Abstract
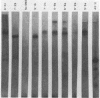
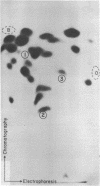
The template for RNA polymerase III in vitro transcription found on the human DNA clone pJP53 was shown in the previous paper to enclose a member of the Alu famiy of interspersed repetitive DNA sequences. We have mapped this transcript onto its template in greater detail by comparison of the template DNA sequence to the base composition of the Tl ribonuclease digestion products of the in vitro transcript. We find that the 5' end of the transcript lies in close proximity to the 5' end of the conserved Alu family sequence as analyzed in the preceding paper. The 3' end of the transcript appears to terminate in a U-rich region beyond the region of Alu family sequence conservation. Analysis of cellular RNA by Northern blotting and hybridization with a DNA probe derived from another Alu family transcription template demonstrates abundant representation of sequences homologous to the reiterated DNA. Cytoplasmic, nonpolyadenylated RNA from human and murine cells contains a monodisperse, 300 nucleotide species, recently determined by Weiner (4) to be the 7S RNA. In contrast, the Alu-homologous transcripts are heterodisperse in mRNA and hnRNA, with the highest specific representation of Alu family sequences being found in oligo(dT)-retained hnRNA.
Full text
PDF


















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Parker B. A., Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:220–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Pictet R., Rutter W. J. Analysis of the regions flanking the human insulin gene and sequence of an Alu family member. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4091–4109. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz E. J., Jr, Murnane M. J., Tonkonow B. L., Berman B. W., Mazur E. M., Cavallesco C., Jenko T., Snyder E. L., Forget B. G., Hoffman R. Embryonic-fetal erythroid characteristics of a human leukemic cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3509–3513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:35–88. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Philipson L., Wall R., Adesnik M. Polyadenylic acid sequences: role in conversion of nuclear RNA into messenger RNA. Science. 1971 Oct 29;174(4008):507–510. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4008.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle W. F., Sapienza C. Selfish genes, the phenotype paradigm and genome evolution. Nature. 1980 Apr 17;284(5757):601–603. doi: 10.1038/284601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Elder J. T., Wang R. R., Forget B. G., de Riel J. K., Weissman S. M. RNA polymerase III transcriptional units are interspersed among human non-alpha-globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5095–5099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Erikson R. L., Henry B., Pace N. R. Comparison of oligonucleotides produced by RNase T1 digestion of 7 S RNA from avian and murine oncornaviruses and from uninfected cells. Virology. 1973 May;53(1):40–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90463-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N., Wellauer P. K., Wall R. Intermolecular duplexes in heterogeneous nuclear RNA from HeLa cells. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):597–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Piatak M., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Determination of RNA sequences by primer directed synthesis and sequencing of their cDNA transcripts. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):580–595. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada F., Kato N. Nucleotide sequences of 4.5S RNAs associated with poly(A)-containing RNAs of mouse and hamster cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1273–1285. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman E., Smith I., Penman S. Electron microscopic studies of detergent-treated HeLa cell nuclei. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):131–135. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Toomey T. P., Leinwand L., Duncan C. H., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Weissman S. M., Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L. Ubiquitous, interspersed repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W., Evans R., Wilson M., Salditt-Georgieff M., Darnell J. E. Oligonucleotides in heterogeneous nuclear RNA: similarity of inverted repeats and RNA from repetitious DNA sites. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 11;17(14):2776–2783. doi: 10.1021/bi00607a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W., Leinwand L. Low molecular weight RNAs hydrogen-bonded to nuclear and cytoplasmic poly(A)-terminated RNA from cultured Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R., PIEKARSKI L. J., HSU T. C. DELETION OF THYMIDINE KINASE ACTIVITY FROM L CELLS RESISTANT TO BROMODEOXYURIDINE. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Aug;31:297–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Brown D. D. Nucleotide sequence of Xenopus borealis oocyte 5S DNA: comparison of sequences that flank several related eucaryotic genes. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1145–1156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohe K., Weissman S. M. The nucleotide sequence of a low molecular weight ribonucleic acid from cells infected with adenovirus 2. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6991–7009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orgel L. E., Crick F. H. Selfish DNA: the ultimate parasite. Nature. 1980 Apr 17;284(5757):604–607. doi: 10.1038/284604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker B. A., Stark G. R. Regulation of simian virus 40 transcription: sensitive analysis of the RNA species present early in infections by virus or viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):360–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.360-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S. RNA metabolism in the HeLa cell nucleus. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S., Rosbash M., Penman M. Messenger and heterogeneous nuclear RNA in HeLa cells: differential inhibition by cordycepin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1878–1885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Partial nucleotide sequence of the 300-nucleotide interspersed repeated human DNA sequences. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):372–374. doi: 10.1038/284372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford T. R., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J. K562 human leukaemic cells synthesise embryonic haemoglobin in response to haemin. Nature. 1979 Jul 12;280(5718):164–165. doi: 10.1038/280164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Origin of retroviruses from cellular moveable genetic elements. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):599–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90420-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan S., Nakazato H., Kopp D. W., Edmonds M. Properties of a small transcribed poly A sequence in heterogeneous nuclear RNA of HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Mar;6(3):1097–1110. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.3.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M. An abundant cytoplasmic 7S RNA is complementary to the dominant interspersed middle repetitive DNA sequence family in the human genome. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilchek M., Gorecki M. Affinity chromatography of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(3):491–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu G. J. Adenovirus DNA-directed transcription of 5.5S RNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2175–2179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G., Penman S. Small RNA species of the HeLa cell: metabolism and subcellular localization. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]