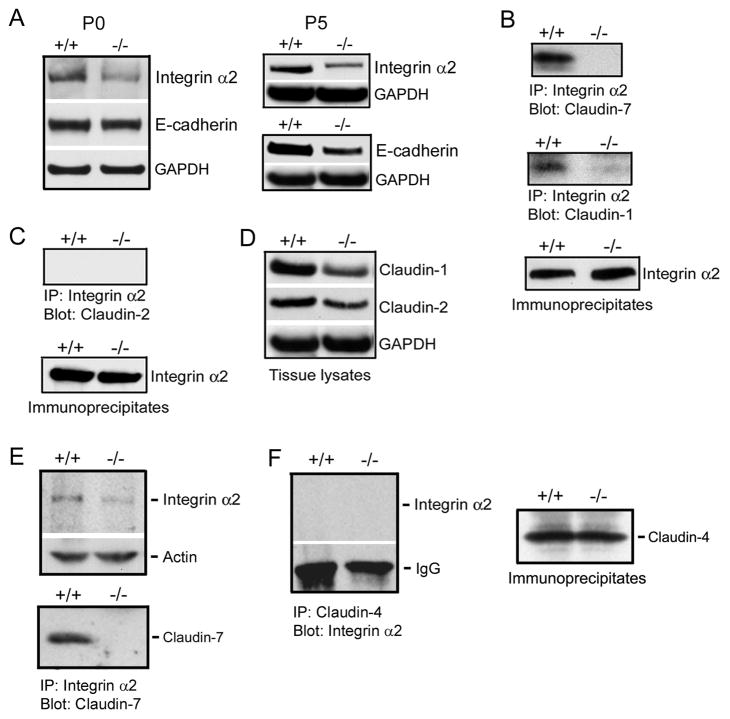
Figure 7.
Disruption of integrin α2/claudin-1 complex in Cldn7−/− intestines. (A) Immunoblotting results showed that integrin α2 expression, but not E-cadherin, was decreased in P0 Cldn7−/− intestines (left), while both integrin α2 and E-cadherin signals were reduced in P5 Cldn7−/− intestines (right). (B) Claudin-7 was co-immunoprecipitated with integrin α2 in Cldn7+/+ (top). Claudin-1 also formed a complex with integrin α2 in Cldn7+/+, but this complex was disrupted in Cldn7−/− (middle). The co-immunoprecipitation experiments were working since integrin α2 was present in the immunoprecipitates (bottom). (C) Claudin-2 did not interact with integrin α2 (top) even though integrin α2 was present in the immunoprecipitates (bottom). (D) Expression levels of claudin-1 and claudin-2 in Cldn7+/+ and Cldn7−/− intestines. (E) Interaction of claudin-7 with integrin α2 in Cldn7+/+ kidneys. Claudin-7 deletion also led to the reduced integrin α2 expression in kidneys (top). Claudin-7 formed an immunoprecipitable protein complex with integrin α2 in Cldn7+/+ kidneys (bottom). (F) Integrin α2 did not interact with claudin-4 (left) even though claudin-4 was present in the immunoprecipitates (right).