Abstract
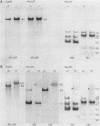
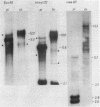
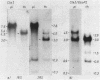
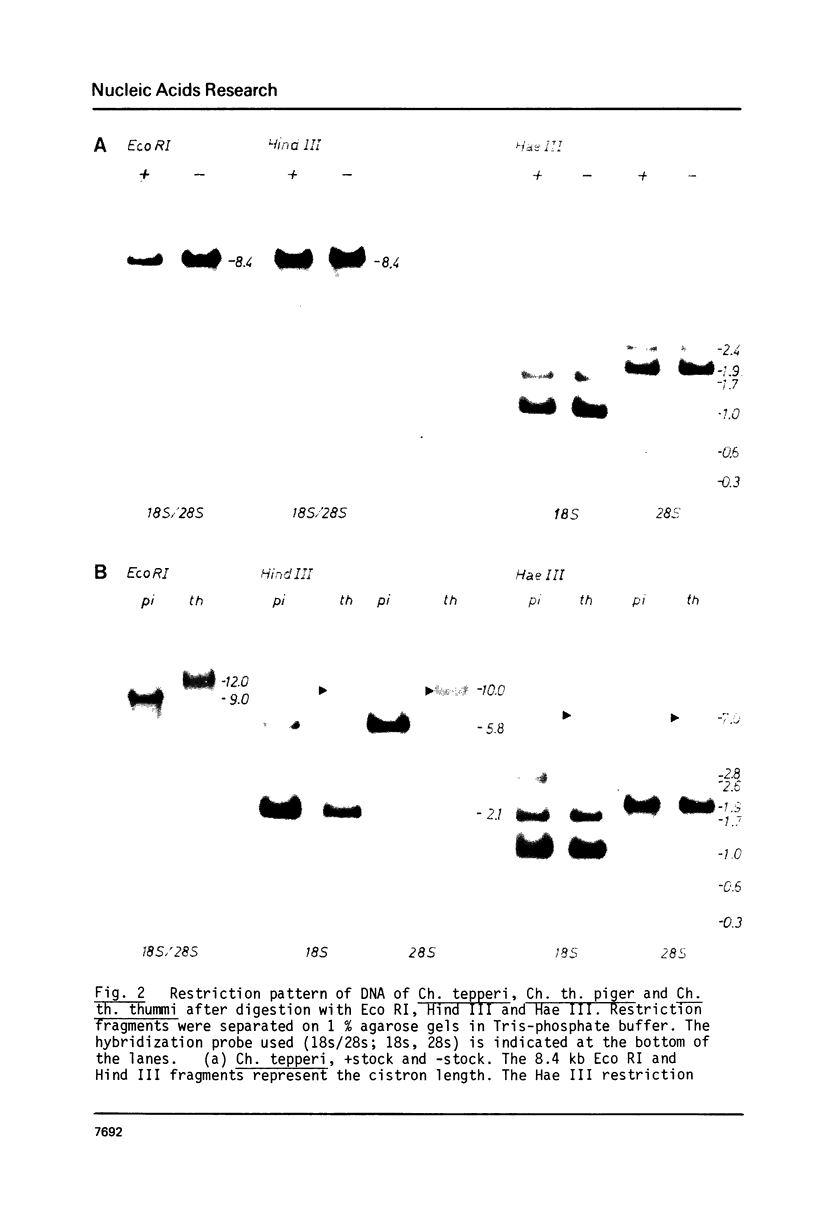
The rDNA of Ch. tepperi is homogeneous in structure with a repeat size of 8.4 kb. This size seems to be typical for the basic repeat unit in Chironomus species. Ch. th. piger rDNA cistrons are slightly increased in length (9.0 kb). In the non-transcribed spacer (NTS) an appr. 0.18 kb segment is additionally present in about 50% of the repeats. Ch. th. thumni DNA contains largely heterogeneous rDNA repeats, mainly between 10 and 16 kb. The heterogeneity is due to varying numbers of 120 bp elements present in the NTS. The different spacer size classes are not randomly distributed. The short repetitive 120 bp elements (Cla I elements) hybridize in situ with the nucleolus and with centromere regions. The Cla I elements are regularly present in the thummi NTS, but are absent in the piger NTS. Only very few piger rDNA cistrons may contain Cla I elements.
Full text
PDF



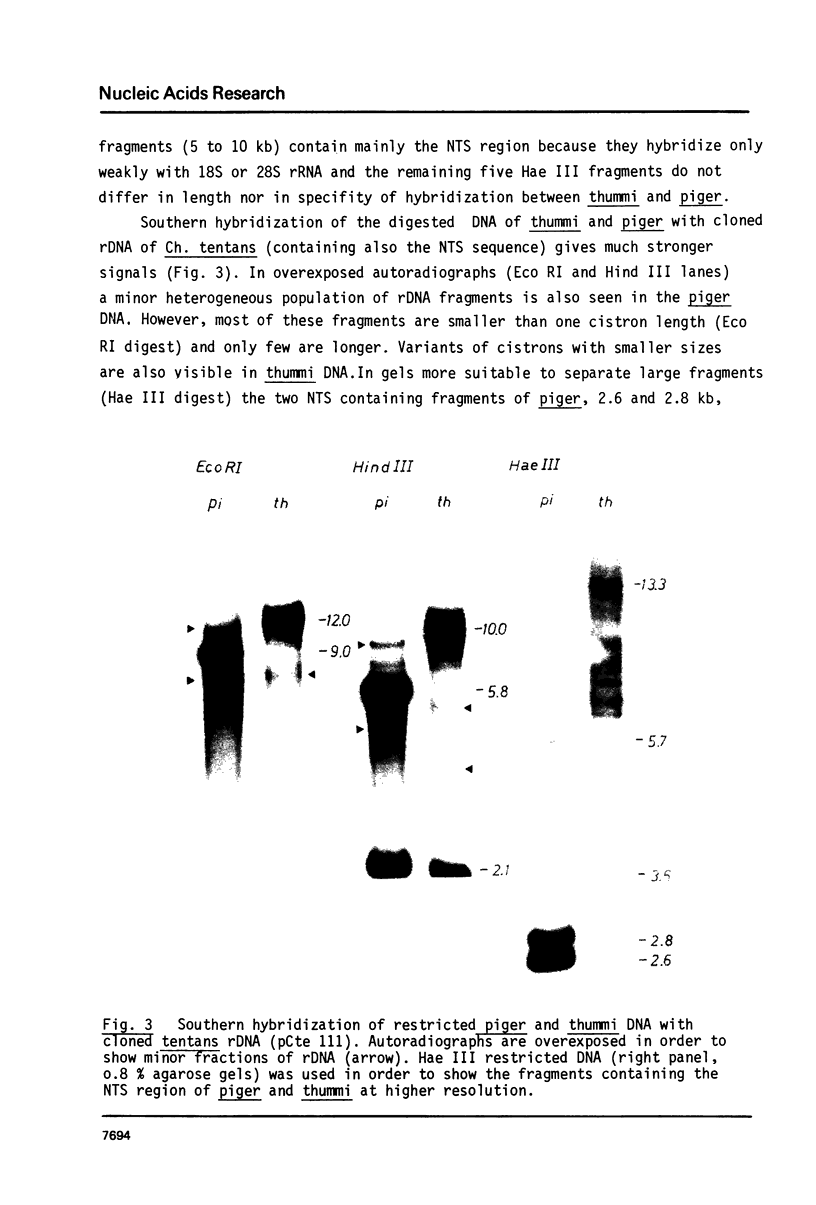
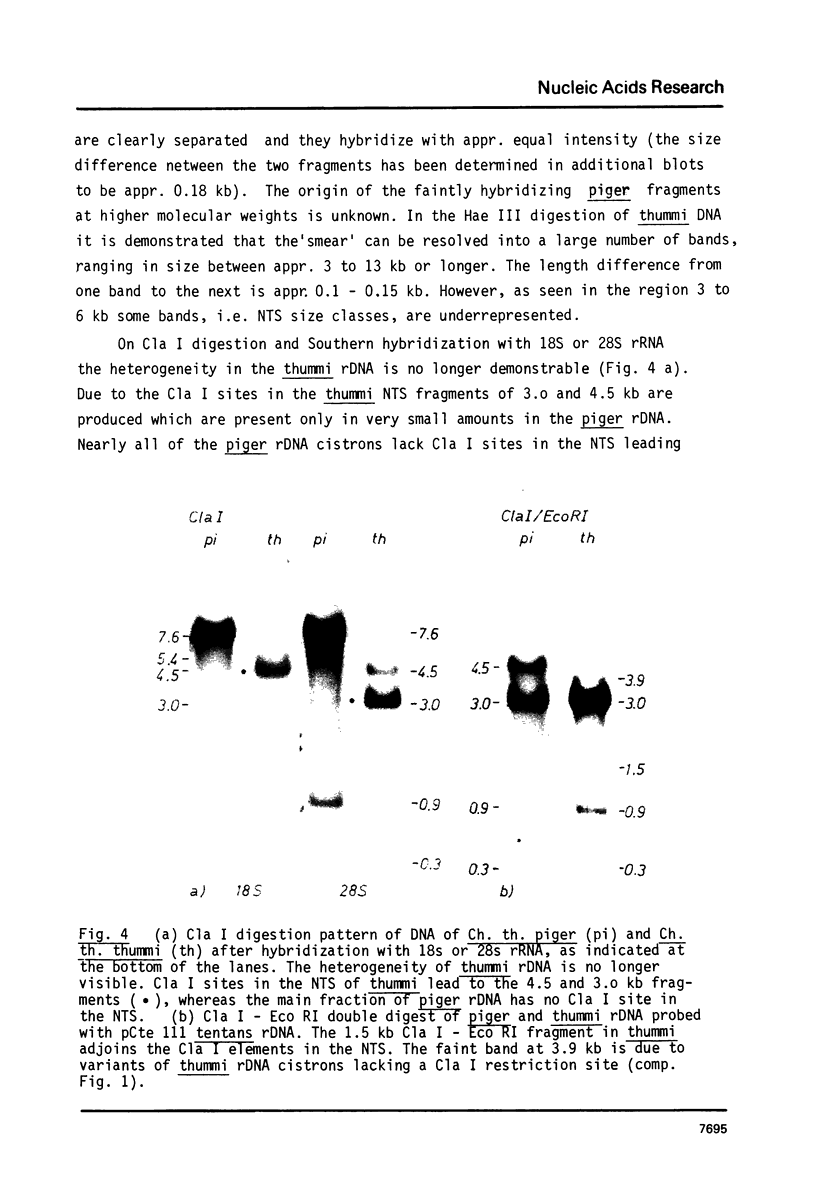





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnheim N., Seperack P., Banerji J., Lang R. B., Miesfeld R., Marcu K. B. Mouse rDNA nontranscribed spacer sequences are found flanking immunoglobulin CH genes and elsewhere throughout the genome. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEERMANN W. [The nucleolus as a component of the cell nucleus essential to life]. Chromosoma. 1960;11:263–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00328655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. J., Pardue M. L. Ecdysone-stimulated RNA synthesis in imaginal discs of Drosophila melanogaster. Assay by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1976 Oct 12;58(1):87–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00293443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs G., Maxson R., Cohn R. H., Kedes L. Orphons: dispersed genetic elements derived from tandem repetitive genes of eucaryotes. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):651–663. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90428-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Commerford S. L. Iodination of nucleic acids in vitro. Biochemistry. 1971 May 25;10(11):1993–2000. doi: 10.1021/bi00787a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B., Wellauer P. K., Long E. O. Ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster. I. Isolation and characterization of cloned fragments. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):749–768. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degelmann A., Royer H. D., Hollenberg C. P. The organization of the ribosomal RNA genes of Chironomus tentans and some closely related species. Chromosoma. 1979 Mar 12;71(3):263–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00287136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derksen J., Trendelenburg M. F., Scheer U., Franke W. W. Spread chromosomal nucleoli of Chironomus salivary glands. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Aug;80(2):476–479. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90327-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigenbrod J. Differences in the number of nucleolus organizers in Chironomus tepperi shown by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1978 Jun 23;67(1):63–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00285648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Files J. G., Hirsh D. Ribosomal DNA of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 25;149(2):223–240. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French C. K., Fouts D. L., Manning J. E. Sequence arrangement of the rRNA genes of the dipteran Sarcophaga bullata. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 11;9(11):2563–2576. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.11.2563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M., Bloomer L. S. Nonrandom alignment of nucleosomes on 5S RNA genes of X. laevis. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):751–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90438-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg C. P. Proportionate representation of rDNA and Balbiani ring DNA in polytene chromosomes of Chironomus tentans. Chromosoma. 1976 Aug 17;57(2):185–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00292917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hägele K. Differential staining of polytene chromosome bands in Chironomus by Giemsa banding methods. Chromosoma. 1977 Feb 3;59(3):207–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00292778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyl H. G. Duplikationen von Untereinheiten der Chromosomalen DNS während der Evolution von Chironomus thummi. Chromosoma. 1965;17(2):139–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00330079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami R., Urano Y., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. Organization of ribosomal RNA gene repeats of the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3219–3233. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal M., D'Eustachio P., Ruddle F. H., Arnheim N. Human nucleolus organizers on nonhomologous chromosomes can share the same ribosomal gene variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5744–5748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz W., Petersen G., Renkawitz-Pohl R., Glätzer K. H., Schäfer M. Distribution of spacer length classes and the intervening sequence among different nucleolus organizers in Drosophila hydei. Chromosoma. 1981;83(2):145–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00286785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentzios G., Stocker A. J. Nucleolar relationships in some Australian chironomus species. Chromosoma. 1979 Nov;75(2):235–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00292210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima-de-Faria A. Classification of genes, rearrangements and chromosomes according to the chromosome field. Hereditas. 1980;93(1):1–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1980.tb01043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. The fractionation of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):251–257. doi: 10.1042/bj1020251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macgregor H. C., Mizuno S. In situ hybridization of "nick-translated" 3H-ribosomal DNA to chromosomes from salamanders. Chromosoma. 1976 Jan 27;54(1):15–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00331829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. A review of the genus Chironomus (Diptera, Chironomidae). IX. The cytology of Chironomus tepperi Skuse. Chromosoma. 1974 Mar 1;45(1):91–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00283832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelling C., Beermann W. Diversity and variation of the nucleolar organizing regions in chironomids. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Dec;23:393–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petes T. D. Unequal meiotic recombination within tandem arrays of yeast ribosomal DNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):765–774. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prensky W. The radioiodination of RNA and DNA to high specific activities. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;13:121–152. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61800-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae P. M., Barnett T., Murtif V. L. Nontranscribed spacers in Drosophila ribosomal DNA. Chromosoma. 1981;82(5):637–655. doi: 10.1007/BF00285773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R., Gerbi S. A., Glätzer K. H. Ribosomal DNA of fly Sciara coprophila has a very small and homogeneous repeat unit. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 May 23;173(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00267685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samal B., Worcel A., Louis C., Schedl P. Chromatin structure of the histone genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):401–409. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer J., Schmidt E. R. Different repetition frequencies of a 120 base-pair DNA-element and its arrangement in Chironomus thummi thummi and Chironomus thummi piger. Chromosoma. 1981;84(1):61–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00293363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer M., Wyman A. R., White R. Length variation in the non-transcribed spacer of Calliphora erythrocephala ribosomal DNA is due to a 350 base-pair repeat. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 25;146(2):179–199. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90431-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh L., Purdom I. F., Jones K. W. Effect of different denaturing agents on the detectability of specific DNA sequences of various base compositions by in situ hybridisation. Chromosoma. 1977 Apr 20;60(4):377–389. doi: 10.1007/BF00292860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Unequal crossover and the evolution of multigene families. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:507–513. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson E. C., Erba H. P., Gall J. G. Histone gene clusters of the newt notophthalmus are separated by long tracts of satellite DNA. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):639–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Wu R. Unequal crossing over in the ribosomal DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):426–430. doi: 10.1038/284426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B., Brown D. D., Reeder R. H. The molecular basis for length heterogeneity in ribosomal DNA from Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Aug 25;105(4):461–486. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B., Brown D. D., Reeder R. H. The molecular basis for length heterogeneity in ribosomal DNA from Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Aug 25;105(4):461–486. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Isolation and sequence organization of human ribosomal DNA. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 5;128(3):289–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90089-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]