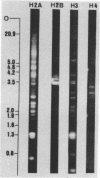
Abstract
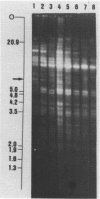
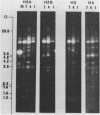
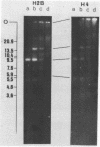
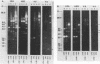
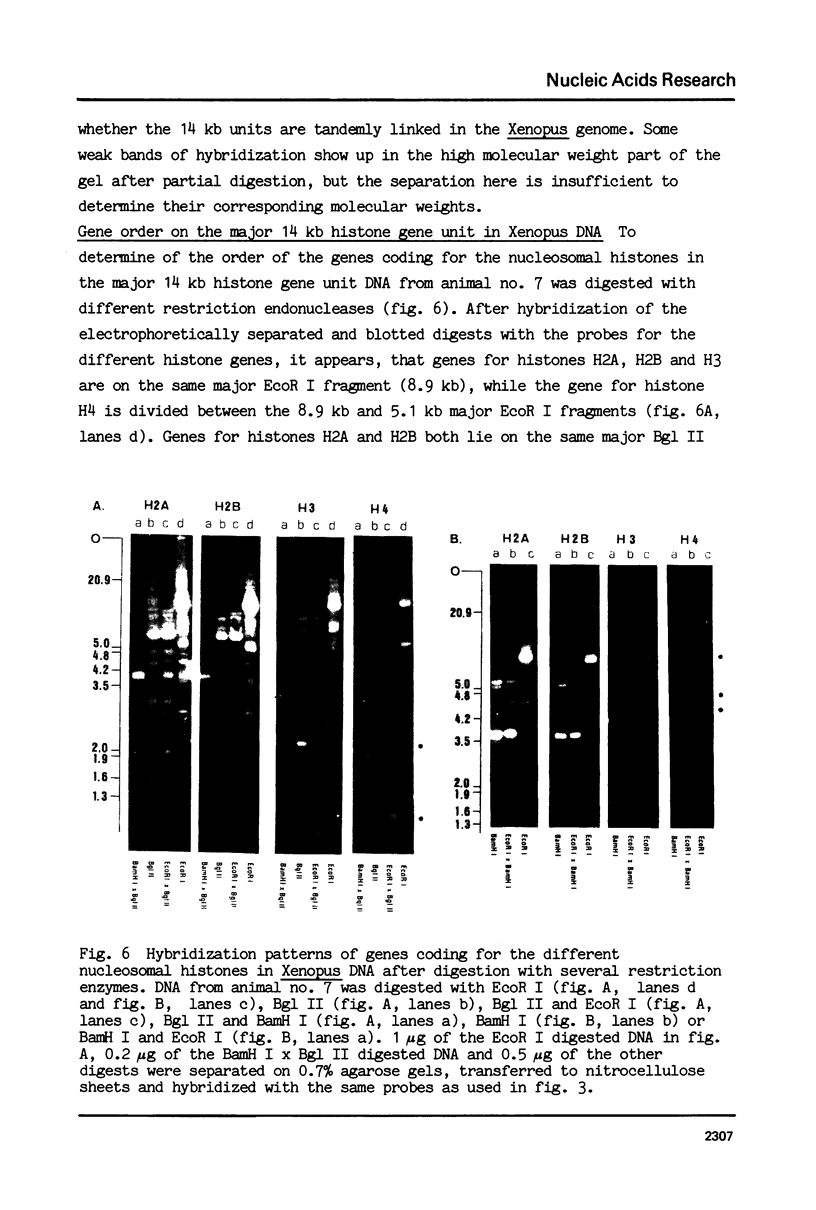
We have studied the organization of the histone genes in the DNA from several individuals of Xenopus laevis. For that purpose, Southern blots of genomic DNA, that was digested with several restriction enzymes, were hybridized with radioactively labeled DNA fragments from clone X1-hi-1 (14), containing genes for Xenopus histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. In the DNA of all animals that were screened we found a major repeating unit of 14 kilobasepairs, which contains genes for histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 (H1 not tested) and is represented up to 30 times in the genome. The order of the genes in this major repeating unit is H4 - H3 - H2A - H2B. This order is different from that in the histone DNA of clone X1-hi-1, i.e. H3 - H4 - H2A - H2B. In addition to the genes in the major repeating unit, histone genes are present in unique restriction fragments in numbers that vary from one animal to another. The restriction patterns for the histone genes in these unique fragments were found to be different for all eight Xenopus individuals that were screened. The cloned Xenopus histone gene fragment X1-hi-1 represents such a unique fragment and is not present in the DNA of each single individual. The total number of genes coding for each of the nucleosomal histones is 45-50 per haploid genome.
Full text
PDF






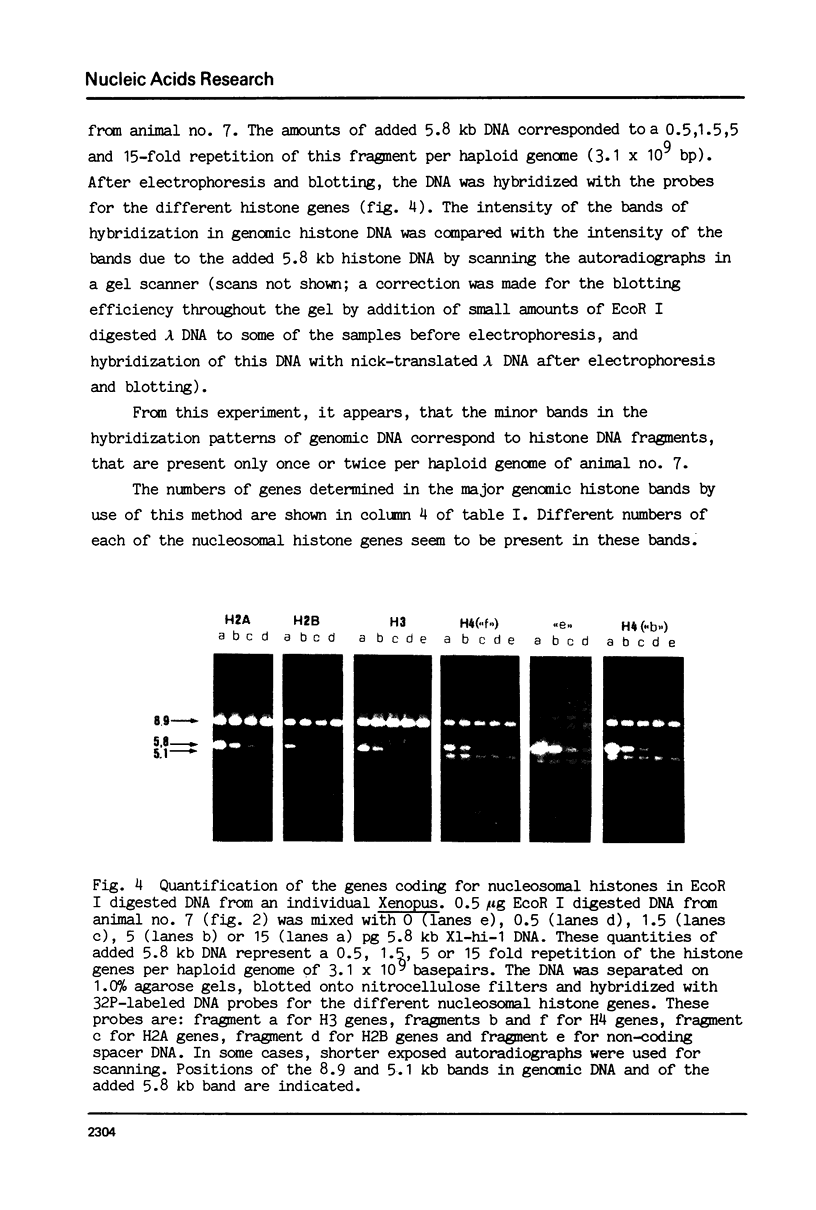
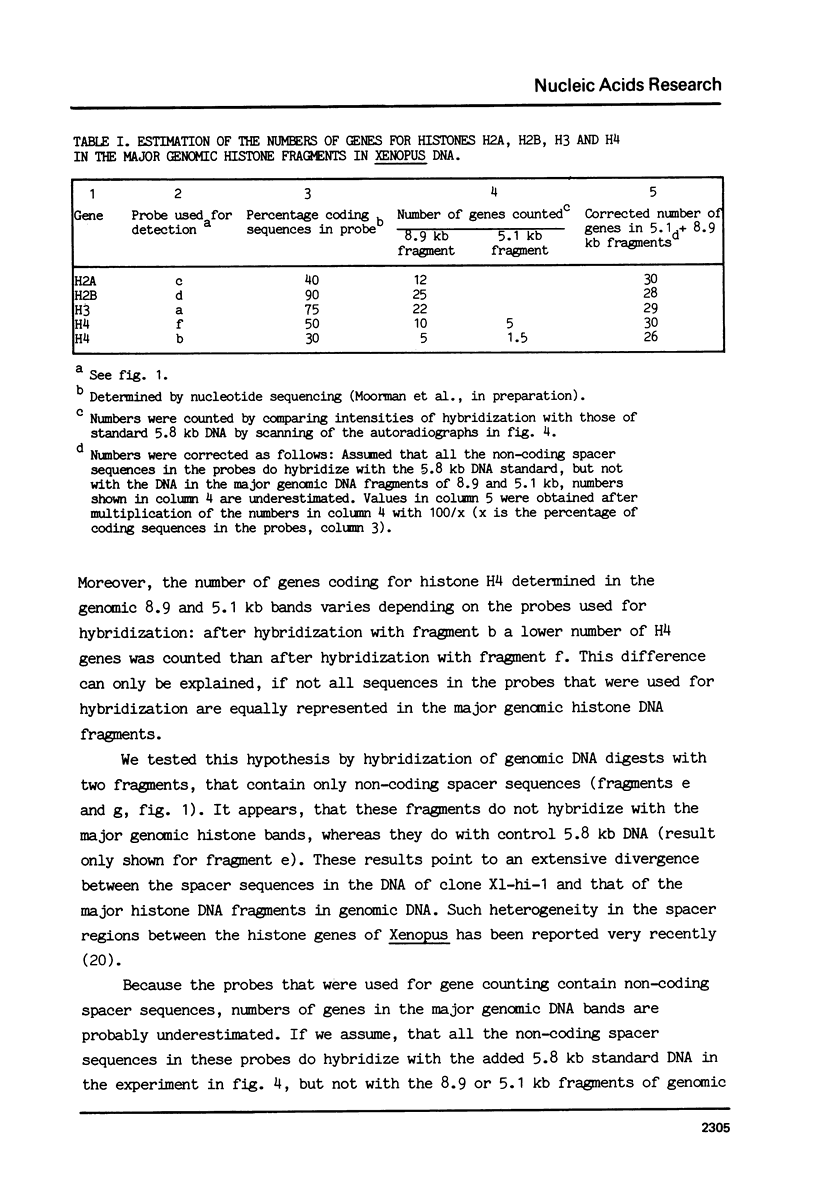
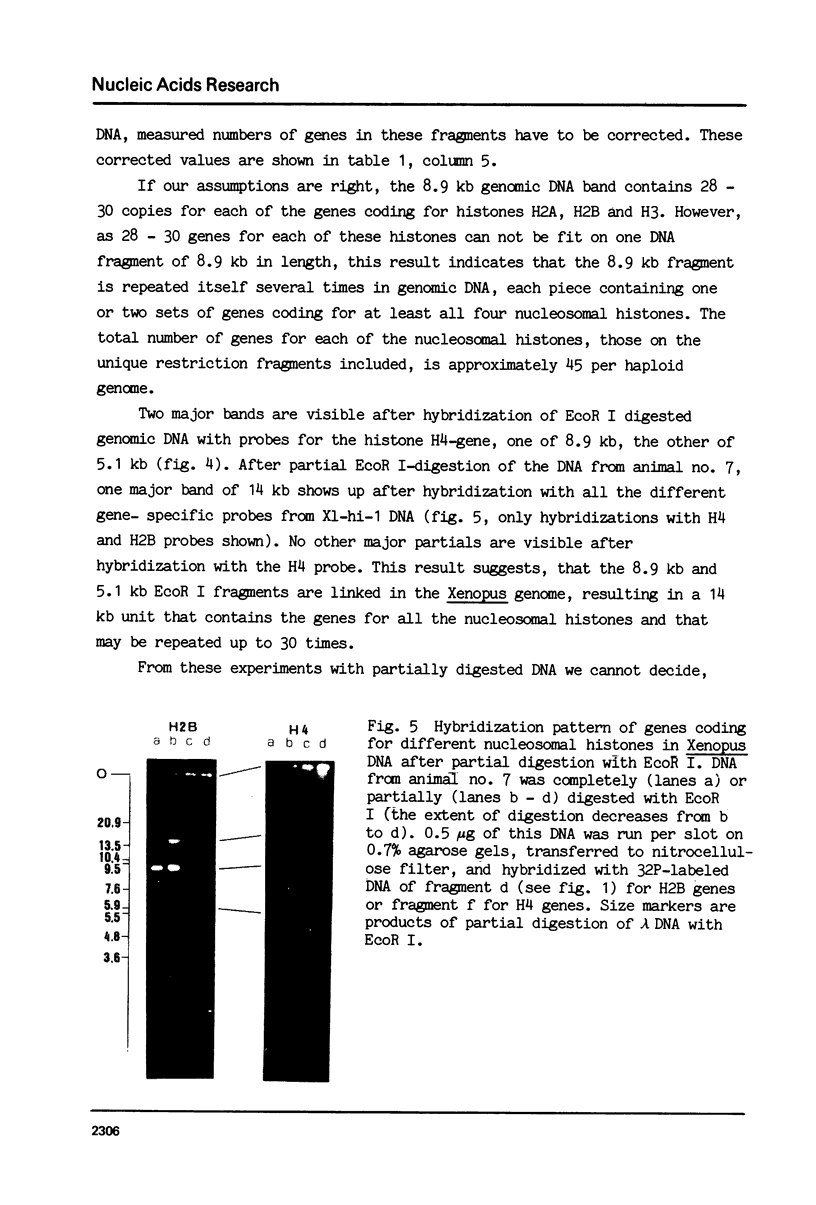




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Busslinger M., Portmann R., Irminger J. C., Birnstiel M. L. Ubiquitous and gene-specific regulatory 5' sequences in a sea urchin histone DNA clone coding for histone protein variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):957–977. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson S. G., Smith H. O., Schaffner W., Gross K. W., Birnstiel M. L. Integration of eukaryotic genes for 5S RNA and histone proteins into a phage lambda receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2617–2632. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn R. H., Kedes L. H. Nonallelic histone gene clusters of individual sea urchins (Lytechinus pictus): polarity and gene organization. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):843–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford R. J., Krieg P., Harvey R. P., Hewish D. A., Wells J. R. Histone genes are clustered with a 15-kilobase repeat in the chicken genome. Nature. 1979 May 10;279(5709):132–136. doi: 10.1038/279132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L., Fahrner K., Woolford J., Jr, Rosbash M., Kaback D. B. Isolation of yeast histone genes H2A and H2B. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1261–1271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howley P. M., Israel M. A., Law M. F., Martin M. A. A rapid method for detecting and mapping homology between heterologous DNAs. Evaluation of polyomavirus genomes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4876–4883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob E. Histone-gene reiteration in the genome of mouse. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 17;65(1):275–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob E., Malacinski G., Birnstiel M. L. Reiteration frequency of the histone genes in the genome of the amphibian, Xenopus laevis. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Oct 1;69(1):45–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Wood D., Simons J. P., Kay R. M., Williams J. G. Linkage of adult alpha- and beta-globin genes in X. laevis and gene duplication by tetraploidization. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):555–564. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H., Birnstiel M. L. Reiteration and clustering of DNA sequences complementary to histone messenger RNA. Nat New Biol. 1971 Apr 7;230(14):165–169. doi: 10.1038/newbio230165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H., Chang A. C., Houseman D., Cohen S. N. Isolation of histone genes from unfractionated sea urchin DNA by subculture cloning in E. coli. Nature. 1975 Jun 12;255(5509):533–538. doi: 10.1038/255533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H. Histone genes and histone messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:837–870. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifton R. P., Goldberg M. L., Karp R. W., Hogness D. S. The organization of the histone genes in Drosophila melanogaster: functional and evolutionary implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1047–1051. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorman A. F., de Laaf R. T., Destrée O. H., Telford J., Birnstiel M. L. Histone genes from Xenopus laevis: molecular cloning and initial characterization. Gene. 1980 Aug;10(3):185–193. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Kunz G., Daetwyler H., Telford J., Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. Genes and spacers of cloned sea urchin histone DNA analyzed by sequencing. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):655–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90249-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sures I., Lowry J., Kedes L. H. The DNA sequence of sea urchin (S. purpuratus) H2A, H2B and H3 histone coding and spacer regions. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1033–1044. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienand U., Schwarz Z., Feix G. Electrophoretic elution of nucleic acids from gels adapted for subsequent biological tests. Application for analysis of mRNAs from maize endosperm. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 15;98(2):319–323. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80208-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zernik M., Heintz N., Boime I., Roeder R. G. Xenopus laevis histone genes: variant H1 genes are present in different clusters. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90557-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]