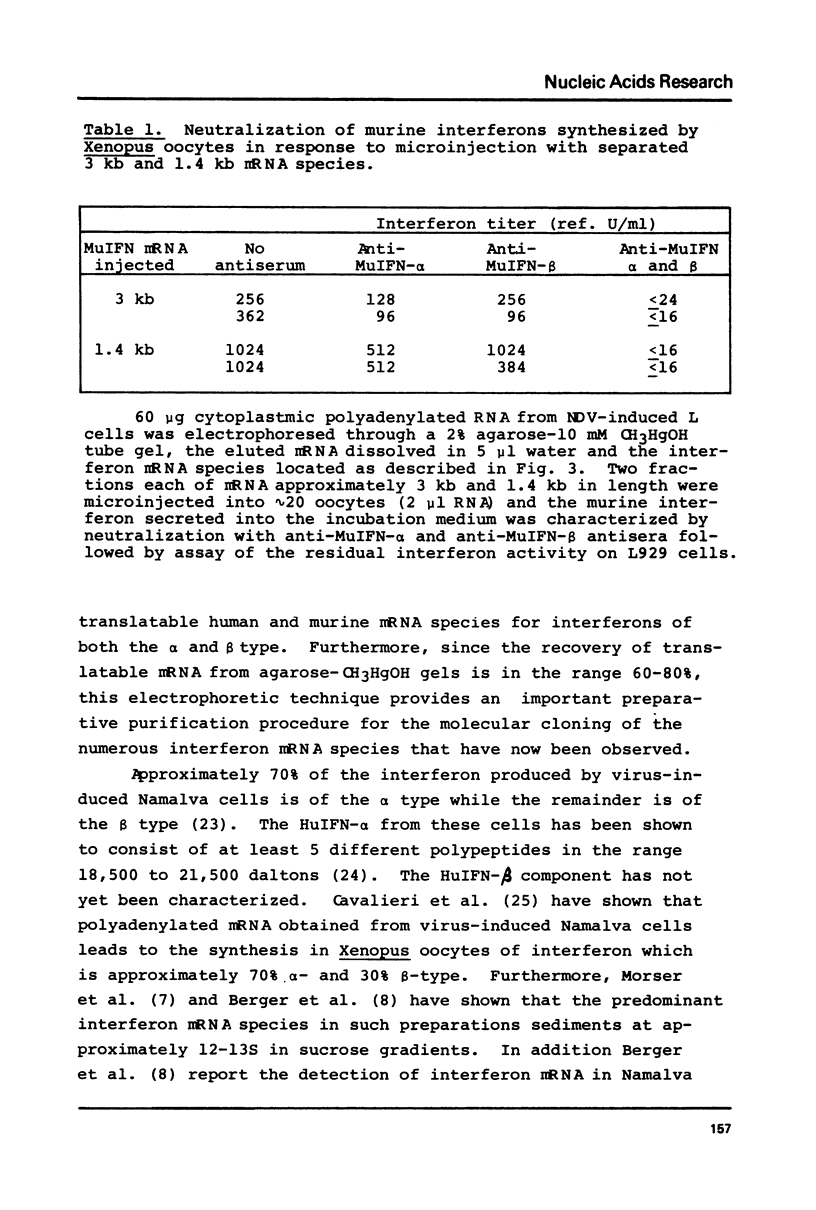
Cytoplasmic polyadenylated RNA preparations obtained from Sendai-induced human lymphoblastoid (Namalva) cells and from Newcastle disease virus (NDV)-induced murine (L) cells were denatured in 10-12.5 mM CH3HgOH and then electrophoresed in 2% agarose tube gels containing 10 mM CH3HgOH, the RNA eluted from gel slices and translationally active interferon mRNA species located using the Xenopus oocyte assay. The interferons synthesized were characterized as alpha or beta types based on neutralization tests using specific antisera against human or murine interferon-alpha and interferon-beta. At least two species of mRNA for human interferon-alpha and two for human interferon-beta were detected in RNA from Sendai-induced Namalva cells. These are (approximate mRNA length in parentheses) alpha (1.3 kb), alpha (1.9 kb), beta (1.1 kb) and beta (1.9 kb). Two populations of murine interferon mRNA of lengths approximately 1.4 kb and 3 kb were detected in mRNA preparations from NDV-induced L cells by electrophoresis. However, since the translation products of each of these two populations of mRNA consist of both murine interferon-alpha and murine interferon-beta it is likely that both the 1.4 kb and 3 kb populations contain at least one species each of murine interferon-alpha and murine interferon-beta mRNA.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abreu S. L., Bancroft F. C., Stewart W. E., 2nd Interferon priming. Effects on interferon messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4114–4118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen G., Fantes K. H. A family of structural genes for human lymphoblastoid (leukocyte-type) interferon. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):408–411. doi: 10.1038/287408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. A. Semi-micro, dye-binding assay for rabbit interferon. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):723–725. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.723-725.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. L., Hitchcock M. J., Zoon K. C., Birkenmeier C. S., Friedman R. M., Chang E. H. Characterization of interferon messenger RNA synthesis in Namalva cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2955–2961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri R. L., Havell E. A., Vilcek J., Pestka S. Synthesis of human interferon by Xenopus laevis oocytes: two structural genes for interferons in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3287–3291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman A., Morser J. Export of proteins from oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):517–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90260-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeyer-Guignard J., Tovey M. G., Gresser I., De Maeyer E. Purification of mouse interferon by sequential affinity chromatography on poly(U)--and antibody--agarose columns. Nature. 1978 Feb 16;271(5646):622–625. doi: 10.1038/271622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. S., Paucker K. Molecular species of interferon induced in mouse L cells by Newcastle disease virus and polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jun;43(3):521–529. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-3-521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Vilcek J. Production of high-titered interferon in cultures of human diploid cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):476–484. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Characteristics of human lymphoblastoid (Namalva) interferon. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jan;38(1):51–59. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-1-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwakura Y., Yonehara S., Kawade Y. Presence of a common structure in the two molecular species of mouse L cell interferon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 16;84(3):557–563. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90742-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakita M., Cabrer B., Taira H., Rebello M., Slattery E., Weideli H., Lengyel P. Purification of interferon from mouse Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):598–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Hunkapiller M. W., Korant B. D., Hardy R. W., Hood L. E. Human fibroblast interferon: amino acid analysis and amino terminal amino acid sequence. Science. 1980 Feb 1;207(4430):525–526. doi: 10.1126/science.7352259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morser J., Flint J., Meager A., Graves H., Baker P. N., Colman A., Burke D. C. Characterization of interferon messenger RNA from human lymphoblastoid cells. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jul;44(1):231–234. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-1-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Taira H., Hall A., Johnsrud L., Streuli M., Ecsödi J., Boll W., Cantell K., Weissmann C. Synthesis in E. coli of a polypeptide with human leukocyte interferon activity. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):316–320. doi: 10.1038/284316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Dobberstein B., Tamm I. Interferon messenger RNA content of human fibroblasts during induction, shutoff, and superinduction of interferon production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3409–3413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Lyles D. S., Tamm I. Superinduction of human fibroblast interferon production: further evidence for increased stability of interferon mRNA. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):186–198. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd Distinct molecular species of interferons. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):80–86. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira H., Broeze R. J., Jayaram B. M., Lengyel P., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Mouse interferons: amino terminal amino acid sequences of various species. Science. 1980 Feb 1;207(4430):528–530. doi: 10.1126/science.7352261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Kawade Y. Antigenicity of mouse interferons: distinct antigenicity of the two L cell interferon species. Virology. 1980 May;103(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K. C., Smith M. E., Bridgen P. J., Anfinsen C. B., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Amino terminal sequence of the major component of human lymphoblastoid interferon. Science. 1980 Feb 1;207(4430):527–528. doi: 10.1126/science.7352260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



