Abstract
With the aid of chemoselective sensors, fluorescence microscopy has emerged as an indispensable tool to visualize the distribution and dynamics of various biologically important molecules in live specimens. Motivated by our interest in understanding the chemistry and biology of mobile zinc underlying its physiological and pathological roles, over the past decade our laboratory has developed an extensive library of zinc fluorescence probes. In this article, we provide essential information about our sensor toolbox in order to assist investigators interested to apply our constructs to study various aspects of mobile zinc biology. We illustrate their use with several examples of imaging both exogenous and endogenous mobile zinc in live cells and tissues using various versions of fluorescence microscopy, including confocal and two-photon microscopy.
Keywords: imaging, fluorescence, sensor, probe, zinc, live cell, hippocampus, mossy fiber, confocal microscopy, two-photon microscopy
1. Introduction
As a ubiquitous element in biology, zinc plays well-documented structural (e.g., zinc-finger proteins) and catalytic (e.g., hydrolytic enzymes) roles in the form of tightly-bound divalent ions in an estimated 3,000 metalloproteins (Vallee and Falchuk, 1993; Maret, 2009). Attracting increasing interest, on the other hand, are dynamic pools of loosely-bound zinc ions – termed mobile zinc here but alternatively referred to as free, labile, chelatable or histochemically active zinc – in many tissues and organs including the hippocampus and olfactory bulb of the brain (Sensi et al, 2009; Chang and Lippard, 2006), the prostate (Costello and Franklin, 2006), and the pancreas (Taylor, 2005). Mobile zinc mediates diverse cellular processes in the physiology of living organisms ranging from signal transduction to proliferation and death to the immune response (Sensi et al, 2009; Franklin and Costello, 2009; Hirano et al, 2008; John et al, 2010). For example, up to millimolar concentrations of zinc stored in synaptic vesicles in the mossy fibers of the hippocampus are proposed to play a role in learning and memory formation during neurotransmission (Sensi et al, 2009; Li et al, 2001). On the other hand, mobile zinc can be cytotoxic, in part owing to its facile coordination with endogenous ligands including proteins and peptides (Vinkenborg et al, 2010). The physiological concentration of mobile zinc in many eukaryotic cells may be as low as picomolar (Frederickson et al, 2005). The pronounced zinc gradients necessitate tight regulation of zinc homeostasis, which is largely effected by families of zinc transporter proteins as well as by metallotheinein (Eide, 2006; Maret, 2009). Disruption of zinc homoestasis is implicated in several neurodegenerative disorders and excitotoxic conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease and ischemia (Sensi et al, 2009). Additionally, a decrease of mobile zinc concentration in the prostate serves as an important marker for early diagnosis of prostate cancer (Ghosh et al, 2010).
To date, many of the mechanisms underlying the function of mobile zinc in both its physiology and pathology remain to be defined. To address this deficiency, of particular value are methods for visualizing mobile zinc in a spectrum of living biological specimens, including cells and tissues. Many early studies relied on histochemical approaches, particularly Timm’s staining (Frederickson and Danscher, 1990), in which mobile zinc is precipitated by sulfide and subsequent silver development allowed visualization with microscopic methods. Although Timm’s staining is still in current use, visualization is only achieved in postmortem specimens and therefore is unable to provide dynamic information in live biological samples. In contrast, fluorescence microscopy has become a predominant technique for imaging live cells with high spatial and temporal resolution (Goldys, 2009). Its widespread use has motivated the invention and expansion of fluorescence probes that produce a readout specific to mobile zinc.
Fluorescent zinc probes must satisfy certain criteria to become broadly useful for biological studies. First, upon zinc binding the probe should elicit a significant fluorescence response, including a large increase of intensity and/or shift of emission wavelength. Visible-rather than UV-light excitation and emission are preferred in order to minimize background caused by autofluorescence and to minimize tissue damage. Second, both thermodynamically and kinetically the probe should offer high selectivity for zinc compared to other biologically abundant metal ions, as well as fluorescence responses that are fast enough to capture the biological event of interest. Third, in complex cellular environments the probe should be biocompatible; included in this requirement are water solubility, non-toxicity, and the ability to detect cellular zinc reversibly with an affinity matching its physiological concentrations. Finally, the probe should be relatively straightforward to synthesize, with the capability for modification to tune its cellular distribution and related properties.
During the past decade our group has constructed a toolbox of fluorescence probes with diverse photophysical and zinc-binding properties (Pluth et al, 2011; Tomat and Lippard, 2010; Nolan and Lippard, 2009; Que et al, 2008; Chang and Lippard, 2006). The present article is intended to provide readers with information required to select the most suitable compound for studying zinc biology. We first present a guide to fluorescent zinc probes based on their photophysical properties, metal-binding ability, and functionalization. In the next section we provide an illustrative protocol for imaging mobile zinc with a particular fluorescence sensor in a given cell type. Finally, we briefly summarize procedures for imaging endogenous zinc in live cells and tissues, including both its static distribution and its dynamic properties following certain stimuli. Our discussion focuses on sensor families developed in our lab, although much information on their use in microscopy may conceivably be extended to similar fluorescence probes. Additionally, versions with improved detection schemes, such as red-emitting or ratiometric probes (see for example Du and Lippard, 2010; Woodroofe and Lippard, 2003; Komatsu et al, 2007; Xu et al, 2009), the underlying chemistry of which is less well understood, are beyond the scope of our discussion.
2. A guide to fluorescent zinc probes
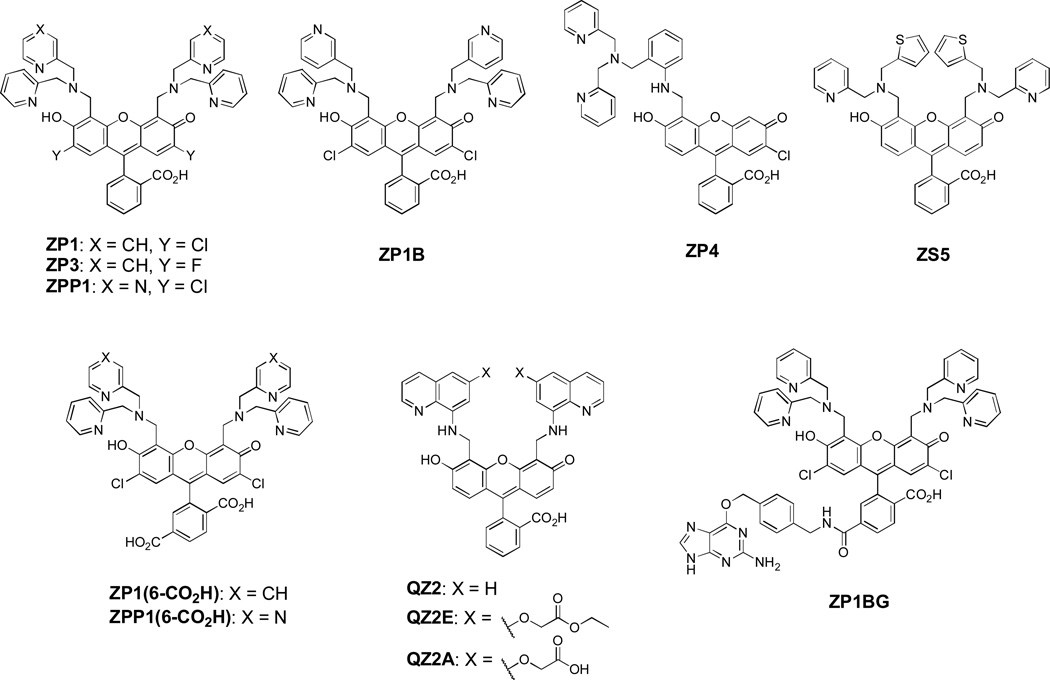
Fluorescent zinc probes developed in our lab (Scheme 1 and Table 1) are largely built upon fluorescein as a platform. We chose fluorescein because of its advantageous properties including brightness (ε ~ 70,000 M−1 cm−1, Φ ~ 1 at pH 7, Brannon and Magde, 1978), good water solubility, and compatibility with the widely-used 488 nm Ar laser line and common filter sets for green fluorescent proteins (GFPs). Compared to many earlier zinc probes (e.g., TSQ, Frederickson et al, 1987), its visible-light excitation is beneficial for live imaging because it avoids the use of tissue-damaging UV light and reduces autofluorescence from biological specimens. The fluorescence sensors are constructed by appending various nitrogen-based zinc-binding units at the 4' and/or 5' positions of the fluorescein ring to yield either monotopic (ZP4) or ditopic (Scheme 1: all but ZP4) probes (Nolan and Lippard, 2009). A variety of zinc-binding units are available, including dipicolylamines (DPAs) and a pyrazine/pyridine analog, which comprise the Zinpyr (ZP) family (including ZP1, ZP3, ZP4, ZP1B, and ZPP1), as well as units containing thioether or 8-aminoquinoline, which define the Zinspy (ZS) and Quinozin (QZ) series (e.g., ZS5 and QZ2). In this section we highlight the characteristics of these various probes, both in the cuvette and in live cells, to help dictate their choice of which to apply for live imaging of mobile zinc.
Scheme 1.
Structures of selected zinc-selective fluorescence probes. Among them ZP1 and ZP4 are commercially available.
Table 1.
Spectroscopic, thermodynamic and kinetic properties of selected zinc fluorescence probes.a
| Absorption (λ (nm), ε×104 (M−1 cm−1)) |
Emission (λ (nm), Φ) b |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unbound | Zn(II) | Unbound | Zn(II) | pKa1c | Kdd | ~DR e |
kon (106 s−1) f |
koff (s−1) f | Ref. | |
| ZP1 | 515, 7.9 | 507, 8.4 | 531, 0.17 | 527, 0.87 | 6.96 ± 0.01 | 0.7 ± 0.1 nM | 5 | 3.3 ± 0.4 | (2.3±0.4)×10−3 | See table footnote. g |
| ZP3 | 502, 7.5 | 492, 8.5 | 521, 0.15 | 516, 0.92 | 6.8 | 0.7 ± 0.1 nM | 7 | 4.3 ± 0.3 | (2.9±0.4)×10−3 | Chang et al, 2004a |
| ZP4 | 506, 6.1 | 495, 6.7 | 521, 0.06 | 515, 0.34 | 7.2 | 0.65 ± 0.1 nM | 6 | 5.2 ± 0.1 | (3.4±0.5)×10−3 | Burdette et al, 2003; Nolan et al, 2005 |
| ZPP1 | 517, 7.5 | 505, 8.2 | 532, 0.052 | 523, 0.70 | 5.97 ± 0.04 | 15.6 ± 0.5 nM | 15 | n.d. | n.d. | Zhang et al, 2008; Buccella et al, 2011 |
| ZP1B | 516, 6.8 | n.d. | 530, 0.03 | 521, 0.70 | 5.6 | 12.9 ± 0.5 µM | 23 | n.d. | n.d. | Wong et al, 2009b |
| ZS5 | 497, 3.3 | 490, 4.2 | 522, 0.36 | 517, 0.80 | 8.0 | 1.5 ± 0.2 µM | 3 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 3.3 | Nolan et al, 2006 |
| QZ2 | 499, 3.72 | 489, 3.36 | ~520, 0.005 | 518, 0.70 | 7.0 | ~770 µM | 150 | 45 ± 3 | (1.6±0.2)×102h | Nolan et al, 2005 |
| QZ2E | 499, 2.72 | 496, 1.6 | 519, 0.004 | 514, 0.73 | n.d. i | 3.5 ± 0.1 mM | 120 | n.d. | n.d. | McQuade and Lippard, 2010 |
| QZ2A | 498, 6.41 | 492, 4.0 | 515, 0.012 | 515, 0.51 | ~5.9 | 220 ± 30 µM, 160 ± 80 µM j | 30 | n.d. | n.d. | McQuade and Lippard, 2010 |
| ZP1(6-CO2H) | 516, 7.6 | 506, 8.1 | 531, 0.21 | 528, 0.63 | 7.1 | 0.16 ± 0.02 nM | 3 | n.d. | n.d. | Woodroofe et al, 2004 |
| ZPP1(6-CO2H) | 519, 7.7 | 505, 8.4 | 534, 0.045 | 525, 0.67 | 6.21 ± 0.01 | 18 ± 1 nM | 14 | n.d. | n.d. | Buccella et al, 2011 |
Measurements were carried out at pH 7 (50 mM PIPES, 100 mM KCl).
Fluorescein in 0.1 N NaOH (Φ = 0.95, Brannon and Magde, 1978) was used as the standard.
pKa1 corresponds to the proton-binding event that results in fluorescence enhancement in the absence of zinc. pKa1 values for ZP1 and ZPP1 were determined from potentiometric titrations, whereas other values were derived from fluorimetric titrations; values obtained from the two types of experiments are similar but not directly comparable.
For ditopic probes where multiple zinc-binding events are possible, the listed Kd value corresponds to the one contributing to the major fluorescence enhancement.
Dynamic range (DR) is the increase of brightness (ε × Φ) as a result of zinc coordination. The increase of Φ upon zinc binding was used for ZP1B. DR and increase of Φ are often close in value.
kon and koff are rate constants for zinc binding and release, respectively, at 25 °C.
References of ZP1 data: absorption and Kd, Walkup et al, 2000; emission and pKa1, Wong et al, 2009a and Nolan and Lippard, 2009; kinetics, Nolan et al, 2005.
Measured at 4.3 °C.
Hydrolysis of ester groups in the probe at low pH prevents accurate measurement of pKa.
Zinc binding to the quinoline picket cannot be distinguished from that to the diacid in QZ2A.
n.d. = not determined.
2.1 Spectroscopic properties
The fluorescence probes discussed here operate by a photoinduced electron transfer (PET) mechanism (Lakowicz, 2006). In their zinc-free form, the excited state is quenched by the metal-binding units (Wong et al, 2009a). Coordination to divalent zinc perturbs the electronic structure such that PET quenching is alleviated, restoring the fluorescence.
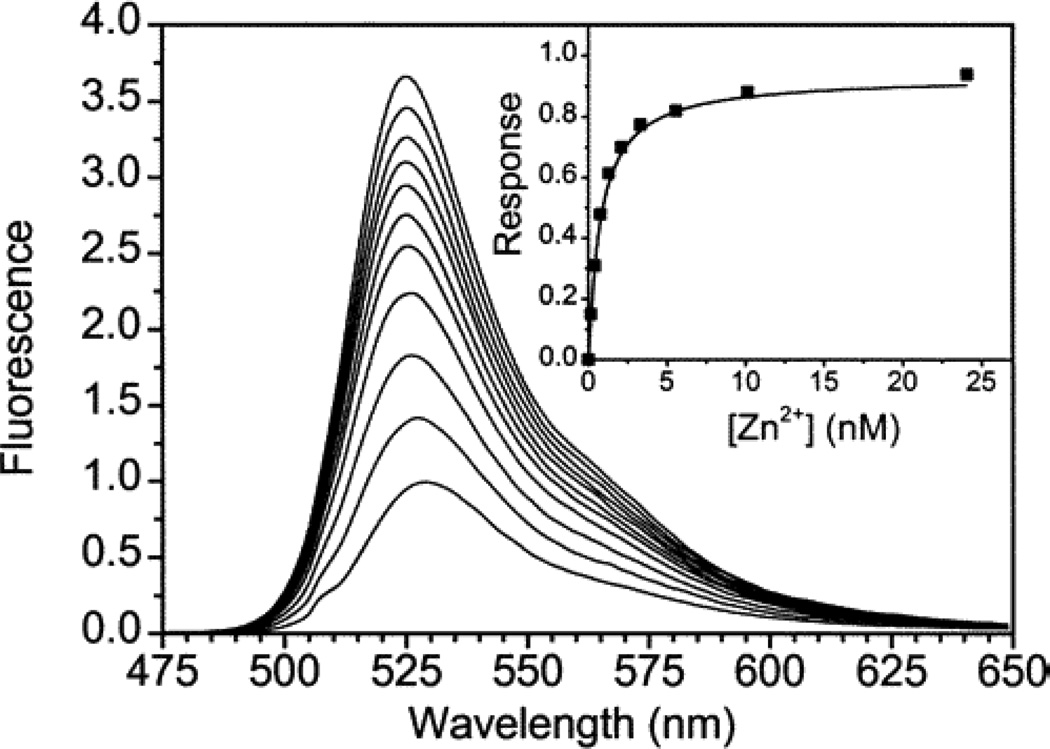
The fluorescence enhancement of a probe from the OFF to the ON state defines its dynamic range, and is quantitated by the change in extinction coefficient (ε) and fluorescence quantum yield (Φ) upon zinc binding. At pH 7.0, Zinpyr-1 (ZP1), a prototype zinc fluorescence sensor based on the di(2-picolyl)amine unit, exhibits 5-fold zinc-induced turn-on (Figure 1, Walkup et al, 2000; Wong et al, 2009a). This moderate dynamic range at physiological pH results mainly from partial protonation of the zinc-binding pockets in the absence of zinc, which alleviates PET and contributes to background fluorescence. We have pinpointed the effect of protonation equilibria on the magnitude of fluorescence turn-on through recent careful potentiometric and fluorescence titrations (Wong et al, 2009a).
Figure 1.
Fluorescence spectra of 0.5 µM ZP1 with incrementally higher concentrations of zinc. Spectra were acquired in pH 7.0 buffer (50 mM PIPES, 100 mM KCl) at 25 °C; λex = 507 nm. The first 10 spectra correspond to free zinc concentration between 0 and 24 nM; the eleventh spectrum was obtained with ~25 µM free zinc. Inset: integrated emission (rectangles) was analyzed by least-squares fitting (solid line) to give a dissociation constant of 0.7 nM. Reprinted with permission from Walkup et al, 2000. Copyright 2000 American Chemical Society.
To minimize such proton-induced turn-on, we employed two strategies to reduce the basicity of the binding pocket. Incorporation of strongly electron-withdrawing fluoride groups on the fluorescein scaffold afforded ZP3 (vs. chloride in ZP1), which exhibits a greater dynamic range of 7-fold (Table 1, Chang et al, 2004a). An alternative approach is to modify the zinc-binding unit, as illustrated by the pyrazine/pyridine-containing donor ligands in ZPP1 (Zhang et al, 2008; Buccella et al, 2011) and (2-picolyl)(4-picolyl)amine in ZP1B (Wong et al, 2009b). Both of these substitutions reduce the pKa of the binding pocket, giving rise to 15- and 23-fold dynamic ranges, respectively, primarily by suppression of proton-induced fluorescence emission in the metal-free form. Moreover, because of its zinc-binding and fluorescent properties, ZPP1 shows an OFF-ON-OFF behavior with a sharp maximum, when incremental amounts of the probe are added to solutions of mobile zinc. This titration protocol has been utilized to quantify mobile zinc that is co-secreted with insulin by Min6 insulinoma cells (Zhang et al, 2008) and to investigate zinc in normal and cancerous prostate tissues (Ghosh et al, 2010).
2.2 Metal-binding properties
The fluorescence enhancement of the ZP, ZS, and QZ probes is selective for divalent zinc ions vs. other metal ions that are abundant in the biological milieu, specifically Na+, K+, Mg2+, and Ca2+, largely imparted by the choice of nitrogen-based ligands (Nolan and Lippard, 2009). Many other transition metal ions in biological specimens, such as Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Ni2+, and Cu2+, readily quench the fluorescence of most probes. Conversely, other ions that result in fluorescence enhancement, including Cd2+ and in some cases Hg2+, do not interfere with zinc detection because of their low concentration in common biological samples. Therefore, fluorescence turn-on in typical cellular systems is specific for zinc ions.
Reversible zinc binding of fluorescence probes is an important feature that enables them to report dynamic zinc levels in live biological samples. The probes of the ZP, ZS, and QZ families do bind zinc ions reversibly. Their turn-on zinc fluorescence is reversed by addition of a high-affinity zinc chelator, such as N,N,N',N'-tetrakis(2-pyridylmethyl)ethylenediamine (TPEN, Kd = 0.3 fM, Anderegg et al, 1977). The zinc-binding affinities (Kd values in Table 1) span from low- and mid-nM (ZP1, ZP3, ZP4 and ZPP1) to low-µM (ZS5 and ZP1B) and mid-µM (QZ2) (Nolan and Lippard, 2009; Buccella et al, 2011; Wong et al, 2009b). This wide range facilitates zinc imaging in various biological samples with concentrations spanning six orders of magnitude.
For experiments requiring temporal resolution, such as time-lapse imaging, the kinetics of both association and dissociation of mobile zinc also must be taken into account. Although probes of the ZP, ZS, and QZ families bind zinc rapidly with rate constants greater than 106 M−1 s−1, the zinc dissociation kinetics from the sensor varies from milliseconds (QZ) to seconds (ZS) and minutes (ZP) (Nolan et al, 2005). When a decrease of zinc concentration is monitored in real time, the dissociation kinetics should be no slower than the time scale of the biological events under consideration.
2.3 Cellular response
Considering the crowded cellular environment filled with endogenous ligands, the turn-on response of a zinc sensor in the cuvette may not always translate into a satisfactory response in live cells. Many of our fluorescein-sensors, nonetheless, are capable of reporting dynamic concentrations of mobile zinc in live cells without introducing significant toxicity (vide infra). Among them, ZP1, ZP3, and ZS5 have been tested most extensively and exhibit robust behavior in various cell types and tissues, including HeLa, COS-7, and HEK293-T cells, dissociated neurons, and both organotypic and acute hippocampal slices (Nolan and Lippard, 2009). ZPP1 responds to endogenous mobile zinc in prostate epithelial cells upon injection into the tail vein of live mice (Ghosh et al, 2010). Besides conventional wide-field fluorescence microscopy, probes in the ZP, ZS, and QZ families are also amenable to more advanced imaging techniques such as confocal and two-photon microscopy (Chang et al, 2004a; Nolan et al, 2006; Chang et al, 2004b; Nolan et al, 2005), the latter being particularly valuable for extending the penetration depth and reducing photo-damage to the biological samples. We have determined that probes in the ZP and QZ families undergo the most efficient two-photon excitation with 780–800 nm light (Chang et al, 2004b; Nolan et al, 2005).
Unlike many polycarboxylate-based calcium sensors that are membrane impermeable (Tsien, 1999), the nitrogen-based zinc probes readily cross plasma membranes and can therefore be loaded into cells simply by incubation with the probe. The choice of zinc-binding unit, however, can alter their cellular uptake and thereby influence the typical incubation periods required for staining. For example, aniline-based probes (ZP4 and QZ2) are less membrane-permeable than tertiary amine-based ones (ZP1, ZP3 and ZS5) (Nolan and Lippard, 2009), and replacing pyridine (ZP1) with pyrazine (ZPP1) in the zinc-binding pockets also decreases cell permeability (Buccella et al, 2011). Whereas additional studies may reveal the mechanism(s) involved in their transport across the cellular membranes and facilitate the design of novel probes, these empirical differences can be taken advantage of to selectively image certain biological specimens. An example is the selective staining of injured neurons in hippocampal tissues with ZP4 while intracellular zinc-containing synaptic vesicles are unlabeled (Burdette et al, 2003), the latter being readily stained with more permeable probes (e.g., ZP1 and ZP3, see Section 4.2 and Chang et al, 2004a).
The zinc sensors often give rise to punctuate fluorescence at specific cellular compartments, and the localization pattern seems to be dictated by the nature of the zinc-binding groups. For example, in HeLa cells many pyridine-containing ZP sensors (e.g., ZP1, ZP3, and ZPP1) localize to the Golgi apparatus, whereas thiophene-containing ZS5 localizes to mitochondria (Nolan et al, 2006). Such localization behavior may offer a valuable opportunity to study the dynamics of mobile zinc at the organelle level.
Cytotoxicity of a fluorescence probe potentially causes artifacts and therefore must be minimized. No evidence of cytotoxicity was observed in our imaging experiments, most of which are shorter than 12 h. Moreover, even after a 24-h exposure to various ZP and ZS probes at low-µM concentrations, most HeLa cells were viable as quantified by MTT assays (Table 2, Nolan et al, 2006). Although ZS5 is considerably less cytotoxic than ZP probes, all are sufficiently non-toxic during prolonged treatment at concentrations typical for fluorescence imaging experiments.
Table 2.
Cytotoxicity of selected probes in HeLa cells.
| % cell survival |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 µM | 5 µM | 10 µM | |
| ZP1 | 96 ± 2 | 68 ± 5 | 40 ± 6 |
| ZP3 | 93 ± 4 | 73 ± 8 | 57 ± 13 |
| ZS5 | 101 ± 1 | 87 ± 2 | 80 ± 4 |
Cell viability was quantified by the MTT assay (mean ± SD). Reproduced with permission from Nolan et al, 2006. Copyright 2006 American Chemical Society.
2.4 Additional probe functionalization
Attracting increasing attention is strategic functionalization of fluorescence probes, an advance that has facilitated protocols for imaging the functions of biological species. Incorporation of functional groups that are orthogonal to fluorescence detection not only imparts features such as impermeability and trappability to the probe itself but also enables bioconjugation to other fluorophores and biologically active molecules for detection schemes such as Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) and for targetable sensing (Tomat and Lippard, 2010).
We have adopted two approaches for efficient functionalization of our fluorescein-based probes. The most versatile method is to incorporate a 6-carboxylate group on the benzoate ring, which introduces minimal perturbation to the photophysics and metal-binding properties of the probe (Woodroofe et al, 2004; Buccella et al, 2011). This functionalized molecule or its N-hydroxysuccinimide ester can be conveniently conjugated with amine-containing biomolecules by amide coupling. This robust strategy has formed the basis for generating targetable and ratiometric sensors (Tomat et al, 2008; Woodroofe et al, 2005). An alternative approach is to derivatize the zinc-binding groups on the xanthene ring, such as the quinoline unit in QZ2 (McQuade and Lippard, 2010).
Application of these functionalization methods has enabled us to develop impermeable and trappable probes for improved control of probe cellular distribution. These constructs overcome an intrinsic limitation of a membrane-permeable probe, which can leak out of cells under dynamic flow conditions and disable time-lapse imaging experiments. Functionalized probes such as ZP1(6-CO2H), ZPP1(6-CO2H), and QZ2A bear negatively charged carboxylate group and do not enter cells and can thus be used to selectively detect extracellular zinc (Woodroofe et al, 2004; Buccella et al, 2011; McQuade and Lippard, 2010). On the other hand, probes carrying certain carboxylate esters (e.g., QZ2E) become trapped inside cells via hydrolysis by endogenous esterases and are well suited for experiments that require continuous perfusion (McQuade and Lippard, 2010).
Functionalization of fluorescence probes can also impart their capability to target specific organelles and thus provide spatial information about zinc compartmentalization at the subcellular level, potentially beyond the diffraction limit of visible light (Tomat and Lippard, 2010). To achieve this goal, we devised the prototypical targetable sensor ZP1BG, a ZP1 analog functionalized with a benzylguanine group. In a protocol introduced by Kai Johnsson and now referred to as SNAP tag methodology (Keppler et al, 2003; Tomat et al, 2008), we first expressed O6-alkylguanine transferase (AGT), a DNA-repair enzyme, in specific subcellular organelles. Subsequent incubation with ZP1BG resulted in covalent linking of ZP1 to the enzyme, and thus ZP1 became localized to the mitochondria or Golgi apparatus. Such targetable probes combine the advantages of synthetic fluorescent sensors with protein engineering and hold considerable potential for visualizing zinc dynamics and identifying target sites.
2.5 Dual-function MRI/fluorescence probes
Whereas fluorescence imaging affords high spatial and temporal resolution, as an optical technique it has limited ability to penetrate deeply into biological specimens, and its applications in live animals are intrinsically limited to surface structures. By contrast, MRI can penetrate non-invasively deep into opaque objects and provide dynamic 3D information by in vivo imaging of live animals, albeit with diminished spatial resolution (Tsien, 2003). These two visualization techniques are therefore complementary, and combining them can provide information not obtainable with either alone.
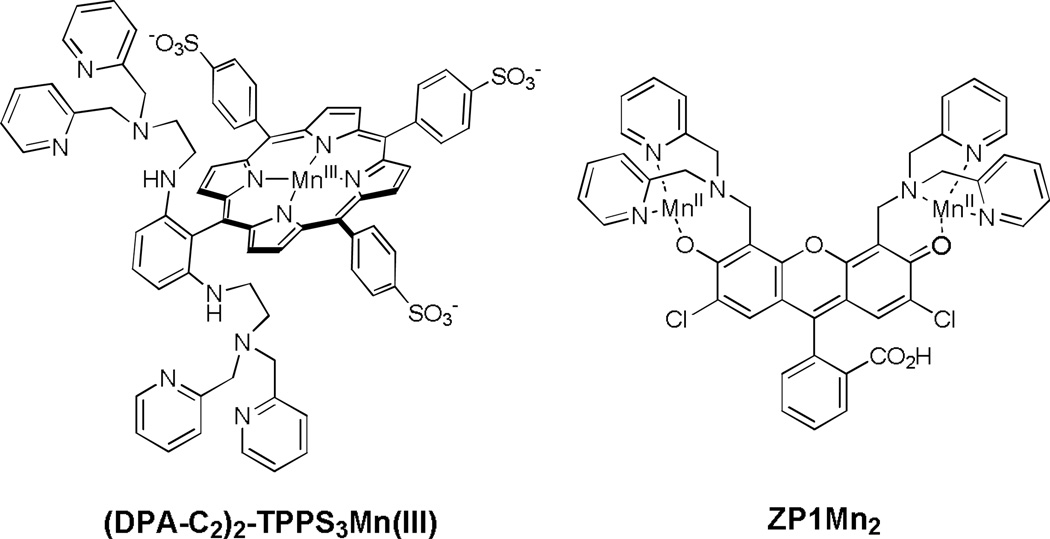
To integrate the advantages of fluorescence and MRI sensing, we have devised dual-function MRI/fluorescence probes that are responsive to mobile zinc in aqueous solutions, including (DPA-C2)2-TPPS3Mn(III) and ZP1Mn2 (Scheme 2, Zhang et al, 2007; You et al, 2010). Zinc-binding to the DPA units in (DPA-C2)2-TPPS3Mn(III) changes the relaxivity of Mn(III)-bound water ligands and influences T1 and T2 relaxation in a manner that depends on pH and ionic strength. In ZP1Mn2, zinc-binding only affects T2 relaxation whereas the T1 relaxation rate remains largely unaltered. With respect to fluorescence, upon binding zinc ZP1Mn2 and the Mn-free form of (DPA-C2)2-TPPS3Mn(III) show 110- and 11-fold increases in fluorescence quantum yield, respectively.
Scheme 2.
Structures of dual-function MRI/fluorescence probes.
Both of the above probes are membrane permeable and therefore able to report changes in intracellular zinc. The use of a porphyrin as an alternative platform imparts sample-dependent localization of (DPA-C2)2-TPPS3Mn(III), which preferentially localizes in the cell nucleus in HEK-293 cells whereas in the brain it is mostly confined to the cytosol. The unique properties of (DPA-C2)2-TPPS3Mn(III) have allowed for MRI imaging of mobile zinc in live rats (Lee et al, 2010).
2.6 Use and storage of fluorescence probes
Among the probes discussed above, ZP1 (CAS number 288574-78-7) and ZP4 (CAS number 502467-23-4) are commercially available from a number of vendors in the US and Europe.
For use of the fluorescein-based probes in biological imaging, we typically prepare stock solutions in anhydrous dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) at concentrations of 1–5 mM. When used for imaging biological samples, small volumes of the stock are either added directly to the culture dish or first diluted with the pre-warmed culture medium before application to a biological specimen (see Section 3.5).
As is true for many colored compounds, the fluorescein-based sensors are light-sensitive. Although we have made no attempt to characterize the decomposition products, we found that photo-degraded samples are often more emissive than the sensors themselves, perhaps due to loss of the zinc-binding appendages, which are responsible for PET fluorescence quenching. Similar photo-dealkylation pathways have been reported for homologous calcium probes (Tsien, 1999). Exposure of zinc probes, both in DMSO and in cell culture media, to ambient light for extended periods of time may give inconsistent imaging performance and should be avoided.
The sensors are more stable as solids than in solutions, possibly because residual water in solutions may result in their hydrolysis. They should therefore typically be stored as solids at ≤ 4 °C when not in use. During use, anhydrous DMSO stock solutions aliquoted into Eppendorf or similar tubes can be stored at −20 °C for brief periods or at −80 °C for longer terms. Samples should be protected from light. An aliquot can be thawed immediately before use, but repeated freeze-thaw cycles should be avoided. We have not experienced problems with samples that are stored according to these methods for at least six months. The stability of probes in various culture media have not been studied extensively, but we have observed that in some instances keeping dye solutions at 37 °C for longer than a few hours may affect imaging performances depending on the nature of the media.
3. Representative procedure for imaging mobile zinc in live cells
Fluorescence imaging often requires extensive optimization of cell culture, dye loading, and microscope setup procedures. These parameters depend on the nature of the biological sample and zinc sensor, the type of microscope, and the nature of the imaging experiment. In this section we present a robust protocol for imaging mobile zinc in live cells that is developed in our lab for a particular cell type (HeLa) and dye (ZP1). We also point out parameters most pertinent to zinc imaging that should be adjusted for use with other cell types and probes. The prototypical procedures can be adapted for imaging endogenous mobile zinc, as discussed in the next section.
We chose HeLa cells as the platform for testing the response of fluorescence sensors in a cellular environment. HeLa cells proliferate rapidly, adhere to glass slides during culture, and contain small nuclei, properties that facilitate fluorescence imaging and the determination of probe localization in the cytoplasm. The low cytosolic concentration of mobile zinc in HeLa maintains most probes in their OFF state until exogenous zinc is added.
3.1 Materials and instrumentation
Mammalian cells
HeLa cells (American Type Culture Collection).
Media
(1) Growth medium: Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM, Mediatech) with 10% heat-deactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS, HyClone) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin (Mediatech); (2) washing media: phosphate buffered saline (PBS, Mediatech), DMEM containing no dye, serum, or antibiotics. The growth medium and PBS should be filtered through 0.22 µm polyethersulfone membranes (Corning). Until use, DMEM-based media and PBS are kept at 4 °C and at room temperature, respectively.
Sensor
4 mM ZP1 stock solution in anhydrous DMSO.
Nuclear stain
4 mM Hoechst 33258 (Sigma) stock solution in water.
Exogenous zinc
10 mM ZnCl2 (99.999%, Aldrich) solution and 20 mM sodium pyrithione (2-mercaptopyridine-N-oxide sodium salt, Aldrich) solution, both in DMSO. The high purity of zinc source assures a fluorescence response that is specific to dynamic levels of zinc and not other metals.
Zinc chelator
20 mM TPEN solution in DMSO.
Cell culture and imaging supplies
Standard supplies for mammalian cell culture, as well as 35 mm glass-bottom culture dishes with 14 mm glass microwell pre-coated with poly-D-lysine (MatTek) for imaging.
Instrumentation
We performed fluorescence imaging experiments on an Axiovert 200M inverted epifluorescence microscope (Zeiss) equipped with an X-Cite 120 metal halide lamp (EXFO), an EM-CCD digital camera C9100 (Hamamatsu), and a MS200 XY Piezo Z stage (Applied Scientific Instruments). Filter sets 49 and 38HE (Zeiss) were used for imaging blue (Hoechst 33258) and green (zinc sensors) channels, respectively. The microscope was operated with Volocity software (Improvision). Images were processed with ImageJ software, freely available from the NIH.
3.2 Cell culture and sensor loading
HeLa cells are cultured according to the supplier’s procedures. In our experiments, we incubate the cells in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin-streptomycin at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2, and passage the cells every 3–4 days at nearly 100% confluence. We typically image cells with passage numbers of 4–20, both to ensure a stable, exponentially growing culture and to avoid cumulative changes at high passage numbers.
Two days before imaging
Plate cells onto 35 mm glass-bottom culture dishes containing 2 mL of pre-warmed growth medium per dish. At the time of imaging the confluence level is ca. 70%.
Ca. half an hour before imaging
Prepare dye-containing medium by adding 2.5 µL of ZP1 and 2 µL of Hoechst 33258 stock solutions to each 2 mL of pre-warmed growth medium to achieve final concentrations of 5 µM ZP1 and 4 µM Hoechst 33258. Remove the growth medium from the culture dishes and add 2 mL of dye-containing medium to each dish. Incubate cells at 37 °C under 5% CO2 for half an hour before imaging.
Right before imaging
Remove the dye-containing media from culture dishes. Rinse cells twice with 2 mL of pre-warmed PBS, then once with 2 mL of dye- and serum-free DMEM, and finally bathe cells in 2 mL of dye- and serum-free DMEM.
3.3 Imaging mobile zinc
Imaging background
Before taking images of the biological specimen, suitable microscope parameters must be determined. Since they are often specific to the microscope type, we omit here details of microscope operation and concentrate instead on general procedures for fluorescence imaging. With the proper imaging parameters, acquire a differential interference contrast (DIC) image and images from both blue (Hoechst 33258) and green (ZP1) channels.
Exogenous zinc
Constitute the zinc/pyrithione complex by combining 10 µL of ZnCl2 and 10 µL of pyrithione stock DMSO solutions, and add the colorless solution thus obtained sporadically to the dish to achieve a final zinc concentration of 50 µM. If necessary, use the signal of the blue channel (nuclear stain) as a reference for focusing purposes. Image the green channel with the same acquisition settings prior to addition of zinc. With pyrithione used as an ionophore to deliver zinc into cells, a fluorescence turn-on is typically observed within seconds.
Zinc chelator control
Add 10 µL of TPEN stock solution in DMSO to the dish to achieve a final concentration of 100 µM. Image the green channel with the same acquisition parameters. It can take 3–5 min to fully reverse the fluorescence signals. It is also important to check cell morphology and viability after adding TPEN because, depending on the imaging conditions and the nature of cell samples, TPEN treatment can result in cell death.
3.4 Image processing and results
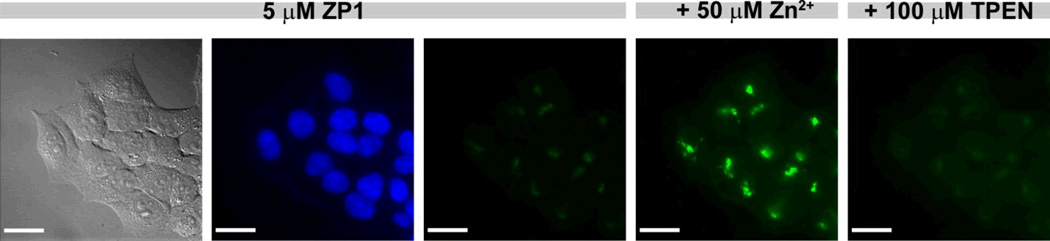
In order to compare the fluorescence intensities before and after addition of exogenous zinc and TPEN, the images acquired with identical parameters need to be adjusted to the same intensity scale. Figure 2 displays a typical series of images on the same intensity scale. Addition of exogenous zinc induced an increase in fluorescence; the punctate pattern of ZP1 fluorescence is consistent with its localization to the Golgi apparatus, determined previously with colocalization studies (Walkup et al, 2000). Upon subsequent addition of TPEN, a cell-permeable zinc chelator, the fluorescence signal is reversed. TPEN addition serves as an important control experiment to ensure that the fluorescence turn-on resulted from zinc-binding to the probe. Failure to reverse fluorescence by TPEN is an indication that the turn-on is, at least in part, due to other mechanisms such as photoactivation. Such data should be discarded. When detecting endogenous zinc, control experiments co-administering dye and chelator are particularly important in identifying the source of fluorescence turn-on.
Figure 2.
Fluorescence imaging of live HeLa cells treated with 5 µM ZP1 (left to right: DIC image, nuclear stain Hoechst 33258, and ZP1). Addition of 50 µM zinc/pyrithione resulted in fluorescence enhancement, which was reversed by treatment with 100 µM TPEN. Scale bar = 25 µm.
3.5 Optimization
The procedure presented above illustrates a method for imaging cellular zinc that has been optimized in our lab for a particular dye and a cell type. The variety among biological specimens and subtle differences between different probes necessitate optimization of many parameters, in particular dye concentration and loading time. Among others properties, the permeability of a dye has a pronounced effect. For example, ZPP1, which is less permeable than ZP1, requires 1–3 h incubation to achieve full fluorescence turn-on in HeLa cells following treatment with zinc/pyrithione (Buccella et al, 2011). Additionally, it is desirable to use minimum dye concentration to reduce background fluorescence. During live-cell imaging, reduced illumination is preferred both to maintain cell health and to prevent dye photobleaching.
The zinc/pyrithione complex is constituted in situ by combining high-purity zinc salt with sodium pyrithione. When a low-affinity probe such as QZ2 is used for imaging intracellular zinc, a substoichiometric amount of ionophore may be used to avoid its competitive binding with zinc inside cells (Nolan et al, 2005).
Although it is convenient to apply directly zinc/pyrithione and TPEN stock solutions in DMSO to the culture dish, mixing DMSO and aqueous media generates heat and the slow diffusion of DMSO often causes non-uniform delivery of mobile zinc. In addition, direct addition of the zinc/pyrithione solution to some media such as Neurobasal may result in precipitation (Nolan et al, 2006). To avoid these issues, DMSO solutions can be first diluted into serum-free medium or PBS before addition to the specimen. For example, one may combine DMSO solutions of ZnCl2 and sodium pyrithione in a 1:2 ratio and dilute 10-fold with DMEM; adding 200 µL of this solution to the dish gives a final zinc concentration of 50 µM. Similarly, diluting 20 mM TPEN stock solution 10-fold with serum-free DMEM and adding 100 µL to the stage yields 100 µM final concentration (Nolan et al, 2006). Moreover, we have observed that dye loading by incubation in DMEM containing only 1% FBS gave better imaging results (Nolan et al, 2006).
3.6 Imaging mobile zinc with a trappable probe
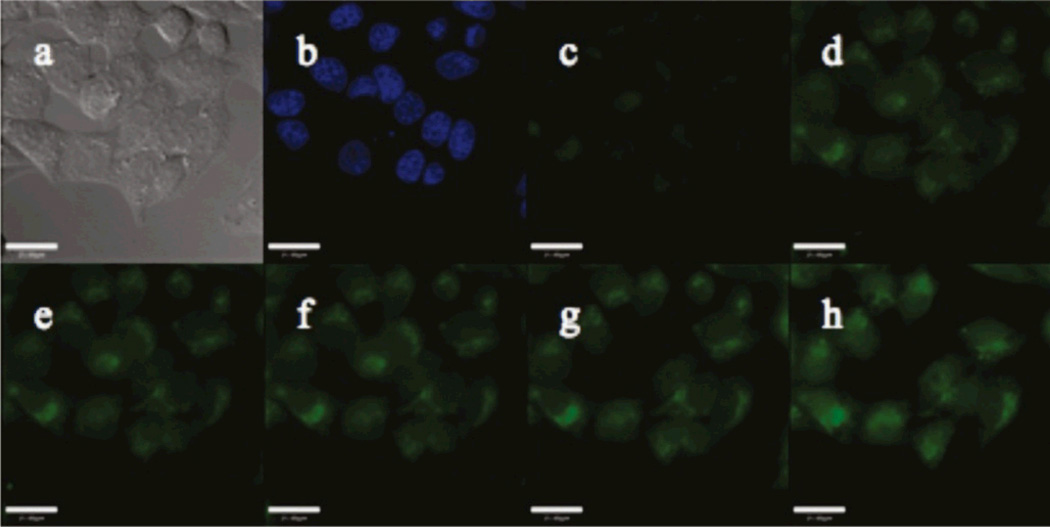
Imaging with trappable probes, which are advantageous for experiments requiring continuous washing or media perfusion, can be carried out in a similar manner as described above for ZP1. For instance, to image with QZ2E, incubate HeLa cells with 5 µM QZ2E for 18 h following the methods described above (McQuade and Lippard, 2010). During this period QZ2E becomes hydrolyzed by intracellular esterases to afford its acid form, QZ2A, which upon addition of 100 µM zinc/pyrithione generates bright green fluorescence (Figure 3). Although cells may be perfused continuously, to mimic such conditions we wash cells every 10 min with 1 mL of serum-free DMEM for three times and bathe them in 2 mL of fresh serum-free DMEM. During this process, the cells are maintained in a microscope incubator at 37 °C under 5% CO2. Despite continuous washing for 45 min, the green fluorescent signals persists inside the cells (Figure 3), suggesting that the resultant acid form is largely retained intracellularly.
Figure 3.
Fluorescence imaging of live HeLa cells incubated with a trappable probe, QZ2E. (a) DIC image, (b) nuclear stain Hoechst 33258, (c) QZ2E, (d) green fluorescence signals 5 min after addition of 100 µM 1:1 Zn/pyrithione, and (e–h) green signals during periodic washing taken at 10 min-intervals. Scale bar = 25 µm. Reprinted with permission from McQuade and Lippard, 2010. Copyright 2010 American Chemical Society.
4. Imaging endogenous neuronal zinc in live cells and tissues
In this section, we provide examples to illustrate how zinc fluorescence probes allow for imaging endogenous mobile zinc in both live cells and tissues. The experiments with hippocampal neurons and slices were carried out using probes of larger dynamic range and varying affinity (low-nM ZP3 and low-µM ZS5, Chang et al, 2004a; Nolan et al, 2006), both to demonstrate their capability to illuminate endogenous pools of mobile zinc and to illustrate their use in studying the dynamics of zinc mobilization. Since many of the challenges reside in sample preparation as discussed in the literature (Banker and Goslin, 1998), for the sake of conciseness without loss of generality we focus on methods most pertinent to zinc imaging.
Fluorescence-imaging experiments were performed with a Zeiss LSM510 laser scanning confocal microscope (Nolan et al, 2006; Chang et al, 2004a), or a two-photon microscope based on an Olympus Fluoview 300 and BX50WI (Chang et al, 2004b). Samples were excited at 488 nm with an Ar laser (confocal) or at 800 nm with a Ti:sapphire laser (two-photon). During imaging the samples were maintained at 37 °C under 5% CO2 with an incubator on the microscope stage.
4.1 Imaging static and dynamic mobile zinc in live dentate gyrus neurons
Since zinc-rich glutamatergic synaptic vesicles are of the highest density in the dentate gyrus (DG) region of the hippocampus, primary cultures of DG neurons are particularly valuable for studying the neurobiology of mobile zinc. In this section, we demonstrate that fluorescence probes of different zinc-binding affinity (ZP3 and ZS5) not only enable to visualize the pool of static endogenous zinc that is present in live DG neurons (Chang et al, 2004a), but also allows for imaging dynamic changes in mobile zinc levels that occur following nitrosative stress (Nolan et al, 2006). In this experiment nitric oxide (NO) is generated in situ from S-nitrosocysteine (SNOC) immediately before use.
Cell culture
Postnatal DG neurons were prepared and cultured as described previously (Chang et al, 2004a; Nolan et al, 2006; Figiel and Kaczmarek, 1997). Briefly, dissect DG regions from the hippocampi of 4-day-old Sprague-Dawley rat pups. Plate the dissociated cells on 24 mm glass cover slips (250 cells/mm2) coated with poly-L-lysine (50 µg/mL). Keep the cells for the first 24 h in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (FCS, Invitrogen), glutamine (2 mM), and penicillin-streptomycin mix (50 µg/mL), and then in Neurobasal medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with B27 (Invitrogen), glutamine (2 mM), KCl (20 mM), and penicillin-streptomycin mix (50 µg/mL).
Cell treatment and imaging
After 7 days in culture, incubate cells in media containing 10 µM ZP3 for 20 min or containing 10 µM ZS5 (B27-free) for 30 min (samples for the ZP3 and ZS5 experiments are prepared independently). Wash cells once with dye-free media before confocal imaging. For the ZS5 experiment, add an aliquot of SNOC to achieve a final concentration of 1.5 mM, and record fluorescence signals at 1-minute intervals. In both experiments, to confirm that the observed fluorescence originates from zinc binding, add an aliquot of TPEN solution to achieve a final concentration of 50 µM (for ZP3) or 200 µM (for ZS5).
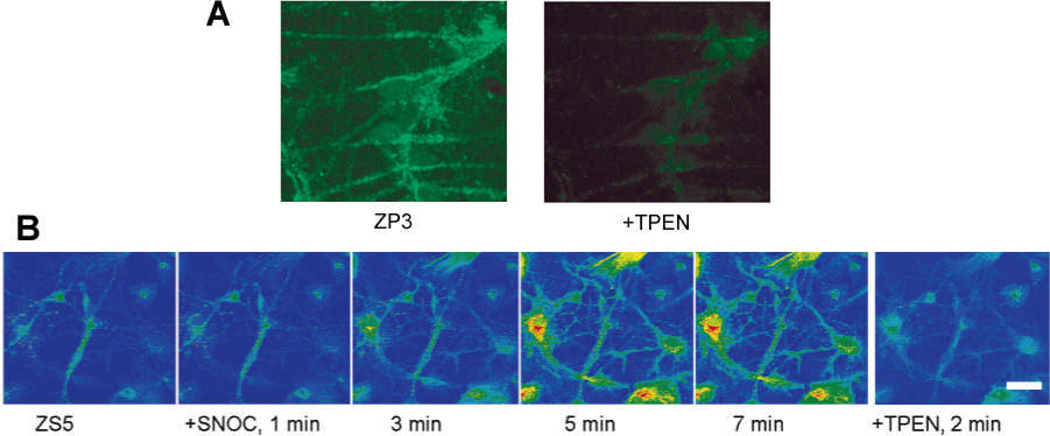
Results
As shown in Figure 4A, the bright fluorescence in DG neurons stained by ZP3, which was reversed upon addition of TPEN, illustrates that the high-affinity probe ZP3 enables visualization of endogenous zinc pools in live neurons (Chang et al, 2004a). In contrast, the low-affinity probe ZS5 showed only weak fluorescence signals (Figure 4B, Nolan et al, 2006). This comparison illustrates how zinc-binding affinity is an important parameter to consider in the choice of zinc probes. On the other hand, the low affinity probe facilitates zinc imaging at higher concentrations (Nolan et al, 2006); after nitrosative stress induced by SNOC, DG neurons gave enhanced ZS5 fluorescence that maximizes at ca. 5 min, demonstrating NO-triggered zinc release from native protein stores. Such signals were also reversed by TPEN treatment.
Figure 4.
Confocal fluorescence images of live dentate gyrus neurons stained with ZP3 or ZS5. (A) ZP3 allowed for visualization of endogenous mobile zinc; (B) ZS5 enabled imaging the dynamics of zinc mobilization following SNOC-triggered nitrosative stress. Signals in both experiments were reversed by TPEN addition. Scale bar in B = 25 µm. Adapted with permission from (A) Chang et al, 2004a and (B) Nolan et al, 2006. Copyright (A) 2004 Elsevier Science Ltd and (B) 2006 American Chemical Society.
4.2 Imaging endogenous zinc in acute hippocampal slices
Compared to dissociated cultures, neuronal tissues may provide a cellular environment that better resembles the native organism. Studies of hippocampal slices may therefore provide information not possible to obtain by using dissociated cultures. In this section we demonstrate that probes such as ZP3 also allow for imaging endogenous zinc in hippocampal slices with both two-photon and confocal microscopy.
Slice preparation and imaging
Acute hippocampal slices were prepared as described previously (Chang et al, 2004a; Chang et al, 2004b). Briefly, remove the whole brain of a 60- or 90-day old Sprague-Dawley rat and dissect its hippocampus into 0.4–1.0 mm-thick slices. Immediately wash the slices twice with zinc-free Krebs ringer buffer (prepared according to Qian et al, 2003), and incubate with 10 µM ZP3 for 20 min at 37 °C under 5% CO2. Wash the slices twice more with zinc-free Krebs ringer buffer to remove excess dye, and transfer to glass-bottom dishes for imaging with two-photon or confocal microscopy. Subsequently treat the slices with 50 µM TPEN for 20 min at 37 °C before imaging again.
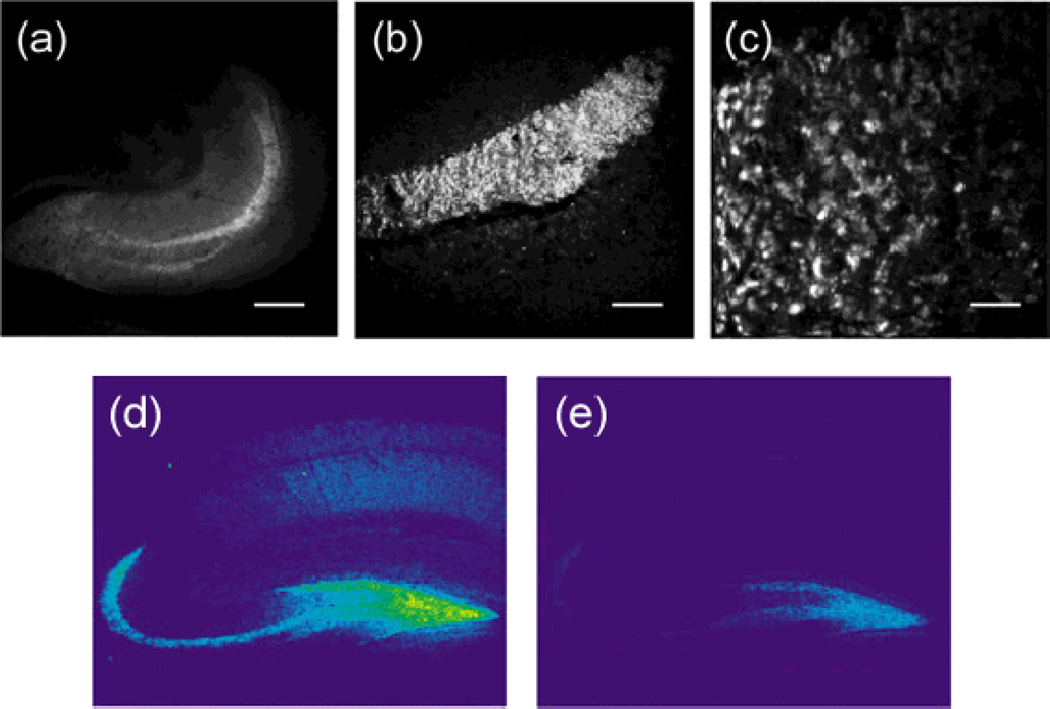
Results
Both two-photon and confocal fluorescence images (Figure 5) showed that the hilus of the dentate gyrus (DG) and the stratum lucidum of the CA3 region were vividly stained by ZP3, and the intensely-stained individual giant mossy fiber boutons were resolved with two-photon microscopy (Chang et al, 2004b; Chang et al, 2004a). Such zinc-induced fluorescence signals were reversed upon TPEN treatment. Our results are consistent with high-concentrations of mobile zinc stored in mossy fiber boutons that project between the DG and CA3 neurons.
Figure 5.
Two-photon and confocal fluorescence images of acute mouse hippocampal slices stained with ZP3. Images acquired with two-photon microscopy show (a) the entire slice section of a hippocampus, (b) the stratum lucidum layer, and (c) individual giant mossy fiber boutons. Confocal microscopy produced similar zinc-evoked fluorescence signals after ZP3 staining (d), which diminished upon addition of TPEN (e). Scale bars = (a) 800 µm, (b) 200 µm, or (c) 10 µm. Adapted with permission from (a–c) Chang et al, 2004b and (d–e) Chang et al, 2004a. Copyright (a–c) 2004 American Chemical Society and (d–e) 2004 Elsevier Science Ltd.
5. Concluding remarks
Fluorescence zinc probes not only provide static pictures of mobile zinc distribution, but are also capable of reporting its dynamics in live biological specimens, thereby opening a window for studying the physiology and pathology of mobile zinc. The selection guide in this article should help readers to identify suitable sensors for their particular research areas of mobile zinc biology, and the representative procedures presented here for imaging mobile zinc in live cells and tissues can serve as a guide of using them for fluorescence microscopy in studies of diverse biological events pertinent to zinc function.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH grant GM065519 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. We thank Dr. E. M. Nolan for insightful discussions, Dr. D. Buccella for valuable comments and assistance in work described in Sections 3.1–3.5, Dr. L. E. McQuade for performing experiments described in Section 3.6, and Drs. C. J. Chang and E. M. Nolan for carrying out work described in Section 4. Drs. J. Jaworski and J. W. Ryu in the lab of M. Sheng and Dr. K.-I. Okamoto in the lab of Y. Hayashi are acknowledged for their assistance on confocal and two-photon microscopy, respectively.
References
- Anderegg G, Hubmann E, Podder NG, Wenk F. Pyridine derivatives as complexing agents. XI. Thermodynamics of metal complex formation with bis-, tris- and tetrakisi(2-pyridyl)methyl]-amines. Helv. Chim. Acta. 1977;60:123–140. [Google Scholar]
- Banker G, Goslin K, editors. Culturing Nerve Cells. MIT Press; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Brannon JH, Magde D. Absolute quantum yield determination by thermal blooming. Fluorescein. J. Phys. Chem. 1978;82:705–709. [Google Scholar]
- Buccella D, Horowitz JA, Lippard SJ. Understanding zinc quantification with existing and advanced ditopic fluorescent Zinpyr sensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011;133:4101–4114. doi: 10.1021/ja110907m. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdette SC, Frederickson CJ, Bu W, Lippard SJ. ZP4, an improved neuronal Zn2+ sensor of the Zinpyr family. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:1778–1787. doi: 10.1021/ja0287377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang CJ, Lippard SJ. Neurodegenerative Diseases and Metal Ions. John Wiley & Sons; 2006. "Zinc metalloneurochemistry: Physiology, pathology, and probes."; pp. 321–370. [Google Scholar]
- Chang CJ, Nolan EM, Jaworski J, Burdette SC, Sheng M, Lippard SJ. Bright fluorescent chemosensor platforms for imaging endogenous pools of neuronal zinc. Chem. Biol. 2004a;11:203–210. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang CJ, Nolan EM, Jaworski J, Okamoto K-I, Hayashi Y, Sheng M, Lippard SJ. ZP8, a neuronal zinc sensor with improved dynamic range; Imaging zinc in hippocampal slices with two-photon microscopy. Inorg. Chem. 2004b;43:6774–6779. doi: 10.1021/ic049293d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello L, Franklin R. The clinical relevance of the metabolism of prostate cancer; zinc and tumor suppression: connecting the dots. Mol. Cancer. 2006;5:17. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-5-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du P, Lippard SJ. A highly selective turn-on colorimetric, red fluorescent sensor for detecting mobile zinc in living cells. Inorg. Chem. 2010;49:10753–10755. doi: 10.1021/ic101569a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide DJ. Zinc transporters and the cellular trafficking of zinc. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2006;1763:711–722. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figiel I, Kaczmarek L. Cellular and molecular correlates of glutamate-evoked neuronal programmed cell death in the in vitro cultures of rat hippocampal dentate gyrus. Neurochem. Int. 1997;31:229–240. doi: 10.1016/s0197-0186(96)00152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin RB, Costello LC. The important role of the apoptotic effects of zinc in the development of cancers. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009;106:750–757. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederickson CJ, Danscher G. Zinc-containing neurons in hippocampus and related CNS structures. Prog. Brain Res. 1990;83:71–84. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)61242-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederickson CJ, Kasarskis EJ, Ringo D, Frederickson RE. A quinoline fluorescence method for visualizing and assaying the histochemically reactive zinc (bouton zinc) in the brain. J. Neurosci. Methods. 1987;20:91–103. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(87)90042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederickson CJ, Koh J-Y, Bush AI. The neurobiology of zinc in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005;6:449–462. doi: 10.1038/nrn1671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh SK, Kim P, Zhang X-a, Yun S-H, Moore A, Lippard SJ, Medarova Z. A novel imaging approach for early detection of prostate cancer based on endogenous zinc sensing. Cancer Res. 2010;70:6119–6127. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldys EM, editor. Fluorescence Applications in Biotechnology and Life Sciences. Wiley-Blackwell; 2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T, Murakami M, Fukada T, Nishida K, Yamasaki S, Suzuki T. Roles of zinc and zinc signaling in immunity: Zinc as an intracellular signaling molecule. Adv. Immunol. 2008;97:149–176. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)00003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John E, Laskow TC, Buchser WJ, Pitt BR, Basse PH, Butterfield LH, Kalinski P, Lotze MT. Zinc in innate and adaptive tumor immunity. J. Transl. Med. 2010;8:118. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-8-118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppler A, Gendreizig S, Gronemeyer T, Pick H, Vogel H, Johnsson K. A general method for the covalent labeling of fusion proteins with small molecules in vivo. Nat. Biotech. 2003;21:86–89. doi: 10.1038/nbt765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu K, Urano Y, Kojima H, Nagano T. Development of an iminocoumarin-based zinc sensor suitable for ratiometric fluorescence imaging of neuronal zinc. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:13447–13454. doi: 10.1021/ja072432g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz JR. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy. New York: Springer; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lee T, Zhang X-a, Dhar S, Faas H, Lippard SJ, Jasanoff A. In vivo imaging with a cell-permeable porphyrin-based MRI contrast agent. Chem. Biol. 2010;17:665–673. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.05.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y, Hough CJ, Frederickson CJ, Sarvey JM. Induction of mossy fiber→CA3 long-term potentiation requires translocation of synaptically released Zn2+ J. Neurosci. 2001;21:8015–8025. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-20-08015.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maret W. Molecular aspects of human cellular zinc homeostasis: redox control of zinc potentials and zinc signals. BioMetals. 2009;22:149–157. doi: 10.1007/s10534-008-9186-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQuade LE, Lippard SJ. Cell-trappable quinoline-derivatized fluoresceins for selective and reversible biological Zn(II) detection. Inorg. Chem. 2010;49:9535–9545. doi: 10.1021/ic1012507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan EM, Jaworski J, Okamoto K-I, Hayashi Y, Sheng M, Lippard SJ. QZ1 and QZ2: Rapid, reversible quinoline-derivatized fluoresceins for sensing biological Zn(II) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005;127:16812–16823. doi: 10.1021/ja052184t. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan EM, Lippard SJ. Small-molecule fluorescent sensors for investigating zinc metalloneurochemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009;42:193–203. doi: 10.1021/ar8001409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan EM, Ryu JW, Jaworski J, Feazell RP, Sheng M, Lippard SJ. Zinspy sensors with enhanced dynamic range for imaging neuronal cell zinc uptake and mobilization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:15517–15528. doi: 10.1021/ja065759a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluth MD, Tomat E, Lippard SJ. Biochemistry of mobile zinc and nitric oxide revealed by fluorescent sensors. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011;80 doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-061009-091643. in press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian W-J, Gee KR, Kennedy RT. Imaging of Zn2+ release from pancreatic β-cells at the level of single exocytotic events. Anal. Chem. 2003;75:3468–3475. doi: 10.1021/ac0341057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Que EL, Domaille DW, Chang CJ. Metals in neurobiology: Probing their chemistry and biology with molecular imaging. Chem. Rev. 2008;108:1517–1549. doi: 10.1021/cr078203u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sensi SL, Paoletti P, Bush AI, Sekler I. Zinc in the physiology and pathology of the CNS. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009;10:780–791. doi: 10.1038/nrn2734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor CG. Zinc, the pancreas, and diabetes: insights from rodent studies and future directions. BioMetals. 2005;18:305–312. doi: 10.1007/s10534-005-3686-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomat E, Lippard SJ. Imaging mobile zinc in biology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010;14:225–230. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.12.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomat E, Nolan EM, Jaworski J, Lippard SJ. Organelle-specific zinc detection using Zinpyr-labeled fusion proteins in live cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:15776–15777. doi: 10.1021/ja806634e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien RY. "Monitoring cell calcium.". In: Carafoli E, Klee C, editors. Calcium as a Cellular Regulator. New York: Oxford University Press; 1999. pp. 28–54. [Google Scholar]
- Tsien RY. Imagining imaging's future. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003;4:SS16–SS21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee BL, Falchuk KH. The biochemical basis of zinc physiology. Physiol. Rev. 1993;73:79–118. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinkenborg JL, Koay MS, Merkx M. Fluorescent imaging of transition metal homeostasis using genetically encoded sensors. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010;14:231–237. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.11.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walkup GK, Burdette SC, Lippard SJ, Tsien RY. A new cell-permeable fluorescent probe for Zn2+ J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000;122:5644–5645. [Google Scholar]
- Wong BA, Friedle S, Lippard SJ. Solution and fluorescence properties of symmetric dipicolylamine-containing dichlorofluorescein-based Zn2+ sensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009a;131:7142–7152. doi: 10.1021/ja900980u. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong BA, Friedle S, Lippard SJ. Subtle modification of 2,2-dipicolylamine lowers the affinity and improves the turn-on of Zn(II)-selective fluorescent sensors. Inorg. Chem. 2009b;48:7009–7011. doi: 10.1021/ic900990w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroofe CC, Lippard SJ. A novel two-fluorophore approach to ratiometric sensing of Zn2+ J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:11458–11459. doi: 10.1021/ja0364930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroofe CC, Masalha R, Barnes KR, Frederickson CJ, Lippard SJ. Membrane-permeable and -impermeable sensors of the Zinpyr family and their application to imaging of hippocampal zinc in vivo. Chem. Biol. 2004;11:1659–1666. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroofe CC, Won AC, Lippard SJ. Esterase-activated two-fluorophore system for ratiometric sensing of biological zinc(II) Inorg. Chem. 2005;44:3112–3120. doi: 10.1021/ic048789s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Z, Baek K-H, Kim HN, Cui J, Qian X, Spring DR, Shin I, Yoon J. Zn2+-triggered amide tautomerization produces a highly Zn2+-selective, cell-permeable, and ratiometric fluorescent sensor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009;132:601–610. doi: 10.1021/ja907334j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- You Y, Tomat E, Hwang K, Atanasijevic T, Nam W, Jasanoff AP, Lippard SJ. Manganese displacement from Zinpyr-1 allows zinc detection by fluorescence microscopy and magnetic resonance imaging. Chem. Commun. 2010;46:4139–4141. doi: 10.1039/c0cc00179a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X-a, Hayes D, Smith SJ, Friedle S, Lippard SJ. New strategy for quantifying biological zinc by a modified zinpyr fluorescence sensor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:15788–15789. doi: 10.1021/ja807156b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X-a, Lovejoy KS, Jasanoff A, Lippard SJ. Water-soluble porphyrins as a dual-function molecular imaging platform for MRI and fluorescence zinc sensing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:10780–10785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702393104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]