Abstract
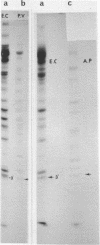
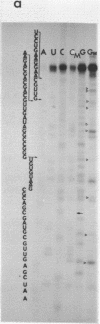
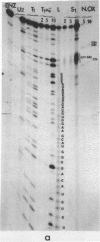
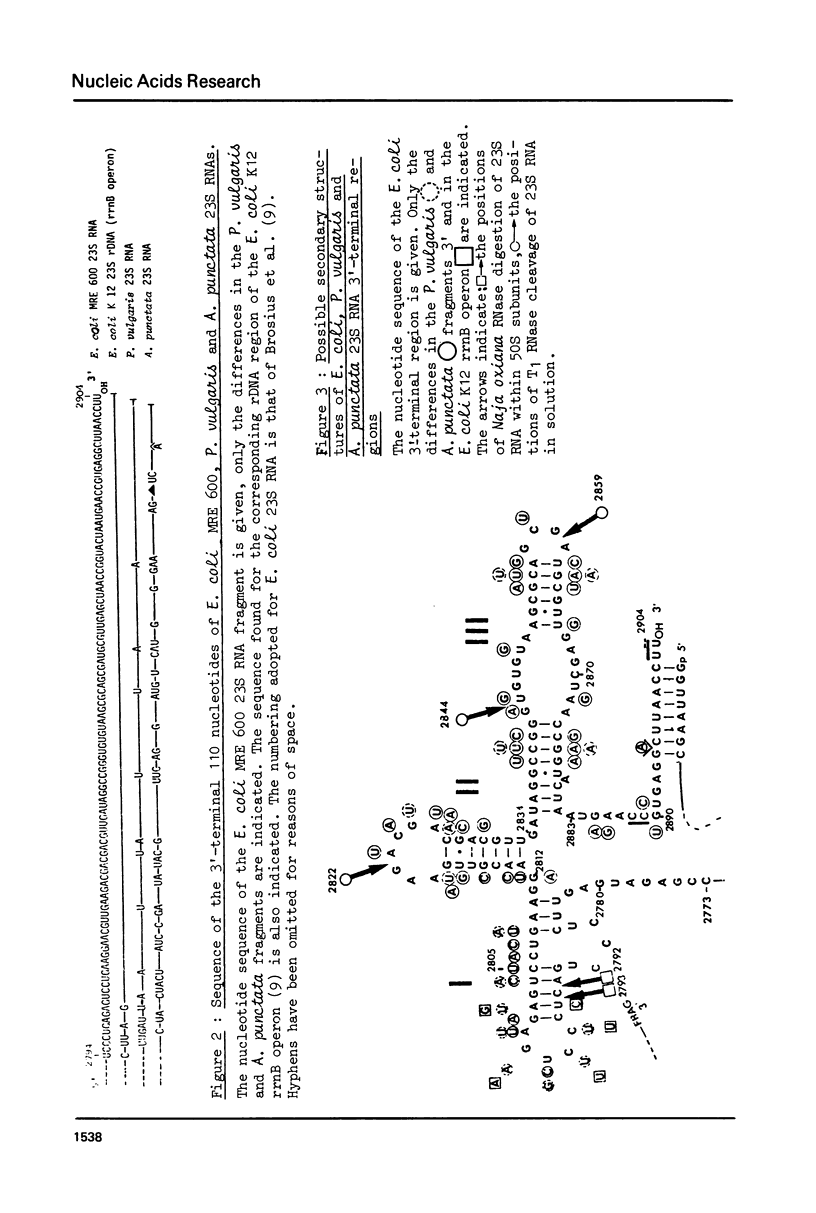
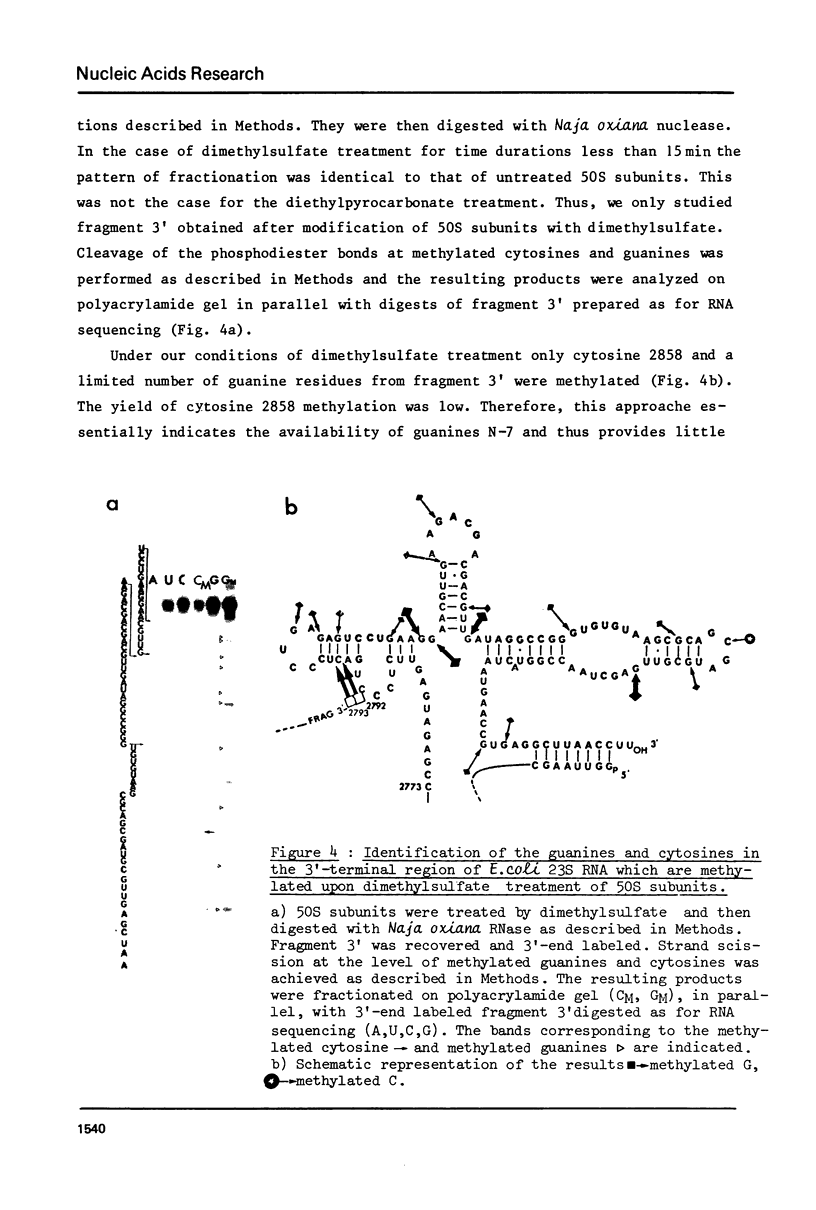
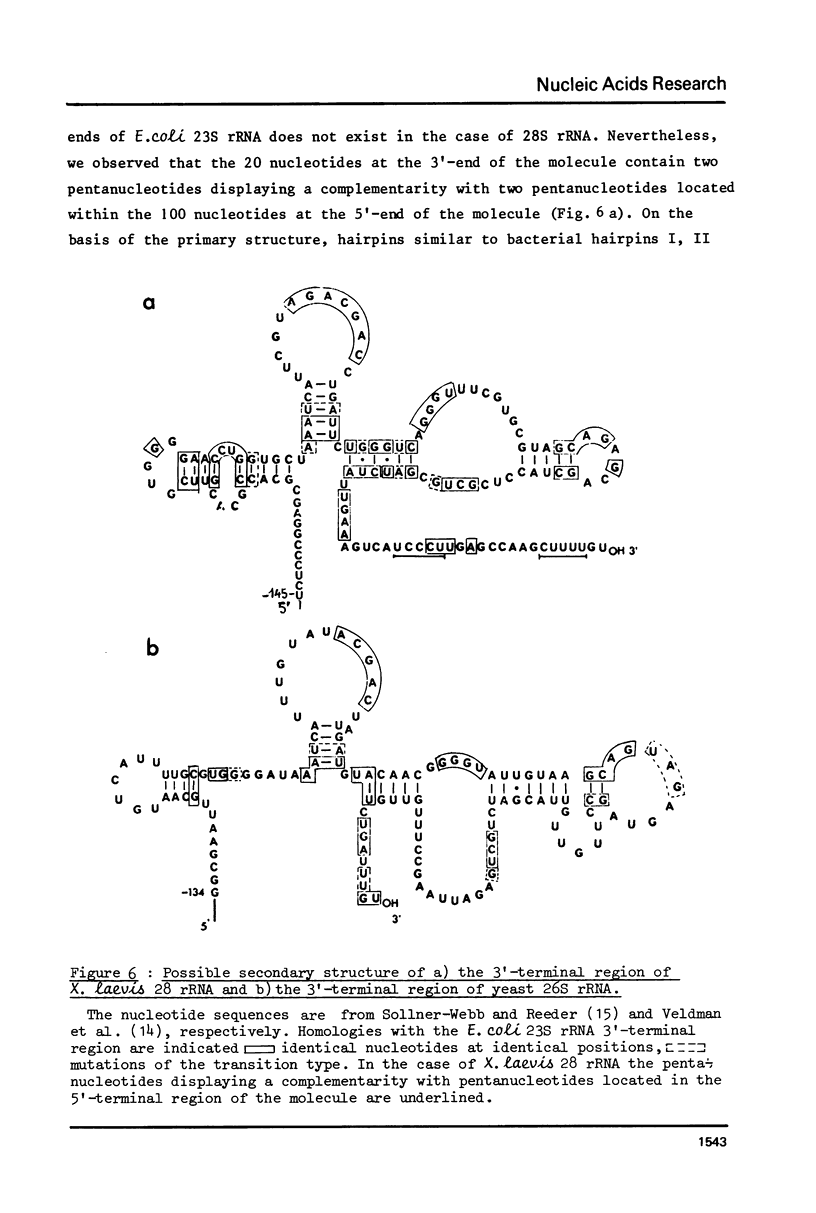
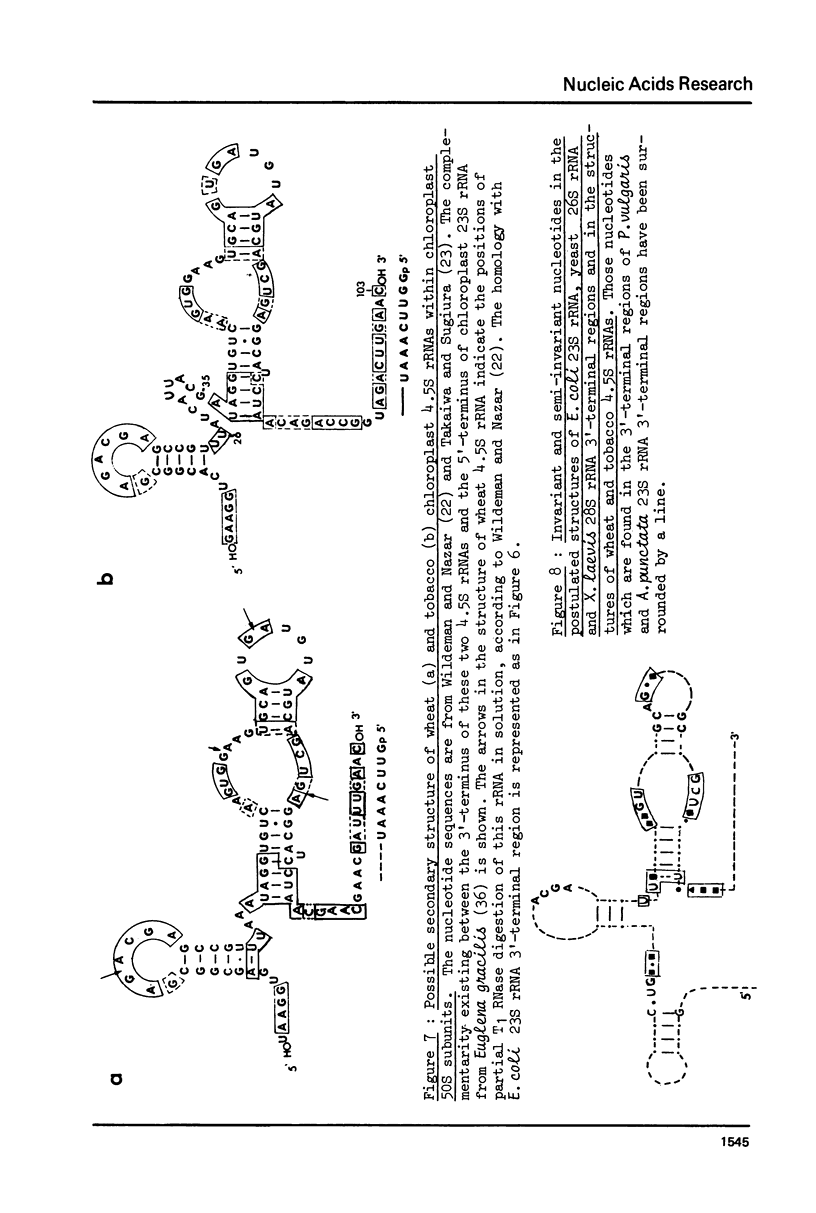
The sequence of the 110 nucleotide fragment located at the 3'-end of E.coli, P.vulgaris and A.punctata 23S rRNAs has been determined. The homology between the E.coli and P.vulgaris fragments is 90%, whereas that between the E.coli and A.punctate fragments is only 60%. The three rRNA fragments have sequences compatible with a secondary structure consisting of two hairpins. Using chemical and enzymatic methods recently developed for the study of the secondary structure of RNA, we demonstrated that one of these hairpins and part of the other are actually present in the three 3'-terminal fragments in solution. This supports the existence of these two hairpins in the intact molecule. Indeed, results obtained upon limited digestion of intact 23S RNA with T1 RNase were in good agreement with the existence of these two hairpins. We observed that the primary structures of the 3'-terminal regions of yeast 26S rRNA and X.laevis 28S rRNA are both compatible with a secondary structure similar to that found at the 3'-end of bacterial 23S rRNAs. Furthermore, both tobacco and wheat chloroplast 4.5S rRNAs can also be folded in a similar way as the 3'-terminal region of bacterial 23S rRNA, the 3'-end of chloroplast 4.5S rRNAs being complementary to the 5'-end of chloroplast 23S rRNA. This strongly reinforces the hypothesis that chloroplast 4.5S rRNA originates from the 3'-end of bacterial 23S rRNA and suggests that this rRNA may be base-paired with the 5'-end of chloroplast 23S rRNA. Invariant oligonucleotides are present at identical positions in the homologous secondary structures of E.coli 23S, yeast 26S, X.laevis 28S and wheat and tobacco 4.5S rRNAs. Surprisingly, the sequences of these oligonucleotides are not all conserved in the 3'-terminal regions of A.punctata or even P.vulgaris 23S rRNAs. Results obtained upon mild methylation of E.coli 50S subunits with dimethylsulfate strongly suggest that these invariant oligonucleotides are involved in RNA tertiary structure or in RNA-protein interactions.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowman C. M., Dyer T. A. 4.5S ribonucleic acid, a novel ribosome component in the chloroplasts of flowering plants. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):605–613. doi: 10.1042/bj1830605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Young R. A., Steitz J. A. The ribonuclease III site flanking 23S sequences in the 30S ribosomal precursor RNA of E. coli. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90513-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Machatt A., Ebel J. P. The secondary structure of the protein L1 binding region of ribosomal 23S RNA. Homologies with putative secondary structures of the L11 mRNA and of a region of mitochondrial 16S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):293–307. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Machatt M. A., Ebel J. P. Structural study of ribosomal 23 S RNA from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 1;107(1):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80490-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Machatt M. A., Ebel J. P. Structural study of ribosomal 23 S RNA from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 1;107(1):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80490-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Sriwidada J., Ebel J. P. Characterization of ribonucleoprotein subparticles from 50 S ribosomal subunits of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov 5;116(3):443–467. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90079-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Widada J. S., Krol A., Ebel J. P. Extensions of the known sequences at the 3' and 5' ends of 23S ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli, possible base pairing between these 23S RNA regions and 16S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jul;3(7):1671–1687. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.7.1671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Widada J. S., Krol A., Ebel J. P. Studies on the primary structure of the ribosomal 23S RNA of Escherichia coli: II. A characterisation and an alignment of 24 sections spanning the entire molecule and its application to the localisation of specific fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Dec;4(12):4323–4345. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.12.4323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 23S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):201–204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Buzash-Pollert E., Studier F. W. Mutations of bacteriophage T7 that affect initiation of synthesis of the gene 0.3 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2741–2745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Uhlenbeck O. C. 3'-terminal labelling of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):560–561. doi: 10.1038/275560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon I. C., Anderson S., Nierlich D. P. Distinctive sequence of human mitochondrial ribosomal RNA genes. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):460–467. doi: 10.1038/286460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Maden B. E. Nucleotide sequence through the 18S-28S intergene region of a vertebrate ribosomal transcription unit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5993–6005. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hapke B., Noll H. Structural dynamics of bacterial ribosomes. IV. Classification of ribosomes by subunit interaction. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 25;105(1):97–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90196-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley M. R. The synthesis and origin of chloroplast low-molecular-weight ribosomal ribonucleic acid in spinach. Eur J Biochem. 1979 May 15;96(2):311–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori H., Osawa S. Evolutionary change in 5S RNA secondary structure and a phylogenic tree of 54 5S RNA species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco E. M., Jr, Rushlow K. E., Dodd J. R., Hallick R. B. Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribosomal RNA transcription units. II. Nucleotide sequence homology between the 16 S--23 S ribosomal RNA spacer and the 16 S ribosomal RNA leader regions. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10997–11003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A., Gilbert W. Chemical probes for higher-order structure in RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4679–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomiya T., Kobayashi M., Sato S. A second site specific endonuclease from Thermus thermophilus 111, Tth111II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 11;8(15):3275–3285. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.15.3275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Jakes K. How ribosomes select initiator regions in mRNA: base pair formation between the 3' terminus of 16S rRNA and the mRNA during initiation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiegler P., Carbon P., Zuker M., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C. Structure secondaire et topographie du RNA ribosomique 16S d'Escherichia coli. C R Seances Acad Sci D. 1980 Dec 8;291(12):937–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaiwa F., Sugiura M. Cloning and characterization of 4.5S and 5S RNA genes in tobacco chloroplasts. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaiwa F., Sugiura M. The nucleotide sequence of 4.5S ribosomal RNA from tobacco chloroplasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4125–4129. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etten R. A., Walberg M. W., Clayton D. A. Precise localization and nucleotide sequence of the two mouse mitochondrial rRNA genes and three immediately adjacent novel tRNA genes. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):157–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilenko S. K., Babkina G. T. Vydelenie i svoistva ribonukleazy iz iada kobry. Biokhimiia. 1965 Jul-Aug;30(4):705–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilenko S. K., Ryte V. C. [Isolation of highly purified ribonuclease from cobra (Naja oxiana) venom]. Biokhimiia. 1975 May-Jun;40(3):578–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Klootwijk J., de Jonge P., Leer R. J., Planta R. J. The transcription termination site of the ribosomal RNA operon in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 25;8(22):5179–5192. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.22.5179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfeld P. R., Leaver C. J., Bottomley W., Atchison B. Low-molecular-weight (4.5S) ribonucleic acid in higher-plant chloroplast ribosomes. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 1;175(3):1103–1112. doi: 10.1042/bj1751103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Nazar R. N. Nucleotide sequence of wheat chloroplastid 4.5 S ribonucleic acid. Sequence homologies in 4.5 S RNA species. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11896–11900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]