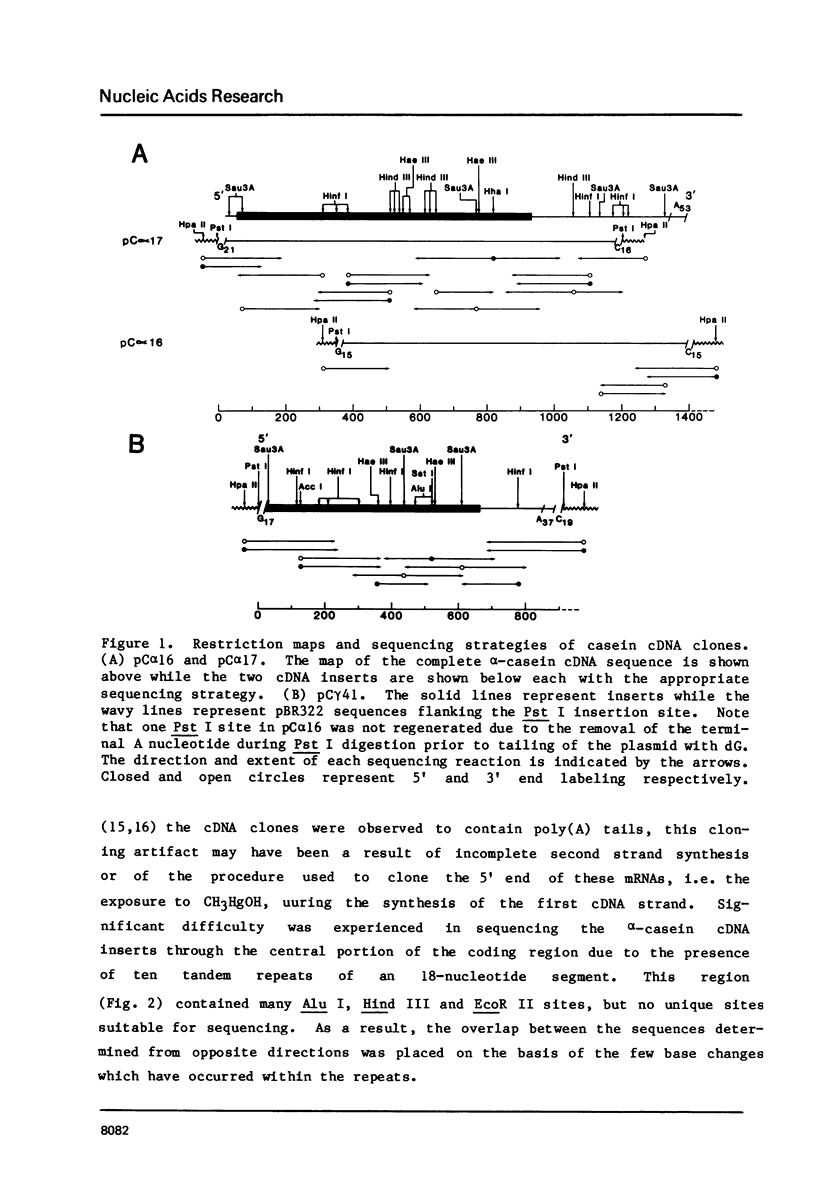
Abstract
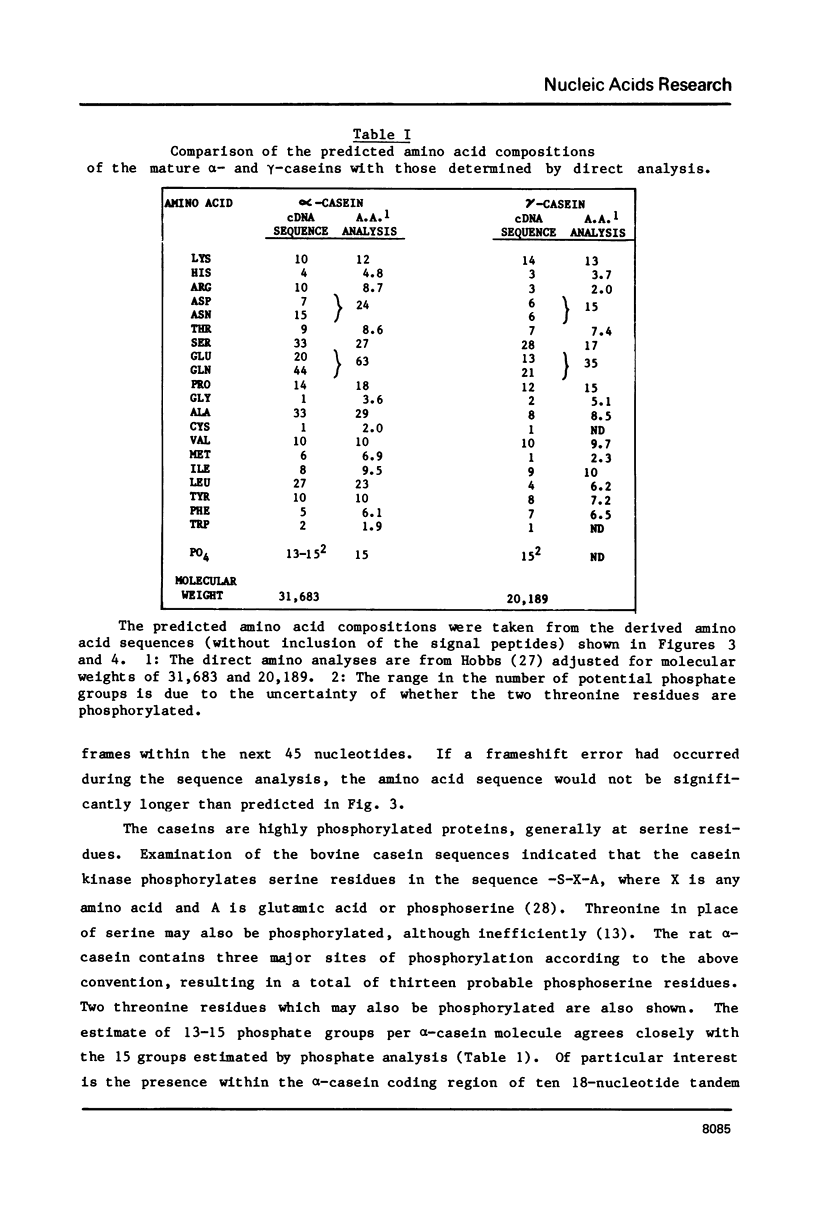
The complete sequences of rat alpha- and gamma-casein mRNAs have been determined. The 1402-nucleotide alpha- and 864-nucleotide gamma-casein mRNAs both encode 15 amino acid signal peptides and mature proteins of 269 and 164 residues, respectively. Considerable homology between the 5' non-coding regions, and the regions encoding the signal peptides and the phosphorylation sites, in these mRNAs as compared to several other rodent casein mRNAs, was observed. Significant homology was also detected between rat alpha- and bovine alpha s1-casein. Comparison of the rodent and bovine sequences suggests that the caseins evolved at about the time of the appearance of the primitive mammals. This may have occurred by intragenic duplication of a nucleotide sequence encoding a primitive phosphorylation site, -(Ser)n-Glu-Glu-, and intergenic duplication resulting in the small casein multigene family. A unique feature of the rat alpha-casein sequence is an insertion in the coding region containing 10 repeated elements of 18 nucleotides each. This insertion appears to have occurred 7-12 million years ago, just prior to the divergence of rat and mouse.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackburn D. E., Hobbs A. A., Rosen J. M. Rat beta casein cDNA: sequence analysis and evolutionary comparisons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 10;10(7):2295–2307. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.7.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Walter P., Chang C. N., Goldman B. M., Erickson A. H., Lingappa V. R. Translocation of proteins across membranes: the signal hypothesis and beyond. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1979;33:9–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brignon G., Ribadeau Dumas B., Mercier J. C., Pelissier J. P., Das B. C. Complete amino acid sequence of bovine alphaS2-casein. FEBS Lett. 1977 Apr 15;76(2):274–279. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80167-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Miller J. H. Transposable elements. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):579–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs G., Maxson R., Cohn R. H., Kedes L. Orphons: dispersed genetic elements derived from tandem repetitive genes of eucaryotes. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):651–663. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90428-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke N. E., Coit D., Weiner R. I., Baxter J. D., Martial J. A. Structure of cloned DNA complementary to rat prolactin messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6502–6510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Leung D. W., Dull T. J., Gross M., Lawn R. M., McCandliss R., Seeburg P. H., Ullrich A., Yelverton E., Gray P. W. The structure of eight distinct cloned human leukocyte interferon cDNAs. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):20–26. doi: 10.1038/290020a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Pastewka J. V. Molecular weights of three mouse milk caseins by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and kappa-like characteristics of a fourth casein. J Dairy Sci. 1976 Oct;59(10):1738–1745. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(76)84431-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R., Groves M. L., Peterson R. F. Amino terminal sequence and location of phosphate groups of the major human casein. J Dairy Sci. 1976 Jun;59(6):1016–1018. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(76)84317-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves M. L., Gordon W. G. The major component of human casein: a protein phosphorylated at different levels. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Sep;140(1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P., Rosen J. M., D'Eustachio P., Ruddle F. H. Localization of the casein gene family to a single mouse chromosome. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):199–204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyette W. A., Matusik R. J., Rosen J. M. Prolactin-mediated transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of casein gene expression. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):1013–1023. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Bovey R., Young R. A. Tissue-specific expression of mouse-alpha-amylase genes: nucleotide sequence of isoenzyme mRNAs from pancreas and salivary gland. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennighausen L. G., Sippel A. E., Hobbs A. A., Rosen J. M. Comparative sequence analysis of the mRNAs coding for mouse and rat whey protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 25;10(12):3733–3744. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.12.3733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs A. A., Richards D. A., Kessler D. J., Rosen J. M. Complex hormonal regulation of rat casein gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3598–3605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Soberon X., Franceschini T., Nakamura K., Itakura K., Inouye M. Role of positive charge on the amino-terminal region of the signal peptide in protein secretion across the membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3438–3441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRESHECK G. C. THE CONFORMATION OF CASEIN IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION. Acta Chem Scand. 1965;19:375–382. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.19-0375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohne D. E. Evolution of higher-organism DNA. Q Rev Biophys. 1970 Aug;3(3):327–375. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg H. M., McDevitt B. E., Majzoub J. A., Nathans J., Sharp P. A., Potts J. T., Jr, Rich A. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of DNA coding for bovine preproparathyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4981–4985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Grez M., Hauser H., Lindenmaier W., Schütz G. 5'-Terminal sequences of eucaryotic mRNA can be cloned with high efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2251–2266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
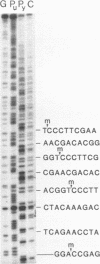
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier J. C., Brignon G., Ribadeau-Dumas B. Structure primaire de la caséine kappa B bovine. Séquence complète. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jun;35(2):222–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier J. C., Chobert J. M., Addeo F. Comparative study of the amino acid sequences of the caseinomacropeptides from seven species. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 31;72(2):208–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80972-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier J. C., Grosclaude F., Ribadeau-Dumas B. Structure primaire de la caséine s1 -bovine. Séquence complète. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Nov 11;23(1):41–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01590.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier J. C., Haze G., Gaye P., Hue D. Amino terminal sequence of the precursor of ovine beta-lactoglobulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jun 29;82(4):1236–1245. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90320-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
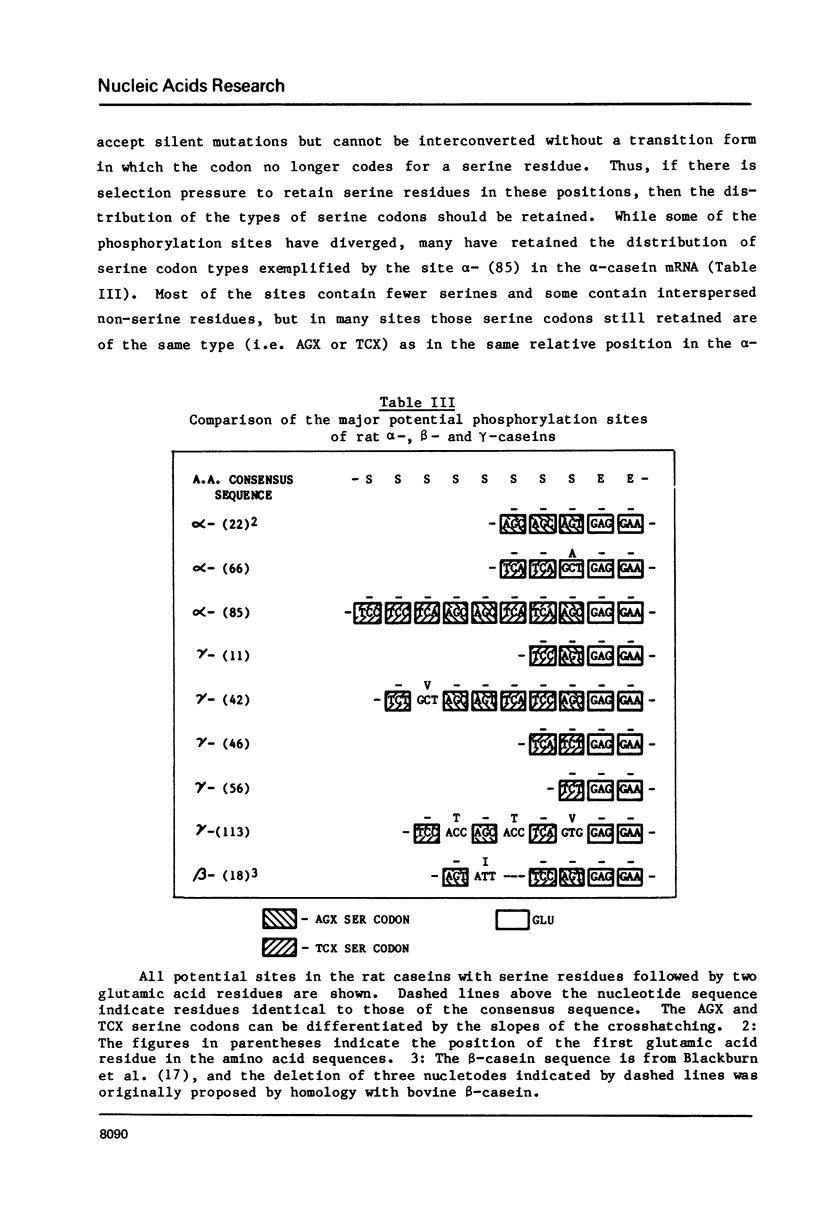
- Mercier J. C. Phosphorylation of caseins, present evidence for an amino acid triplet code posttranslationally recognized by specific kinases. Biochimie. 1981 Jan;63(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(81)80141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L., Coit D., Baxter J. D., Martial J. A. Cloning of bovine prolactin cDNA and evolutionary implications of its sequence. DNA. 1981;1(1):37–50. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1981.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. Molecular cloning of DNA complementary to bovine growth hormone mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7521–7524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata T., Yasunaga T., Nishida T. Nucleotide sequence divergence and functional constraint in mRNA evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7328–7332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Hogness D. S. An expandable gene that encodes a Drosophila glue protein is not expressed in variants lacking remote upstream sequences. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):1041–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90467-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., Schimke R. T. Methylmercury hydroxide enhancement of translation and transcription of ovalbumin and conalbumin mRNA's. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7636–7642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K., Devereux J., Wilson D. R., Sheldon E., Larkins B. A. Cloning and sequence analysis reveal structural variation among related zein genes in maize. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):1015–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90465-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribadeau Dumas B., Brignon G., Grosclaude F., Mercier J. C. Structure primaire de la caséine beta bovine. Séquence complète. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Feb;25(3):505–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards D. A., Blackburn D. E., Rosen J. M. Restriction enzyme mapping and heteroduplex analysis of the rat milk protein cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):533–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards D. A., Rodgers J. R., Supowit S. C., Rosen J. M. Construction and preliminary characterization of the rat casein and alpha-lactalbumin cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):526–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson B. C., Mercier J. C. The primary structure of the ovine beta-caseins. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Sep;99(2):285–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodakis G. C., Kafatos F. C. Origin of evolutionary novelty in proteins: how a high-cysteine chorion protein has evolved. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3551–3555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J. M. Isolation and characterization of purified rat casein messenger ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 30;15(24):5263–5271. doi: 10.1021/bi00669a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J. M., Woo S. L., Comstock J. P. Regulation of casein messenger RNA during the development of the rat mammary gland. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2895–2903. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasavage N. L., Nilson J. H., Horowitz S., Rottman F. M. Nucleotide sequence of bovine prolactin messenger RNA. Evidence for sequence polymorphism. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):678–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Shine J., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D., Goodman H. M. Nucleotide sequence and amplification in bacteria of structural gene for rat growth hormone. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):486–494. doi: 10.1038/270486a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Speculations on RNA splicing. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Further procedures for sequence analysis by computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Mar;5(3):1013–1016. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.3.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topper Y. J. Multiple hormone interactions in the development of mammary gland in vitro. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1970;26:287–308. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571126-5.50011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Purification of a membrane-associated protein complex required for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7112–7116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]