Abstract
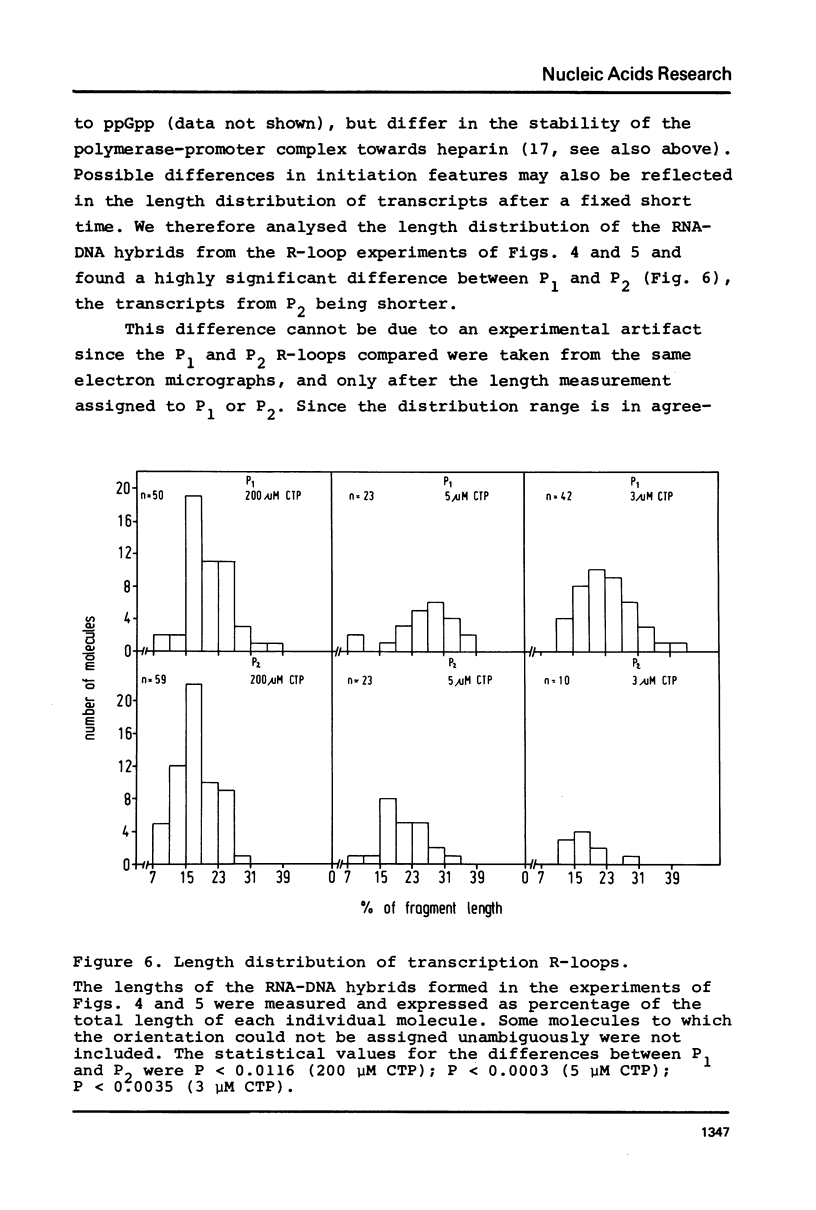
Transcription in vitro of the E. coli ribosomal RNA operon, rrnE, was analysed by electron microscopy. The transcription initiation sites of the two rrnE promoters in tandem, P1 and P2, were mapped and the transcription from both sites was compared. The first and the second transcription initiation site are about equally used when all nucleotides are present at 200 microM. Lowering the concentration of the second promoter's start nucleotide CTP to 3 microM reduces the use of the P2 site sharply. At all CTP concentrations used the nascent RNA chains from P1 are in the average longer than those from P2 after a fixed transcription time. Most probably, this difference is caused by a longer average interval before formation of the productive complex with the second promoter.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony D. D., Goldthwait D. A., Wu C. W. Studies with the ribonucleic acid polymerase. II. Kinetic aspects of initiation and polymerization. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):246–256. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnberg A. C., Van Ommen G. J., Grivell L. A., Van Bruggen E. F., Borst P. Some yeast mitochondrial RNAs are circular. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90505-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros I., Kiss A., Venetianer P. Physical map of the seven ribosomal RNA genes of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;6(5):1817–1830. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.5.1817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C. Electron microscopic analysis of transcription: mapping of initiation sites and direction of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3164–3168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Palmer M. L., Kennedy P. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon P., Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B., Ebel J. P. The sequence of Escherichia coli ribosomal 16 S RNA determined by new rapid gel methods. FEBS Lett. 1978 Oct 1;94(1):152–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80926-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csordás-Tóth E., Boros I., Venetianer P. Structure of the promoter region for the rrnB gene in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2189–2197. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert S. F., de Boer H. A., Nomura M. Identification of initiation sites for the in vitro transcription of rRNA operons rrnE and rrnA in E. coli. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser G., Cashel M. In vitro transcripts from the rrn B ribosomal RNA cistron originate from two tandem promoters. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90192-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamming J., Ab G., Gruber M. E coli RNA polymerase-rRNA promoter interaction and the effect of ppGpp. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 11;8(17):3947–3963. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.17.3947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamming J., Gruber M., AB G. Interaction between RNA polymerase and a ribosomal RNA promoter of E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 25;7(4):1019–1033. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.4.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenerley M. E., Morgan E. A., Post L., Lindahl L., Nomura M. Characterization of hybrid plasmids carrying individual ribosomal ribonucleic acid transcription units of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;132(3):931–949. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.3.931-949.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss A., Sain B., Venetianer P. The number of rRNA genes in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 1;79(1):77–79. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80354-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss I., Boros I., Udvardy A., Venetianer P., Delius H. RNA-polymerase binding at the promoters of the rRNA genes of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 17;609(3):435–447. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. Initiation of Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA synthesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5480–5484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller K., Oebbecke C., Förster G. Capacity of ribosomal RNA promoters of E. coli to bind RNA polymerase. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):121–130. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierman W. C., Chamberlin M. J. The effect of low substrate concentrations on the extent of productive RNA chain initiation from T7 promoters A1 and A2 by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4495–4500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oostra B. A., Gruber M. Involvement of DNA gyrase in the transcription of ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4235–4246. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oostra B. A., van Ooyen A. J., Gruber M. In vitro transcription of three different ribosomal RNA cistrons of E. coli; heterogeneity of control regions. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Mar 28;152(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF00264932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace N. R. Structure and synthesis of the ribosomal ribonucleic acid of prokaryotes. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Dec;37(4):562–603. doi: 10.1128/br.37.4.562-603.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. Multiple modes of ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):605–609. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Nomura M. Isolation of lambda transducing phages carrying rRNA genes at the metA-purD region of the Escherichia coli chromosome. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 31;72(2):256–261. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80981-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Steitz J. A. Tandem promoters direct E. coli ribosomal RNA synthesis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer H. A., Gilbert S. F., Nomura M. DNA sequences of promoter regions for rRNA operons rrnE and rrnA in E. coli. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer H., Nomura M. In vivo transcription of rRNA operons in Escherichia coli initiates with purine nucleoside triphosphates at the first promoter and with CTP at the second promoter. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5609–5612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]