Abstract
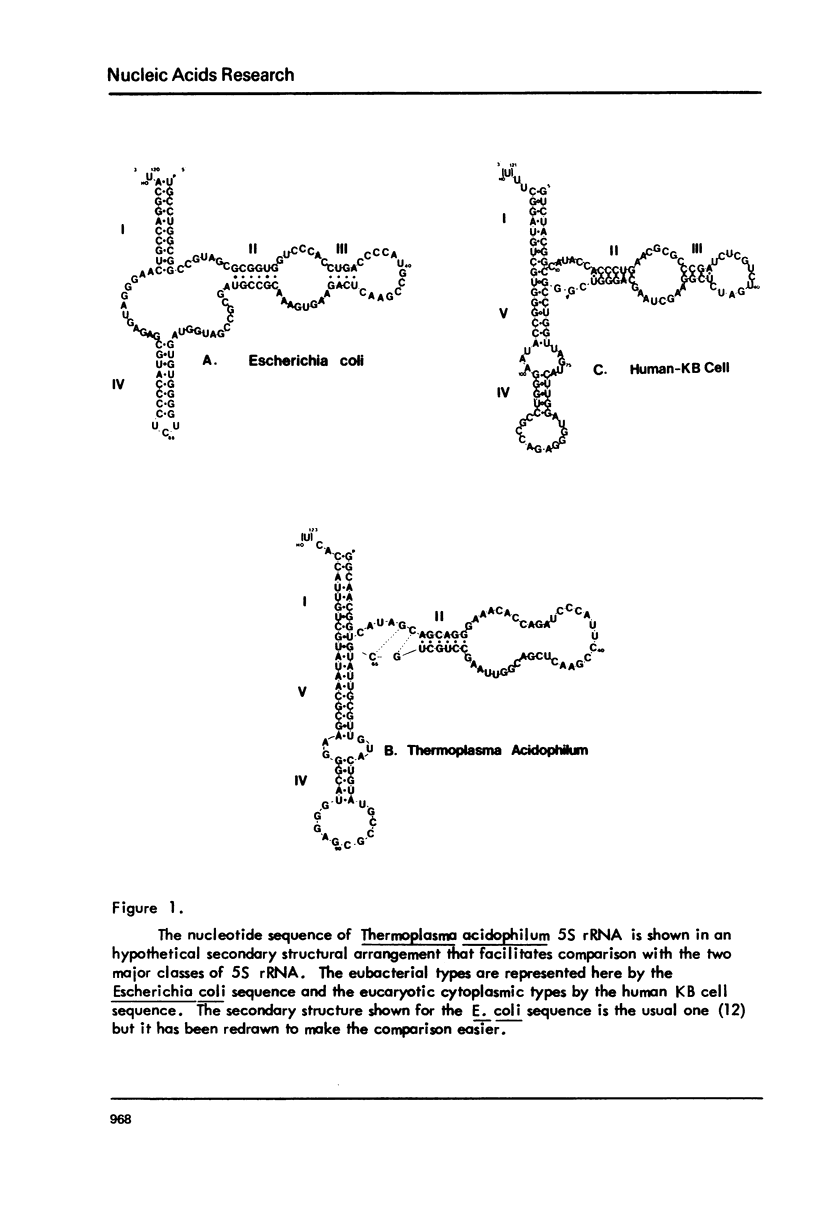
The complete nucleotide sequence of the 5S ribosomal RNA isolated from the archaebacterium Thermoplasma acidophilum has been determined. The sequence is: pG GCAACGGUCAUAGCAGCAGGGAAACACCAGAUCCCAUUCCGAACUCGACGGUUAAGCCUGCUGCGUAUUGCGUUGUACU GUAUGCCGCGAGGGUACGGGAAGCGCAAUAUGCUGUUACCAC(U)OH. The homology with the 55 rRNA from another archaebacterial species, Halobacterium cutirubrum, is only 60.6% and other 55 rRNAs are even less homologous. Examination of the potential for forming secondary structure is revealing. T. acidophilum does not conform to the usual models employed for either procaryotic or eucaryotic 5S rRNAs. Instead this 5S rRNA has a mixture of the characteristic features of each. On the whole this 5S rRNA does however appear more eucaryotic than eubacterial. These results give further support to the notion that the archaebacteria represent an extremely early divergence among entities with procaryotic organization.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Domdey H., Gross H. J. RNA sequence determination in the nanogram range by a combination of in vitro labeling procedures. Anal Biochem. 1979 Mar;93(2):321–328. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80158-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H. Phy M: an RNase activity specific for U and A residues useful in RNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 25;8(14):3133–3142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.14.3133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Uhlenbeck O. C. 3'-terminal labelling of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):560–561. doi: 10.1038/275560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Woese C. R. 5S RNA secondary structure. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):505–507. doi: 10.1038/256505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori H. Molecular evolution of 5S RNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 May 7;145(2):119–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00269583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. S., Tittensor J. R., Walker R. T. The chemical composition of the nucleic acids and other macromolecular constituents of Mycoplasma mycoides var. capri. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Sep;40(3):405–411. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-3-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick M. W., Walker R. T. The nucleotide sequence of glycine tRNA from Mycoplasma mycoides sp. capri. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2783–2786. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp G., Gross H. J. Rapid RNA sequencing: nucleases from Staphylococcus aureus and Neurospora crassa discriminate between uridine and cytidine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3481–3490. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok Y., Wong J. T. Evolutionary relationship between Halobacterium cutirubrum and eukaryotes determined by use of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases as phylogenetic probes. Can J Biochem. 1980 Mar;58(3):213–218. doi: 10.1139/o80-029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Takemura S. Structure and function of 5S ribosomal ribonucleic acid from Torulopsis utilis. II. Partial digestion with ribonucleases and derivation of the complete sequence. J Biochem. 1974 Nov;76(5):935–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. Use of in vitro 32P labeling in the sequence analysis of nonradioactive tRNAs. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:58–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Bonen L., Schaup H. W., Lewis B. J., Zablen L., Woese C. The use of ribonuclease U2 in RNA sequence determination. Some corrections in the catalog of oligomers produced by ribonuclease T1 digestion of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Evol. 1974 Feb 28;3(1):63–77. doi: 10.1007/BF01795977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne R., Jordan B. R. Partial enzyme digestion studies on Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas, Chlorella, Drosophila, HeLa and yeast 5S RNAs support a general class of 5S RNA models. J Mol Evol. 1977 Sep 20;10(1):77–86. doi: 10.1007/BF01796136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. T., RajBhandary U. L. The nucleotide sequence of formylmethionine tRNA from Mycoplasma mycoides sp. capri. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jan;5(1):57–70. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Magrum L. J., Fox G. E. Archaebacteria. J Mol Evol. 1978 Aug 2;11(3):245–251. doi: 10.1007/BF01734485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Maniloff J., Zablen L. B. Phylogenetic analysis of the mycoplasmas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):494–498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


