Abstract
Two closely related cDNA clones, pSpec1 and pSpec2, specifying two developmentally regulated tissue specific mRNAs from sea urchin embryos were used to probe a sea urchin genomic lambda library. Screening 10,000 phage by plaque hybridization yielded several hundred positive signals. With more stringent wash procedures, only two to three phage were positive. Three of these phage, one isolated by stringent wash procedures and two isolated by standard wash procedures were further investigated by restriction analysis, RNA gel blots, and DNA sequencing. The phage isolated by the stringent wash procedure appears to be a gene coding for the Specl mRNA. The other phage contain only partial homology to pSpec1 and pSpec2, 150 to 200 base pairs of the 3' untranslated region of the Spec1 and Spec2 mRNAs. It is concluded that the Spec1 and Spec2 mRNAs contain a highly repetitive element near their 3' end. The element is present at 2000 to 3000 copies per genome and may be transcribed at some sites other than those coding for the Spec1 and Spec2 genes. The possible function and evolutionary origin of the repetitive element is discussed.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Gene regulation for higher cells: a theory. Science. 1969 Jul 25;165(3891):349–357. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3891.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruskin A. M., Tyner A. L., Wells D. E., Showman R. M., Klein W. H. Accumulation in embryogenesis of five mRNAs enriched in the ectoderm of the sea urchin pluteus. Dev Biol. 1981 Oct 30;87(2):308–318. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabretta B., Robberson D. L., Maizel A. L., Saunders G. F. mRNA in human cells contains sequences complementary to the Alu family of repeated DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6003–6007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campo M. S., Bishop J. O. Two classes of messenger RNA in cultured rat cells: repetitive sequence transcripts and unique sequence transcripts. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 25;90(4):649–663. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90530-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantini F. D., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Message sequences and short repetitive sequences are interspersed in sea urchin egg poly(A)+ RNAs. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):111–117. doi: 10.1038/287111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Regulation of gene expression: possible role of repetitive sequences. Science. 1979 Jun 8;204(4397):1052–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.451548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dina D., Meza I., Crippa M. Relative positions of the "repetitive", "unique" and poly(A) fragments of mRNA. Nature. 1974 Apr 5;248(448):486–490. doi: 10.1038/248486a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle W. F., Sapienza C. Selfish genes, the phenotype paradigm and genome evolution. Nature. 1980 Apr 17;284(5757):601–603. doi: 10.1038/284601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galau G. A., Klein W. H., Davis M. M., Wold B. J., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Structural gene sets active in embryos and adult tissues of the sea urchin. Cell. 1976 Apr;7(4):487–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90200-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes S. R., Jelinek W. R. Low molecular weight RNAs transcribed in vitro by RNA polymerase III from Alu-type dispersed repeats in Chinese hamster DNA are also found in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6130–6134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough B. R., Smith M. J., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Sequence complexity of heterogeneous nuclear RNA in sea urchin embryos. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):291–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel A. R., Firtel R. A. A family of short, interspersed repeat sequences at the 5' end of a set of Dictyostelium single-copy mRNAs. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):787–796. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein W. H., Murphy W., Attardi G., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Distribution of repetitive and nonrepetivite sequence transcripts in HeLa mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1785–1789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein W. H., Thomas T. L., Lai C., Scheller R. H., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Characteristics of individual repetitive sequence families in the sea urchin genome studied with cloned repeats. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):889–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moormann R. J., van der Velden H. M., Dodemont H. J., Andreoli P. M., Bloemendal H., Schoenmakers J. G. An unusually long non-coding region in rat lens alpha-crystallin messenger RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):4813–4822. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.4813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Wahl G. M., Stark G. R. Properties of dispersed, highly repeated DNA within and near the hamster CAD gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;2(3):302–307. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.3.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Mukai T., Morrow J. F. Repeated DNA sequences near the 5'-end of the silk fibroin gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):4033–4041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posakony J. W., Scheller R. H., Anderson D. M., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Repetitive sequences of the sea urchin genome. III. Nucleotide sequences of cloned repeat elements. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 15;149(1):41–67. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheller R. H., Anderson D. M., Posakony J. W., McAllister L. B., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Repetitive sequences of the sea urchin genome. II. Subfamily structure and evolutionary conservation. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 15;149(1):15–39. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90258-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheller R. H., McAllister L. B., Crain W. R., Jr, Durica D. S., Posakony J. W., Thomas T. L., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Organization and expression of multiple actin genes in the sea urchin. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;1(7):609–628. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.7.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchurikov N. A., Naumova A. K., Zelentsova E. S., Georgiev G. P. A cloned unique gene of Drosophila melanogaster contains a repetitive 3' exon whose sequence is present at the 3' ends of many different mRNAs. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90354-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. L., Posakony J. W., Anderson D. M., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Molecular structure of maternal RNA. Chromosoma. 1981;84(3):319–335. doi: 10.1007/BF00286022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada T., Watanabe Y., Nakai Y., Imura H., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Repetitive DNA sequences in the human corticotropin-beta-lipotrophin precursor gene region: Alu family members. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1471–1479. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B., Ryffel G. U., Weber R. Vitellogenesis and the vitellogenin gene family. Science. 1981 Apr 17;212(4492):298–304. doi: 10.1126/science.7209528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold B. J., Klein W. H., Hough-Evans B. R., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Sea urchin embryo mRNA sequences expressed in the nuclear RNA of adult tissues. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):941–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90348-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
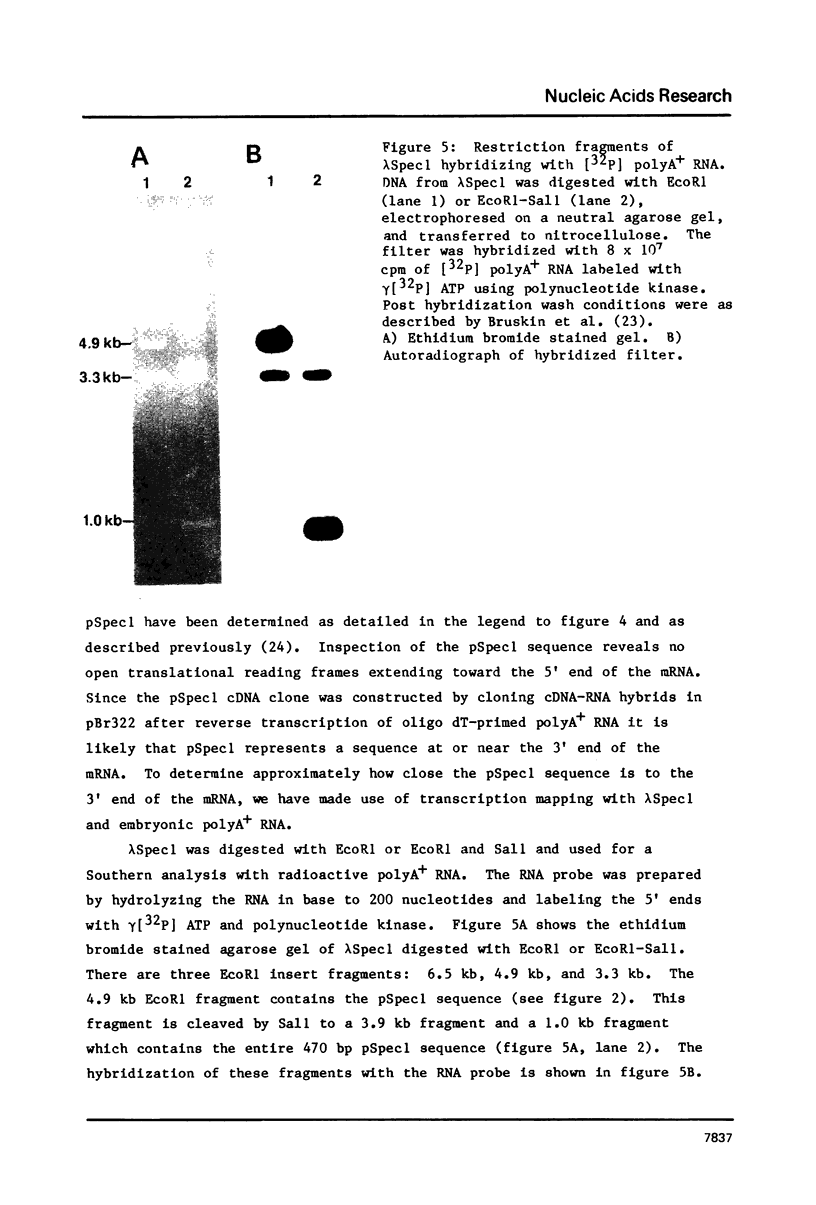
- Zuker C., Lodish H. F. Repetitive DNA sequences cotranscribed with developmentally regulated Dictyostelium discoideum mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5386–5390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]