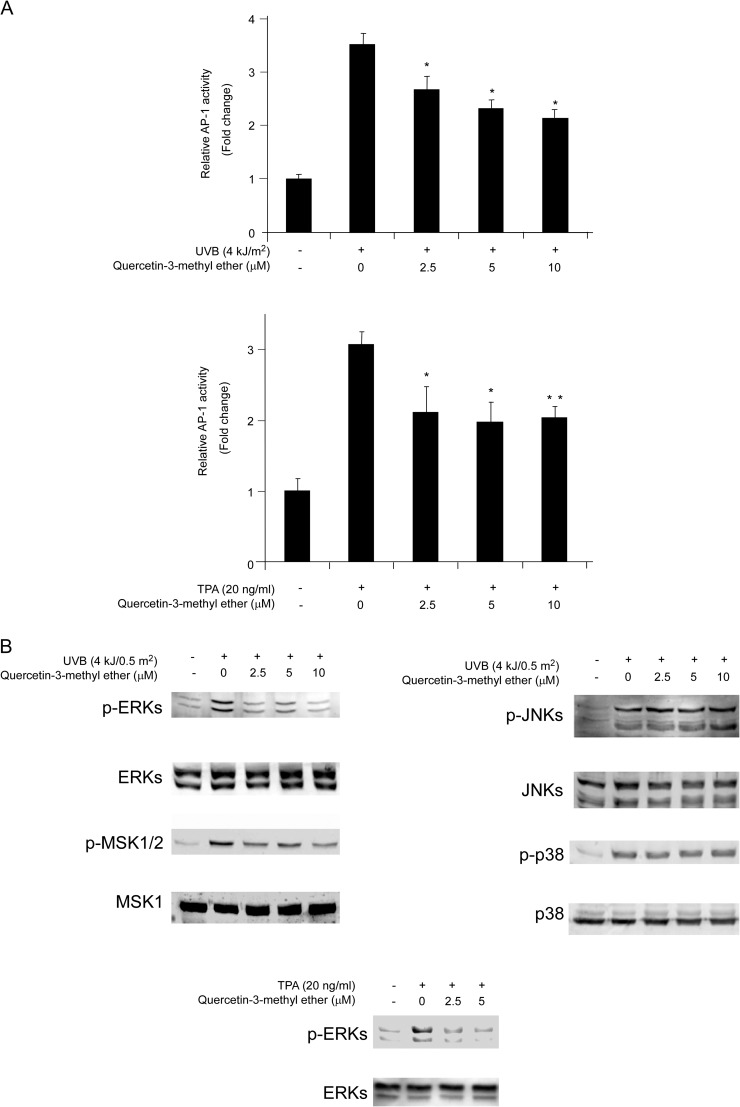
Fig. 4.
Quercetin-3-methyl ether blocks UVB/TPA-induced AP-1 transactivation in JB6 cells by attenuating ERKs signaling. (A) For the luciferase assay, JB6 cells stably transfected with an AP-1 luciferase reporter plasmid were cultured in 5% FBS/EMEM. Cells were starved in serum-free medium for 24 h and then treated with quercetin-3-methyl ether (0–10 μM) or its vehicle dimethyl sulfoxide (control) in 5% FBS/EMEM for 2 h. Cells were then exposed to 4 kJ/m2 UVB (upper panel) or 20 ng/ml TPA (lower panel) and harvested at 3 or 12 h, respectively. Luciferase activity was assessed and AP-1 activity is expressed relative to control cells without UVB or TPA treatment. Data are shown as means ± SE. The asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.001) between groups treated with UVB/TPA and quercetin-3-methyl ether compared with the group treated with UVB/TPA alone. (B) Quercetin-3-methyl ether inhibits UVB/TPA-induced phosphorylation of ERKs but not JNKs or p38. Cells were treated with quercetin-3-methyl ether at the indicated concentrations (0–10 μM) for 2 or 6 h and then exposed to 4 kJ/0.5 m2 UVB or 20 ng/ml TPA and harvested 30 min later. The levels of phosphorylated and total ERKs, mitogen-and stress activated protein kinase. JNKs and p38 proteins were determined by western blot analysis.