Abstract
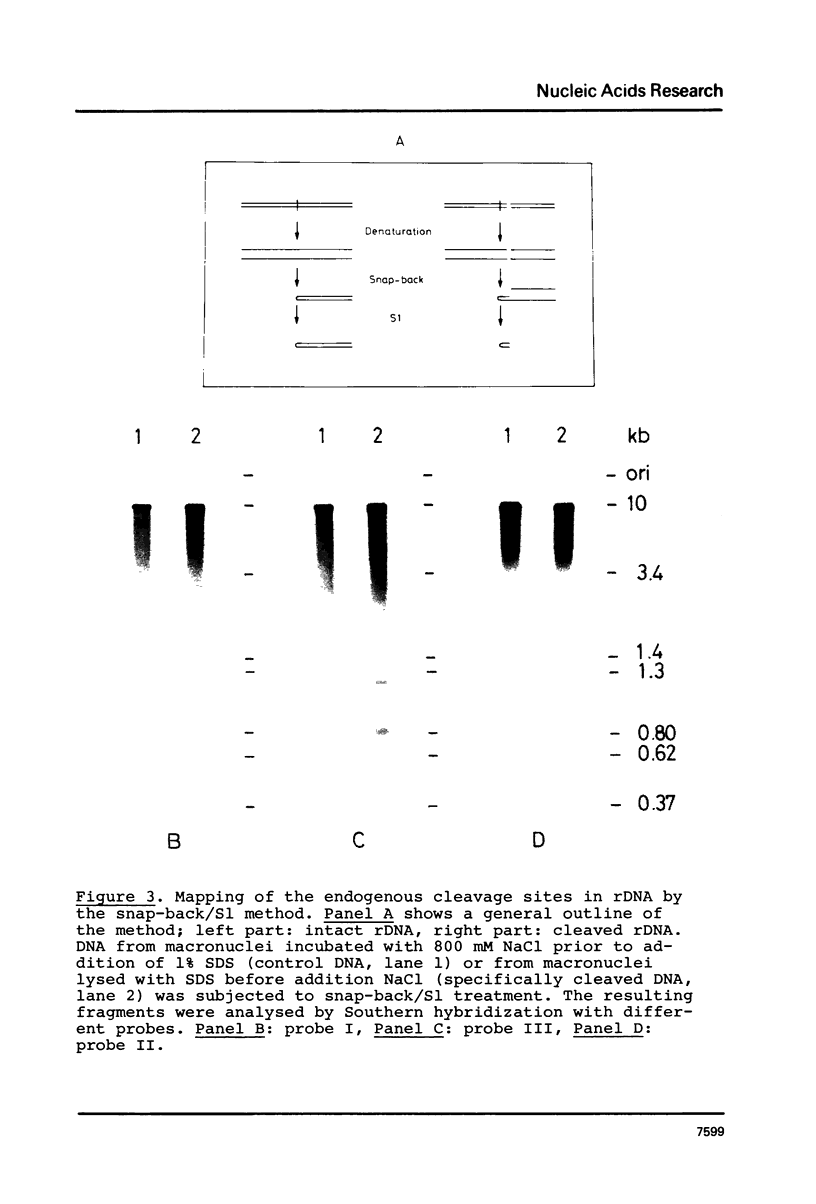
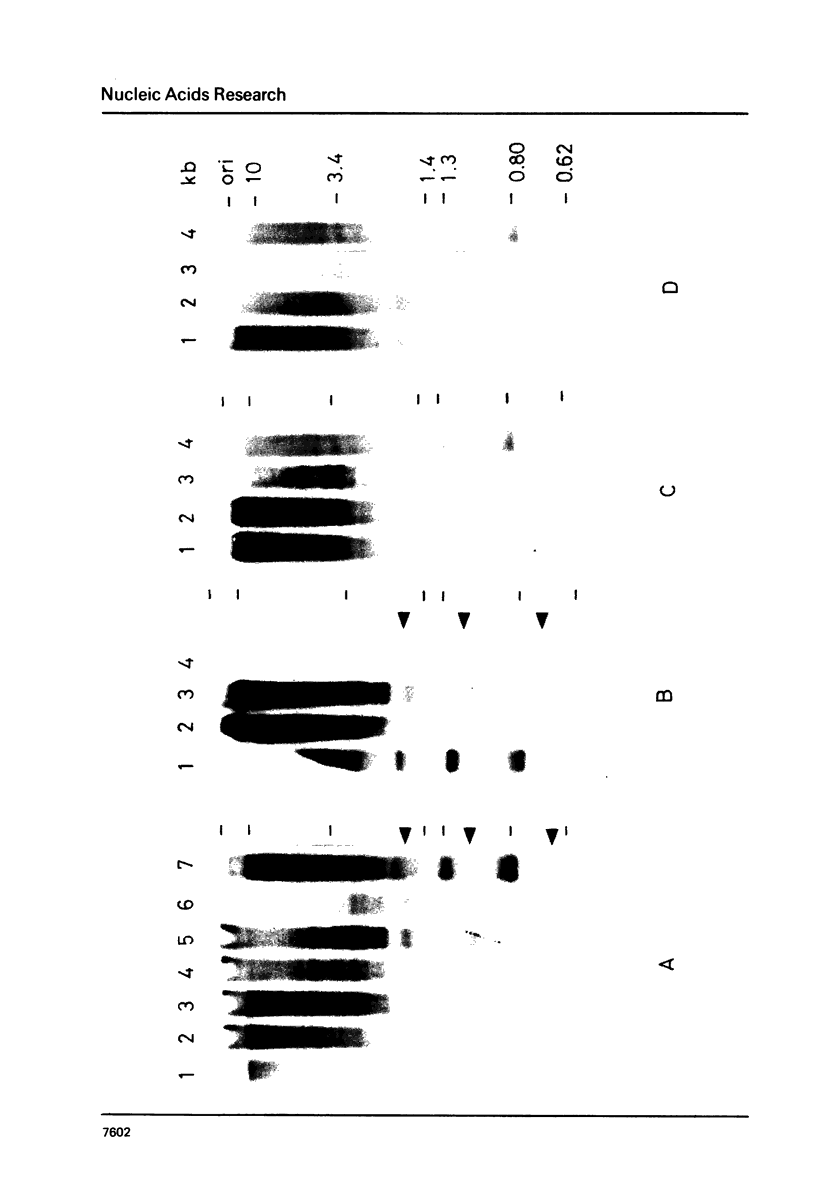
A novel nuclease activity have been detected at three specific sites in the chromatin of the spacer region flanking the 5'-end of the ribosomal RNA gene from Tetrahymena. The endogenous nuclease does not function catalytically in vitro, but is in analogy with the DNA topoisomerases activated by strong denaturants to cleave DNA at specific sites. The endogenous cleavages have been mapped at positions +50, -650 and -1100 relative to the 5'-end of the pre-35S rRNA. The endogenous cleavage sites are associated with micrococcal nuclease hypersensitive sites and DNase I hypersensitive regions. Thus, a single well-defined micrococcal nuclease hypersensitive site is found approximately 130 bp upstream from each of the endogenous cleavages. Clusters of defined sites, the majority of which fall within the 130 bp regions defined by vicinal micrococcal nuclease and endogenous cleavages, constitute the DNase I hypersensitive regions.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borchsenius S., Bonven B., Leer J. C., Westergaard O. Nuclease-sensitive regions on the extrachromosomal r-chromatin from Tetrahymena pyriformis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jul;117(2):245–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06329.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carin M., Jensen B. F., Jentsch K. D., Leer J. C., Nielsen O. F., Westergaard O. In vitro splicing of the ribosomal RNA precursor in isolated nucleoli from Tetrahymena. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5551–5566. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Brehm S. L. Replication of the extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA genes of Tetrahymena thermophilia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3531–3543. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremisi C. The appearance of DNase I hypersensitive sites at the 5' end of the late SV40 genes is correlated with the transcriptional switch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5949–5964. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. DNAase I-hypersensitive sites of chromatin. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engberg J., Nasir-ud-Din, Eckert W. A., Kaffenberger W., Pearlman R. E. Detailed transcription map of the extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA genes in Tetrahymena thermophila. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):289–313. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90274-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engberg J., Nilsson J. R., Pearlman R. E., Leick V. Induction of nucleolar and mitochondrial DNA replication in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):894–898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher L. M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Ohmori H., Gellert M. Site-specific interaction of DNA gyrase with DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4165–4169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:879–910. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gocke E., Leer J. C., Nielsen O. F., Westergaard O. Transcriptional properties of nucleoli isolated from Tetrahymena. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Nov;5(11):3993–4006. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.11.3993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Eisenman R., Weintraub H. Chromatin structure of endogenous retroviral genes and activation by an inhibitor of DNA methylation. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):311–317. doi: 10.1038/292311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Weintraub H. Activation of globin genes during chicken development. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90329-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiney D. G., Helinski D. R. Relaxation complexes of poasmid DNA and protein. III. Association of protein with the 5' terminus of the broken DNA strand in the relaxed complex of plasmid ColE1. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8796–8803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiney D. G., Helinski D. R. The DNA-protein relaxation complex of the plasmid RK2: location of the site-specific nick in the region of the proposed origin of transfer. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 3;176(2):183–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00273212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karrer K. M., Gall J. G. The macronuclear ribosomal DNA of Tetrahymena pyriformis is a palindrome. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 25;104(2):421–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene M. A., Corces V., Lowenhaupt K., Elgin S. C. DNase I hypersensitive sites in Drosophila chromatin occur at the 5' ends of regions of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):143–146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard K., Wang J. C. Mapping the topography of DNA wrapped around gyrase by nucleolytic and chemical probing of complexes of unique DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90435-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer J. C., Nielsen O. F., Piper P. W., Westergaard O. Isolation of the ribosomal RNA gene from Tetrahymena in the state of transcriptionally active chromatin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 20;72(2):720–731. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Wood W. I., Dolan M., Engel J. D., Felsenfeld G. A 200 base pair region at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A., Cozzarelli N. R. Contacts between DNA gyrase and its binding site on DNA: features of symmetry and asymmetry revealed by protection from nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1416–1420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niles E. G., Sutiphong J., Haque S. Structure of the Tetrahymena pyriformis rRNA gene. Nucleotide sequence of the transcription initiation region. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12849–12856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samal B., Worcel A., Louis C., Schedl P. Chromatin structure of the histone genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):401–409. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragosti S., Moyne G., Yaniv M. Absence of nucleosomes in a fraction of SV40 chromatin between the origin of replication and the region coding for the late leader RNA. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz A., Galas D. J. The interaction of RNA polymerase and lac repressor with the lac control region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):111–137. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Wigmore D. J. Sites in simian virus 40 chromatin which are preferentially cleaved by endonucleases. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1511–1518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Larsen A., Engel J. D., Dolan M., Groudine M., Weintraub H. Tissue-specific DNA cleavages in the globin chromatin domain introduced by DNAase I. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90631-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truett M. A., Gall J. G. The replication of ribosomal DNA in the macronucleus of Tetrahymena. Chromosoma. 1977 Dec 6;64(4):295–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00294937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Sundin O. H., Bohn M. J. SV40 viral minichromosome: preferential exposure of the origin of replication as probed by restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3469–3477. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Sundin O., Bohn M. A stretch of "late" SV40 viral DNA about 400 bp long which includes the origin of replication is specifically exposed in SV40 minichromosomes. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):453–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldeck W., Föhring B., Chowdhury K., Gruss P., Sauer G. Origin of DNA replication in papovavirus chromatin is recognized by endogenous endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5964–5968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Beug H., Groudine M., Graf T. Temperature-sensitive changes in the structure of globin chromatin in lines of red cell precursors transformed by ts-AEV. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):931–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Larsen A., Groudine M. Alpha-Globin-gene switching during the development of chicken embryos: expression and chromosome structure. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Bingham P. M., Livak K. J., Holmgren R., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: I. Evidence for higher order domains of defined DNA sequence. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Gilbert W. Tissue-specific exposure of chromatin structure at the 5' terminus of the rat preproinsulin II gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1577–1580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wong Y. C., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: II. Disruption of chromatin structure during gene activity. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]