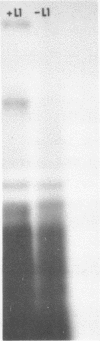
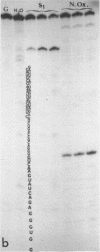
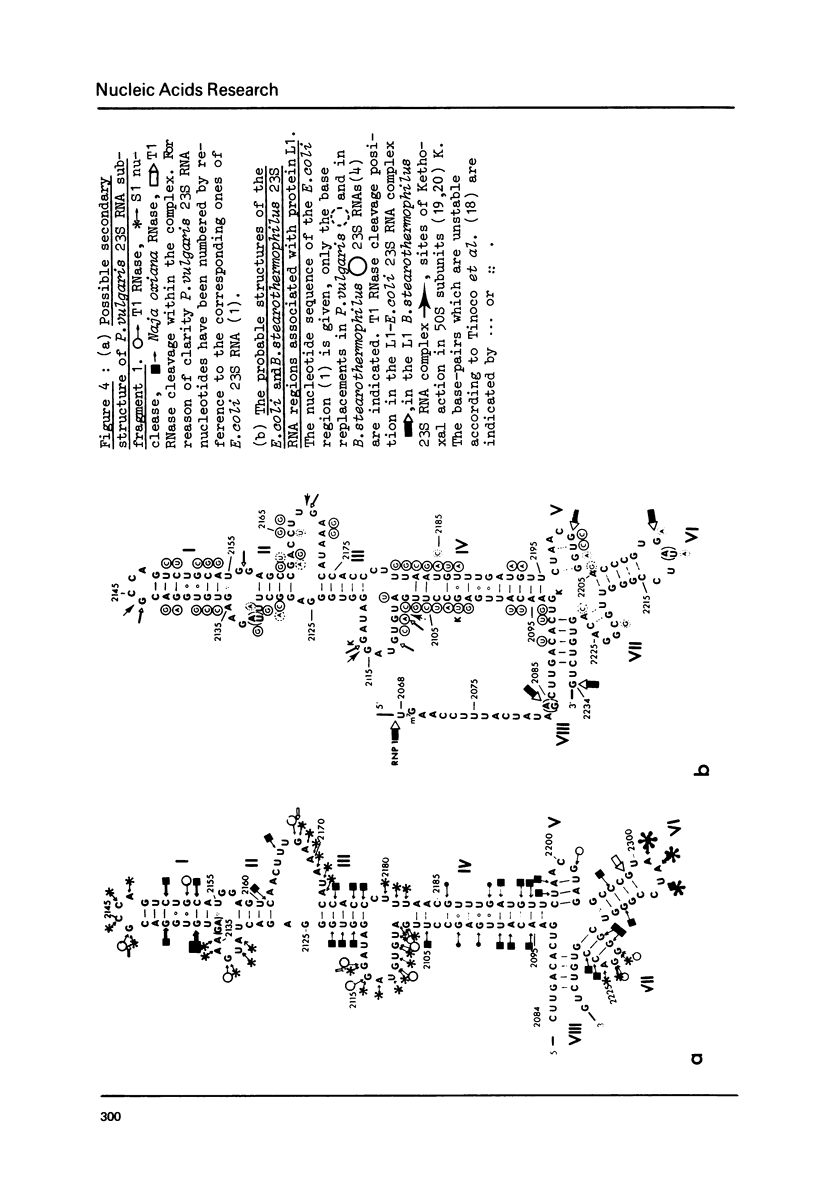
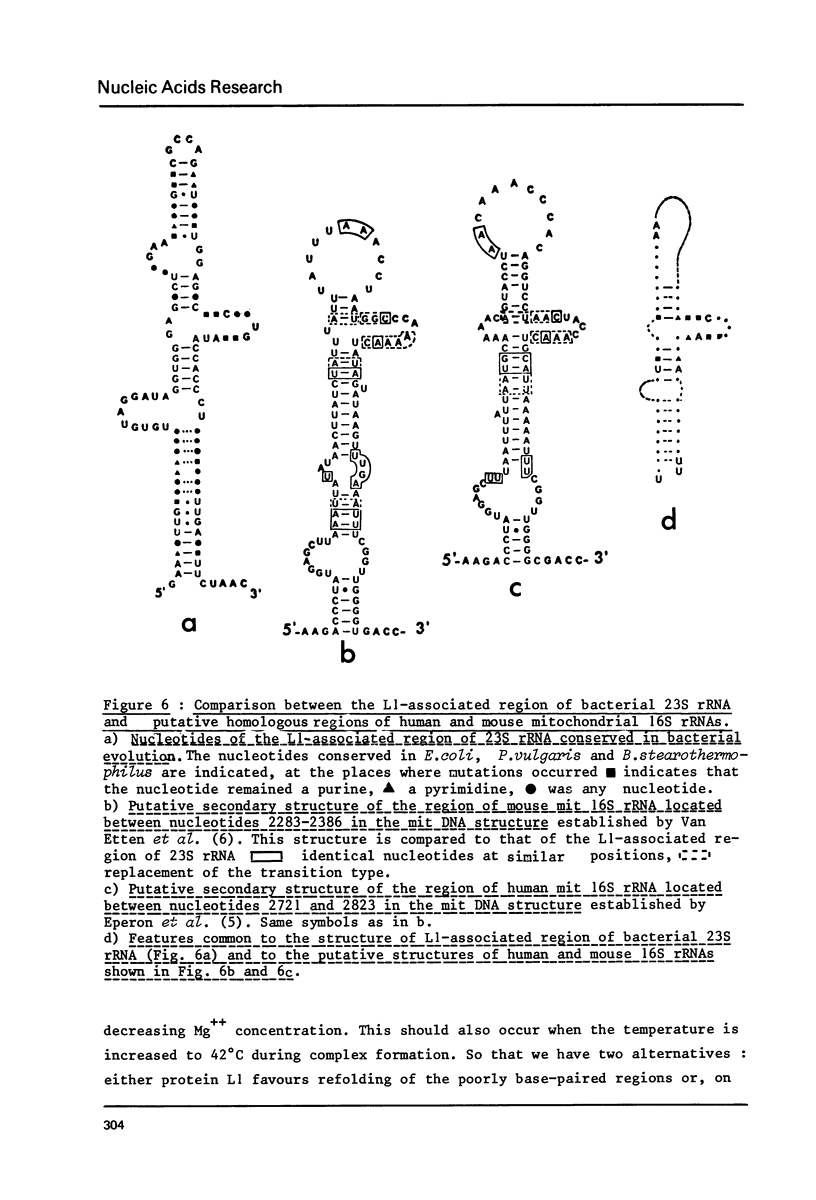
Abstract
An heterologous complex was formed between E. coli protein L1 and P. vulgaris 23S RNA. We determined the primary structure of the RNA region which remained associated with protein L1 after RNase digestion of this complex. We also identified the loci of this RNA region which are highly susceptible to T1, S1 and Naja oxiana nuclease digestions respectively. By comparison of these results with those previously obtained with the homologous regions of E. coli and B. stearothermophilus 23S RNAs, we postulate a general structure for the protein L1 binding region of bacterial 23S RNA. Both mouse and human mit 16S rRNAs and Xenopus laevis and Tetrahymena 28S rRNAs contain a sequence similar to the E. coli 23s RNS region preceding the L1 binding site. The region of mit 16S rRNA which follows this sequence has a potential secondary structure bearing common features with the L1-associated region of bacterial 23S rRNA. The 5'-end region of the L11 mRNA also has several sequence potential secondary structures displaying striking homologies with the protein L1 binding region of 23S rRNA and this probably explains how protein L1 functions as a translational repressor. One of the L11 mRNA putative structures bears the features common to both the L1-associated region of bacterial 23S rRNA and the corresponding region of mit 16S rRNA.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branlant C., Korobko V., Ebel J. P. The binding site of protein L1 on 23-S ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli. 3. Nucleotide sequence. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 15;70(2):471–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Machatt M. A., Ebel J. P. Structural study of ribosomal 23 S RNA from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 1;107(1):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80490-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Sriwidada J., Brimacombe R. RNA sequences associated with proteins L1, L9, and L5, L18, L25, in ribonucleoprotein fragments isolated from the 50-S subunit of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 15;70(2):483–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Sriwidada J., Fellner P., Crichton R. The identification of the RNA binding site for a 50 S ribosomal protein by a new technique. FEBS Lett. 1973 Sep 15;35(2):265–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80301-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brot N., Caldwell P., Weissbach H. Autogenous control of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein L10 synthesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2592–2595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee G. G., Sanger F. Nucleotide sequences from the low molecular weight ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1967 Feb 14;23(3):337–353. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D., Nomura M. Feedback regulation of ribosomal protein gene expression in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3590–3594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon I. C., Anderson S., Nierlich D. P. Distinctive sequence of human mitochondrial ribosomal RNA genes. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):460–467. doi: 10.1038/286460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda R. Autogenous regulation of the synthesis of ribosomal proteins, L10 and L7/12, in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;178(2):483–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00270505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., LEVINTHAL C. A fine-structure genetic and chemical study of the enzyme alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. I. Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., Gerbi S. A. Fine structure of ribosomal RNA. IV. Extraordinary evolutionary conservation in sequences that flank introns in rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3623–3637. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Noller H. F. Nucleotide sequences of accessible regions of 23S RNA in 50S ribosomal subunits. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 24;17(2):307–315. doi: 10.1021/bi00595a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazemie M. Binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to reconstituted subparticles of Escherichia coli large ribosomal subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 16;67(2):373–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H., Dohme F. Total reconstitution of functionally active 50S ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4713–4717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Strycharz G. D., Nomura M., Lewis H., Dennis P. P. Nucleotide sequence of the ribosomal protein gene cluster adjacent to the gene for RNA polymerase subunit beta in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1697–1701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spierer P., Zimmerman R. A., Mackie G. A. RNA-protein interactions in the ribosome. Binding of 50-S-subunit proteins to 5' and 3' terminal segments of the 23-S RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Apr 1;52(3):459–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J., Sloof P., Ebel J. P. The binding site of ribosomal protein L1 from Escherichia coli on the 23-S ribosomal RNA from Bacillus stearothermophilus. A possible base-pairing scheme differing from that proposed for Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(1):309–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12240.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etten R. A., Walberg M. W., Clayton D. A. Precise localization and nucleotide sequence of the two mouse mitochondrial rRNA genes and three immediately adjacent novel tRNA genes. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):157–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilenko S. K., Babkina G. T. Vydelenie i svoistva ribonukleazy iz iada kobry. Biokhimiia. 1965 Jul-Aug;30(4):705–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilenko S. K., Ryte V. C. [Isolation of highly purified ribonuclease from cobra (Naja oxiana) venom]. Biokhimiia. 1975 May-Jun;40(3):578–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede P., Wurst R., Vournakis J., Rich A. Conformational changes of yeast tRNAPhe and E. coli tRNA2Glu as indicated by different nuclease digestion patterns. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9608–9616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Arfsten A. E., Nomura M. In vitro expression of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein genes: autogenous inhibition of translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1837–1841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Nomura M. E. coli ribosomal protein L4 is a feedback regulatory protein. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):517–522. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90489-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]