Abstract
By linkage mapping of quantitative trait loci, we previously identified at least 11 natural genetic variants that significantly modulate Caenorhabditis elegans life-span (LS), many of which would have eluded discovery by knock-down or mutation screens. A region on chromosome IV between markers stP13 and stP35 had striking effects on longevity in three inter-strain crosses (each P < 10−9). In order to define the limits of that interval, we have now constructed two independent lines by marker-based selection during 20 backcross generations, isolating the stP13–stP35 interval from strain Bergerac-BO in a CL2a background. These congenic lines differed significantly from CL2a in LS, assayed in two environments (each P < 0.001). We then screened for exchange of flanking markers to isolate recombinants that partition this region, because fine-mapping the boundaries for overlapping heteroallelic spans can greatly narrow the implicated interval. Recombinants carrying the CL2a allele at stP35 were consistently long-lived compared to those retaining the Bergerac-BO allele (P < 0.001), and more resistant to temperature elevation and paraquat (each ∼1.7-fold, P < 0.0001), but gained little protection from ultraviolet or peroxide stresses. Two rounds of recombinant screening, followed by fine-mapping of break-points and survival testing, narrowed the interval to 0.18 Mb (13.35–13.53 Mb) containing 26 putative genes and six small-nuclear RNAs – a manageable number of targets for functional assessment.
Keywords: longevity; life-span; thermotolerance; oxidative stress; ultraviolet irradiation, C. elegans; recombinant-congenic lines; linkage mapping
Introduction
Longevity is largely under genetic control in all animal species studied, with genetic factors contributing roughly half of life-span (LS) variance in Caenorhabditis elegans (Johnson and Wood, 1982; Ebert et al., 1993, 1996; Ayyadevara et al., 2001, 2003). Specific genes controlling LS were first discovered through screens for long-lived mutants of C. elegans (Klass, 1983; Yang and Wilson, 1999) or from study of mutants originally noted for other phenotypes in this nematode (Apfeld and Kenyon, 1999; McElwee et al., 2004; Morley and Morimoto, 2004; Hansen et al., 2005; Ayyadevara et al., 2008). Longevity effects were subsequently observed for orthologous genes in yeast, Drosophila, and mice (Guarente and Kenyon, 2000; Tatar et al., 2001; Barbieri et al., 2003; Quarrie and Riabowol, 2004; Wood et al., 2004; Curtis et al., 2007; Kim, 2007; McElwee et al., 2007; Taguchi et al., 2007; Zahn and Kim, 2007). Life-extending mutations in the nematode comprise several distinct pathways, although considerable evidence implies convergence or cross-talk among those genetic circuits (Kondo et al., 2005; Berdichevsky et al., 2006; Gami et al., 2006; Matsumoto et al., 2006; Troemel et al., 2006; Greer et al., 2007; Shmookler Reis et al., 2009; Tazearslan et al., 2009).
Multiple genetic elements, jointly controlling a complex phenotype such as longevity, can be resolved by identification of naturally occurring polymorphisms – allelic variants at quantitative trait loci (QTLs) – that influence the aging process. Analysis of QTLs may reveal gene-sequence alternatives that arose by natural selection in diverse environments and genetic backgrounds during evolution. At least some of these genes might be quite distinct from those implicated in mutagenesis studies, and may interact in allele-specific combinations (Larsen et al., 1995) inferable from polygene mapping data.
Life-span QTLs were first mapped via linkage in C. elegans (Ebert et al., 1993, 1996; Shook et al., 1996; Shook and Johnson, 1999; Ayyadevara et al., 2001, 2003), soon followed by parallel interval-mapping studies in Drosophila (Nuzhdin et al., 1997; Leips and Mackay, 2000; Pasyukova et al., 2000; Vieira et al., 2000; Reiwitch and Nuzhdin, 2002; Geiger-Thornsberry and Mackay, 2004), including a trait-extreme genotyping strategy (Luckinbill and Golenberg, 2002) similar to ours. The Mackay group has identified genetic variants that interact with one another and with known candidate-gene mutants to jointly influence Drosophila longevity (Geiger-Thornsberry and Mackay, 2004; Pasyukova et al., 2004; Magwire et al., 2010), whereas genome-wide association in humans has implicated many candidate genes contributing to complex signatures that predict extreme-longevity (Beekman et al., 2010). It has long been predicted that genes which influence longevity would exhibit antagonistic pleiotropy, wherein alleles that are beneficial to early survival or fecundity are detrimental to survival later in life (Kirkwood and Rose, 1991; Rose et al., 2002). Evidence has accumulated indicating pleiotropy of many genes for age- and stress-related traits, and a subset of these which show “antagonism” between longevity and early fecundity (Ebert et al., 1993, 1996; Shook and Johnson, 1999; Ayyadevara et al., 2001, 2003; Leips et al., 2006; Magwire et al., 2010). Pleiotropy between stress-survival traits and longevity has been found repeatedly, evidenced both by coincident mapping of QTLs (Shmookler Reis et al., 2007) and by the observation of extended LS in mutants or drugs initially screened for a specific stress-resistance (Sampayo et al., 2000; Benedetti et al., 2008), or vice versa (Ayyadevara et al., 2008; Onken and Driscoll, 2010; Shmookler Reis et al., 2011). Although such pleiotropy is predominantly concordant, it can also be antagonistic (Magwire et al., 2010); that is, the longer-lived allele is usually but not always the more stress-resistant allele.
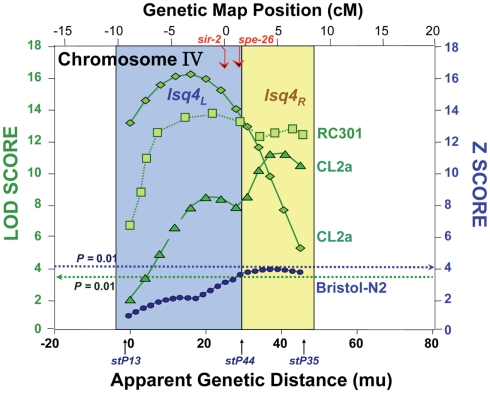
In the nematode, we positioned at least 11 QTLs that strongly and significantly affect longevity in four independent cross-progeny populations arising from three pairings of wild-type strains. For each cross, a high-transposon “marker” strain, Bergerac-BO (∼500 Tc1-insertions), was crossed to a low-transposon strain, either Bristol-N2, CL2a, or RC301 (each having 25–35 Tc1 elements). Additional crosses using DH424 as the high-copy strain produced results identical to those employing Bergerac-BO (Ebert et al., 1996), and direct comparison of Tc1-insertion sites implied a recent laboratory derivation of DH424 from Bergerac-BO (Egilmez et al., 1995). Many marker pairs showed highly significant interactions (Ayyadevara et al., 2003), lending support to the concept that longevity in natural populations depends on interactive networks of polymorphic genes (Leips and Mackay, 2002; Ayyadevara et al., 2003; Geiger-Thornsberry and Mackay, 2004). One or two QTLs on chromosome IV, initially termed lsq4a, b (Ebert et al., 1993, 1996; Ayyadevara et al., 2001, 2003; Shmookler Reis et al., 2007) but here designated as lsq4, were highly significant in five studies of aging cohorts comprising segregants from three distinct inter-strain crosses. Peak LOD scores for longevity were 3.9–16.3, well above the P < 0.01 genome-wide significance threshold (which permutation tests placed at LOD ∼3.5). QTL peaks on chromosome IV, from all three strain pairings, are illustrated in Figure 1 (data compiled from Ebert et al., 1993; Ayyadevara et al., 2001, 2003). They appear to define two adjacent QTLs: lsq4a between −8 and +2 on the genetic-map (upper axis scale in Figure 1) and lsq4b between +2 and +8. Both loci showed a significant interaction with stP127 (chromosome III), affecting Darwinian fitness (Bonferroni-adjusted, genome-wide P < 0.05 in both young and longevity-selected worms); however, no interactions affecting LS were significant between lsq4 and any other marker locus tested (Ayyadevara et al., 2003).
Figure 1.
Composite of multiple mappings for crosses between Bergerac-BO (a common reference strain with >500 transposon markers) and other C. elegans strains. Data are drawn from references (Ebert et al., 1993; Ayyadevara et al., 2003, 2001). The Bristol-N2 × BO cross was analyzed by non-parametric interval mapping, which produces Z scores as output (right ordinate), while the others (RC301 × BO and two independent CL2a × BO crosses) were analyzed by categorical trait interval-mapping (Ayyadevara et al., 2003), for which likelihood results are generated as LOD scores (log of odds ratio; green curves refer to the left ordinate). Note that the RC301 × BO data shown here correspond to the same cross presented previously (Ayyadevara et al., 2001), but reanalyzed by our categorical trait interval-mapping procedure (Ayyadevara et al., 2003). Dashed horizontal lines indicate empirical P = 0.01 false-positive thresholds based on 1000 interval-mappings, permuting genotype with respect to LS.
We now describe the construction of congenic (near-isogenic) lines spanning this LS QTL region, by marker-directed selection during 20 generations of backcrossing, and the isolation of recombinants to dissect the interval. The results confirm the existence of a longevity QTL close to the dimorphic sTP35 marker, with significant effects on median and “maximal” (90th-percentile) longevity. Less extensive backcrossing in the opposite direction also implies the presence of a LS locus near sTP35. The same region of chromosome IV modulates thermotolerance and paraquat resistance by almost twofold, but has far less influence on resistance to hydrogen peroxide or ultraviolet (UV) irradiation.
High-throughput genetic fine-mapping (Ayyadevara et al., 2000a,b), coupled with SNP discovery and analysis in this region, greatly increased marker coverage and map resolution, defining the genetic boundaries of introgressed chromosome segments in seven lsq4 recombinants. By comparing longevity and stress–response data among strains with overlapping “foreign” (heteroallelic) chromosomal segments, we were able to assign the QTL to a discrete 0.3-Mb interval. A second round of recombinant screening further narrowed this span to less than 0.2 Mb, providing a manageable set of positional candidate genes to examine for expression and coding-sequence differences, and to test for functional consequences of altered expression – results that will be presented elsewhere (Ayyadevara et al., submitted).
Results
Survival analysis of backcrossed lines
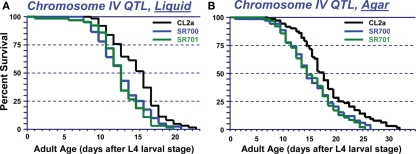
Since QTL-mapping in several C. elegans inter-strain crosses had indicated the existence of a natural polymorphism, termed lsq4, near the center of chromosome IV with strong effects on longevity and stress-resistance (Ebert et al., 1996, 1993; Ayyadevara et al., 2003, 2001; Shmookler Reis et al., 2007), we attempted to define that region by isolating genetic recombinants from a cross between strains CL2a (DR1345) and Bergerac-BO (RW7000), after 20 generations of marker-directed backcrossing into CL2a to remove most of the Bergerac-BO-derived DNA not tightly linked to lsq4. Figure 2A shows survival curves in liquid suspension culture for strain CL2a, and for two congenic lines (SR700 and SR701) in which the lsq4 interval from strain Bergerac-BO replaced that segment of the CL2a genome. CL2a had a median adult LS of 15.5 days, 24% longer than either congenic line [12.5 days; each P < 0.001 by Cox–Mantel test (Lee and Wang, 2003)].
Figure 2.
Survivals of C. elegans wild-type strain CL2a, and two congenic lines derived from CL2a by introgression of the chromosome IV stP13–stP35 region from Bergerac-BO. SR700 and SR701 are independent congenic lineages generated by 20 generations of backcrossing, with marker-based selection of the Bergerac-BO allele for stP13, stP44, and stP35. Homozygotes for the introduced lsq4 region were ascertained, expanded, and used to measure survival at 20°C. (A) Survivals in liquid medium. (B) Survivals on solid agar medium. Protocols for nematode culture, scoring, and survival analysis are described in the “Materials and Methods” section. Each survival group was initiated with 56–70 worms at late L4, on two plates; after exclusion of censored losses, total numbers of natural deaths ranged from 50 to 65. Adult age is measured from the L4/adult molt; total age is the indicated “adult age” plus 2.5 days for all strains.
Very similar allelic effects on LS were seen when worms were maintained on the surface of solidified agar medium, demonstrating that the difference in longevity between lsq4 alleles is not restricted to a specific environment. Survival curves on agar (e.g., Figure 2B) indicate a median LS of 17.5 days for CL2a, 3 days (20%) longer than either SR700 or SR701 (each P < 0.001). For either genotype, median LSs were 2–3 days (17–21%) longer on agar than in liquid medium, while 90th-percentile and maximal survival times benefited considerably more from growth on agar: 8 days (42%) for CL2a, and 7–8 days (47–52%) for the lsq4-congenic lines.
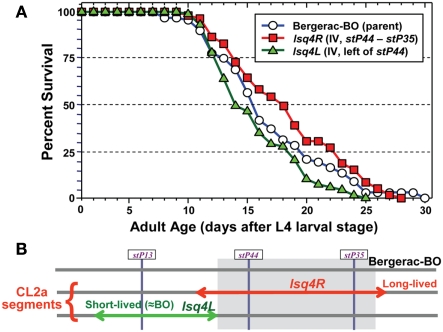
The converse introgression, of the CL2a allele into a Bergerac-BO background, is more difficult for technical reasons – i.e., infertility of Bergerac-BO males, and the need to score loss rather than gain of transposable-element markers, against a background of several hundred nearly identical transposon insertions (Egilmez et al., 1995). Nevertheless, we were able to conduct a limited backcross over three generations, sufficient to reduce the CL2a contribution on other chromosomes (or on distal parts of chromosome IV) by ∼94%. Survival assays were then conducted on agar medium. As shown in Figure 3, retention of a CL2a segment including both stP44 and stP35 (the “center-right” of the lsq4 interval as initially defined) extended median LS from 15.5 to 18 days, while a CL2a region just to the left of this (“lsq4L,” including marker stP13 but not stP44 or stP35) reduced it to 14 days. Thus, the CL2a allele of lsq4 again conferred ∼2.5 days (16%) longer median LS than the Bergerac-BO allele. These data imply that the major longevity QTL on chromosome IV resides in the center-right portion of this interval (Figure 3). Although they also suggest the existence of a weaker, countervailing QTL to its left, the survivals for Bergerac-BO and the lsq4L recombinant did not differ significantly (Figure 3) or reproducibly.
Figure 3.
Survivals of C. elegans wild-type strain Bergerac-BO, and two recombinant-congenic lines derived from Bergerac-BO by introgression of stP13–stP35 segments from chromosome IV of CL2a. The lineage designated “4L” retained the Bergerac-BO allele only at marker stP44, while the “lsq4 (center-right)” cohort retained the Bergerac-BO allele for stP13 and stP35. Homozygotes for the introduced lsq4 region were ascertained, expanded, and used to measure survival at 20°C. Procedures for nematode culture, scoring, and survival analysis are described in Experimental Procedures. Each survival began with 60–65 worms in two dishes, cultured on agar medium. Adult age is measured from the L4 larval-stage; total age is the indicated adult age plus 3 days, for Bergerac-BO and strains derived by backcrossing into it.
These data decisively confirm the presence of a longevity QTL on chromosome IV between the markers stP13 (−2 cM) and stP35 (+10 cM), a span encompassing more than 1000 genes. Evidence from recombinants, as described above, can partition that interval. In order to define and narrow the region implicated in the more tractable CL2a background, recombinants were selected based on loss of the introgressed (BO-allele) marker near either the left (stP13) or right (stP35) end of the QTL region, as indicated by marker-specific polymerase chain reaction (PCR). An intermediate marker, stP44, provided additional information useful in comparing recombinants. We thus created seven independent recombinant-congenic lines: three retaining BO-alleles at the left and center markers (stP13, stP44), three retaining only the rightmost marker (stP35), and one with both the center and right hand markers (stP44, stP35) introgressed from the BO strain.
Survival analysis of lsq4 recombinants
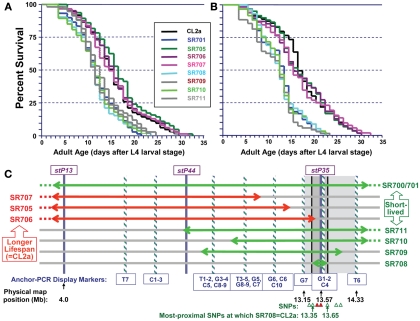
Figure 4 illustrates survivals in liquid medium for two independent assays of lsq4 recombinants, with median and maximum LSs summarized in Table 1. Within each experiment the recombinants fell into two groups, for which survivals closely followed those of either CL2a or the short-lived lsq4-congenic line, SR701. Recombinant lines SR705, SR706, and SR707 had median post-larval LSs of 14.5–16.5 days in both experiments, not significantly different from the CL2a parental strain (median LSs of 14.5 and 16.5 days in repeat survivals; each P ≥ 0.7 by Cox–Mantel test). In contrast, median adult survival for the lsq4-congenic line SR701 was 3 days less than that of CL2a in each experiment, and recombinants SR708, SR709, SR710, and SR711 all fell in the same range – with medians for this group averaging 11.7 ± 0.4 days (±SD) in the first assay, and 12.9 ± 0.5 days in the second. The other recombinants, along with CL2a controls, survived for 24 and 28% longer (means of medians were 15.3 ± 1.0 and 16.0 ± 0.6 days in the respective experiments). Every strain in the short-lived cluster differed significantly from CL2a by Cox–Mantel test, with each P < 0.001, and a combined P (comparing the clusters by t-test, both experiments combined) of <2 × 10−6.
Figure 4.
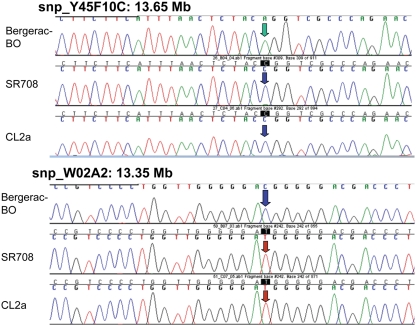
Survivals of C. elegans wild-type strain CL2a, the lsq4- congenic line SR701, and seven recombinants derived from SR701 during two final generations of backcross to CL2a. These recombinants were detected by loss of the Bergerac-BO allele at one or two of the lsq4 markers (stP13, stP44, stP35), and homozygotes of each were ascertained, expanded, and used to measure survival in liquid medium at 20°C. (A,B) are independent survival experiments conducted sequentially. Procedures for nematode culture, scoring, and survival analysis are described in the “Materials and Methods” section. Numbers of worms initiated and scored per survival, median, and maximal life-spans, and significance of differences among the groups, are summarized in Table 1. Adult age is measured in days following the L4 larval stage; total age is therefore the indicated adult age plus 2.5 days. (C) Diagram of lsq4 mapping data. Markers in the stP13–stP35 region are indicated by vertical bars. Horizontal two-headed arrows represent genetic-map spans of the introgressed (Bergerac-BO allele) regions, for congenic line SR701 and seven recombinants thereof. Long-lived recombinant lines (life-spans similar to CL2a) are named at the left, while those named on the right were shorter-lived. The 26 new markers obtained by Anchor-PCR Display, and three previously determined markers in this vicinity (Williams et al., 1992), were ordered into 10 groups by the seven recombinant lines; eight of these are indicated by cross-striped vertical bars. Based on these data, the longevity QTL lies between marker groups G7 and T6 (shaded rectangle, 13.15–14.33 Mb). Several of the SNPs in this region that distinguish between parental strains are indicated by triangles at the figure bottom; symbols are green/open if SR708 carries the CL2a allele; and red/filled if SR708 carries the Bergerac-BO allele. SNPs shown here, named for YAC clones in which they reside, are: snp_Y67H2A (13.27 Mb), snp_W02A2/pkP4053 (13.35 Mb), snp_Y45F10A/pkP4059 (13.49 Mb), snp_Y45F10B (13.55 Mb), snp_Y45F10C (13.65 Mb), snp_Y37A1A (13.83), and snp_C27H2 (13.95). SNPs with “pkP” are snip-SNPs.
Table 1.
Survival data for lsq4 recombinant-congenic lines in liquid medium.
| Strain | N | Lost | Median life-span | P | 90th-percentile | MLS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXPERIMENT 1 | ||||||
| CL2a | 61 | 4 | 14.5 days | – | 25.5 days | 29.5 days |
| SR705 | 63 | 3 | 16.5 days | 0.8 | 25.5 days | 32.5 days |
| SR706 | 64 | 2 | 15.5 days | 0.7 | 25.5 days | 31.5 days |
| SR707 | 61 | 6 | 14.5 days | 0.7 | 26.5 days | 31.5 days |
| Mean ± SD | 15.25 ± 1.0 | 25.75 ± 0.5 | 31.25 ± 1.3 | |||
| SR701 | 61 | 5 | 11.5 days | <0.001 | 18.5 days | 21.5 days |
| SR708 | 64 | 3 | 11.5 days | <0.001 | 18.5 days | 23.5 days |
| SR709 | 54 | 5 | 12.5 days | <0.001 | 17.5 days | 24.5 days |
| SR710 | 66 | 2 | 11.5 days | <0.001 | 18.5 days | 22.5 days |
| SR711 | 58 | 4 | 11.5 days | <0.001 | 16.5 days | 23.5 days |
| Mean ± SD | 11.7 ± 0.4 | 17.9 ± 0.9 | 23.1 ± 1.1 | |||
| EXPERIMENT 2 | ||||||
| CL2a | 62 | 3 | 16.5 days | – | 24.5 days | 30.5 days |
| SR705 | 60 | 3 | 16.5 days | 0.8 | 26.5 days | 30.5 days |
| SR706 | 55 | 1 | 15.5 days | 0.7 | 25.5 days | 30.5 days |
| SR707 | 66 | 2 | 15.5 days | 0.7 | 25.5 days | 32.5 days |
| Mean ± SD: | 16.0 ± 0.6 | 25.5 ± 0.8 | 31.0 ± 1.0 | |||
| SR701 | 66 | 2 | 13.5 days | <0.001 | 18.5 days | 22.5 days |
| SR708 | 58 | 2 | 12.5 days | <0.001 | 17.5 days | 22.5 days |
| SR709 | 70 | 7 | 12.5 days | <0.001 | 19.5 days | 23.5 days |
| SR710 | 60 | 4 | 12.5 days | <0.001 | 18.5 days | 23.5 days |
| SR711 | 69 | 6 | 13.5 days | <0.001 | 20.5 days | 21.5 days |
| Mean ± SD: | 12.9 ± 0.5 | 18.9 ± 1.1 | 22.7 ± 0.8 | |||
In a similar way, we demonstrated highly significant differences between the two clusters, in two measures of maximal longevity. The 90th-percentile values for the long-lived group (CL2a, SR705, SR706, SR707) averaged 25.8 ± 0.5 and 25.5 ± 0.8 days in the two experiments, 35–44% greater than the shorter-lived group (SR701, SR708, SR709, SR710, and SR711) which respectively averaged 17.9 ± 0.9 and 18.9 ± 1.1 days (combined P < 2 × 10−11). The maximum life-span (MLS; maximal LS, defined as the survival time of the last worm to die in a cohort) for the long-lived cluster averaged 31.3 ± 1.3 and 31.0 ± 1.0 days in the two assays, 35–37% greater than the short-lived group which averaged 23.1 ± 1.1 and 22.7 ± 0.8 (each t-test P < 10−11).
Fine-mapping analysis by anchor-PCR display
We analyzed the seven independent recombinants by a fine-mapping technique developed in our laboratory (Ayyadevara et al., 2000a). In this procedure (see Materials and Methods for details), DNA sequences adjacent to Tc1 transposons were amplified by “anchor-PCR” using a nested-primer protocol with fluor-tagged primers in the second stage. Products were visualized on gels, and employed as genetic markers based on presence or absence in recombinants. Using this method, 26 new dimorphic markers (i.e., ±Tc1) were found and positioned between stP13 and stP35 by routine genetic-mapping – ignoring uninformative marker bands common to parental strains CL2a and SR701. The resulting data array, comprising seven recombinant lines typed for 29 markers (26 new and three previously assessed markers, stP13, stP44, and stP35), implies a unique ordering of the markers into 10 groups as indicated at the bottom of Figure 4C (striped bars labeled T7, C1, C2, C3, etc.). Markers within a given group are not necessarily in close physical or genetic proximity, but were not resolved by this set of seven recombinants; that is, no recombination break-points fell within that group. Because SR708, the smallest introgression mapped, carries the BO-allele trait for lsq4 (shorter LS), whereas SR706 does not, the QTL is inferred to lie between markers G7 and T6, in the vicinity of stP35, G1, G2, and C4.
SNP mapping and second-round screening for recombinants
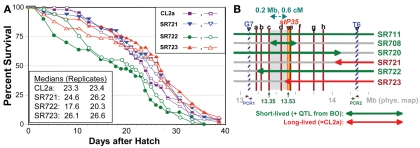
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), which occur roughly one to nine times per kilobase pair between any two independently isolated C. elegans strains (Koch et al., 2000), are the most abundant form of genetic variation. Many such polymorphisms were originally detected between strains Bristol-N2 and Hawaiian strain CB4856, but over 75% of 98 SNPs tested were shared among multiple strains, and on average >3 of the 10 strains tested carried the non-N2 allele (Koch et al., 2000). A subset of SNPs (“snip-SNPs”) alter restriction cleavage sites, and thus are easily and robustly assayed (Koch et al., 2000). “Snip-SNPs” and conventional SNPs, including new SNPs discovered by intermittent sequencing in regions devoid of reported SNPs, were assessed for strain CL2a, the initial congenic line SR701, and congenic recombinants SR706, SR708, and SR709. Figure 5 illustrates sequencing runs confirming the most proximal SNPs at which the SR708 sequence is identical to that of the recurrent-parental strain CL2a, but differs from Bergerac-BO. SNP typing thus narrowed the LS QTL interval from 1.2 to 0.3 Mb in length, extending from 13.35–13.65 Mb on chromosome IV (Figure 4C). A second-round screen (Figure 6) turned up four new recombinants in this area, placing the QTL to the left of stP35 and reducing the implicated QTL interval to less than 0.2 Mb (13.35–13.53 Mb; see Figure 6B).
Figure 5.
Sequencing data for single-nucleotide polymorphisms that distinguish between parental strains Bergerac-BO and CL2a. SNPs are shown only if informative to determine the parental origin of that site in lsq4-congenic strain SR708. At the two indicated SNPs, Y45F10C at 13.65 Mb and WO2A2 at 13.35 Mb, SR708 has the CL2a genotype, indicating that the introgressed BO-like segment of SR708 must lie within that interval.
Figure 6.
Second-round screen for lsq4 recombinants. (A) Survivals of C. elegans wild-type strain CL2a and three recombinant-congenic lines derived from SR711 (see Figure 4) during three further generations of backcross to CL2a. Recombinants were identified and endpoints mapped as described for the initial screening cycle (see Figure 4). (B) Map based on survival data [(A) and Figure 4], and fine-mapping of endpoints for introgressed (BO-derived) segments. In addition to the three recombinant-congenic lines assessed in (A), (B) summarizes fine-mapping and survival data for lines SR711, SR708, and SR720 (Figure 4 and data not shown). Red lines a–h indicate positions of eight informative SNPs mapped within the G7 – T6 interval; b–h correspond to SNP triangles in Figure 4C). Lsq4 lies to the right of “c” (because SR708 = CL2a at that marker, but carries the BO/shorter life-span trait of lsq4), and left of stP35 (because SR723 = BO there but carries the CL2a/longer life-span trait). PCR1 and PCR2 indicate polymerase chain reaction assays used to genotype flanking markers G7 and T6, respectively, to ascertain recombinants in sublines. PCR1 primers: F, 5′-ACTCTTCGAAGACAACTC-3′; R, 5′-TCTTCAGAATGCTCCGCC-3′. PCR2 primers: F, 5′-TTTGGAGAAGGGTGTAATGC-3′; R, 5′-GGAAGATTTGGAGAAGGGTG-3′.
Stress-resistance associated with lsq4 alleles
Thermotolerance assay
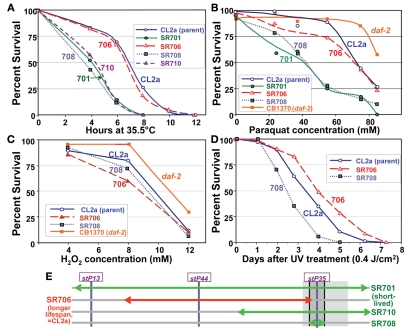
Several of the recombinant-congenic lines, including those defining the limits of the lsq4 interval, were tested for thermotolerance, operationally defined as survival time after transfer from 20 to 35.5°C. Survival curves for these strains are shown in Figure 7A. Although they mirror closely the order of survival under normal, isothermal conditions (20°C), the differences among strains were accentuated by “heat shock.” The backcross parent CL2a and recombinant SR706 had almost identical survival curves at 35.5°C. Their median survival times averaged 6.8 ± 0.1 hr, 70% longer than any of the three short-lived strains (the original congenic line SR701 and recombinant sublines SR708 and SR710) which averaged 4.0 ± 0.4 h (mean of medians, ±SD). Each short-lived strain differed significantly in survival from CL2a by log-rank test, with P < 0.0001. These results place narrow bounds on a gene affecting thermotolerance: it must lie between the SNPs that define the limits of the BO-like segment in SR708 (snp_W02A2 – snp_Y45F10C), i.e., 13.35–13.65 Mb on Chromosome IV (compare Figures 4C and 7E). Thus, to this level of resolution, the QTLs for longevity and thermotolerance coincide, indicating that both traits are very likely to be governed by the same gene.
Figure 7.
Stress-survival assays. Worms of each line were grown as synchronous cultures at 20°C. Hermaphrodites were picked as L4 larvae and tested as young adults 1–4 days later. Nematodes were scored as dead if they failed to move spontaneously or in response to prodding. SR701 is an lsq4-congenic line, retaining the Bergerac-BO-derived lsq4 region of chromosome IV in a CL2a background; CL2a is the parental wild-type strain; and SR706, 708 and 710 are recombinant-congenic lines derived from SR701 during the last two generations of backcrossing into CL2a (see Figure 4). CB1370 is a daf-2 mutant strain bearing the e1370 hypomorphic allele (life-span ∼2× wild-type) in a Bristol-N2 background. (A) Thermotolerance assays. Worms were picked as L4 larvae in groups of ≥50, onto agar/NGM plates, and tested as pregravid young adults 1 day later. Survival was assessed at 2-h intervals during incubation at 35.5 ± 0.4°C. (B) Paraquat resistance assays. Adult worms at 3 days post-hatch were transferred in groups of 30 to liquid survival medium without E. coli. After 30 min for digestion of enteral bacteria, paraquat was added to a final concentration of 0–85 mM and replaced daily, with assessment after 3 days at 20°C. (C) Hydrogen peroxide resistance assays. Congenic and recombinant-congenic lines, and parental strain CL2a, were exposed to varying concentrations of hydrogen peroxide (0, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12 mM). Mature adult hermaphrodites were treated and the number of live worms was counted after 4 h of continuous exposure. (D) Survival of ultraviolet (UV) irradiation. Groups of 30 worms, 4 days post-hatch, were placed on agar plates without food at 20°C, and exposed to ultraviolet light at 0.4 joules/cm2. Worms were transferred to fresh plates seeded with E. coli (var. OP50); viability was assessed as above at 20.0 ± 0.4°C, at 1-day intervals. (E) Schematic of QTL-mapping data for resistance to temperature shift, paraquat or UV.
Resistance to oxidative-stresses and UV light
The lsq4-congenic lines and their recurrent–backcross parent were exposed to either paraquat or hydrogen peroxide to induce oxidative stress via reactive oxygen species. Lsq4-congenic lines SR701 and SR708 (substituting the Bergerac-BO allele of lsq4 in a CL2a background) were nearly twice as sensitive to paraquat as the parental strain (Figure 7B; each P < 0.0001). The allelic effect, 1.8, is comparable to that conferred by the oxidative-stress-resistant daf-2(e1370) mutation (orange curve, Figure 7B). Based on the phenotypes of recombinants tested, this trait also maps to the identical interval as LS and thermotolerance. In contrast, hydrogen peroxide toxicity was essentially indifferent to the allele present at lsq4 (Figure 7C). A fifth trait, the ability of worms to survive UV radiation, was moderately improved (1.35-fold longer survival time, P < 0.01) by presence of the CL2a rather than the BO allele of lsq4 (Figure 7D), again mapping to the same locus. The same allele improved survival in each of the four assays that registered any effect: longevity, thermotolerance, paraquat resistance, and UV resistance (Figure 7E) – consistent with these being pleiotropic effects of an allelic change to a single gene.
Discussion
Caenorhabditis elegans has provided a valuable model for studies of the aging process, and many of the genetic modulators of LS discovered in this nematode have proven to be conserved in other metazoans including mammals (Bonafe et al., 2003; Hansen et al., 2005; Curran and Ruvkun, 2007; Smith et al., 2007; Carrano et al., 2009; Kapahi et al., 2010).
We previously estimated the broad-sense heritability of LS (H2) in C. elegans to be ∼0.5 (Ebert et al., 1993, 1996). It appears that no more than three dozen polymorphic genetic loci strongly affect nematode longevity, and have contributed to evolutionary modulation of its LS (Ayyadevara et al., 2003). Although numerous loci have been identified in C. elegans, at which mutations can extend LS (Kenyon et al., 1993; Lithgow et al., 1995; Wong et al., 1995; Lakowski and Hekimi, 1996, 1998; Tissenbaum and Ruvkun, 1998; Apfeld and Kenyon, 1999; Lin et al., 2000; Wolkow et al., 2000; Lithgow and Walker, 2002; McElwee et al., 2004; Morley and Morimoto, 2004; Hansen et al., 2005), most such mutations are expected to reduce fitness under natural selection. Indeed, this must be true in at least some environments, to explain the absence of those long-lived alleles from wild-derived populations, where they would have quickly become fixed if they conferred any fitness benefit. Considering that wild-type alleles have been honed by natural selection over countless generations, the likelihood must be quite small that any given random mutation would improve the primary function of the gene product. QTL mapping, in contrast, compares the effects of naturally occurring variants that have already “proven” their benefit (or neutrality) with respect to fitness selection. Among quantitative trait loci, the longer-lived allele may also show reduced Darwinian fitness, but this is not true of most such loci (Ayyadevara et al., 2003, 2008; Shmookler Reis et al., 2007, 2009).
We have now demonstrated that a region on chromosome IV near marker stP35 (genetic position + 10 cM; 13.53 Mb on the chromosome IV physical map) contains a QTL polymorphism affecting LS in C. elegans. The two tested alleles of this lsq4 polymorphism differ in longevity by 14–28%, whether worms were maintained in liquid suspension culture or on agar, and with little apparent regard for which parent provided the genetic background (through recurrent backcrossing). Seven independent recombinant lines derived from one of these congenic lines confirmed a marked allelic effect on longevity; i.e., median longevities in the longer-lived lines were 24–28% greater than those observed in the shorter-lived group.
Fine-mapping of the seven recombinant lines by “anchor-PCR display” (Ayyadevara et al., 2000a) expanded the initial set of three dimorphic markers to a total of 29, covering the region from stP13 to just beyond stP35. The recombinants partition these 29 markers into 10 clusters or subregions, in a unique order, allowing the position of lsq4 to be defined in absolute terms. Whereas interval mapping can only indicate QTL location stochastically, as a likelihood distribution (Ebert et al., 1996, 1993; Lynch and Walsh, 1998; Ayyadevara et al., 2001, 2003), mapping of congenic lines and their recombinants sets true proximal-marker boundaries for the QTL, and allows their placement on the physical map. In this case, lsq4 must lie between markers G7 and T6, situated at 13.15 and 14.33 Mb in the chromosome IV genomic sequence of C. elegans (Figure 4), based on PCR sequencing of Tc1-flanking DNA in the corresponding bands. Because markers G1, G2, and C4 always agreed (i.e., were allele-concordant) with stP35, no further narrowing of the interval is possible without adding new markers and/or recombinants. We conducted simultaneous discovery and typing of SNPs by determining genomic sequences for the initial strains and all recombinants terminating within the G7–T6 interval. The QTL interval was thus narrowed from 1.18 to 0.30 Mb, as indicated in Figure 4C. At this level of resolution (∼0.3% of the genome), resistance to stresses was shown to co-localize with the lsq4 longevity QTL (Figure 7).
A second-round of recombinant screening further narrowed the QTL interval for longevity. The introgressed, BO-derived segment in line SR706 includes snp_W02A2 from the left (Figure 4C), while the BO-derived region in SR723 crosses stP35 from the right (Figure 4C), yet neither line differs from CL2a in longevity. Thus, the QTL interval must be smaller than the span from snp_W02A2 (13.35 Mb) to stP35 (13.53 Mb), i.e., roughly 180 kbp. No further rounds were attempted because as intervals shorten, the frequency of further narrowing by recombination declines, requiring greater effort to achieve diminishing returns.
In terms of effect on median LS, the lsq4 alleles differ by 19 ± 1.6% (for eight comparisons of CL2a to the initial congenic lines, SR700 and SR701) or 31 ± 7% (for 10 comparisons of CL2a to SR701 and four further-outcrossed recombinants, as listed in Table 1). The difference between these estimates may reflect separation of lsq4 from nearby countervailing QTLs of lesser effect (which are suggested by the data of Figure 3). In view of the large number of QTLs influencing a highly polygenic trait such as LS (Ayyadevara et al., 2003; Magwire et al., 2010), QTLs with such large allelic effects must be exceptional. To place this in perspective, an allelic effect on LS of 19–31% is comparable to those of many mutations to “longevity genes,” most of which increase wild-type survival by 10–50% (Friedman and Johnson, 1988; Malone et al., 1996; Cypser and Johnson, 1999; Yang and Wilson, 1999; McKay et al., 2004). With respect to thermotolerance survival time, the ≥1.7-fold difference between lsq4 alleles is actually larger than effects observed for most longevity mutants (Duhon et al., 1996; Shmookler Reis et al., 2007; Ayyadevara et al., 2008).
The 26 genes situated in the lsq4 interval encode some interesting candidate proteins for which plausible functional roles in longevity could be proposed. FAR-6, a fatty-acid/retinol binding protein, is intriguing because of the known role of lipid composition in inflammation, innate immunity and longevity (see Shmookler Reis et al., 2011 and references therein); it actually lies immediately outside the lsq4 interval defined by SNP analyses, but may be involved indirectly (see below). REC-8 is a “cohesin” required for meiotic recombination (Ayyadevara et al., submitted), and AGT-1 is an O6-alkyl-guanosine DNA-methyltransferase important in DNA repair (Jena and Bansal, 2011); each could contribute to longevity via the maintenance of genomic stability (Garcia et al., 2010). Three putative transcription factors, including MEX-5 (a dual-zinc-finger protein), could underlie some of the transcript-profile changes observed for longevity mutants (Gems and McElwee, 2005; Kim, 2007; Ayyadevara et al., 2009). SRSX-25 is a 7-transmembrane receptor of the rhodopsin family, while NLP-17 is a putative neuropeptide; either may mediate sensory signaling implicated in nematode longevity (Apfeld and Kenyon, 1999; Greer et al., 2008; McGrath et al., 2009). RPA-2 is a large ribosomal subunit protein, PUF-3 a translational repressor, NOL-9 a presumed nucleolar protein, and DCAP-2 an mRNA decapping enzyme, each with the potential to extend LS by attenuating translation (Hansen et al., 2007). RAB-19 is a presumed RAS family member, while TBC-9 has RabGAP/TBC homology; these two members of the RAS (small monomeric GTPase) family may be involved in age-dependent modulation of cell-membrane signaling receptors (Nanji et al., 2005; Curran and Ruvkun, 2007; Lai et al., 2007). MAU-8, a mitochondrial inner-membrane protein, and a ferredoxin-like oxidoreductase, are electron transporters involved in cell energetics as well as oxidative-damage defense (Dillin et al., 2002; Lai et al., 2007). In addition, three protein kinases and a putative phosphatase could affect longevity via diverse signal-transduction pathways (Greer and Brunet, 2009; Tazearslan et al., 2009).
Evidence presented elsewhere (Ayyadevara et al., submitted) strongly implicates rec-8 as a dimorphic gene which (based on transcript levels and the effects of their disruption by RNA interference, (RNAi) could account for all of the traits associated with lsq4. Curiously, interference with expression of the far-6 gene (lying only 20 kbp from rec-8) also increases longevity – although somewhat less than rec-8 RNAi. It is not known whether life extension actually results from the combined effects of two dimorphic longevity-affecting genes that are phase-coupled via tight linkage, or arises solely from dimorphic rec-8 expression, with far-6 “artifactually” implicated through an indirect mechanism such as transcriptional coupling (Wang et al., 2011).
Materials and Methods
Strains
Caenorhabditis elegans strain CL2a (DR1345), isolated in California in 1972, is a wild-type strain with 28 Tc1 transposons embedded in its genome. Bergerac-BO (RW7000), isolated in France in 1949, is a “high-copy” strain with ∼500 Tc1 elements. Stock samples of Bergerac-BO (RW7000) and CL2a (DR1345) were obtained from the Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (St. Paul, MN, USA).
General methods
Worms were grown on plates of 1.7% agar in nematode growth medium (NGM; Sulston and Hodgkin, 1988) at 20°C. The plates were spotted with freshly grown E. coli (strain OP50, a leaky auxotroph for uracil) as described previously (Sulston and Hodgkin, 1988).
Generation of backcrossed lines
We constructed crosses in which 4–5 CL2a males were placed on each 35-mm agar/NGM plate (Sulston and Hodgkin, 1988), with a single immature (L4 larval-stage) Bergerac-BO hermaphrodite. Parental worms are transferred to fresh plates each 24 h, and the percent of males is assessed at maturity for each progeny plate. Although the predominant form of C. elegans is hermaphroditic (XX), mating occurs preferentially over self-fertilization in the presence of males (XO) and is indicated by the appearance of ∼50% males among the progeny. In subsequent “backcross” generations, four CL2a males are mated to single L4 hermaphrodites from the previous generation, on each of 10–12 35-mm plates. After successful mating, parental hermaphrodites are lysed for genotyping to determine the strain of origin for markers of the implicated QTL interval. Genotypes are determined by Tc1-dependent multiplex PCR, as described previously (Williams et al., 1992; Ebert et al., 1993). Progeny of tested worms, that retain the Bergerac-BO (Tc1+) allele at all three QTL markers, are used in subsequent backcross generations, for a total of 20 generations. Two lines constructed in this way, SR700 and SR701, were maintained as independent lineages for the final 10 generations. Homozygotes are not directly distinguished from heterozygotes in this PCR assay, but were identified by genotyping four progeny, followed by a further eight if all of the initial four were Tc1+ for all QTL markers. The probability of observing 12/12 Tc1+ progeny by chance from a heterozygote is 0.7512 or ∼0.03 (0.75 being the chance that any given offspring of a heterozygous worm will have one or two Tc1+ alleles).
Recombinants on chromosome IV
Recombinants were identified among SR701 progeny during the two final backcross generations to CL2a, essentially as described in the preceding section, by PCR screening for loss of either the stP13 (left-boundary) or stP35 (right-boundary) BO/Tc1 marker. Seven independent lineages were found harboring recombinations within the lsq4 interval: SR705, 706, and 707 retaining the stP13 and stP44 Tc1 markers from the BO parent (but losing stP35), SR711 retaining stP44 and stP35 (losing stP13), and SR708, 709, and 710 retaining only stP35 (see Figure 4C). From each of these lineages, 12 F3 hermaphrodites were picked to individual plates and allowed to self-fertilize in order to create homozygous lines as detailed above.
Second-round recombinants were screened for loss of either the G7 (left) or T6 (right) Tc1 marker of Bergerac-BO parental origin. DNA for each marker was excised from Anchor-PCR display gels, extracted and sequenced, allowing physical locations to be established by BLAST interrogation of the C. elegans genome. PCR assays were then designed (see the Figure 6B legend for details). Three new recombinants were found that had lost the BO-origin G7 marker (SR721, 722, and 723), and one that had lost the T6 marker (SR720), as depicted in Figure 6B.
Survival procedures
After worms had been grown for several generations without depletion of bacteria, they were harvested by washing with S buffer (Sulston and Hodgkin, 1988) into 15-mL plastic tubes (Falcon). Adults and older larvae were allowed to settle for 5 min, and then 100-μL aliquots of suspension containing only L1 larvae were transferred to fresh agar plates containing the OP50 strain of E. coli. These were monitored and transferred daily onto fresh plates with bacterial lawns. Survival cultures were set up 1 day after the L4/adult molt, incubated at 20°C, and were counted and transferred daily to fresh survival medium. Worms were considered dead when they failed to move, either spontaneously or in response to touch. Survival calculations exclude worms that die from surface desiccation (stranding) or internal hatching of progeny (bagging), or that are lost by burrowing or in transfer.
For assessment of survival in liquid medium, groups of ∼30 worms were transferred to 60-mm plates containing 3 mL of survival medium (S-basal + 10 μg/mL cholesterol + 109 bacteria/mL). To block development of progeny, 100 μM each of 5-fluoro-2′deoxyuracil (FUdR, Sigma) and uridine monophosphate (UMP, as 2′,3′ mixed isomers, Sigma) were added to the survival medium through day 10. For survivals on solidified agar medium, adult worms were picked as above in sets of 30, to 35-mm plates containing 1.7% agar in NGM as described above. These plates had been allowed to absorb a small volume of FUdR/UMP stock (to 100 μM each, final concentration) just before seeding with OP50 E. coli, 24 h before adding worms.
Multiplex PCR reactions to assess lsq4 genotypes
Worms were picked individually to 0.5-mL microfuge tubes containing 10 μL of lysis solution (50 mM KCl, 10 mM Tris pH 8.3, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 0.45% NP40, 0.45% Tween-20, 0.01% gelatin, 60 μg/mL proteinase K) and processed as described (Williams et al., 1992). Tubes were incubated at −70°C for 1 h, followed by 65°C for 75 min, and then 94°C for 30 min; finally, tubes were briefly centrifuged (15 s at 3000 rpm) to remove condensation. PCR buffer consists of 50-mM Tris–Cl pH 8.5, 1.5-mM MgCl2, 20-mM KCl, 0.5 mg/mL bovine serum albumen, 2.5% (w/v) Ficoll (Sigma), and 1-mM tartrazine. PCR was performed on an Idaho Technology hot-air thermal cycler, in sealed capillary tubes containing a final volume of 10 μL. Oligonucleotide primers, synthesized by Integrated DNA Technologies, include three “flanking” primers specific for the stP13, stP44, and stP35 Tc1-insertion sites in Bergerac-BO (Williams et al., 1992), and a common opposing primer from a conserved subterminal sequence of Tc1, “Tc1-20.” These three site-specific primers span the lsq4 region of chromosome IV, as most broadly defined from QTL-mapping. PCR reactions, in 10 μL, contain 1.0 μL worm lysate (0.1 worm-equivalent), 2.0 μL PCR buffer, 1.0 μL dNTPs, 1.4 μL common primer Tc1-20 (final concentration, 1.4 μM), 1.0 μL each of flanking primers (final concentration, 1.0 μM each), 0.1 μL Taq DNA polymerase (GIBCO/BRL), and 4.7 μL ddH2O.
After initial denaturation (45 s at 94°C), 38 PCR cycles each comprised denaturation (3s at 94°C), annealing (30 s at 54°C), and extension (30 s at 72°C), followed by final extension for 7 min at 72°C. Amplification products were electrophoresed 1.5 h at 10 V/cm on 2% agarose gels – a 3:1 mixture of NuSieve (FMC) and low-melting-point agarose (Sigma) – and stained in ethidium bromide, 0.5 μg/mL. Fragment sizes were determined by comparison to a 100-bp DNA ladder (GIBCO/BRL).
Anchor-PCR display for fine-mapping
An anchor comprising two partial–duplex oligonucleotides is ligated to cohesive ends generated by restriction cleavage of genomic DNA (employing, in this case, Sau3AI endonuclease). Tc1-specific primers were selected from subterminal sequences conserved among most or all Tc1 elements; in principle, any conserved, interspersed repeat sequence could be similarly employed provided its insertion sites differ among strains. PCR must initiate from the Tc1-specific primers, because an anchor primer, identical to one strand of the anchor (but non-complementary to the other strand due to intentional mismatch), can anneal only after full-length extension from the Tc1 primer creates its true complementary strand. Each anchor primer is designed to extend one base beyond the anchor sequence, terminating in a 3′ C, G, or T which thus reduces the complexity of PCR products fourfold.
Nematode DNA was purified using a Puregene kit and protocol, digested with Sau3A restriction enzyme (6 units per μg DNA, 1 h at 37°C), and then ligated to an “anchor” partial duplex consisting of oligonucleotides 5′UAW and 5′UAC (Ayyadevara et al., 2000a). PCR for fine-mapping of initial recombinants followed a two-stage, nested-primer protocol to increase specificity (Ayyadevara et al., 2000a). (1) Ligated DNA, isolated using QIAquick™ PCR purification (Qiagen), was amplified using a universal anchor primer (UAP) and “Tc1-20” primer (Ayyadevara et al., 2000a), thus specifying targets adjoining Tc1-insertions. Rapid thermal cycling (Idaho Technology ATC™) comprised an initial denaturation step (45 s at 94°C), then 12 cycles each consisting of 10 s at 94°C, 30 s at 58°C, and 60 s at 72°C, followed by a final extension of 15 min at 72°C. (2) For the second amplification stage, full-length DNA products were recovered (QIAquick, as above), diluted 1000-fold, and further amplified with a fluor-tagged Tc1-E primer (annealing to Tc1 terminal-repeat sequence distal to Tc1-20) and one of three UAP anchor primers, modified by addition of a 3′ C, G, or T to reduce the complexity of PCR products. Products from parental and recombinant PCRs were combined, electrophoresed (with the three different base extensions loaded in separate lanes), and visualized by differential fluorescent labeling of parental vs. recombinant amplimers.
For the second-round of recombinants, only a single UAP anchor primer was needed due to the already limited complexity of Tc1-derived bands in the starting material.
Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) assays
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms and restriction–cleavage–differential SNPs (snip-SNPs) in the lsq4 vicinity were tested for dimorphism between parental strains CL2a and Bergerac-BO. Candidate sites were selected from a SNP database (http://www.wormbase.org/db/searches/strains). We utilized primers, as listed in the C. elegans SNP database, to amplify the snip-SNP DNA fragment from strains Bergerac-BO, CL2a, and SR708. PCR was performed in a thermal cycler (MJ Research) for 30 cycles, each comprising the following steps: denaturation at 94°C for 10 s, annealing at 58°C for 20 s, and extension at 72°C for 30 s. The 30 PCR cycles were preceded by a 45 s initial denaturation at 94°C, and followed by a final 15-min extension at 72°C. Snip-SNP PCR products were digested with the appropriate restriction enzyme and electrophoresed in 1% agarose gels to resolve the resulting DNA fragments. The following snip-SNPs were indeed dimorphic between strains Bergerac-BO and CL2a (and were used to map congenic recombinants thereof): snp_F58D2[2] (13.18 Mb, in gene gadr-1), pkP4058 (13.35 Mb, in the rec-8 gene, W02A2), pkP4059 (13.49 Mb, in Y45F10A.6), pkP4091 (13.81 Mb, in Y45F10D), and pkP4092 (13.95 Mb, in C27H2.2/C27H2.3).
Clones carrying a reported conventional SNP (F09E8, F78D2, C48D1, JC8, Y52G2, Y45F10B, C08F11, Y45F10C, T23G4, F52D4, Y37A1A, C52H2, and Y37A1B) were PCR-amplified using primers flanking the SNP. Sequence information for primers was obtained from the same SNP database (see above); amplification conditions were the same for conventional SNP-containing targets as for snip-SNP PCR (see above).
SNP discovery by DNA sequencing
Typing strains for known SNPs enabled further narrowing of the recombination break-points in the lsq4 interval, but left several gaps devoid of markers. To seek additional SNPs in those residual intervals, we determined sequences of DNA fragments amplified by PCR, reading 600–750 nucleotides by capillary electrophoresis every ∼50 kbp. Amplified SNP fragments were electrophoresed in a 1% agarose gel and bands were eluted with a DNA gel extraction kit (Qiagen). The DNA obtained from gel purification was used for sequence determination on a CEQ8000 (Beckman) or ABI 3100 (Perkin-Elmer) capillary electrophoresis system, with both forward and reverse primers. Sequencing was used both to determine marker typing in fine-mapping of recombinants, and to confirm key results obtained by PCR assays.
Thermotolerance assay
Assay conditions were modified from Lithgow et al. (1995). After propagation for several generations without depletion of bacteria, L1 larvae of strains/lines CL2a, SR701, SR706, SR708, and SR710 were synchronized by settling (see above) and allowed to mature at 20°C. One day after the L4/young–adult molt, worms were picked into 60-mm agar plates and incubated by immersion to a depth of 0.5 cm in a 35.5°C water bath, supported by a perforated metal stand. Plates were removed individually at 4 h and at 2-h intervals thereafter, and worms were scored (in the same sequence) for spontaneous motility, provoked movement, and pharyngeal pumping. Worms failing to display any of these traits were scored as dead.
Paraquat resistance assay
Worms were exposed as 3-day old adults, in groups of 30, to varying concentrations of paraquat (0–85 mM) in liquid survival medium at 20°C. Medium with paraquat was replaced daily, and the number of live worms was counted after 3 days of exposure (conditions modified from Ishii et al., 1998 and Cypser and Johnson, 1999).
Hydrogen peroxide resistance assay
At 5 days post-hatch, replicate groups of 50 adult worms were washed in magnesium-free M9 medium (Sulston and Hodgkin, 1988) and then incubated 4 h at 20°C with 4–12 mM H2O2 (freshly diluted from a newly opened bottle of 3% peroxide, Sigma) in fresh magnesium-free M9 with gentle agitation; conditions of exposure were modified from (Ebert et al., 1996). Viability was assessed as above, immediately after the 4-h exposure period.
Ultraviolet resistance assay
Young adult worms (4 days post-hatch), in groups of 30 from each strain, were transferred onto 60-mm dishes without bacteria and were irradiated from above with UV light (Stratagene Model 1800 Stratalinker, at 0.4 J/cm2) while on the surface of NGM/agar plates without E. coli at 20°C. Worms were then transferred to fresh agar plates seeded with E. coli strain OP50. Survival of the worms was assayed at 24-h intervals until all worms were dead.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We thank Vasudha Kondopally, Rajani Ayyadevara, Sen Hou and Ramani Alla for expert technical assistance. This work was funded by grants R01-AG091413 and P01-AG20641 from the National Institute on Aging (National Institutes of Health), and by support to Robert J. Shmookler Reis from the Department of Veteran Affairs, including a Research Career Scientist Award.
Abbreviations
BO, C. elegans var. Bergerac-BO (here, strain RW7000 from R. Waterston); cDNA, complementary DNA; CL2a, C. elegans var. Cl2a (here strain DR1345 from D. Riddle); LS, life-span, MLS, maximum life-span (i.e., the life-span of the last-surviving worm in a cohort); N2, C. elegans var. Bristol-N2 (here, subline N2-DRM from D. Riddle); NC, no change; NGM, nematode growth medium; NS, not significant; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; QTL, quantitative trait locus; RNAi, RNA interference; RT-PCR, real-time, reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction; SD, standard deviation; SEM, standard error of the mean; SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism; UV, ultraviolet.
References
- Apfeld J., Kenyon C. (1999). Regulation of lifespan by sensory perception in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 402, 804–809 10.1038/45544 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayyadevara S., Alla R., Thaden J. J., Shmookler Reis R. J. (2008). Remarkable longevity and stress resistance of nematode PI3K-null mutants. Aging Cell 7, 13–22 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2007.00348.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayyadevara S., Ayyadevera R., Hou S., Thaden J. J., Shmookler Reis R. J. (2001). Genetic mapping of quantitative trait loci governing longevity of Caenorhabditis elegans in recombinant-inbred progeny of a Bergerac-BO × RC301 interstrain cross. Genetics 157, 655–666 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayyadevara S., Ayyadevera R., Vertino A., Galecki A., Thaden J. J., Shmookler Reis R. J. (2003). Genetic loci modulating fitness and life span in Caenorhabditis elegans: categorical trait interval mapping in CL2a × Bergerac-BO recombinant-inbred worms. Genetics 163, 557–570 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayyadevara S., Tazearslan C., Alla R., Bharill P., Siegel E. R., Shmookler Reis R. J. (2009). C. elegans PI3K mutants reveal novel genes underlying exceptional stress resistance and lifespan. Aging Cell 8, 706–725 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2009.00524.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayyadevara S., Thaden J. J., Shmookler Reis R. J. (2000a). Anchor polymerase chain reaction display: a high-throughput method to resolve, score, and isolate dimorphic genetic markers based on interspersed repetitive DNA elements. Anal. Biochem. 284, 19–28 10.1006/abio.2000.4635 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayyadevara S., Thaden J. J., Shmookler Reis R. J. (2000b). Discrimination of primer 3′-nucleotide mismatch by Taq DNA polymerase during polymerase chain reaction. Anal. Biochem. 284, 1–18 10.1006/abio.2000.4635 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri M., Bonafe M., Franceschi C., Paolisso G. (2003). Insulin/IGF-I-signaling pathway: an evolutionarily conserved mechanism of longevity from yeast to humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 285, E1064–E1071 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beekman M., Nederstigt C., Suchiman H. E., Kremer D., van der Breggen R., Lakenberg N., Alemayehu W. G., de Craen A. J., Westendorp R. G., Boomsma D. I., de Geus E. J., Houwing-Duistermaat J. J., Heijmans B. T., Slagboom P. E. (2010). Genome-wide association study (GWAS)-identified disease risk alleles do not compromise human longevity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 18046–18049 10.1073/pnas.1003540107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti M. G., Foster A. L., Vantipalli M. C., White M. P., Sampayo J. N., Gill M. S., Olsen A., Lithgow G. J. (2008). Compounds that confer thermal stress resistance and extended lifespan. Exp. Gerontol. 43, 882–891 10.1016/j.exger.2008.08.049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berdichevsky A., Viswanathan M., Horvitz H. R., Guarente L. (2006). C. elegans SIR-2.1 interacts with 14-3-3 proteins to activate DAF-16 and extend life span. Cell 125, 1165–1177 10.1016/j.cell.2006.04.036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonafe M., Barbieri M., Marchegiani F., Olivieri F., Ragno E., Giampieri C., Mugianesi E., Centurelli M., Franceschi C., Paolisso G. (2003). Polymorphic variants of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) receptor and phosphoinositide 3-kinase genes affect IGF-I plasma levels and human longevity: cues for an evolutionarily conserved mechanism of life span control. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88, 3299–3304 10.1210/jc.2002-021810 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrano A. C., Liu Z., Dillin A., Hunter T. (2009). A conserved ubiquitination pathway determines longevity in response to diet restriction. Nature 460, 396–399 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran S. P., Ruvkun G. (2007). Lifespan regulation by evolutionarily conserved genes essential for viability. PLoS Genet. 3, e56. 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030056 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis C., Landis G. N., Folk D., Wehr N. B., Hoe N., Waskar M., Abdueva D., Skvortsov D., Ford D., Luu A., Badrinath A., Levine R. L., Bradley T. J., Tavare S., Tower J. (2007). Transcriptional profiling of MnSOD-mediated lifespan extension in Drosophila reveals a species-general network of aging and metabolic genes. Genome Biol. 8, R262. 10.1186/gb-2007-8-12-r262 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cypser J. R., Johnson T. E. (1999). The spe-10 mutant has longer life and increased stress resistance. Neurobiol. Aging 20, 503–512 10.1016/S0197-4580(99)00085-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillin A., Hsu A. L., Arantes-Oliveira N., Lehrer-Graiwer J., Hsin H., Fraser A. G., Kamath R. S., Ahringer J., Kenyon C. (2002). Rates of behavior and aging specified by mitochondrial function during development. Science 298, 2398–2401 10.1126/science.1074240 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duhon S. A., Murakami S., Johnson T. E. (1996). Direct isolation of longevity mutants in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Genet. 18, 144–153 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert R. H., Cherkasova V. A., Dennis R. A., Wu J. H., Ruggles S., Perrin T. E., Shmookler Reis R. J. (1993). Longevity-determining genes in Caenorhabditis elegans: chromosomal mapping of multiple noninteractive loci. Genetics 135, 1003–1010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert R. H., Shammas M. A., Sohal B. H., Sohal R. S., Egilmez N. K., Ruggles S., Shmookler Reis R. J. (1996). Defining genes that govern longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Genet. 18, 131–143 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egilmez N. K., Ebert R. H., Shmookler Reis R. J. (1995). Strain evolution in Caenorhabditis elegans: transposable elements as markers of interstrain evolutionary history. J. Mol. Evol. 40, 372–381 10.1007/BF00164023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. B., Johnson T. E. (1988). A mutation in the age-1 gene in Caenorhabditis elegans lengthens life and reduces hermaphrodite fertility. Genetics 118, 75–86 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gami M. S., Iser W. B., Hanselman K. B., Wolkow C. A. (2006). Activated AKT/PKB signaling in C. elegans uncouples temporally distinct outputs of DAF-2/insulin-like signaling. BMC Dev. Biol. 6, 45. 10.1186/1471-213X-6-45 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia A. M., Calder R. B., Dolle M. E., Lundell M., Kapahi P., Vijg J. (2010). Age- and temperature-dependent somatic mutation accumulation in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS Genet. 6, e1000950. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000950 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger-Thornsberry G. L., Mackay T. F. (2004). Quantitative trait loci affecting natural variation in Drosophila longevity. Mech. Ageing Dev. 125, 179–189 10.1016/j.mad.2003.12.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gems D., McElwee J. J. (2005). Broad spectrum detoxification: the major longevity assurance process regulated by insulin/IGF-1 signaling? Mech. Ageing Dev. 126, 381–387 10.1016/j.mad.2004.09.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer E. L., Brunet A. (2009). Different dietary restriction regimens extend lifespan by both independent and overlapping genetic pathways in C. elegans. Aging Cell 8, 113–127 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2009.00459.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer E. L., Dowlatshahi D., Banko M. R., Villen J., Hoang K., Blanchard D., Gygi S. P., Brunet A. (2007). An AMPK-FOXO pathway mediates longevity induced by a novel method of dietary restriction in C. elegans. Curr. Biol. 17, 1646–1656 10.1016/j.cub.2007.08.047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer E. R., Perez C. L., Van Gilst M. R., Lee B. H., Ashrafi K. (2008). Neural and molecular dissection of a C. elegans sensory circuit that regulates fat and feeding. Cell Metab. 8, 118–131 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.06.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Kenyon C. (2000). Genetic pathways that regulate ageing in model organisms. Nature 408, 255–262 10.1038/35041700 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M., Hsu A. L., Dillin A., Kenyon C. (2005). New genes tied to endocrine, metabolic, and dietary regulation of lifespan from a Caenorhabditis elegans genomic RNAi screen. PLoS Genet. 1, 119–128 10.1371/journal.pgen.0010017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M., Taubert S., Crawford D., Libina N., Lee S. J., Kenyon C. (2007). Lifespan extension by conditions that inhibit translation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Aging Cell 6, 95–110 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2006.00267.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii N., Fujii M., Hartman P. S., Tsuda M., Yasuda K., Senoo-Matsuda N., Yanase S., Ayusawa D., Suzuki K. (1998). A mutation in succinate dehydrogenase cytochrome b causes oxidative stress and ageing in nematodes. Nature 394, 694–697 10.1038/29331 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jena N. R., Bansal M. (2011). Mutagenicity associated with O6-methylguanine-DNA damage and mechanism of nucleotide flipping by AGT during repair. Phys. Biol. 8, 046007. 10.1088/1478-3975/8/4/046007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson T. E., Wood W. B. (1982). Genetic analysis of life span in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 6603–6607 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4088 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapahi P., Chen D., Rogers A. N., Katewa S. D., Li P. W., Thomas E. L., Kockel L. (2010). With TOR, less is more: a key role for the conserved nutrient-sensing TOR pathway in aging. Cell Metab. 11, 453–465 10.1016/j.cmet.2010.05.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon C., Chang J., Gensch E., Rudner A., Tabtiang R. (1993). A C. elegans mutant that lives twice as long as wild type. Nature 366, 461–464 10.1038/366461a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K. (2007). Common aging pathways in worms, flies, mice and humans. J. Exp. Biol. 210, 1607–1612 10.1242/jeb.004887 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood T. B., Rose M. R. (1991). Evolution of senescence: late survival sacrificed for reproduction. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 332, 15–24 10.1098/rstb.1991.0028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klass M. R. (1983). A method for the isolation of longevity mutants in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans and initial results. Mech. Ageing Dev. 22, 279–286 10.1016/0047-6374(83)90082-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch R., van Luenen H. G., van der Horst M., Thijssen K. L., Plasterk R. H. (2000). Single nucleotide polymorphisms in wild isolates of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genome Res. 10, 1690–1696 10.1101/gr.GR-1471R [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo M., Yanase S., Ishii T., Hartman P. S., Matsumoto K., Ishii N. (2005). The p38 signal transduction pathway participates in the oxidative stress-mediated translocation of DAF-16 to Caenorhabditis elegans nuclei. Mech. Ageing Dev. 126, 642–647 10.1016/j.mad.2004.11.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. Q., Parnell L. D., Lyman R. F., Ordovas J. M., Mackay T. F. (2007). Candidate genes affecting Drosophila life span identified by integrating microarray gene expression analysis and QTL mapping. Mech. Ageing Dev. 128, 237–249 10.1016/j.mad.2006.12.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowski B., Hekimi S. (1996). Determination of life-span in Caenorhabditis elegans by four clock genes. Science 272, 1010–1013 10.1126/science.272.5264.1010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowski B., Hekimi S. (1998). The genetics of caloric restriction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95, 13091–13096 10.1073/pnas.95.22.13091 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. L., Albert P. S., Riddle D. L. (1995). Genes that regulate both development and longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 139, 1567–1583 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. T., Wang J. W. (2003). Statistical Methods for Survival Analysis New York: John Wiley and Sons [Google Scholar]
- Leips J., Gilligan P., Mackay T. F. (2006). Quantitative trait loci with age-specific effects on fecundity in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 172, 1595–1605 10.1534/genetics.105.048520 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leips J., Mackay T. F. (2000). Quantitative trait loci for life span in Drosophila melanogaster: interactions with genetic background and larval density. Genetics 155, 1773–1788 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leips J., Mackay T. F. (2002). The complex genetic architecture of Drosophila life span. Exp. Aging Res. 28, 361–390 10.1080/03610730290080399 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. J., Defossez P. A., Guarente L. (2000). Requirement of NAD and SIR2 for life-span extension by calorie restriction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science 289, 2126–2128 10.1126/science.289.5487.2126 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lithgow G. J., Walker G. A. (2002). Stress resistance as a determinate of C. elegans lifespan. Mech. Ageing Dev. 123, 765–771 10.1016/S0047-6374(01)00422-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lithgow G. J., White T. M., Melov S., Johnson T. E. (1995). Thermotolerance and extended life-span conferred by single-gene mutations and induced by thermal stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92, 7540–7544 10.1073/pnas.92.16.7540 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckinbill L. S., Golenberg E. M. (2002). Genes affecting aging: mapping quantitative trait loci in Drosophila melanogaster using amplified fragment length polymorphisms (AFLPs). Genetica 114, 147–156 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch M., Walsh B. (1998). Genetics and Analysis of Quantitative Traits Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates [Google Scholar]
- Magwire M. M., Yamamoto A., Carbone M. A., Roshina N. V., Symonenko A. V., Pasyukova E. G., Morozova T. V., Mackay T. F. (2010). Quantitative and molecular genetic analyses of mutations increasing Drosophila life span. PLoS Genet. 6, e1001037. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone E. A., Inoue T., Thomas J. H. (1996). Genetic analysis of the roles of daf-28 and age-1 in regulating Caenorhabditis elegans dauer formation. Genetics 143, 1193–1205 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto M., Han S., Kitamura T., Accili D. (2006). Dual role of transcription factor FoxO1 in controlling hepatic insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 2464–2472 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElwee J. J., Schuster E., Blanc E., Piper M. D., Thomas J. H., Patel D. S., Selman C., Withers D. J., Thornton J. M., Partridge L., Gems D. (2007). Evolutionary conservation of regulated longevity assurance mechanisms. Genome Biol. 8, R132. 10.1186/gb-2007-8-7-r132 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElwee J. J., Schuster E., Blanc E., Thomas J. H., Gems D. (2004). Shared transcriptional signature in Caenorhabditis elegans Dauer larvae and long-lived daf-2 mutants implicates detoxification system in longevity assurance. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 44533–44543 10.1074/jbc.M406207200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath P. T., Rockman M. V., Zimmer M., Jang H., Macosko E. Z., Kruglyak L., Bargmann C. I. (2009). Quantitative mapping of a digenic behavioral trait implicates globin variation in C. elegans sensory behaviors. Neuron 61, 692–699 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.02.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay J. P., Raizen D. M., Gottschalk A., Schafer W. R., Avery L. (2004). Eat-2 and eat-18 are required for nicotinic neurotransmission in the Caenorhabditis elegans pharynx. Genetics 166, 161–169 10.1534/genetics.166.1.161 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley J. F., Morimoto R. I. (2004). Regulation of longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans by heat shock factor and molecular chaperones. Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 657–664 10.1091/mbc.E03-07-0532 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanji M., Hopper N., Gems D. (2005). LET-60 RAS modulates effects of insulin/IGF-1 signaling on development and aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Aging Cell 4, 235–245 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2005.00166.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuzhdin S. V., Pasyukova E. G., Dilda C. L., Zeng Z. B., Mackay T. F. (1997). Sex-specific quantitative trait loci affecting longevity in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94, 9734–9739 10.1073/pnas.94.18.9734 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onken B., Driscoll M. (2010). Metformin induces a dietary restriction-like state and the oxidative stress response to extend C. elegans healthspan via AMPK, LKB1, and SKN-1. PLoS ONE 5, e8758. 10.1371/journal.pone.0008758 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasyukova E. G., Roshina N. V., Mackay T. F. (2004). Shuttle craft: a candidate quantitative trait gene for Drosophila lifespan. Aging Cell 3, 297–307 10.1111/j.1474-9728.2004.00114.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasyukova E. G., Vieira C., Mackay T. F. (2000). Deficiency mapping of quantitative trait loci affecting longevity in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 156, 1129–1146 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarrie J. K., Riabowol K. T. (2004). Murine models of life span extension. Sci. Aging Knowledge Environ. 2004, re5. 10.1126/sageke.2004.31.re5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiwitch S. G., Nuzhdin S. V. (2002). Quantitative trait loci for lifespan of mated Drosophila melanogaster affect both sexes. Genet. Res. 80, 225–230 10.1017/S0016672302005943 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. R., Drapeau M. D., Yazdi P. G., Shah K. H., Moise D. B., Thakar R. R., Rauser C. L., Mueller L. D. (2002). Evolution of late-life mortality in Drosophila melanogaster. Evolution 56, 1982–1991 10.1554/0014-3820(2002)056[1416:EITRWS]2.0.CO;2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampayo J. N., Jenkins N. L., Lithgow G. J. (2000). Using stress resistance to isolate novel longevity mutations in Caenorhabditis elegans. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 908, 324–326 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06665.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shmookler Reis R. J., Bharill P., Tazearslan C., Ayyadevara S. (2009). Extreme-longevity mutations orchestrate silencing of multiple signaling pathways. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1790, 1075–1083 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shmookler Reis R. J., Kang P., Ayyadevara S. (2007). Quantitative trait loci define genes and pathways underlying genetic variation in longevity. Exp. Gerontol. 41, 1046–1054 10.1016/j.exger.2006.06.047 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shmookler Reis R. J., Xu L., Lee H., Chae M., Thaden J. J., Bharill P., Tazearslan C., Siegel E., Alla R., Zimniak P., Ayyadevara S. (2011). Modulation of lipid biosynthesis contributes to stress resistance and longevity of C. elegans mutants. Aging (Albany NY) 3, 125–147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shook D. R., Brooks A., Johnson T. E. (1996). Mapping quantitative trait loci affecting life history traits in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 142, 801–817 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shook D. R., Johnson T. E. (1999). Quantitative trait loci affecting survival and fertility-related traits in Caenorhabditis elegans show genotype-environment interactions, pleiotropy and epistasis. Genetics 153, 1233–1243 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. D., Kennedy B. K., Kaeberlein M. (2007). Genome-wide identification of conserved longevity genes in yeast and worms. Mech. Ageing Dev. 128, 106–111 10.1016/j.mad.2006.11.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J., Hodgkin J. (1988). “Methods,” in The Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, ed. Wood W. B. (Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; ), 587–606 [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi A., Wartschow L. M., White M. F. (2007). Brain IRS2 signaling coordinates life span and nutrient homeostasis. Science 317, 369–372 10.1126/science.1142179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatar M., Kopelman A., Epstein D., Tu M. P., Yin C. M., Garofalo R. S. (2001). A mutant Drosophila insulin receptor homolog that extends life-span and impairs neuroendocrine function. Science 292, 107–110 10.1126/science.1057987 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazearslan C., Ayyadevara S., Bharill P., Shmookler Reis R. J. (2009). Positive feedback between transcriptional and kinase suppression in nematodes with extraordinary longevity and stress resistance. PLoS Genet. 5, e1000452. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000452 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissenbaum H. A., Ruvkun G. (1998). An insulin-like signaling pathway affects both longevity and reproduction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 148, 703–717 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troemel E. R., Chu S. W., Reinke V., Lee S. S., Ausubel F. M., Kim D. H. (2006). p38 MAPK regulates expression of immune response genes and contributes to longevity in C. elegans. PLoS Genet. 2, e183. 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020183 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira C., Pasyukova E. G., Zeng Z. B., Hackett J. B., Lyman R. F., Mackay T. F. (2000). Genotype-environment interaction for quantitative trait loci affecting life span in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 154, 213–227 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. Z., Lercher M. J., Hurst L. D. (2011). Transcriptional coupling of neighboring genes and gene expression noise: evidence that gene orientation and noncoding transcripts are modulators of noise. Genome Biol. Evol. 3, 320–331 10.1093/gbe/evr049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. D., Schrank C., Huynh R., Shownkeen R., Waterston R. H. (1992). A genetic mapping system in Caenorhabditis elegans based on polymorphic sequence-tagged sites. Genetics 131, 609–624 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolkow C. A., Kimura K. D., Lee M. S., Ruvkun G. (2000). Regulation of C. elegans life-span by insulin like signaling in the nervous system. Science 290, 147–150 10.1126/science.290.5489.147 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong A., Boutis P., Hekimi S. (1995). Mutations in the clk-1 gene of Caenorhabditis elegans affect developmental and behavioral timing. Genetics 139, 1247–1259 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Rogina B., Lavu S., Howitz K., Helfand S. L., Tatar M., Sinclair D. (2004). Sirtuin activators mimic caloric restriction and delay ageing in metazoans. Nature 430, 686–689 10.1038/nature02790 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y., Wilson D. L. (1999). Characterization of a life-extending mutation in age-2, a new aging gene in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 54, B137–B142 10.1093/gerona/54.4.B137 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn J. M., Kim S. K. (2007). Systems biology of aging in four species. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 18, 355–359 10.1016/j.copbio.2007.07.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]