Abstract
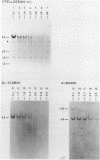
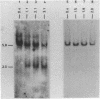
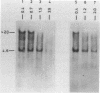
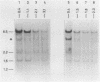
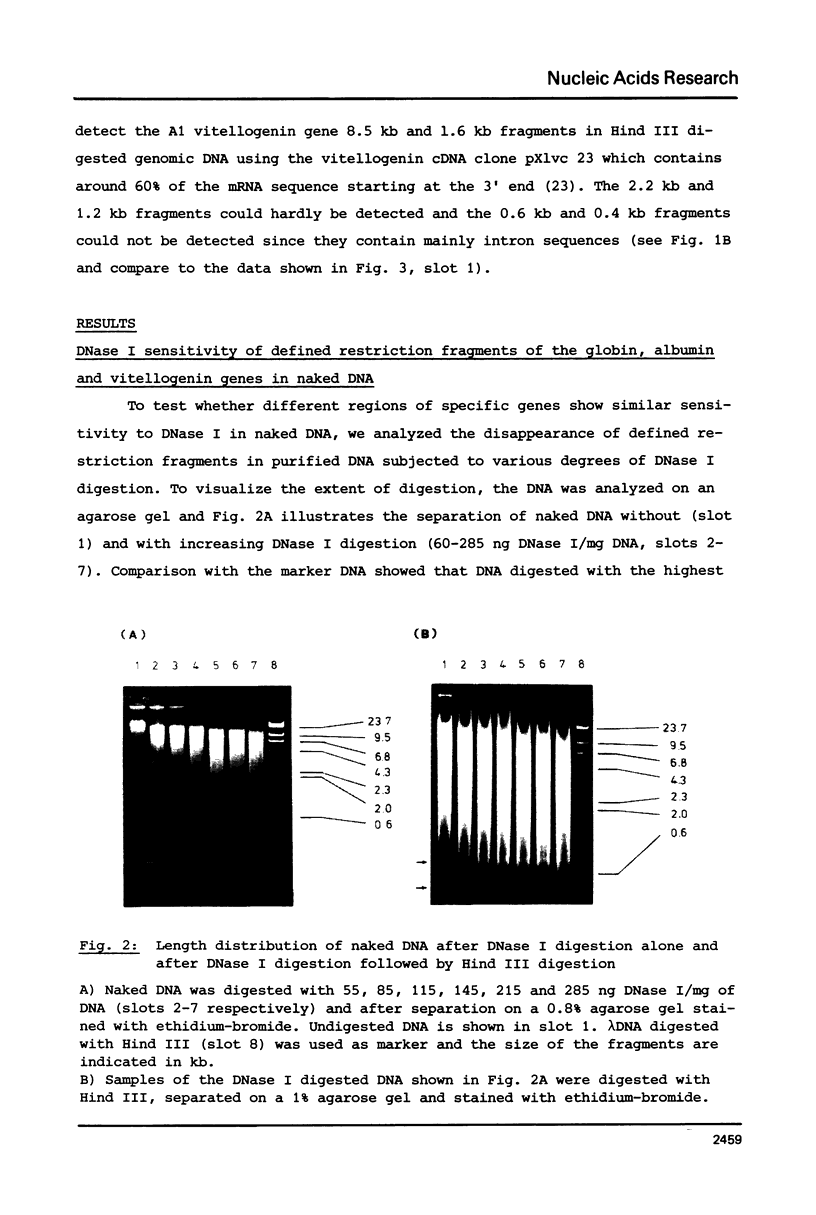
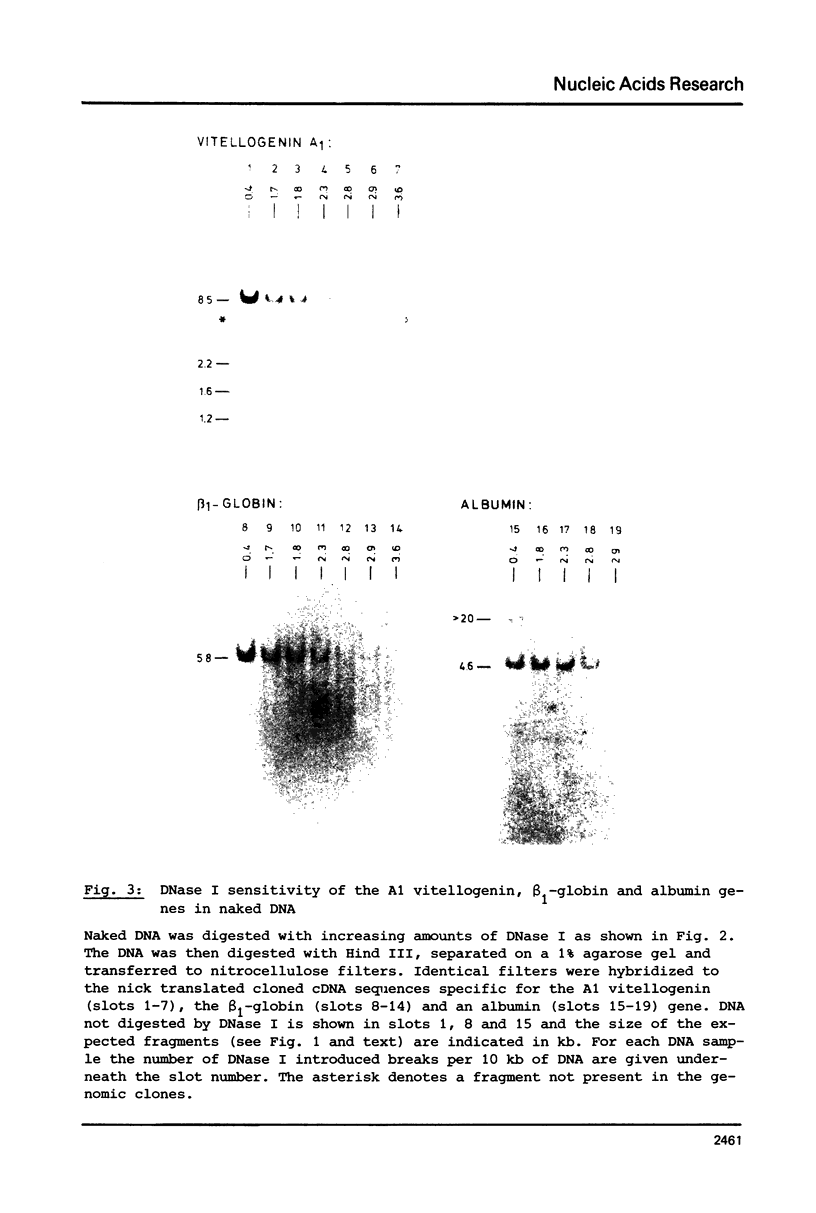
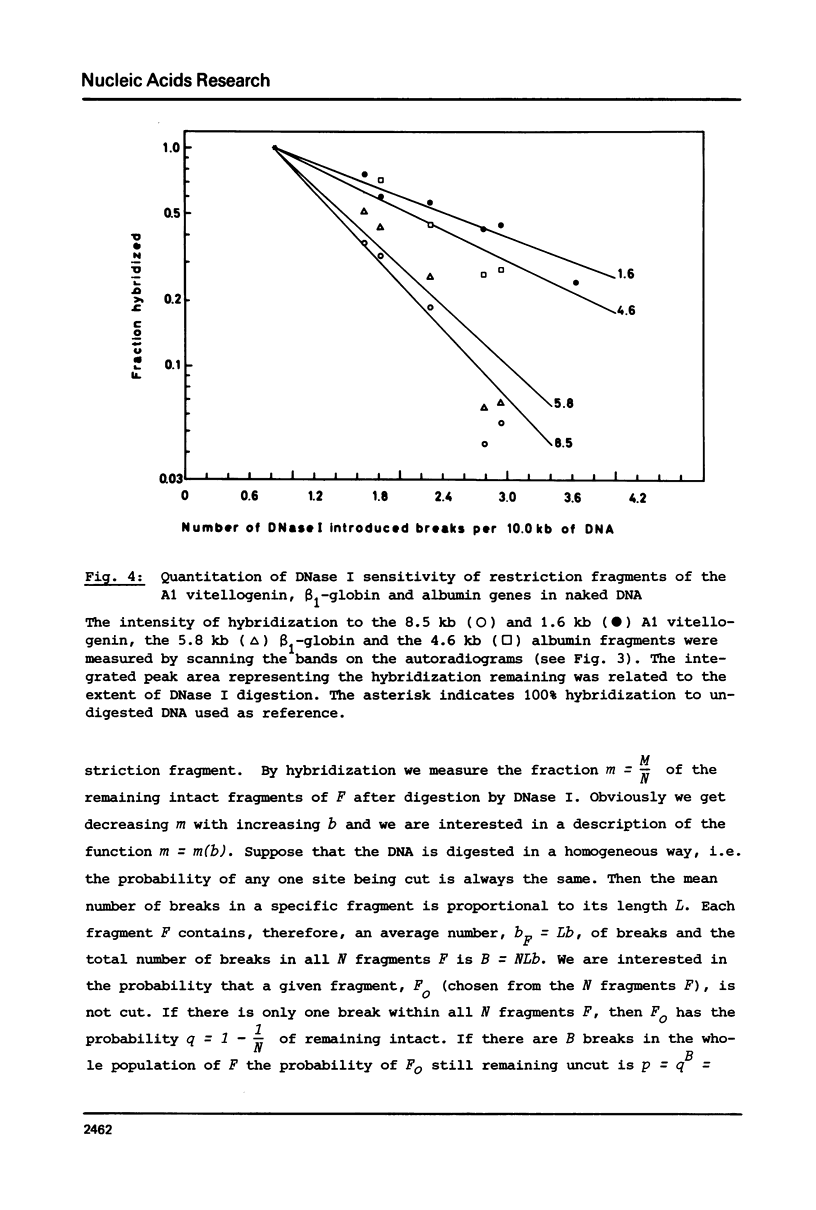
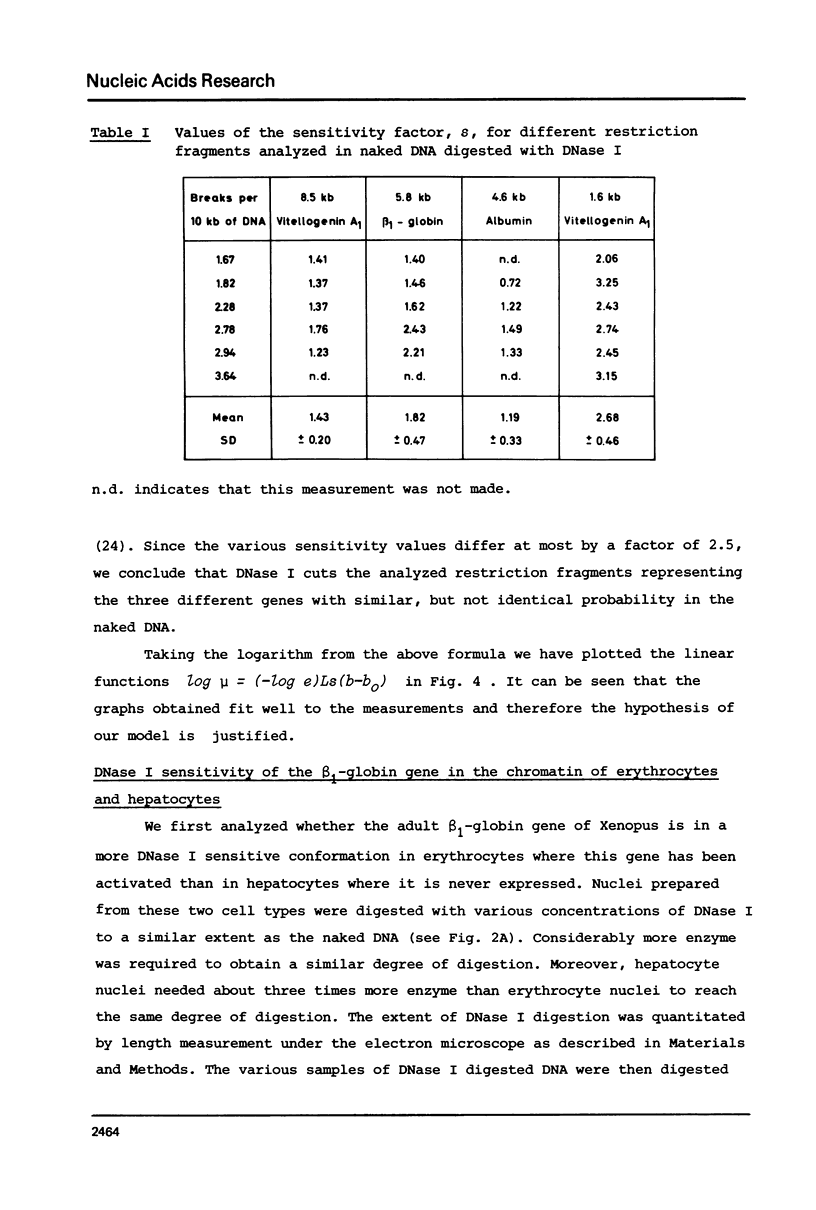
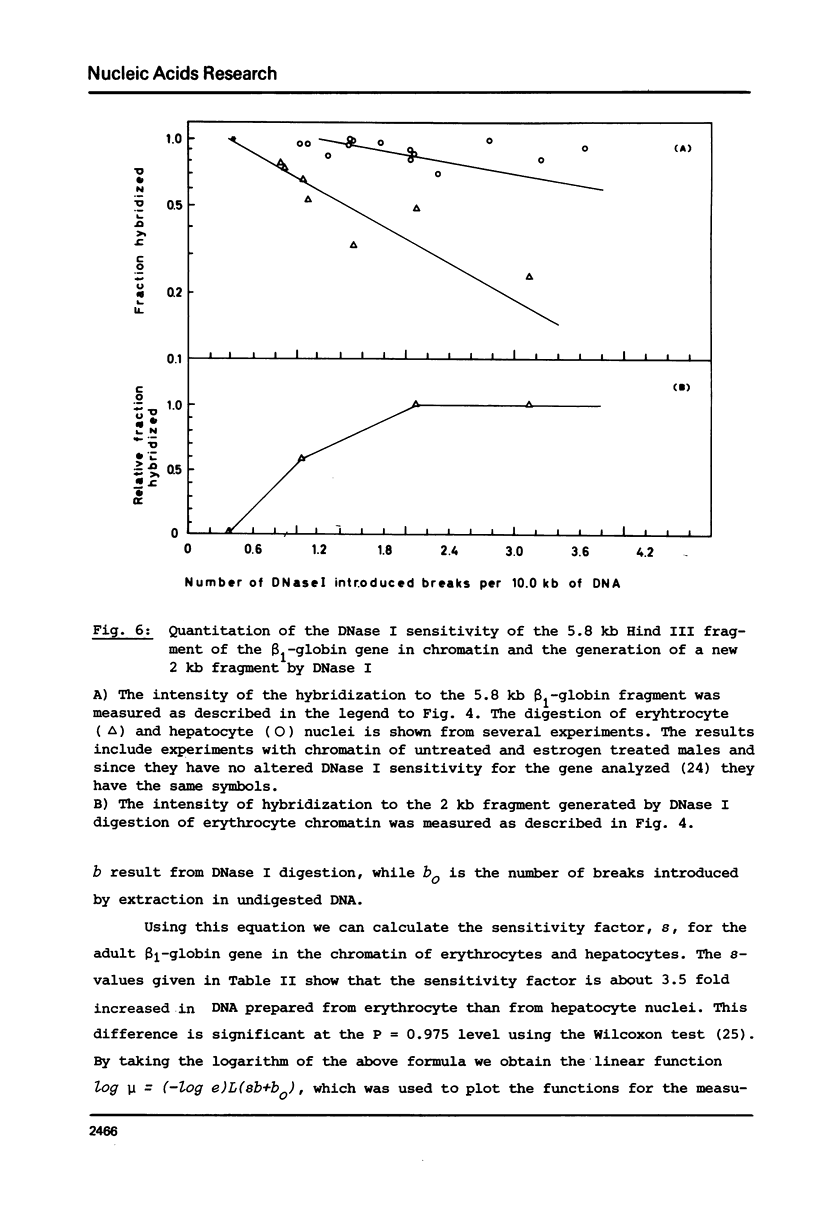
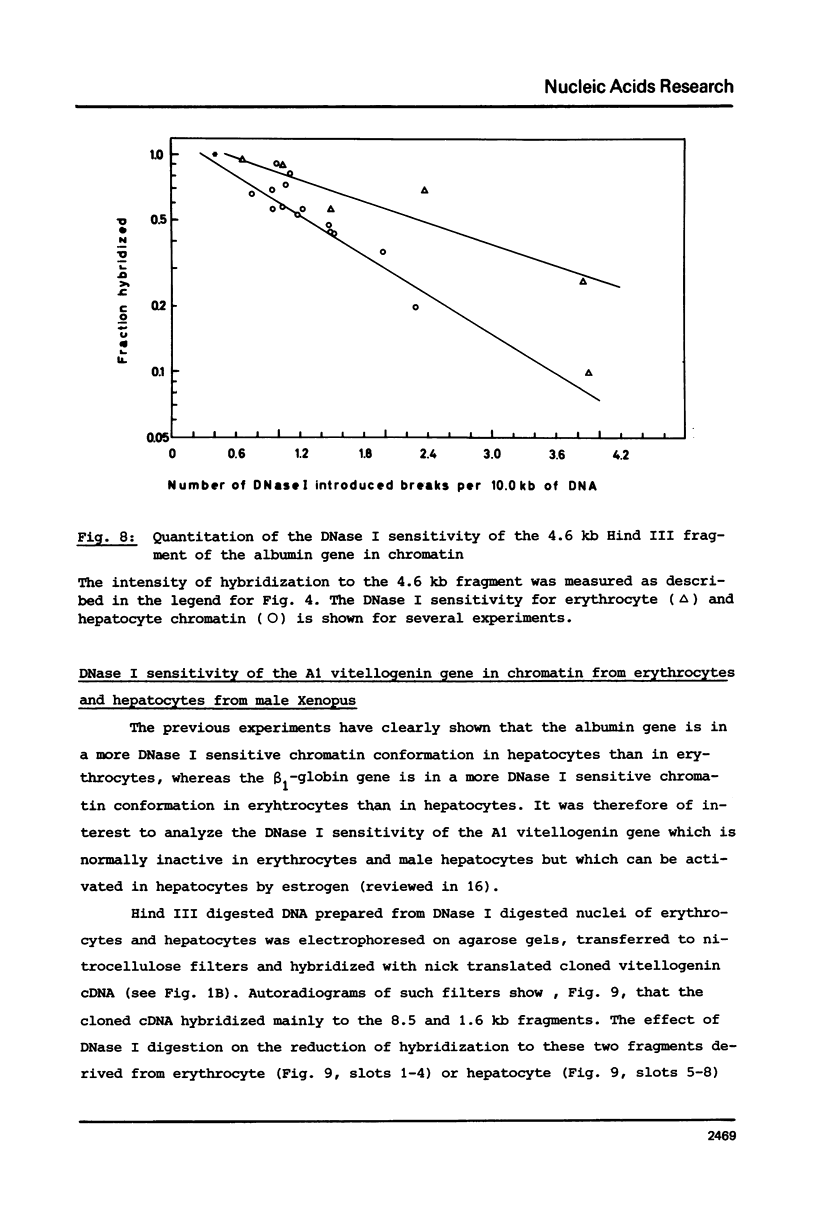
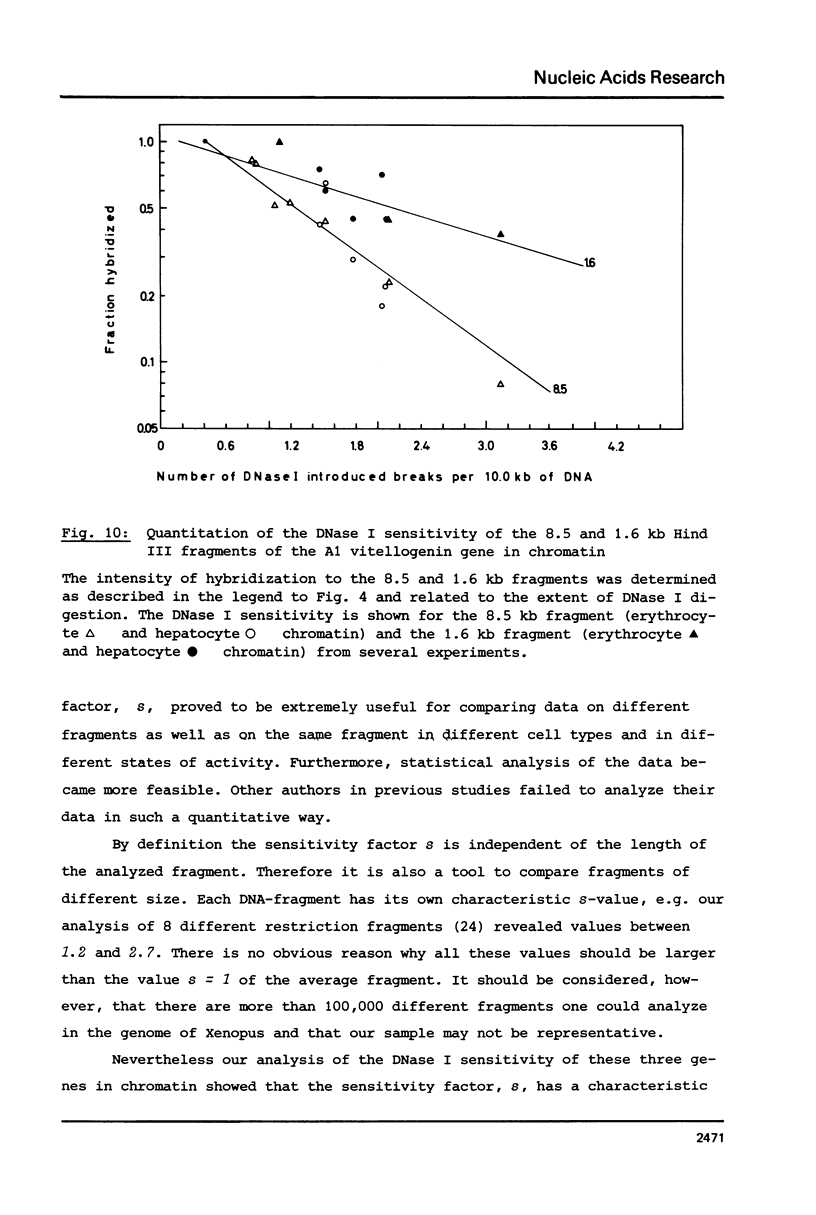
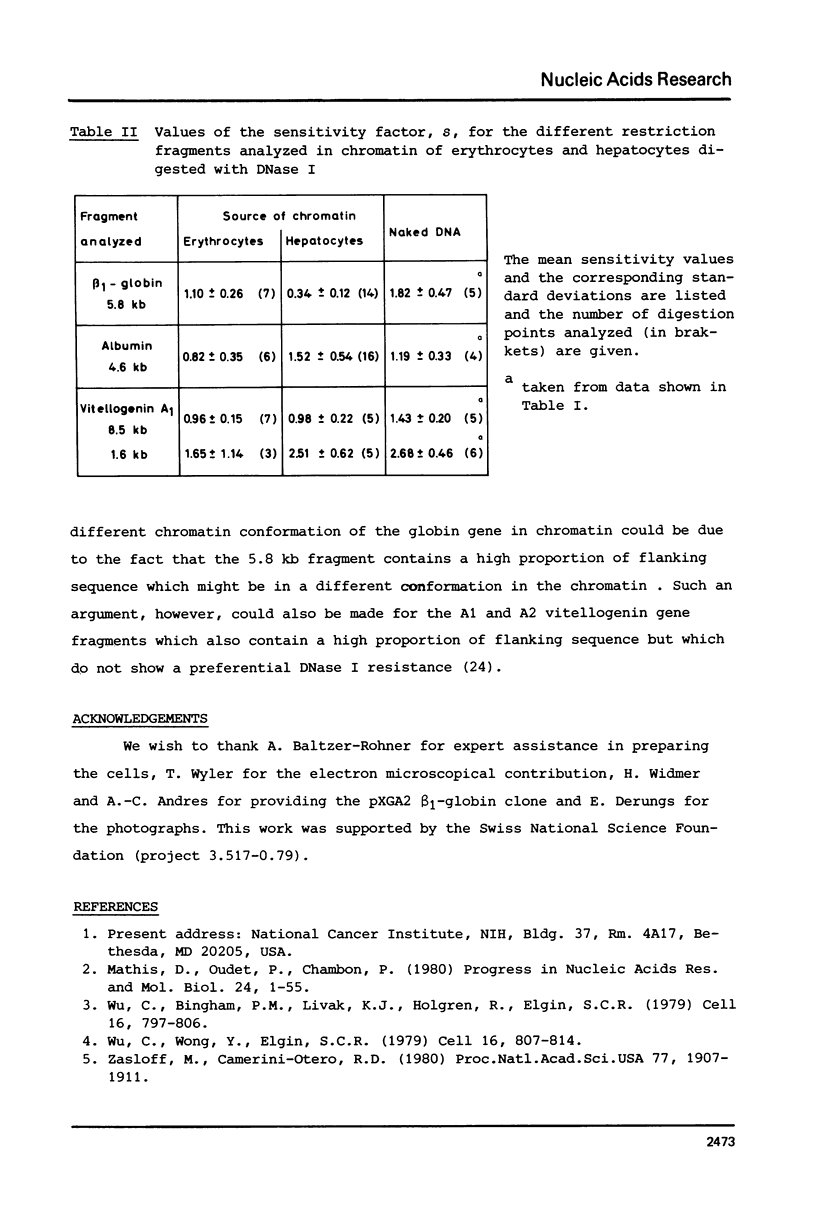
The disappearance of defined restriction fragments of the beta 1-globin, an albumin and the A1 vitellogenin gene was quantitated after DNase I digestion and expressed by a sensitivity factor defined by a mathematical model. Analysis of naked DNA showed that the gene fragments have similar but not identical sensitivity factors. DNase I digestion of chromatin revealed for the same gene fragments sensitivity factors differing over a much wilder range. This is correlated to the activity of the genes analyzed: the beta 1-globin gene fragment is more sensitive to DNase I in chromatin of erythrocytes compared to hepatocytes whereas the albumin gene fragment is more sensitive to DNase I in chromatin of hepatocytes. The A1 vitellogenin gene has the same DNase I sensitivity in both cell types. Comparing the DNase I sensitivity of the three genes in their inactive state we suggest that different chromatin conformations may exist for inactive genes.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellard M., Kuo M. T., Dretzen G., Chambon P. Differential nuclease sensitivity of the ovalbumin and beta-globin chromatin regions in erythrocytes and oviduct cells of laying hen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2737–2750. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber B. K., Maurhofer S., Jaggi R. B., Wyler T., Wahli W., Ryffel G. U., Weber R. Isolation and translation in vitro of four related vitellogenin mRNAs of estrogen-stimulated Xenopus laevis. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;105(1):17–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R. M., Harris R., Patient R. K., Williams J. G. Molecular cloning of cDNA sequences coding for the major alpha- and beta-globin polypeptides of adult Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2691–2707. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo M. T., Mandel J. L., Chambon P. DNA methylation: correlation with DNase I sensitivity of chicken ovalbumin and conalbumin chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2105–2113. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patient R. K., Elkington J. A., Kay R. M., Williams J. G. Internal organization of the major adult alpha- and beta-globin genes of X. laevis. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):565–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90494-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Groudine M., Dodgson J. B., Engel J. D., Weintraub H. Hb switching in chickens. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):973–980. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Larsen A., Engel J. D., Dolan M., Groudine M., Weintraub H. Tissue-specific DNA cleavages in the globin chromatin domain introduced by DNAase I. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90631-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanchfield J. E., Yager J. D., Jr An estrogen responsive primary amphibian liver cell culture system. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Oct 15;116(2):239–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90445-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B. Isolation of two closely related vitellogenin genes, including their flanking regions, from a Xenopus laevis gene library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1437–1441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B., Wyler T., Jaggi R. B., Weber R., Ryffel G. U. Vitellogenin in Xenopus laevis is encoded in a small family of genes. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B., Wyler T., Weber R., Ryffel G. U. Comparative analysis of the structural organization of two closely related vitellogenin genes in X. laevis. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):107–117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90239-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Wyler T., Weber R., Ryffel G. U. Electron-microscopic demonstration of terminal and internal initiation sites for cDNA synthesis on vitellogenin mRNA. Eur J Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):225–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12303.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wangh L. J., Osborne J. A., Hentschel C. C., Tilly R. Parenchymal cells purified from Xenopus liver and maintained in primary culture synthesize vitellogenin in response to estradiol-17 beta and serum albumin in response to dexamethasone. Dev Biol. 1979 Jun;70(2):479–499. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer H. J., Jaggi R. B., Weber R., Ryffel G. U. Enrichment and characterization of the DNA coding for vitellogenin in Xenopus laevis. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 15;99(1):23–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Bingham P. M., Livak K. J., Holmgren R., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: I. Evidence for higher order domains of defined DNA sequence. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wong Y. C., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: II. Disruption of chromatin structure during gene activity. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Camerini-Otero R. D. Limited DNase I nicking as a probe of gene conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1907–1911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]