Abstract
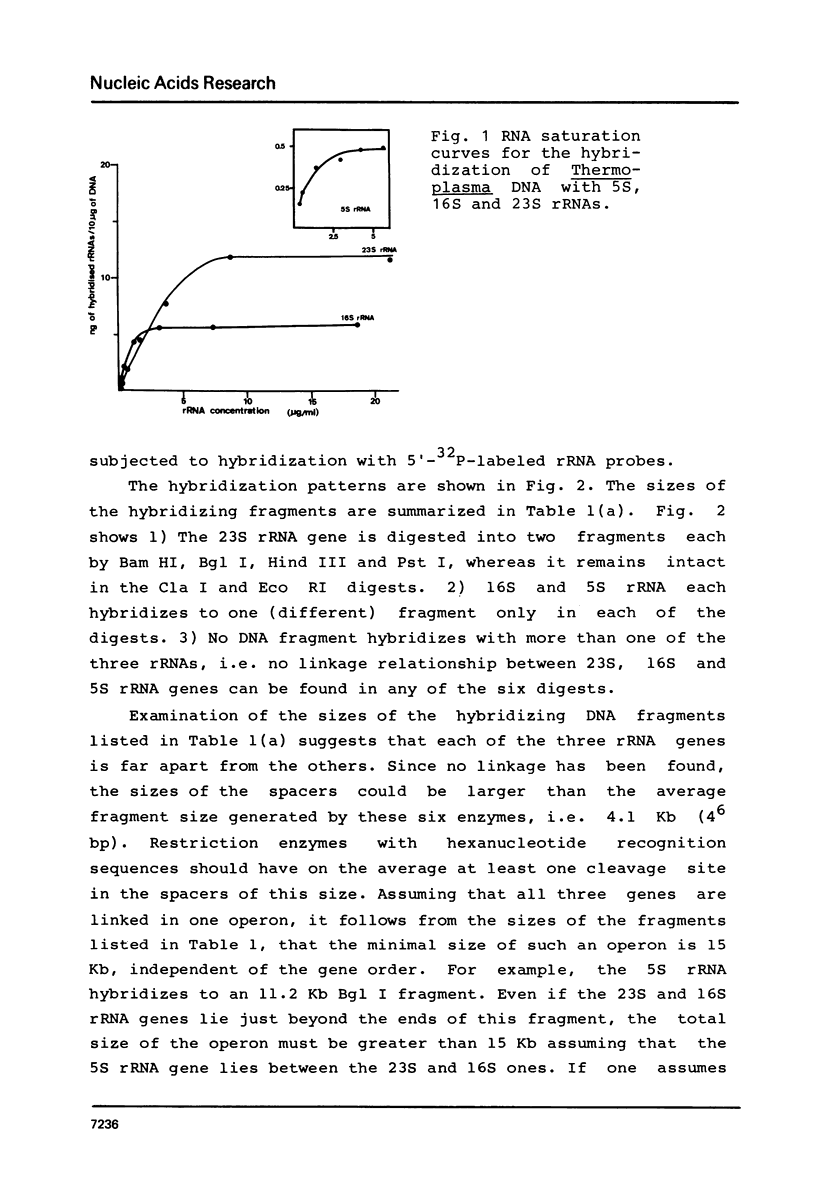
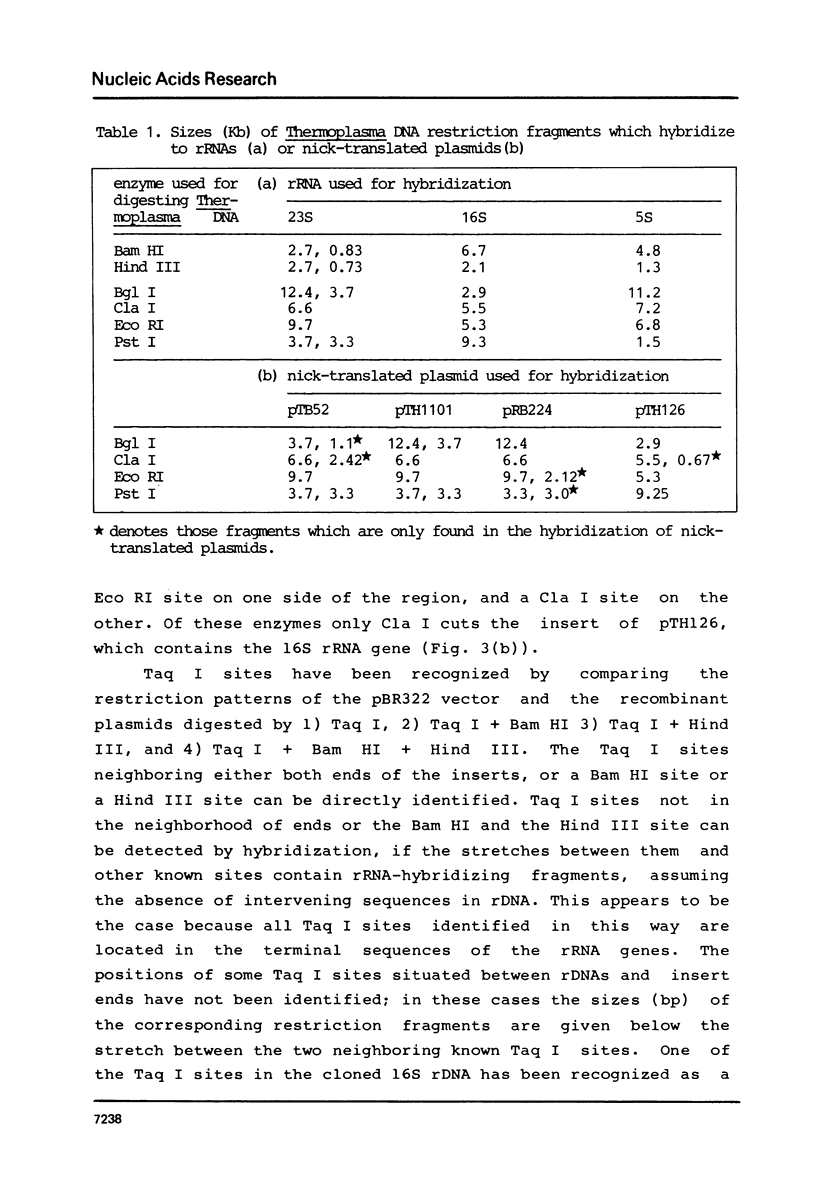
In the archaebacterium Thermoplasma acidophilum, each of the structural genes for 5S, 16S and 23S rRNA occur once per genome. In contrast to those of eubacteria and eukaryotes, they appear unlinked. The distance between the 16S and the 23S rDNA is at least 7.5 Kb, that between 23S and 5S rDNA at least 6 Kb and that between 16S and 5S rDNA at least 1.5 Kb. No linkage between those genes has been found by the analysis of recombinant plasmids carrying Bam HI and Hind III rDNA fragments as by hybridizing those plasmids to fragments of Thermoplasma DNA generated by 6 individual restriction endonucleases, recognizing hexanucleotide sequences.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Parker B. A., Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:220–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedbrook J. R., Kolodner R., Bogorad L. Zea mays chloroplast ribosomal RNA genes are part of a 22,000 base pair inverted repeat. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., DeGennaro L. J., Gelfand D. H., Bishop R. J., Valenzuela P., Rutter W. J. Ribosomal RNA genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. I. Physical map of the repeating unit and location of the regions coding for 5 S, 5.8 S, 18 S, and 25 S ribosomal RNAs. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8118–8125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaconas G., van de Sande J. H. 5'-32P labeling of RNA and DNA restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Adams J. M. A very large repeating unit of mouse DNA containing the 18S, 28S and 5.8S rRNA genes. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90292-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darland G., Brock T. D., Samsonoff W., Conti S. F. A thermophilic, acidophilic mycoplasma isolated from a coal refuse pile. Science. 1970 Dec 25;170(3965):1416–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3965.1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Ley J., De Smedt J. Improvements of the membrane filter method for DNA:rRNA hybridization. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1975;41(3):287–307. doi: 10.1007/BF02565064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugaiczyk A., Boyer H. W., Goodman H. M. Ligation of EcoRI endonuclease-generated DNA fragments into linear and circular structures. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):171–184. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90189-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser R. S., Creanor J. Rapid and selective inhibition of RNA synthesis in yeast by 8-hydroxyquinoline. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):67–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03597.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbach R. W., Bollen-de Boer J. E., van Bruggen E. F., Borst P. Conservation of the sequence and position of the ribosomal RNA genes in Tetrahymena pyriformis mitochondrial DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 21;521(1):187–197. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90261-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbach R. W., Borst P., Bollen-de Boer J. E., van Bruggen E. F. The organization of ribosomal RNA genes in the mitochondrial DNA of Tetrahymena pyriformis strain ST. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 21;521(1):169–186. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90260-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. L., Lifton R. P., Stark G. R., Williams J. G. Isolation of specific RNA's using DNA covalently linked to diazobenzyloxymethyl cellulose or paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:206–220. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb A., Daniel V. Mapping of transcription units in the bacteriophage T4 tRNA gene cluster. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 15;146(4):393–412. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Grimm M. F., Goewert R. R., Collins R. A., Cole M. D., Lambowitz A. M., Heckman J. E., Yin S., RajBhandary U. L. Transcripts and processing patterns for the ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA region of Neurospora crassa mitochondrial DNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):2027–2034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm M. F., Lambowitz A. M. The 32 S RNA of Neurospora crassa mitochondria is not a precursor of the mitochondrial ribosomal RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 5;134(3):667–672. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90373-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A., Lindan C. P., D'Andrea A. D., Johnsrud L. The use of DNA fragments of defined sequence for the study of DNA damage and repair. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):235–248. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckman J. E., RajBhandary U. L. Organization of tRNA and rRNA genes in N. crassa mitochondria: intervening sequence in the large rRNA gene and strand distribution of the RNA genes. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):583–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman J. D., Lau R. H., Doolittle W. F. The number, physical organization and transcription of ribosomal RNA cistrons in an archaebacterium: Halobacterium halobium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1321–1333. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannella C. A., Collins R. A., Green M. R., Lambowitz A. M. Defective splicing of mitochondrial rRNA in cytochrome-deficient nuclear mutants of Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2635–2639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco E. M., Jr, Gray P. W., Hallick R. B. Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribosomal RNA transcription units. I. The location of transfer RNA, 5 S, 16 S, and 23 S ribosomal RNA genes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10991–10996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco E. M., Jr, Rushlow K. E., Dodd J. R., Hallick R. B. Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribosomal RNA transcription units. II. Nucleotide sequence homology between the 16 S--23 S ribosomal RNA spacer and the 16 S ribosomal RNA leader regions. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10997–11003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Magnesium precipitation of ribonucleoprotein complexes. Expedient techniques for the isolation of undergraded polysomes and messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3606–3615. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Ovalbumin messenger ribonucleic acid translation. Comparable rates of polypeptide initiation and elongation on ovalbumin and globin messenger ribonucleic acid in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2095–2106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Molecular weight estimation and separation of ribonucleic acid by electrophoresis in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):668–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., La Torre J., Kelley D. E., Greenberg J. R. On the lability of poly(A) sequences during extraction of messenger RNA from polyribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkerton T. C., Paddock G., Abelson J. Nucleotide sequence determination of bacteriophage T4 leucine transfer ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6348–6365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J. M., Woo S. L., Holder J. W., Means A. R., O'Malley B. W. Preparation and preliminary characterization of purified ovalbumin messenger RNA from the hen oviduct. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):69–78. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders J. P., Heyting C., Borst P. The organization of genes in yeast mitochondrial DNA. I. The genes for large and small ribosomal RNA are far apart. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 22;65(2):699–707. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Dyer T. A., Lonsdale D. M. Organization of the mitochondrial ribosomal RNA genes of maize. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 11;10(11):3333–3340. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.11.3333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. pBR322 restriction map derived from the DNA sequence: accurate DNA size markers up to 4361 nucleotide pairs long. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Aug;5(8):2721–2728. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.8.2721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu J. K., Prangishvilli D., Huber H., Wildgruber G., Zillig W., Stetter K. O. Taxonomic relations between archaebacteria including 6 novel genera examined by cross hybridization of DNAs and 16S rRNAs. J Mol Evol. 1982;18(2):109–114. doi: 10.1007/BF01810829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Gupta R. Are archaebacteria merely derived 'prokaryotes'? Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):95–96. doi: 10.1038/289095a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Davidson N., Attardi G., Aloni Y. Expression of the mitochondrial genome in HeLa cells. XIV. The relative positions of the 4 S RNA genes and of the ribosomal RNA genes in mitochondrial DNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 28;71(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90402-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries H., de Jonge J. C., Bakker H., Meurs H., Kroon A. Laboratory of Physiological Chemistry, State University Groningen, Netherlands. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;6(5):1791–1803. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.5.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






