Abstract
The sequence of a 2 kb DNA fragment containing the chloroplast 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Chlamydomonas reinhardii and its flanking regions has been determined. The algal 16S rRNA sequence (1475 nucleotides) and secondary structure are highly related to those found in bacteria and in the chloroplasts of higher plants. In contrast, the flanking regions are very different. In C. reinhardii the 16S rRNA gene is surrounded by AT rich segments of about 180 bases, which are followed by a long stretch of complementary bases separated from each other by 1833 nucleotides. It is likely that these structures play an important role in the folding and processing of the precursor of 16S rRNA. The primary and secondary structures of the binding sites of two ribosomal proteins in the 16SrRNAs of E. coli and C. reinhardii are considerably related.
Full text
PDF


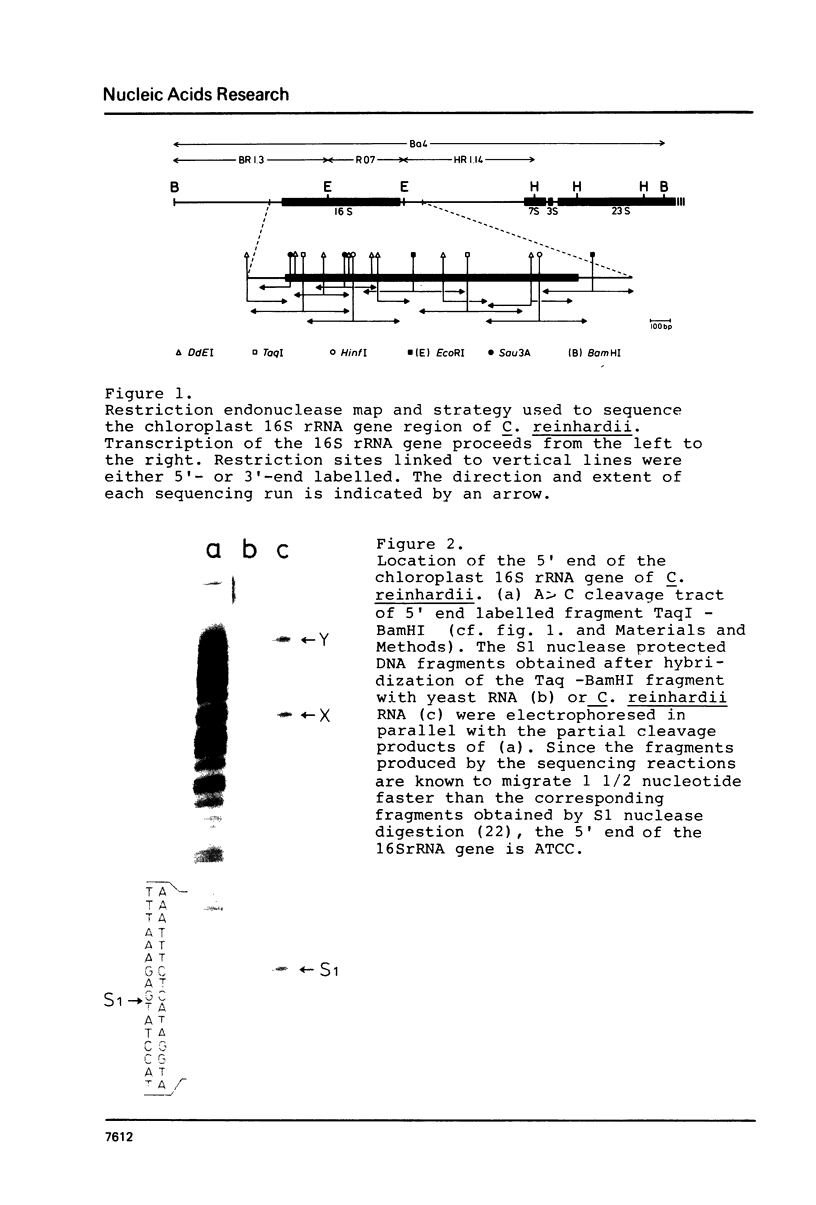


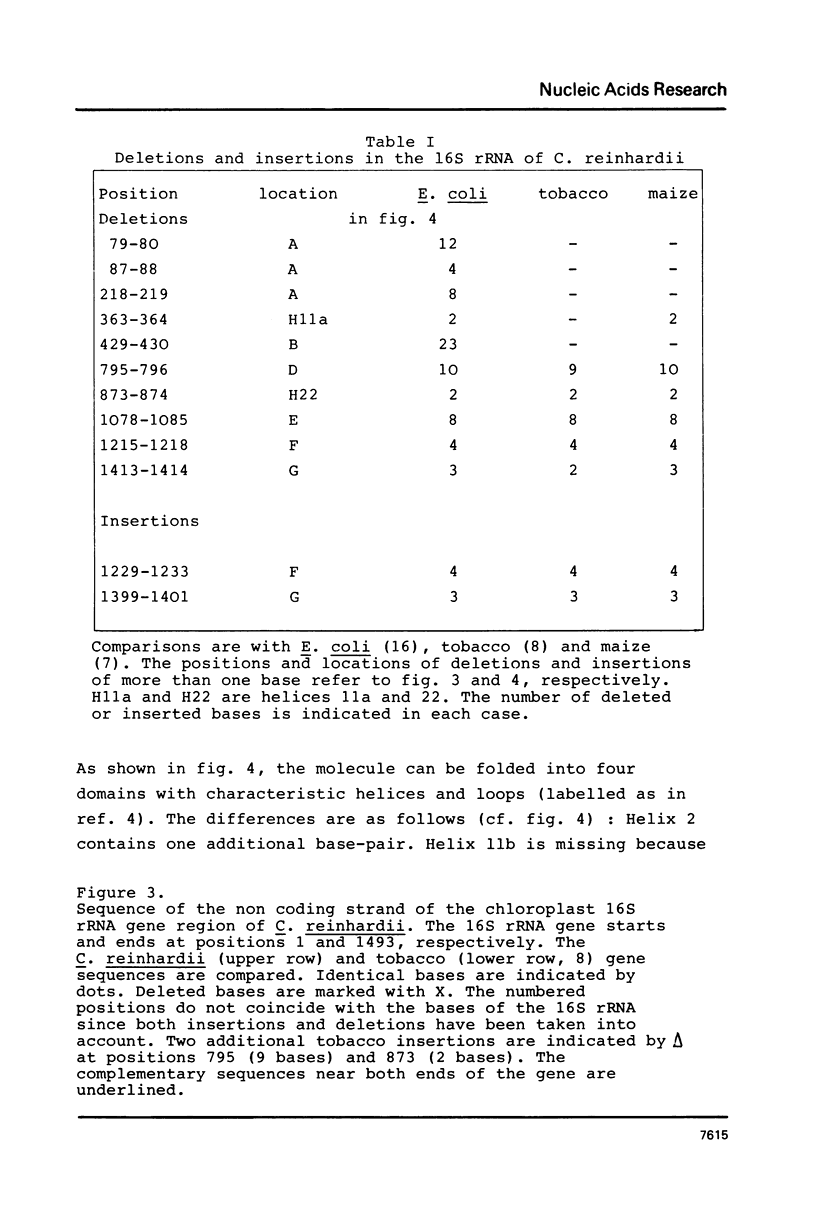
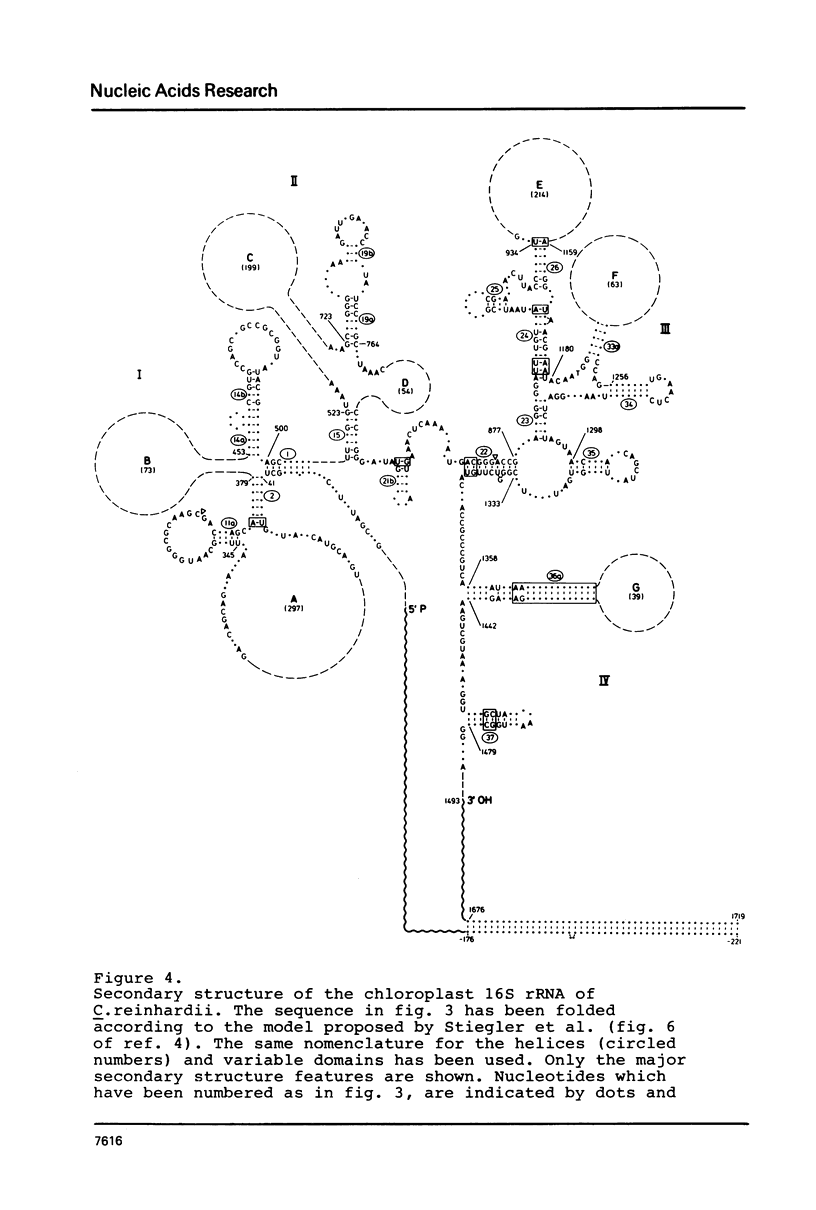



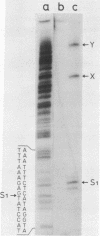
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Palmer M. L., Kennedy P. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Kingsbury D. T., Helinski D. R. Stimulation by cyclic adenosine monophosphate of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid replication and catabolite repression of the plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):577–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.577-591.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Woese C. R. Secondary structure of 16S ribosomal RNA. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):403–411. doi: 10.1126/science.6163215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Yates J. L., Dean D., Post L. E. Feedback regulation of ribosomal protein gene expression in Escherichia coli: structural homology of ribosomal RNA and ribosomal protein MRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7084–7088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco E. M., Jr, Rushlow K. E., Dodd J. R., Hallick R. B. Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribosomal RNA transcription units. II. Nucleotide sequence homology between the 16 S--23 S ribosomal RNA spacer and the 16 S ribosomal RNA leader regions. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10997–11003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochaix J. D., Darlix J. L. Composite structure of the chloroplast 23 S ribosomal RNA genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Evolutionary and functional implications. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 15;159(3):383–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90290-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneeman R., Surzycki S. E. coli ribosomal proteins are cross reactive with antibody prepared against Chlamydomonas reinhardi chloroplast ribosomal subunit. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 2;176(1):95–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00334300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz Z., Kössel H., Schwarz E., Bogorad L. A gene coding for tRNA is located near 5' terminus of 16S rRNA gene in Zea mays chloroplast genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4748–4752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiegler P., Carbon P., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C. A general secondary-structure model for procaryotic and eucaryotic RNAs from the small ribosomal subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Dec;120(3):487–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiegler P., Carbon P., Zuker M., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C. Structural organization of the 16S ribosomal RNA from E. coli. Topography and secondary structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 11;9(9):2153–2172. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.9.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohdoh N., Sugiura M. The complete nucleotide sequence of 16S ribosomal RNA gene from tobacco chloroplasts. Gene. 1982 Feb;17(2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. C., Surzycki S. J. Extensive sequence homology in the DNA coding for elongation factor Tu from Escherichia coli and the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2264–2267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Fox G. E., Zablen L., Uchida T., Bonen L., Pechman K., Lewis B. J., Stahl D. Conservation of primary structure in 16S ribosomal RNA. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):83–86. doi: 10.1038/254083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Magrum L. J., Gupta R., Siegel R. B., Stahl D. A., Kop J., Crawford N., Brosius J., Gutell R., Hogan J. J. Secondary structure model for bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA: phylogenetic, enzymatic and chemical evidence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2275–2293. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Steitz J. A. Complementary sequences 1700 nucleotides apart form a ribonuclease III cleavage site in Escherichia coli ribosomal precursor RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3593–3597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C., Glotz C., Brimacombe R. Secondary structure comparisons between small subunit ribosomal RNA molecules from six different species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3621–3640. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]