Abstract
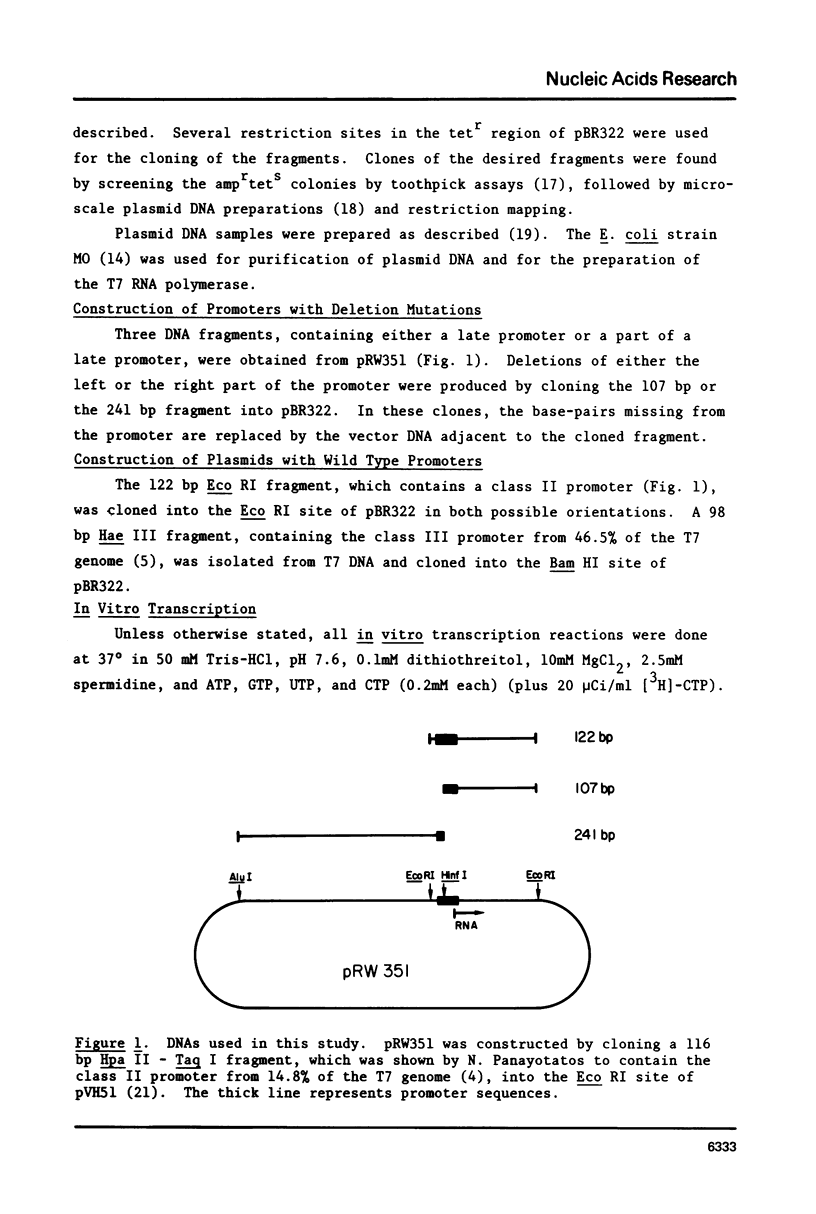
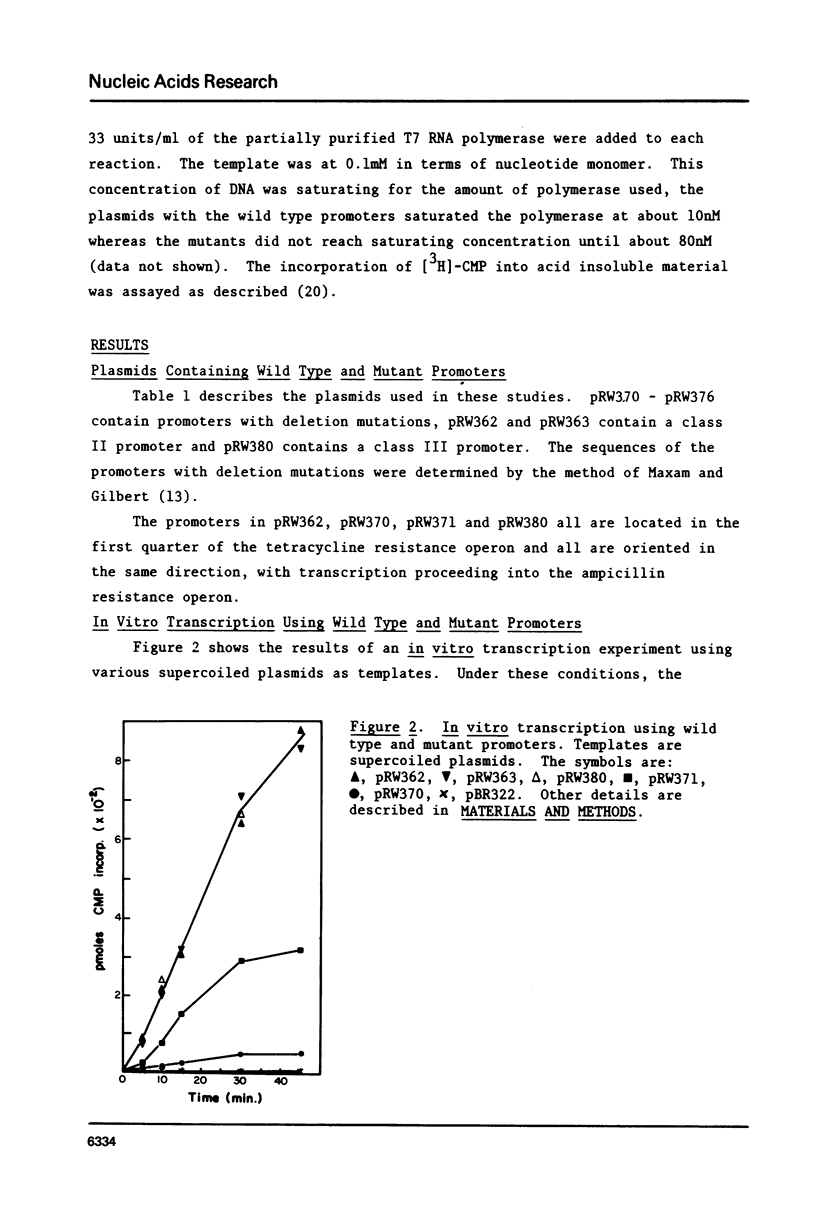
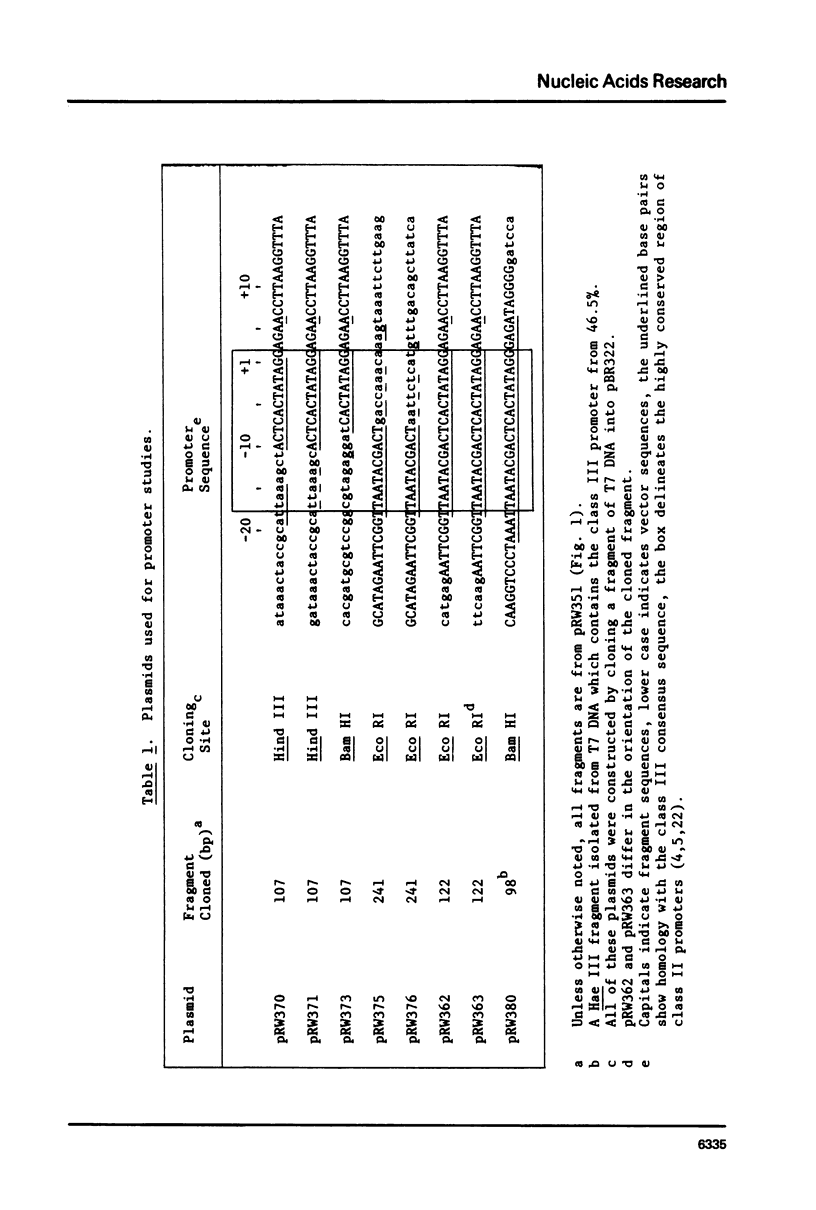
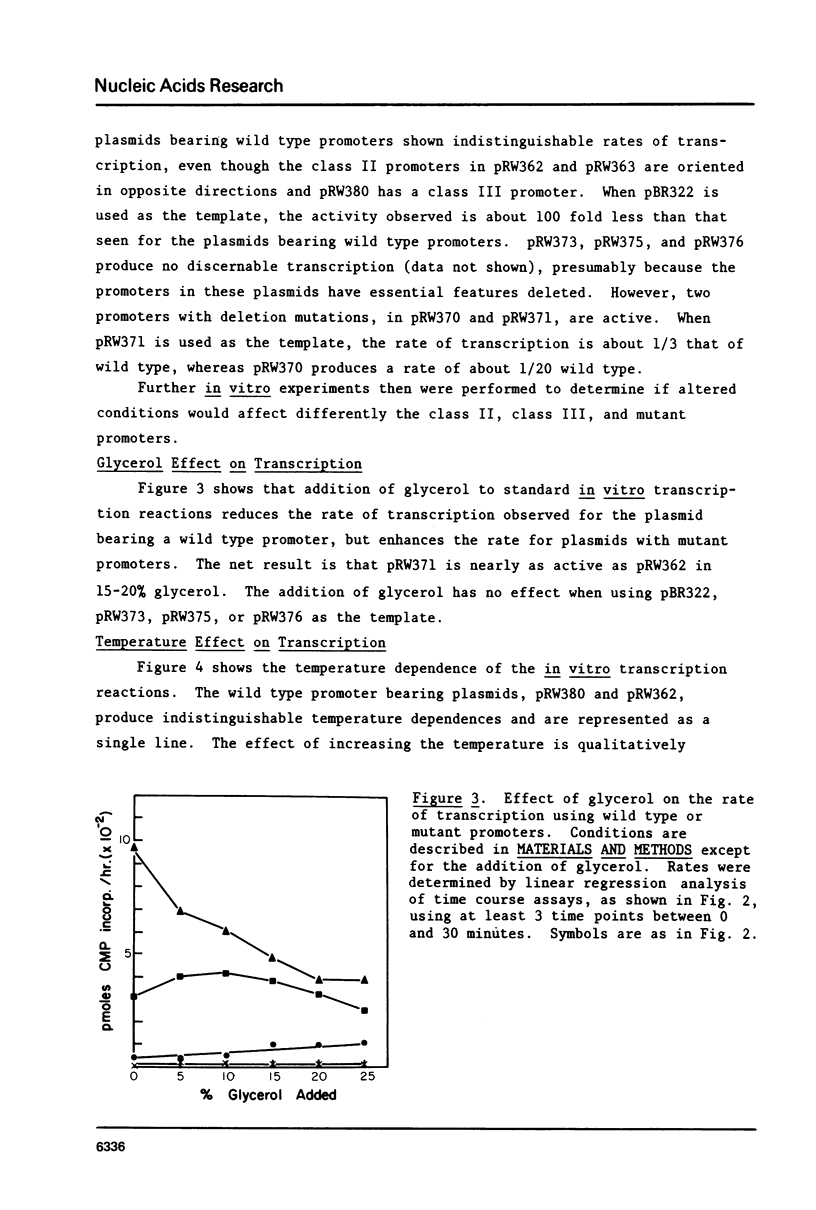
The construction of plasmids containing T7 class I promoters with deletion mutants was described. Restriction fragments, ending at the Hinf I site located at position -10 in the promoter from 14.8% of the T7 genome, were cloned into pBR322. This produced the deletion of either the left or the right part of the promoter. The in vitro transcription properties of these plasmids were determined. Control plasmids were obtained by cloning wild type class II and class III promoters into pBR322. These plasmids also were used to compare the in vitro transcription properties of the two classes of late promoters. Much of the leftward part of a T7 late promoter can be deleted without abolishing activity, but deletion of the right part eliminates promoter activity. Class II, class III, and the mutated promoters have characteristic responses to changes in ionic strength, exogenous glycerol, and temperature.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes W. M. Plasmid detection and sizing in single colony lysates. Science. 1977 Jan 28;195(4276):393–394. doi: 10.1126/science.318764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothroyd J. C., Hayward R. S. New genes and promoters suggested by the DNA sequence near the end of the coliphage T7 early operon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1931–1943. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter A. D., Morris C. E., McAllister W. T. Revised transcription map of the late region of bacteriophage T7 DNA. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):636–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.636-642.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M., McGrath J., Waskell L. New RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T7. Nature. 1970 Oct 17;228(5268):227–231. doi: 10.1038/228227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wyngaert M., Hinkle D. C. Involvement of DNA gyrase in replication and transcription of bacteriophage T7 DNA. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):529–535. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.529-535.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene P. J., Heyneker H. L., Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Betlach M. C., Covarrubias A. A., Backman K., Russel D. J., Tait R., Boyer H. W. A general method for the purification of restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2373–2380. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardies S. C., Patient R. K., Klein R. D., Ho F., Reznikoff W. S., Wells R. D. Construction and mapping of recombinant plasmids used for the preparation of DNA fragments containing the Escherichia coli lactose operator and promoter. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5527–5534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood S. J., Schendel P. F., Wells R. D. Micrococcus luteus deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. Studies of the enzymic reaction and properties of the deoxyribonucleic acid product. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5614–5624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Involvement of DNA gyrase in bacteriophage T7 DNA replication. Nature. 1977 Nov 3;270(5632):78–80. doi: 10.1038/270078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Chamberlin M. J. Mapping of class II promoter sites utilized in vitro by T7-specific RNA polymerase on bacteriophage T7 DNA. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):196–208. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.196-208.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. D., Selsing E., Wells R. D. A rapid microscale technique for isolation of recombinant plasmid DNA suitable for restriction enzyme analysis. Plasmid. 1980 Jan;3(1):88–91. doi: 10.1016/s0147-619x(80)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister W. T., Carter A. D. Regulation of promoter selection by the bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 24;8(20):4821–4837. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.20.4821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister W. T., Morris C., Rosenberg A. H., Studier F. W. Utilization of bacteriophage T7 late promoters in recombinant plasmids during infection. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):527–544. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90406-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister W. T., Wu H. L. Regulation of transcription of the late genes of bacteriophage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley J. L., Strothkamp R. E., Sarris A. H., Coleman J. E. T7 RNA polymerase: promoter structure and polymerase binding. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 6;18(3):528–537. doi: 10.1021/bi00570a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterman H. L., Coleman J. E. T7 ribonucleic acid polymerase-promotor interactions. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):4884–4892. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Wells R. D. Cloning and localization of the in vitro functional origin of replication of bacteriophage T7 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5555–5561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Wells R. D. Recognition and initiation site for four late promoters of phage T7 is a 22-base pair DNA sequence. Nature. 1979 Jul 5;280(5717):35–39. doi: 10.1038/280035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa M. D. Four T7 RNA polymerase promoters contain an identical 23 bp sequence. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. J., Wells R. D. Coumerimycin A1: A preferential inhibitor of replicative DNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. II. In vivo characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 24;15(17):3778–3782. doi: 10.1021/bi00662a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sgaramella V. Enzymatic oligomerization of bacteriophage P22 DNA and of linear Simian virus 40 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3389–3393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strothkamp R. E., Oakley J. L., Coleman J. E. Promoter melting by T7 ribonucleic acid polymerase as detected by single-stranded endonuclease digestion. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1074–1080. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Bacteriophage T7. Science. 1972 Apr 28;176(4033):367–376. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4033.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Identification and mapping of five new genes in bacteriophage T7. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90404-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


