Abstract
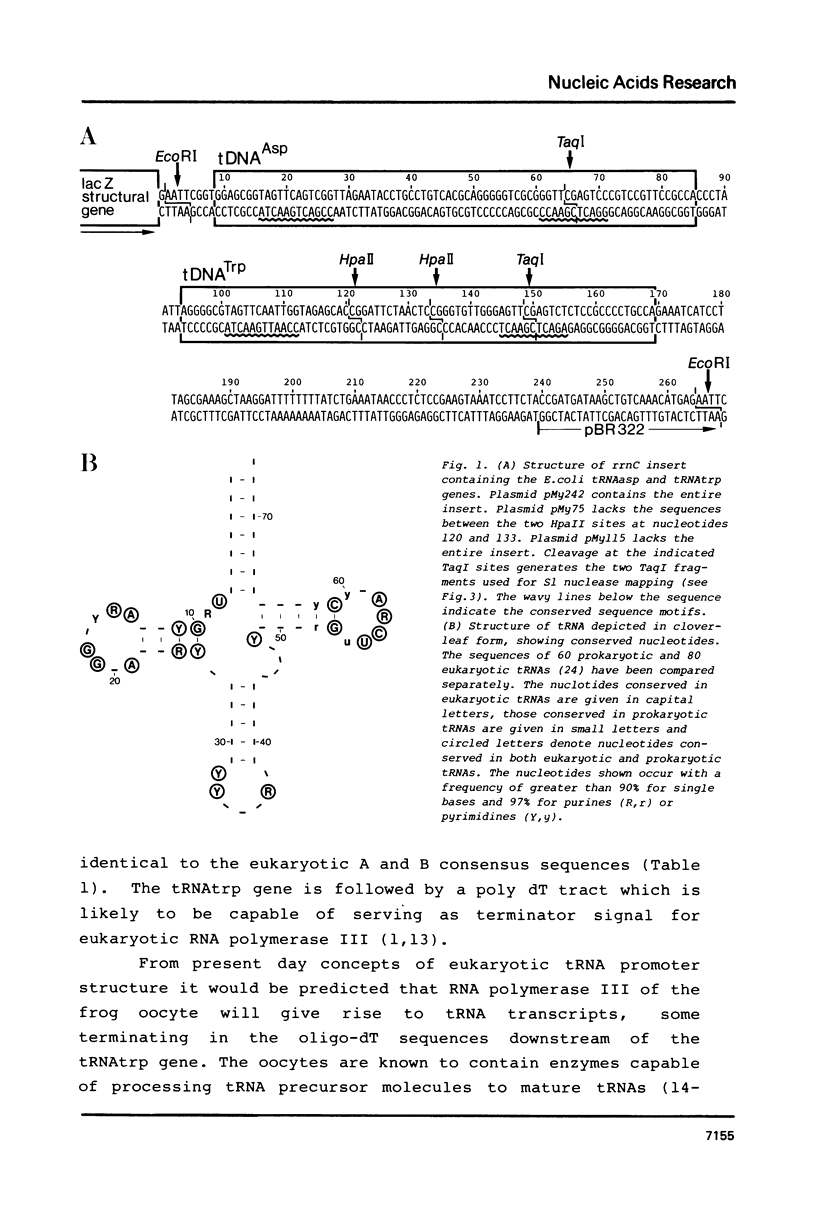
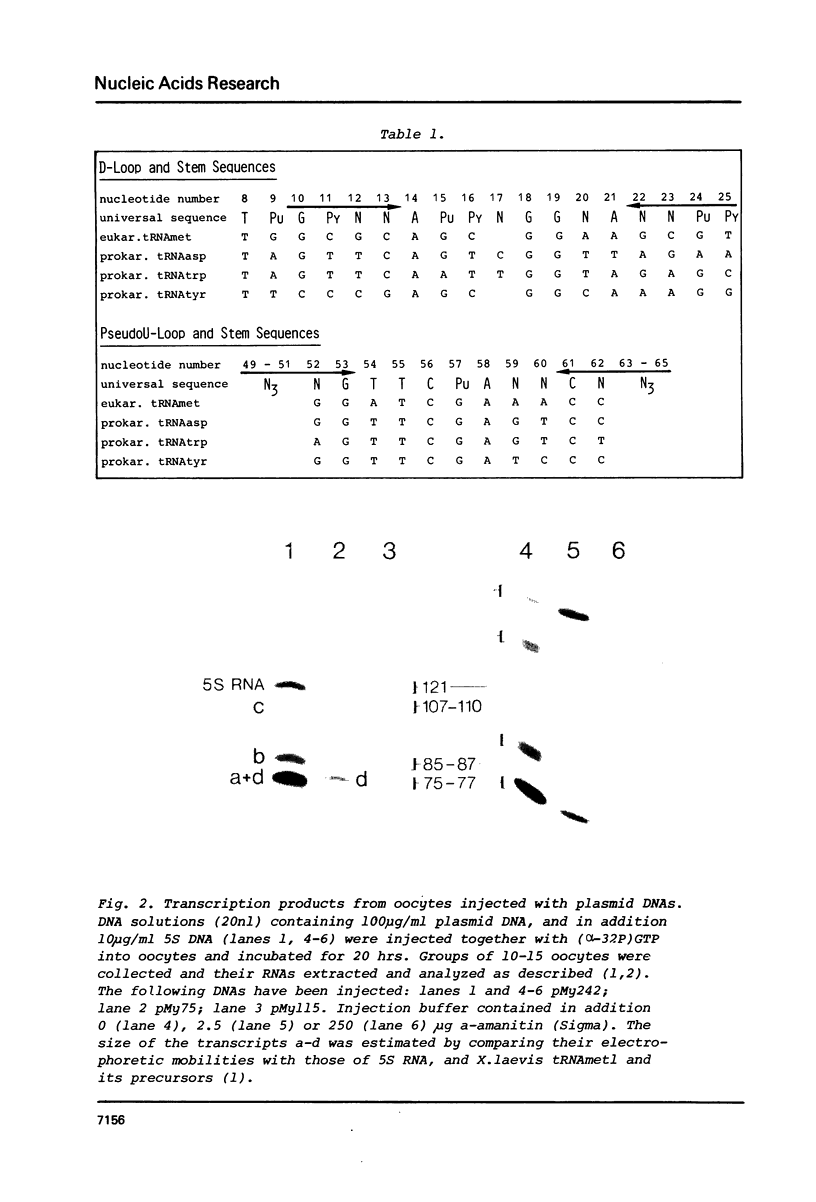
E. coli genes for tRNAasp and tRNAtrp are transcribed by eukaryotic RNA polymerase III upon injection into nuclei of Xenopus oocytes. This indicates that some bacterial tRNA genes contain RNA polymerase III promoter sequences. We discuss evolutionary aspects of this finding.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription termination. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90522-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrara G., Di Segni G., Otsuka A., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Deletion of the 3' half of the yeast tRNA-Leu3 gene does not abolish promotor function in vitro. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90420-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D., Brown D. D. Adjacent repeating units of Xenopus laevis 5S DNA can be heterogeneous in length. Cell. 1976 Apr;7(4):477–486. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90199-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Castagnoli L., Melton D. A., Cortese R. Promoter of a eukaryotic tRNAPro gene is composed of three noncontiguous regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1195–1199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Traboni C., Cortese R. Relationship between the two components of the split promoter of eukaryotic tRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1921–1925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigen M., Winkler-Oswatitsch R. Transfer-RNA, an early gene? Naturwissenschaften. 1981 Jun;68(6):282–292. doi: 10.1007/BF01047470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigen M., Winkler-Oswatitsch R. Transfer-RNA: the early adaptor. Naturwissenschaften. 1981 May;68(5):217–228. doi: 10.1007/BF01047323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Birnstiel M. L. Two conserved sequence blocks within eukaryotic tRNA genes are major promoter elements. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):626–631. doi: 10.1038/294626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss D. H., Sprinzl M. Compilation of tRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):r1–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Prescott D. M., Greenberg B. M., Hallick R. B. Transcription of E. coli and Euglena chloroplast tRNA gene clusters and processing of polycistronic transcripts in a HeLa cell-free system. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. D., Clarkson S. G., Tocchini-Valentini G. Transcription initiation of eucaryotic transfer RNA genes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter H., Kressman A., Birnstiel M. L. A split promoter for a eucaryotic tRNA gene. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):573–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J. Transcription of Xenopus 5S ribosomal RNA genes. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):101–105. doi: 10.1038/295101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kressmann A., Hofstetter H., Di Capua E., Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. A tRNA gene of Xenopus laevis contains at least two sites promoting transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1749–1763. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J., Schmidt O., Söll D. Dimeric transfer RNA precursors in S. pombe. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):509–516. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90488-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Cortese R. Transcription of cloned tRNA genes and the nuclear partitioning of a tRNA precursor. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1165–1172. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., De Robertis E. M., Cortese R. Order and intracellular location of the events involved in the maturation of a spliced tRNA. Nature. 1980 Mar 13;284(5752):143–148. doi: 10.1038/284143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. A., Ikemura T., Lindahl L., Fallon A. M., Nomura M. Some rRNA operons in E. coli have tRNA genes at their distal ends. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90202-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traboni C., Ciliberto G., Cortese R. A novel method for site-directed mutagenesis: its application to an eukaryotic tRNAPro gene promoter. EMBO J. 1982;1(4):415–420. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01184.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarus M., McMillan C., 3rd, Cline S., Bradley D., Snyder M. Construction of a composite tRNA gene by anticodon loop transplant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5092–5096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]