Abstract
In the past 200 years, an enormous number of synthetic chemicals with diverse structural features have been produced for industrial, medical and domestic purposes. These chemicals, originally thought to have little or no biological toxicity, are widely used in our daily lives as well as are commonly present in foods. It was not until the first World Wildlife Federation Wingspread Conference held in 1994 were concerns about the endocrine disrupting (ED) effects of these chemicals articulated. The potential hazardous effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) on human health and ecological well-being are one of the global concerns that affect the health and propagation of human beings. Considerable numbers of studies indicated that endocrine disruption is linked to “the developmental basis of adult disease,” highlighting the significant effects of EDC exposure on a developing organism, leading to the propensity of an individual to develop a disease or dysfunction in later life. In this review, we intend to provide environmental, epidemiological and experimental data to associate pollutant exposure with reproductive disorders, in particular on the development and function of the male reproductive system. Possible effects of pollutant exposure on the processes of embryonic development, like sex determination and masculinization are described. In addition, the effects of pollutant exposure on hypothalamus-pituitary-gonadal axis, testicular signaling, steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis are also discussed.
Key words: hypothalamus-pituitary, masculinization, testis, metabolism, oxidative stress
Industrialization, Chemical Contamination and Human Health
In the past century, the drastic advancement in industrialization and technology and the growth in human population have driven a change to the environment to a scope that is unprecedented in human history. The production of large amounts of synthetic industrial and biomedical chemicals, as well as unwanted pollutants pose destructive consequences to our ecosystem and impose negative health effects to wildlife and humans.1–4 A recent review highlighted that about 40% of human death (62 million per year) is attributed to the exposure of chemical pollutants.5 In the past 60 years, more than 140,000 synthetic chemical compounds were made and approximately 1,000–2,000 new chemicals are produced each year.6 These chemicals are ubiquitous and are dispersed in air, water, soil and food. A study from the US Center for Disease Control (CDC) reported that Americans of all ages have accumulated over 116 extraneous chemicals into their bodies.7 Over 358 industrial chemicals and pesticides have been detected in the cord blood of American infants.8 Some of the more damaging chemical contaminants are classified as endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) since they can interfere with the synthesis, metabolism and action of endogenous hormones (Fig. 1).2 They are known to exert different biological effects via a diverse mechanism of actions.9 Most of the understanding of the EDC elicited-effects is derived from experimental studies conducted on animals and/or cell culture, but little direct evidence of effects has been compiled for humans. Nevertheless, the potential hazardous effects of EDCs on human health are currently strengthening via epidemiological studies and clinical observations10 and have been shown to impose long-term effects on metabolism, immune system defects, cancer development, decreased fertility and reproductive health.9,11–15
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of sex steroid hormones (testosterone, estrogen), natural metabolite (retinoic acid) and some common EDCs (BPA, DDT, DEHP, PCB, PFOS, dioxin).
Environmental Pollution and Reproductive Health
Exposure to environmental pollutants is suggested to be one of the culprits to reproductive problems worldwide. This exposure-effect relationship has long been established in wildlife and in laboratory animal studies.16–23 Adverse biological effects to male reproductive functions were first reported in wild animals where an accidental exposure to pollutants caused feminization or a change in reproductive behavior in the animals.24 In the 1980s, the adult male alligators in Apopka Lake that were exposed to agricultural wastes, produced low testosterone levels and presented micro-penis and disorganized testes.25–27 Effects of mercury exposure on reproductive behavior and sexual preference of white ibises were reported in reference 28.
In humans, increased incidences of birth defects, precocious puberty, reproductive cancers and infertility have been reported in reference 29–32. From the data of World Bank 2005, total fertility rate had decreased from 1970 to 2002 in both developed and industrialized countries.33 According to the 2001 World Health Organization (WHO) report “Current practices and Controversies in Assisted Reproduction,” at least 80 million people worldwide were estimated to be affected by infertility, of which the most common cause has been identified to be the “male factor”.34 Among all the infertility cases, over 10% of infertility cannot be explained medically. Given the adverse effects of EDC exposure on wildlife and laboratory animals, negative effects of environmental pollutants/chemicals on human fecundity are extrapolated. This postulation was supported by a study from Carlsen and coworkers in 1992, highlighting that the estrogenic-like activity of EDC was the cause of the decline in male fertility.35 However the scientific accuracy of the paper remains questionable, as numerous flaws have been recognized in the study.36–38 Although the accuracy of the Carlsen's paper is controversial, the paper motivated many follow-up investigations to re-analyze the data or to identify putative causative agents responsible for the declined human fecundity. Since there are variations in the quality of the methodologies and the great heterogeneity of the recruited subjects (i.e., different in age, behaviors and lifestyles), the general outcomes of these investigations are still not conclusive.39,40 At present the possible involvement of EDCs in human fecundity can neither be confirmed nor rejected.40 However it is generally agree that in utero chronic exposure to environmental pollutants might impose significant effects on fetal development.11,41–43
Effects of EDC on Sex Ratio and Early Testicular Development
In human epidemiologic studies, significant reductions in the ratio of “male birth to total number of birth” were recorded in highly polluted areas. The incidences of low male-to-female sex ratio at birth were reported in Aamjiwnaang First Nation community (areas close to industrial areas) in Canada,44 Seveso Italy,45 the Austrian chloracne cohort,46 and the victims in the Yucheng oil disaster, Taiwan.47 Possible explanation for the change in sex ratio at birth has not been elucidated. In mammals, sex development in embryonic stage depends on a delicate balance between male and female sex determining pathways.48–50 It is generally believed that the development of ovary from genital ridges is a default mechanism while the development of testis depends on the activity of Y chromosome testis-determining gene (Sry) and its downstream/associated factors [i.e., SRY-box containing gene 9 (Sox9), doublesex and mab-3 related transcription factor 1 (Dmrt1), prostaglandin D synthase, anti-Müllerian hormone (Amh) and testosterone].51–54 The spatiotemporal action of SRY to switch the supporting cells of genital ridges from the female to male pathway is essential and has to be undertaken within a critical programming time window.55 Any disruption in the early steps of the male pathway would lead to the mal-development of testes or an engagement of ovary development. Other subtle effects of EDCs on the masculinization process resulted in reproductive disorders similar to testicular dysgenesis syndrome (TDS). In the Study for Future Families in the United States, a correlation of prenatal exposure to several phthalates with shortening of the anogenital index and incomplete testicular descent were observed.56,57 Using rat models, adverse effects of phthalates on the male offspring such as absent/underdeveloped epididymis and germ cell loss were demonstrated.58,59 Epidemiological studies reported an increased risk of genital malformations and cryptorchidism in children of workers who were exposed to pesticides.60,61 The effects observed in laboratory animal studies seems to correlate with increased incidences of malformation of genital tracts in both European and US populations,62–64 however the exploitation of animal data to human cases is still controversial.65,66
Effects of EDC on HPG Circuitry Signaling in Neonatal and Pubertal Development
Mammalian spermatogenesis is a complicated cascade process that is under the tight control of the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis as well as the de novo auto/paracrine circuit.67 The primary role of the hormones involved is to enable a coordinated regulation of the process that allows the development of highly differentiated spermatozoa within the seminiferous tubules. The process depends on a functional hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular (HPT) axis. The hypothalamic kisspeptin-1 (KiSS-1) and its G protein-coupled receptor (GPR54) act as the gatekeeper to control the secretion of gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH), which regulates the anterior pituitary hormones—luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), and testicular hormones—testosterone, activin and inhibin B.41,68,70,71 Since neuroendocrine actions of EDCs have been shown,72–74 HPG circuitry signaling can be the EDC target during perinatal development. Any interruption on the hypothalamic circuitry, hormonal mediated regulation or on the constituents at the microenvironments in seminiferous tubules may result in a transient/long-term modification of the hormonal feedback circuitry, leading to the disturbance of spermatogenesis.15,75 In the following sections, some examples of the HPG-related systems that have been shown to be affected by EDCs are discussed.
Considerable numbers of studies have revealed effects of EDCs on the hypothalamic KiSS-1/GPR54 system and the HPG axis.15,76 The alteration of the HPG axis upon EDCs exposure [i.e., polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), lead, cadmium] has been shown from piscine to rodent,77–80 although their actions may vary in different development stages.81 Using nonhuman primate and mouse models, Leranth and coworkers demonstrated the effects of BPA exposure on spine synapse formation in brains.12,82 The observation provides profound insights on the effects of EDC on neuronal circuit development. This presumption has been supported by other studies where prenatal PCBs exposure interrupted neuronal development and receptor expression in rat hypothalamus.83 In rodent models, bisphenol A (BPA) exposures were found to affect hypothalamic kisspeptin fiber density, KiSS-1 and estrogen receptor-α (ERα) mRNA expression.84–88 In our recent study, we demonstrated that prenatal exposure to BPA exerted considerable effects on the functional circuitry of HPG axis in mice.84 The disruption of the normal functioning of the hypothalamic circuitry may lead to an interruption of GnRH, LH and FSH release for the regulation of sexual development and gametogenesis (Fig. 2 and arrow A).89 In addition to the modulation of hormone release from hypothalamus-pituitary level, the decrease in testosterone and sperm production can be the consequence of the reduced testicular expression levels of receptors for gonadotrophin, as demonstrated in perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) exposed mice (Fig. 2 and arrow B).90
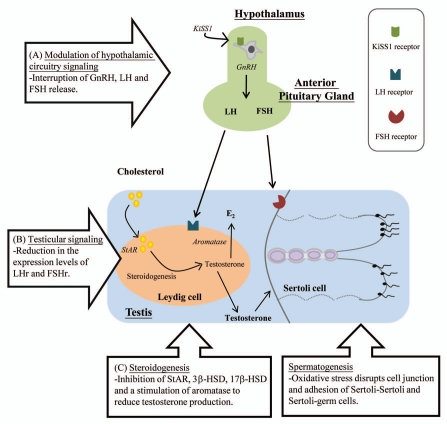
Figure 2.
A schematic diagram depicts the effects of EDCs on HPG axis. (A) EDCs modulated the neural circuit in hypothalamus (KiSS-1/GPR54 and HPG axis) leading to the dysregulation of gonadotrophin hormones (FSH/LH) secretion by the pituitary. (B) In the testis, EDC exposure caused the reduction in the expression of gonadotrophin receptors (LHr and FSHr). (C) EDCs interfered with the enzymes (StAR, P450scc, 3β-HSD, 17β-HSD) involved in steroidogenesis. (D) In addition to the reduction of testosterone level, oxidative stress elicited by EDCs caused disruption of cell-cell interaction and perturbed the process of spermatogenesis.
Although the biological and physiological outcomes of EDC exposures have been reported, the possible molecular targets at the HPG axis have not been elucidated. Since some of the EDCs bear very similar chemical structures to the endogenous hormones,91 the interaction between nuclear hormone receptors (NHRs) and EDCs has been proposed as the elementary action on endocrine disruption.92,93 It is generally believed that EDCs can affect the hormonal system via (but not limited to) estrogenic, androgenic, anti-androgenic and anti-thyroid mechanisms.30,94 The mechanistic aspects of endocrine disruption may be via the roles as (1) agonist or antagonist, (2) selective modulators in the recruitment of coactivators/co-repressor in transcriptional complex or/and (3) in cross-talk between NHRs.95 Among different EDCs, the molecular targets and the mechanistic actions of dioxins are well characterized. Dioxins are known to impose biological effects via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR), which belongs to a member of the basic helix-loop-helix/Per-Arnt-Sim (bHLH/PAS) family of transcription factors. AHR exhibits its transcriptional activity primarily via ligand-dependent nuclear translocation.96 Other regulatory functions mediated by dioxin/AHR complex include the modulation of other transcriptional factors, including retinoblastoma (Rb)/elongation factor-2 (E2F), nuclear factor-κB (NFκB) and the estrogen receptors (ERα and ERβ) and androgen receptors.97–103 Comparable to the dioxin/AHR mediated actions, EDCs that possess estrogenic and/or anti-estrogenic activities, have also been shown to have striking effect on animals.104 This is particularly true if we look at it from an evolutionary perspective where the DNA-binding domain and the ligand-binding domain of ERα are conserved across metazoans.105,106 Global environmental contaminants, persistent organic pollutants (i.e., dichlorodiphenyl-trichloroethane (DDT), hydroxylated PCBs, BPA, p-nonylphenol and dioxins) and heavy metals (i.e., cadmium and mercury) were shown to have either or both estrogenic and androgenic activity.104,107,108 In addition, BPA was found to able to activate membrane G-protein coupled estrogen receptor.109 Some newly identified emerging contaminants, like perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) and flame retardants were also reported to possess estrogenic activities.110,111
Effects of EDC on Adult Spermatogenesis
The modulation of steroidogenic enzymes.
In addition to the NHR-mediated effects, recent hypothesis has highlighted that steroidogenesis is the major target for EDCs (Fig. 2 and arrow C).112,113 Steroidogenesis is the process for steroid hormone production. It is an enzymatic-mediated process catalyzed by several enzymes from two main categories: the cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP11A and CYP17A), and hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (HSD) enzymes (3β-HSD and 17β-HSD).114 Negative influences of EDC exposure on steroidogenesis have been reported in both in vivo and in vitro studies. Inhibitory effects of BPA, PCBs, PFCs, dioxins and some of the phthalates on the expression levels of some steroidogenic enzymes were elucidated.115–122 Mostly downregulation of the expression levels of CYP11A and CYP17A were observed, resulting in the reduction of testosterone production. This hypothesis is rational as receptor binding affinities of most EDCs are generally low as compared to the endogenous ligands.123 Although the additive/synergistic effects of mixture of EDCs cannot be neglected, it seems unlikely that EDC can compete with the endogenous ligand for receptor binding. Retrospectively it is more likely that EDCs interfere with steroidogenesis and modulate the release of endogenous steroid hormones. The altered serum levels of the steroid hormones may cause subsequent reproductive dysfunction by interfering with the feedback regulatory mechanisms of the HPG axis. For example, BPA is a weak estradiol agonist, its estrogenic effect in animal bodies is probably mediated by its stimulatory action on gonadal aromatase to increase serum estradiol (E2) levels.84,124 Consistently using H295R human adenocarcinoma cells, BPA treatment caused an increase of E2 production.125 Another EDC, dioxin was shown to reduce testosterone production in rat primary Leydig cell culture via the inhibition of human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG)-stimulated cAMP and CYP11A levels.126 The effects of EDCs on fetal testis seem to be more striking as the disruption of steroidogenesis at this early developmental stage can also affect the proliferation of germ cells and Sertoli cells.113,127,128 Notably it may interfere with the formation of the Sertoli-germ cell complex which supports the maximum number of sperm that can be produced in adulthood.129,130 More importantly, the effects on germ cell development can be inherited via epigenetic actions of EDCs.11,131 Although the underlying action of EDCs on epigenetic modification is not known, this hypothesis is supported by data from other laboratory animal studies.132,133 Retrospectively the effects of EDCs on fetal testis can be long-lasting and transgenerational.127,128,134 In contrary, the effects on adult testis may be short-term and reversible upon the reduced exposure to the chemicals.
The induction of oxidative stress.
As mentioned above, the effects of EDs are believed to be mediated by their direct and/or indirect actions on steroid hormone receptors and steroidogenesis.30 However, these effects may be limited to EDCs with particular chemical structures. The effects of other heterogeneous structures of EDCs may not be accounted for.135 Recently, oxidative stress is identified as a common mechanism of action for EDC in affecting cellular structures and functions.136 Induction of oxidative stress was detected in epididymal sperms of rats, exposed to BPA.137 Specifically EDC-induced oxidative stress caused disruption to tight and adherens junctions between Sertoli-Sertoli cells and Sertoli-germ cells.67,138 The underlying mechanism of the dysregulation is found to be associated with the modulation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/c-Src/focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-signaling, in affecting the metabolism of some polarity proteins [e.g., occludin, zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) and N-cadherin].139 The disruption of the junctional structures leads to the dysregulation of spermatogenesis (Fig. 2 and arrow D).140,141 Since there are two recent excellent reviews from Cheng's group that have covered most of the updated information on this aspect,139,142 the underlying mechanisms of EDC-induced oxidative stress in mediating disruption to cell junctions will not be discussed in this review.
The alternation of body metabolism.
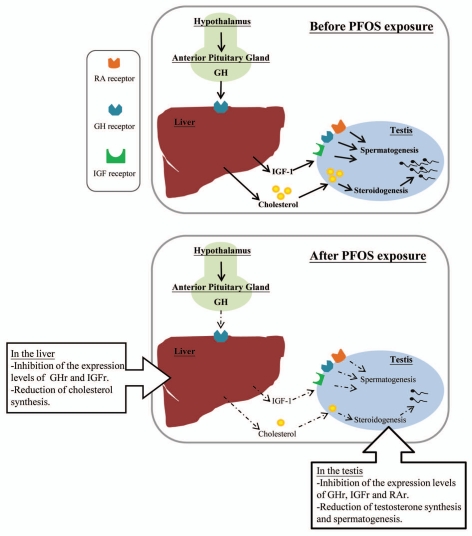
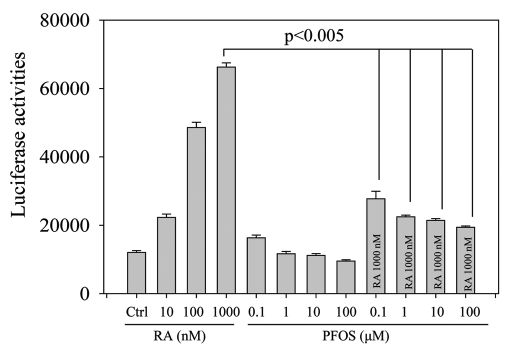
The maintenance of normal male reproductive function is not exclusively controlled by gonadotrophin and testicular hormones/factors (i.e., testosterone, activins, inhibins).143–145 Possible influence from body metabolic disturbances on testicular functions is discussed in recent years.146 Perturbation of the testicular steroidogenesis can be due to the inhibitory action of EDC on the gene expression levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and its receptor in rat testes as shown by perfluorododecanoic acid (PFDoA) exposure.117 Similarly, our recent data demonstrated that PFOS-induced testicular dysfunctions and metabolic disorders may be related to the reduction in the expression levels of receptors for growth hormone (GH) and IGF in both liver and testis of mice (Fig. 3).90 The effects of GH and IGF-1 are known to stimulate the transcription of CYP11A gene encoding cytochrome P450 side-chain cleavage (P450scc), for the conversion of free cholesterol into pregnenolone in the early steps of steroidogenesis.147 A decrease of signal interaction between GH/IGF-1 and HPG axis would therefore affect steroidogenesis.144,148 Furthermore the GH/IGF-1 axis has been suggested to link with the adipocytokine signaling system.149–151 Leptin plays a regulatory role on the HPG axis via leptin-kisspeptin-GnRH pathway, leading to the hormonal regulation of LH and FSH.152–155 Indeed, serum leptin was found to be negatively correlated with serum testosterone. Reduced interaction of leptin with Leydig or germ cells would lead to the reduction in the expression of steroidogenic enzymes156,157 and the impairment of sperm mobility.155,158–160 In gestational exposure of EDCs (i.e., phthalate), plasma leptin level was reduced and was accompanied by the reduction of anogenital distance and the expression levels of several steroidogenic enzymes such as steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR), CYP11A, CYP17 in fetal male rats.156 Leptin synthesis was also found to be inhibited in cadmium exposure.161 In addition to leptin, another adipocytokines such as adiponectin and retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4) have been suggested to be modulated by EDC exposure. For instance, BPA treatment diminished adiponectin production in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.162 Long-term exposure of DDT caused a reduction of serum RBP4 levels, leading to an inadequate intake of vitamin A,163 which is an important factor for the regulation of spermatogenesis.164 Intriguingly using retinoic acid (RA) reporter assay, PFOS was found to inhibit RA-mediated transactivation of retinoic acid response element (RARE) (unpublished data, Fig. 4). The data indicate that PFOS may act as a RA antagonist to interfere with retinoid signaling to inhibit spermatogenesis.165
Figure 3.
A schematic diagram illustrates the influence of PFOS on GH/IGF-signaling and testicular functions. Our recent data demonstrated that PFOS-induced testicular dysfunctions and metabolic disorders via the reduction in the expression levels of receptors for GH and IGF in both liver and testis, leading to the inhibition of steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis.
Figure 4.
PFOS inhibits RA-mediated transactivation of retinoic acid response element (RARE), as illustrated using luciferase reporter assay. The day before transfection, MCF7 cells were plated into 24-well tissue culture dishes at a density reaching 70–80% confluence by the time of transfection. Transfection was performed using LipofectAMINE™ 2000 reagent (Invitrogen) and OPTI-MEM®I medium (GIBCO) with 250 ng of retinoic acid reporter (Addgene). Six hours after transfection, the transfection medium was replaced by a complete medium and different doses of retinoic acid (10–1,000 nM) or PFOS (0.1–100 µM) or co-treatment of retinoic acid (1,000 nM) and PFOS (0.1–100 µM) were added. After 24 h incubation, the cells were then lysed in the passive lysis buffer. Firefly luciferase activities were measured using the Luciferase reporter assay system (Promega) and the multilabel reader VICTOR™X4 (PerkinElmer).
Conclusion
Adverse effects of EDCs on male reproductive dysfunction are well recognized from the epidemiological and laboratory animal data. However tens of thousands of industrial chemicals or pollutants are still produced or discharged extensively on a daily basis.166–169 They are ubiquitous and the possible routes of human exposure to EDCs are from the environments, consumer products and foods. Effects of EDCs on animal reproductive function can be multi-faceted and pleiotropic. Exposures to EDCs can interfere with cell signaling via direct/indirect “hormonal” and/or oxidative stress related pathways in HPG axis and other body tissues (i.e., liver). These direct and indirect effects disrupt the homeostasis at different levels of feedback regulatory mechanisms (neuron communication, endocrine, autocrine and paracrine) for the regulation of testicular development and functions (i.e., steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis). However current cell culture- and animal-based experiments can only produce limited data on human risk assessment in reproductive impairment.170,171 Since most of the adverse health responses in laboratory animals are demonstrated when animals are exposed to doses that are greater than those found in the environment, this leads to the difficulty to assess the potential low-dose human exposure risk. Prenatal exposure to EDCs seems to be particularly critical in affecting neural circuits at hypothalamus-pituitary axis and fetal testicular development, leading to long-term, irreversible consequences in reproductive dysfunction.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Collaborative Research Fund (HKBU 1/CRF/08), University Grants Committee.
References
- 1.CHEMTrust, author. Effects of pollutants on the reproductive health of male vertebrate wildlife—males under threat. :1–43. 11-11-2008. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Bourguignon JP, Giudice LC, Hauser R, Prins GS, Soto AM, et al. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: an Endocrine Society scientific statement. Endocr Rev. 2009;30:293–342. doi: 10.1210/er.2009-0002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rhind SM. Endocrine disruptors and other food-contaminating environmental pollutants as risk factors in animal reproduction. Reprod Domest Anim. 2008;43:15–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0531.2008.01138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rhind SM. Anthropogenic pollutants: a threat to ecosystem sustainability? Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009;364:3391–3401. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2009.0122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pimentel D, Cooperstein S, Randell H, Filiberto D, Sorrentio S, Kaye B, et al. Ecology of increasing diseases: population growth and environmental degradation. Hum Ecol. 2007;35:653–668. doi: 10.1007/s10745-007-9128-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Judson R, Richard A, Dix DJ, Houck K, Martin M, Kavlock R, et al. The toxicity data landscape for environmental chemicals. Environ Health Perspect. 2009;117:685–695. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0800168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Center for Disease Control (CDC), author Second national report on human exposure to environmental chemicals. Atlanta, Georgia: CDC; 11-11-2003. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Environmental Working Group (EWG), author Pollution in people, blood contaminants in minority newborns. 2009 [Google Scholar]
- 9.Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Palioura E, Kandarakis SA, Koutsilieris M. The impact of endocrine disruptors on endocrine targets. Horm Metab Res. 2010;42:543–552. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1252034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Carpenter DO, Arcaro KF, Bush B, Niemi WD, Pang S, Vakharia DD. Human health and chemical mixtures: an overview. Environ Health Perspect. 1998;6:1263–1270. doi: 10.1289/ehp.98106s61263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Anway MD, Skinner MK. Epigenetic programming of the germ line: effects of endocrine disruptors on the development of transgenerational disease. Reprod Biomed Online. 2008;16:23–25. doi: 10.1016/s1472-6483(10)60553-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Leranth C, Szigeti-Buck K, MacLusky NJ, Hajszan T. Bisphenol A prevents the synaptogenic response to testosterone in the brain of adult male rats. Endocrinology. 2008;149:988–994. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rier SE. Environmental immune disruption: a comorbidity factor for reproduction? Fertil Steril. 2008;89:103–108. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2007.12.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Soto AM, Sonnenschein C. Environmental causes of cancer: endocrine disruptors as carcinogens. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010 doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2010.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tena-Sempere M. Kisspeptin/GPR54 system as potential target for endocrine disruption of reproductive development and function. Int J Androl. 2010;33:360–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2009.01012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mansfield KG, Land ED. Cryptorchidism in Florida panthers: prevalence, features and influence of genetic restoration. J Wildl Dis. 2002;38:693–698. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-38.4.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.De Guise S, Lagace A, Beland P. True hermaphroditism in a St. Lawrence beluga whale (Delphinapterus leucas) J Wildl Dis. 1994;30:287–290. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-30.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Oskam IC, Ropstad E, Dahl E, Lie E, Derocher AE, Wiig O, et al. Organochlorines affect the major androgenic hormone, testosterone, in male polar bears (Ursus maritimus) at Svalbard. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2003;66:2119–2139. doi: 10.1080/15287390390211342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fry DM. Reproductive effects in birds exposed to pesticides and industrial chemicals. Environ Health Perspect. 1995;103:165–171. doi: 10.1289/ehp.95103s7165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hayes T, Haston K, Tsui M, Hoang A, Haeffele C, Vonk A. Atrazine-induced hermaphroditism at 0.1 ppb in American leopard frogs (Rana pipiens): laboratory and field evidence. Environ Health Perspect. 2003;111:568–575. doi: 10.1289/ehp.5932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jobling S, Coey S, Whitmore JG, Kime DE, Van Look KJ, McAllister BG, et al. Wild intersex roach (Rutilus rutilus) have reduced fertility. Biol Reprod. 2002;67:515–524. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod67.2.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Aravindakshan J, Paquet V, Gregory M, Dufresne J, Fournier M, Marcogliese DJ, et al. Consequences of xenoestrogen exposure on male reproductive function in spottail shiners (Notropis hudsonius) Toxicol Sci. 2004;78:156–165. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfh042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Barnhoorn IE, Bornman MS, Pieterse GM, van Vuren JH. Histological evidence of intersex in feral sharptooth catfish (Clarias gariepinus) from an estrogen-polluted water source in Gauteng, South Africa. Environ Toxicol. 2004;19:603–608. doi: 10.1002/tox.20068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Vos JG, Dybing E, Greim HA, Ladefoged O, Lambre C, Tarazona JV, et al. Health effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals on wildlife, with special reference to the European situation. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2000;30:71–133. doi: 10.1080/10408440091159176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Guillette LJ, Jr, Guillette EA. Environmental contaminants and reproductive abnormalities in wildlife: implications for public health? Toxicol Ind Health. 1996;12:537–550. doi: 10.1177/074823379601200325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Guillette LJ, Jr, Gross TS, Gross DA, Rooney AA, Percival HF. Gonadal steroidogenesis in vitro from juvenile alligators obtained from contaminated or control lakes. Environ Health Perspect. 1995;103:31–36. doi: 10.1289/ehp.95103s431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Guillette LJ, Jr, Gross TS, Masson GR, Matter JM, Percival HF, Woodward AR. Developmental abnormalities of the gonad and abnormal sex hormone concentrations in juvenile alligators from contaminated and control lakes in Florida. Environ Health Perspect. 1994;102:680–688. doi: 10.1289/ehp.94102680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Frederick P, Jayasena N. Altered pairing behaviour and reproductive success in white ibises exposed to environmentally relevant concentrations of methylmercury. Proc Biol Sci. 2011;278:1851–1857. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2010.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Buck Louis GM, Gray LE, Jr, Marcus M, Ojeda SR, Pescovitz OH, Witchel SF, et al. Environmental factors and puberty timing: expert panel research needs. Pediatrics. 2008;121:192–207. doi: 10.1542/peds.1813E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Phillips KP, Foster WG. Key developments in endocrine disrupter research and human health. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2008;11:322–344. doi: 10.1080/10937400701876194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Phillips KP, Tanphaichitr N. Human exposure to endocrine disrupters and semen quality. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2008;11:188–220. doi: 10.1080/10937400701873472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Roy JR, Chakraborty S, Chakraborty TR. Estrogen-like endocrine disrupting chemicals affecting puberty in humans—a review. Med Sci Monit. 2009;15:137–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.World Bank, author. 2005 http://www.worldbank.org. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sharlip ID, Jarow JP, Belker AM, Lipshultz LI, Sigman M, Thomas AJ, et al. Best practice policies for male infertility. Fertil Steril. 2002;77:873–882. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(02)03105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Carlsen E, Giwercman A, Keiding N, Skakkebaek NE. Evidence for decreasing quality of semen during past 50 years. BMJ. 1992;305:609–613. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6854.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Farrow S. Falling sperm quality: fact or fiction? BMJ. 1994;309:1–2. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6946.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Becker S, Berhane K. A meta-analysis of 61 sperm count studies revisited. Fertil Steril. 1997;67:1103–1108. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(97)81446-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fisch H, Goluboff ET. Geographic variations in sperm counts: a potential cause of bias in studies of semen quality. Fertil Steril. 1996;65:1044–1046. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)58284-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Fisch H. Declining worldwide sperm counts: disproving a myth. Urol Clin North Am. 2008;35:137–146. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2008.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.te VE, Burdorf A, Nieschlag E, Eijkemans R, Kremer JA, Roeleveld N, et al. Is human fecundity declining in western countries? Hum Reprod. 2010;25:1348–1353. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deq085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hamlin HJ, Guillette LJ., Jr Embryos as targets of endocrine disrupting contaminants in wildlife. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2011;93:19–33. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.20202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Janesick A, Blumberg B. Endocrine disrupting chemicals and the developmental programming of adipogenesis and obesity. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2011;93:34–50. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.20197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wohlfahrt-Veje C, Main KM, Skakkebaek NE. Testicular dysgenesis syndrome: foetal origin of adult reproductive problems. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2009;71:459–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2009.03545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mackenzie CA, Lockridge A, Keith M. Declining sex ratio in a first nation community. Environ Health Perspect. 2005;113:1295–1298. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mocarelli P, Gerthoux PM, Ferrari E, Patterson DG, Jr, Kieszak SM, Brambilla P, et al. Paternal concentrations of dioxin and sex ratio of offspring. Lancet. 2000;355:1858–1863. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02290-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Moshammer H, Neuberger M. Sex ratio in the children of the Austrian chloracne cohort. Lancet. 2000;356:1271–1272. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)73872-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.del Rio Gomez I, Marshall T, Tsai P, Shao YS, Guo YL. Number of boys born to men exposed to polychlorinated byphenyls. Lancet. 2002;360:143–144. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)09386-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Piprek RP. Molecular and cellular machinery of gonadal differentiation in mammals. Int J Dev Biol. 2010;54:779–786. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.092939rp. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Veitia RA. FOXL2 versus SOX9: a lifelong “battle of the sexes”. Bioessays. 2010;32:375–380. doi: 10.1002/bies.200900193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Schlessinger D, Garcia-Ortiz JE, Forabosco A, Uda M, Crisponi L, Pelosi E. Determination and stability of gonadal sex. J Androl. 2010;31:16–25. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.109.008201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Piprek RP. Genetic mechanisms underlying male sex determination in mammals. J Appl Genet. 2009;50:347–360. doi: 10.1007/BF03195693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cool J, Capel B. Mixed signals: development of the testis. Semin Reprod Med. 2009;27:5–13. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1108005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sim H, Argentaro A, Harley VR. Boys, girls and shuttling of SRY and SOX9. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2008;19:213–222. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2008.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ferguson-Smith M. The evolution of sex chromosomes and sex determination in vertebrates and the key role of DMRT1. Sex Dev. 2007;1:2–11. doi: 10.1159/000096234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Hiramatsu R, Matoba S, Kanai-Azuma M, Tsunekawa N, Katoh-Fukui Y, Kurohmaru M, et al. A critical time window of Sry action in gonadal sex determination in mice. Development. 2009;136:129–138. doi: 10.1242/dev.029587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Swan SH, Main KM, Liu F, Stewart SL, Kruse RL, Calafat AM, et al. Decrease in anogenital distance among male infants with prenatal phthalate exposure. Environ Health Perspect. 2005;113:1056–1061. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Jurewicz J, Hanke W. Exposure to phthalates: reproductive outcome and children health. A review of epidemiological studies. Int J Occup Med Environ Health. 2011;24:115–141. doi: 10.2478/s13382-011-0022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Mylchreest E, Cattley RC, Foster PM. Male reproductive tract malformations in rats following gestational and lactational exposure to Di(n-butyl) phthalate: an antiandrogenic mechanism? Toxicol Sci. 1998;43:47–60. doi: 10.1006/toxs.1998.2436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Gray LE, Jr, Wolf C, Lambright C, Mann P, Price M, Cooper RL, et al. Administration of potentially antiandrogenic pesticides (procymidone, linuron, iprodione, chlozolinate, p,p'-DDE and ketoconazole) and toxic substances (dibutyl- and diethylhexyl phthalate, PCB 169 and ethane dimethane sulphonate) during sexual differentiation produces diverse profiles of reproductive malformations in the male rat. Toxicol Ind Health. 1999;15:94–118. doi: 10.1177/074823379901500109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Garcia-Rodriguez J, Garcia-Martin M, Nogueras-Ocana M, de Dios Luna-del-Castillo, Espigares GM, Olea N, et al. Exposure to pesticides and cryptorchidism: geographical evidence of a possible association. Environ Health Perspect. 1996;104:1090–1095. doi: 10.1289/ehp.104-1469503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Weidner IS, Moller H, Jensen TK, Skakkebaek NE. Cryptorchidism and hypospadias in sons of gardeners and farmers. Environ Health Perspect. 1998;106:793–796. doi: 10.1289/ehp.98106793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Toppari J, Virtanen HE, Main KM, Skakkebaek NE. Cryptorchidism and hypospadias as a sign of testicular dysgenesis syndrome (TDS): environmental connection. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2010;88:910–919. doi: 10.1002/bdra.20707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Wang MH, Baskin LS. Endocrine disruptors, genital development and hypospadias. J Androl. 2008;29:499–505. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.108.004945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Hsieh MH, Breyer BN, Eisenberg ML, Baskin LS. Associations among hypospadias, cryptorchidism, anogenital distance and endocrine disruption. Curr Urol Rep. 2008;9:137–142. doi: 10.1007/s11934-008-0025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Fisch H, Hyun G, Hensle TW. Rising hypospadias rates: disproving a myth. J Pediatr Urol. 2010;6:37–39. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2009.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kalfa N, Philibert P, Sultan C. Is hypospadias a genetic, endocrine or environmental disease or still an unexplained malformation? Int J Androl. 2009;32:187–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2008.00899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Cheng CY, Wong EW, Yan HH, Mruk DD. Regulation of spermatogenesis in the microenvironment of the seminiferous epithelium: new insights and advances. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010;315:49–56. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2009.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Silveira LF, Teles MG, Trarbach EB, Latronico AC. Role of Kisspeptin/GPR54 System in Human Reproductive Axis. Front Horm Res. 2010;39:13–24. doi: 10.1159/000312689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Hameed S, Dhillo WS. Biology of Kisspeptins. Front Horm Res. 2010;39:25–36. doi: 10.1159/000312691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Hameed S, Jayasena CN, Dhillo WS. Kisspeptin and fertility. J Endocrinol. 2011;208:97–105. doi: 10.1677/JOE-10-0265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Roseweir AK, Millar RP. The role of kisspeptin in the control of gonadotrophin secretion. Hum Reprod Update. 2009;15:203–212. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmn058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Kodavanti PR, Curras-Collazo MC. Neuroendocrine actions of organohalogens: thyroid hormones, arginine vasopressin and neuroplasticity. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2010;31:479–496. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2010.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Gore AC. Neuroendocrine targets of endocrine disruptors. Hormones (Athens) 2010;9:16–27. doi: 10.14310/horm.2002.1249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Ottinger MA, Lavoie ET, Abdelnabi M, Quinn MJ, Jr, Marcell A, Dean K. An overview of dioxin-like compounds, PCB and pesticide exposures associated with sexual differentiation of neuroendocrine systems, fluctuating asymmetry and behavioral effects in birds. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 2009;27:286–300. doi: 10.1080/10590500903310229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Sokol RZ. Endocrinology of male infertility: evaluation and treatment. Semin Reprod Med. 2009;27:149–158. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1202303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bellingham M, Fowler PA, Amezaga MR, Rhind SM, Cotinot C, Mandon-Pepin B, et al. Exposure to a complex cocktail of environmental endocrine-disrupting compounds disturbs the kisspeptin/GPR54 system in ovine hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Environ Health Perspect. 2009;117:1556–1562. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0900699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Khan IA, Thomas P. Disruption of neuroendocrine control of luteinizing hormone secretion by aroclor 1254 involves inhibition of hypothalamic tryptophan hydroxylase activity. Biol Reprod. 2001;64:955–964. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod64.3.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Khan IA, Thomas P. Aroclor 1254-induced alterations in hypothalamic monoamine metabolism in the Atlantic croaker (Micropogonias undulatas): correlation with pituitary gonadotropin release. Neurotoxicology. 1997;18:553–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Sokol RZ, Okuda H, Nagler HM, Berman N. Lead exposure in vivo alters the fertility potential of sperm in vitro. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1994;124:310–316. doi: 10.1006/taap.1994.1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Sokol RZ. Reversibility of the toxic effect of lead on the male reproductive axis. Reprod Toxicol. 1989;3:175–180. doi: 10.1016/0890-6238(89)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Lafuente A, Marquez N, Perez-Lorenzo M, Pazo D, Esquifino AI. Pubertal and postpubertal cadmium exposure differentially affects the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis function in the rat. Food Chem Toxicol. 2000;38:913–923. doi: 10.1016/s0278-6915(00)00077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Leranth C, Hajszan T, Szigeti-Buck K, Bober J, MacLusky NJ. Bisphenol A prevents the synaptogenic response to estradiol in hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of ovariectomized nonhuman primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:14187–14191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0806139105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Dickerson SM, Cunningham SL, Gore AC. Prenatal PCBs disrupt early neuroendocrine development of the rat hypothalamus. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011;252:36–46. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2011.01.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Wei X, Lee CK, Yeung WS, Giesy JP, Wong MH, Zhang X, et al. Effect of perinatal and postnatal bisphenol A exposure to the regulatory circuits at the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonadal axis of CD-1 mice. Reprod Toxicol. 2011;31:409–417. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2010.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Patisaul HB, Todd KL, Mickens JA, Adewale HB. Impact of neonatal exposure to the ERalpha agonist PPT, bisphenol-A or phytoestrogens on hypothalamic kisspeptin fiber density in male and female rats. Neurotoxicology. 2009;30:350–357. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2009.02.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Navarro VM, Sanchez-Garrido MA, Castellano JM, Roa J, Garcia-Galiano D, Pineda R, et al. Persistent impairment of hypothalamic KiSS-1 system after exposures to estrogenic compounds at critical periods of brain sex differentiation. Endocrinology. 2009;150:2359–2367. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Fernandez M, Bianchi M, Lux-Lantos V, Libertun C. Neonatal exposure to bisphenol a alters reproductive parameters and gonadotropin releasing hormone signaling in female rats. Environ Health Perspect. 2009;117:757–762. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0800267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Ceccarelli I, Della SD, Fiorenzani P, Farabollini F, Aloisi AM. Estrogenic chemicals at puberty change ERalpha in the hypothalamus of male and female rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2007;29:108–115. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2006.10.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Milardi D, Giampietro A, Baldelli R, Pontecorvi A, De Marinis L. Fertility and hypopituitarism. J Endocrinol Invest. 2008;31:71–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Wan HT, Zhao YG, Wong MH, Lee KF, Yeung WS, Giesy JP, et al. Testicular signaling is the potential target of perfluorooctanesulfonate-mediated subfertility in male mice. Biol Reprod. 2011;84:1016–1023. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.110.089219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Crews D, McLachlan JA. Epigenetics, evolution, endocrine disruption, health and disease. Endocrinology. 2006;147:4–10. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-1122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.le Maire A, Bourguet W, Balaguer P. A structural view of nuclear hormone receptor: endocrine disruptor interactions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010;67:1219–1237. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0249-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Ruegg J, Penttinen-Damdimopoulou P, Makela S, Pongratz I, Gustafsson JA. Receptors mediating toxicity and their involvement in endocrine disruption. EXS. 2009;99:289–323. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7643-8336-7_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Phillips KP, Foster WG, Leiss W, Sahni V, Karyakina N, Turner MC, et al. Assessing and managing risks arising from exposure to endocrine-active chemicals. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2008;11:351–372. doi: 10.1080/10937400701876657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Casals-Casas C, Desvergne B. Endocrine disruptors: from endocrine to metabolic disruption. Annu Rev Physiol. 2011;73:135–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-012110-142200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Mimura J, Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Functional role of AhR in the expression of toxic effects by TCDD. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1619:263–268. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(02)00485-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Puga A, Barnes SJ, Dalton TP, Chang C, Knudsen ES, Maier MA. Aromatic hydrocarbon receptor interaction with the retinoblastoma protein potentiates repression of E2F-dependent transcription and cell cycle arrest. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:2943–2950. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.4.2943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Vogel CF, Sciullo E, Li W, Wong P, Lazennec G, Matsumura F. RelB, a new partner of aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated transcription. Mol Endocrinol. 2007;21:2941–2955. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Ohtake F, Takeyama K, Matsumoto T, Kitagawa H, Yamamoto Y, Nohara K, et al. Modulation of oestrogen receptor signalling by association with the activated dioxin receptor. Nature. 2003;423:545–550. doi: 10.1038/nature01606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Matthews J, Wihlen B, Thomsen J, Gustafsson JA. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated transcription: ligand-dependent recruitment of estrogen receptor alpha to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-responsive promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:5317–5328. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.13.5317-5328.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Beischlag TV, Perdew GH. ER alpha-AHR-ARNT protein-protein interactions mediate estradiol-dependent transrepression of dioxin-inducible gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:21607–21611. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C500090200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Wormke M, Stoner M, Saville B, Walker K, Abdelrahim M, Burghardt R, et al. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor mediates degradation of estrogen receptor alpha through activation of proteasomes. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:1843–1855. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.6.1843-1855.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Ohtake F, Baba A, Takada I, Okada M, Iwasaki K, Miki H, et al. Dioxin receptor is a ligand-dependent E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nature. 2007;446:562–566. doi: 10.1038/nature05683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.McLachlan JA. Environmental signaling: what embryos and evolution teach us about endocrine disrupting chemicals. Endocr Rev. 2001;22:319–341. doi: 10.1210/edrv.22.3.0432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Thornton JW, Need E, Crews D. Resurrecting the ancestral steroid receptor: ancient origin of estrogen signaling. Science. 2003;301:1714–1717. doi: 10.1126/science.1086185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.McLachlan JA. Functional toxicology: a new approach to detect biologically active xenobiotics. Environ Health Perspect. 1993;101:386–387. doi: 10.1289/ehp.93101386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Martin MB, Reiter R, Pham T, Avellanet YR, Camara J, Lahm M, et al. Estrogen-like activity of metals in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Endocrinology. 2003;144:2425–2436. doi: 10.1210/en.2002-221054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Johnson MD, Kenney N, Stoica A, Hilakivi-Clarke L, Singh B, Chepko G, et al. Cadmium mimics the in vivo effects of estrogen in the uterus and mammary gland. Nat Med. 2003;9:1081–1084. doi: 10.1038/nm902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Bouskine A, Nebout M, Brucker-Davis F, Benahmed M, Fenichel P. Low doses of bisphenol A promote human seminoma cell proliferation by activating PKA and PKG via a membrane G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor. Environ Health Perspect. 2009;117:1053–1058. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0800367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Maras M, Vanparys C, Muylle F, Robbens J, Berger U, Barber JL, et al. Estrogen-like properties of fluorotelomer alcohols as revealed by mcf-7 breast cancer cell proliferation. Environ Health Perspect. 2006;114:100–105. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Meerts IA, Letcher RJ, Hoving S, Marsh G, Bergman A, Lemmen JG, et al. In vitro estrogenicity of polybrominated diphenyl ethers, hydroxylated PDBEs and polybrominated bisphenol A compounds. Environ Health Perspect. 2001;109:399–407. doi: 10.1289/ehp.01109399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Sanderson JT. The steroid hormone biosynthesis pathway as a target for endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Toxicol Sci. 2006;94:3–21. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfl051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Scott HM, Mason JI, Sharpe RM. Steroidogenesis in the fetal testis and its susceptibility to disruption by exogenous compounds. Endocr Rev. 2009;30:883–925. doi: 10.1210/er.2009-0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Miller WL, Auchus RJ. The molecular biology, biochemistry and physiology of human steroidogenesis and its disorders. Endocr Rev. 2011;32:81–151. doi: 10.1210/er.2010-0013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Nakamura D, Yanagiba Y, Duan Z, Ito Y, Okamura A, Asaeda N, et al. Bisphenol A may cause testosterone reduction by adversely affecting both testis and pituitary systems similar to estradiol. Toxicol Lett. 2010;194:16–25. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Lai KP, Mak NK, Wei X, Wong RN, Wong MH, Wong CK. Bifunctional modulating effects of an indigo dimer (bisindigotin) to CYP1A1 induction in H4IIE cells. Toxicology. 2006;226:188–196. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2006.06.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Shi Z, Feng Y, Wang J, Zhang H, Ding L, Dai J. Perfluorododecanoic acid-induced steroidogenic inhibition is associated with steroidogenic acute regulatory protein and reactive oxygen species in cAMP-stimulated Leydig cells. Toxicol Sci. 2010;114:285–294. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Shi Z, Ding L, Zhang H, Feng Y, Xu M, Dai J. Chronic exposure to perfluorododecanoic acid disrupts testicular steroidogenesis and the expression of related genes in male rats. Toxicol Lett. 2009;188:192–200. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2009.04.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Song R, He Y, Murphy MB, Yeung LW, Yu RM, Lam MH, et al. Effects of fifteen PBDE metabolites, DE71, DE79 and TBBPA on steroidogenesis in the H295R cell line. Chemosphere. 2008;71:1888–1894. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Peretz J, Gupta RK, Singh J, Hernandez-Ochoa I, Flaws JA. Bisphenol A impairs follicle growth, inhibits steroidogenesis and downregulates rate-limiting enzymes in the estradiol biosynthesis pathway. Toxicol Sci. 2011;119:209–217. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Han DY, Kang SR, Park OS, Cho JH, Won CK, Park HS, et al. Polychlorinated biphenyls have inhibitory effect on testicular steroidogenesis by downregulation of P450(17alpha) and P450(scc) Toxicol Ind Health. 2010;26:287–296. doi: 10.1177/0748233710364961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Murugesan P, Balaganesh M, Balasubramanian K, Arunakaran J. Effects of polychlorinated biphenyl (Aroclor 1254) on steroidogenesis and antioxidant system in cultured adult rat Leydig cells. J Endocrinol. 2007;192:325–338. doi: 10.1677/joe.1.06874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Vandenberg LN, Maffini MV, Sonnenschein C, Rubin BS, Soto AM. Bisphenol-A and the great divide: a review of controversies in the field of endocrine disruption. Endocr Rev. 2009;30:75–95. doi: 10.1210/er.2008-0021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Lai KP, Wong MH, Wong CK. Effects of TCDD in modulating the expression of Sertoli cell secretory products and markers for cell-cell interaction. Toxicology. 2005;206:111–123. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2004.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Zhang X, Chang H, Wiseman S, He Y, Higley E, Jones P, et al. Bisphenol A Disrupts Steroidogenesis in Human H295R Cells. Toxicol Sci. 2011;121:320–327. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Lai KP, Wong MH, Wong CK. Inhibition of CYP450scc expression in dioxin-exposed rat Leydig cells. J Endocrinol. 2005;185:519–527. doi: 10.1677/joe.1.06054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Sharpe RM. Pathways of endocrine disruption during male sexual differentiation and masculinization. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;20:91–110. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2005.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Sharpe RM. Environmental/lifestyle effects on spermatogenesis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2010;365:1697–1712. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2009.0206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Orth JM, Gunsalus GL, Lamperti AA. Evidence from Sertoli cell-depleted rats indicates that spermatid number in adults depends on numbers of Sertoli cells produced during perinatal development. Endocrinology. 1988;122:787–794. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-3-787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Orth JM, Jester WF, Li LH, Laslett AL. Gonocyte-Sertoli cell interactions during development of the neonatal rodent testis. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2000;50:103–124. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(00)50006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Anway MD, Cupp AS, Uzumcu M, Skinner MK. Epigenetic transgenerational actions of endocrine disruptors and male fertility. Science. 2005;308:1466–1469. doi: 10.1126/science.1108190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Walker DM, Gore AC. Transgenerational neuroendocrine disruption of reproduction. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011;7:197–207. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2010.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Baccarelli A, Bollati V. Epigenetics and environmental chemicals. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2009;21:243–251. doi: 10.1097/mop.0b013e32832925cc. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Guerrero-Bosagna CM, Skinner MK. Epigenetic transgenerational effects of endocrine disruptors on male reproduction. Semin Reprod Med. 2009;27:403–408. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1237428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Hauser R, Sokol R. Science linking environmental contaminant exposures with fertility and reproductive health impacts in the adult male. Fertil Steril. 2008;89:59–65. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2007.12.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Braconi D, Bernardini G, Santucci A. Linking protein oxidation to environmental pollutants: Redox proteomic approaches. J Proteomics. 2011 doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2011.06.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Chitra KC, Latchoumycandane C, Mathur PP. Induction of oxidative stress by bisphenol A in the epididymal sperm of rats. Toxicology. 2003;185:119–127. doi: 10.1016/s0300-483x(02)00597-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Wong EW, Cheng CY. Polarity proteins and cell-cell interactions in the testis. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2009;278:309–353. doi: 10.1016/S1937-6448(09)78007-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Wong EW, Cheng CY. Impacts of environmental toxicants on male reproductive dysfunction. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2011;32:290–299. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2011.01.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Mathur PP, D'Cruz SC. The effect of environmental contaminants on testicular function. Asian J Androl. 2011;13:585–591. doi: 10.1038/aja.2011.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Turner TT, Lysiak JJ. Oxidative stress: a common factor in testicular dysfunction. J Androl. 2008;29:488–498. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.108.005132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Cheng CY, Wong EW, Lie PP, Li MW, Su L, Siu ER, et al. Environmental toxicants and male reproductive function. Spermatogenesis. 2011;1:2–13. doi: 10.4161/spmg.1.1.13971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Barakat B, O'Connor AE, Gold E, de Kretser DM, Loveland KL. Inhibin, activin, follistatin and FSH serum levels and testicular production are highly modulated during the first spermatogenic wave in mice. Reproduction. 2008;136:345–359. doi: 10.1530/REP-08-0140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Rocha JS, Bonkowski MS, de Franca LR, Bartke A. Effects of mild calorie restriction on reproduction, plasma parameters and hepatic gene expression in mice with altered GH/IGF-I axis. Mech Ageing Dev. 2007;128:317–331. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2007.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Misrahi M, Beau I, Meduri G, Bouvattier C, Atger M, Loosfelt H, et al. Gonadotropin receptors and the control of gonadal steroidogenesis: physiology and pathology. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;12:35–66. doi: 10.1016/s0950-351x(98)80444-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Goulis DG, Tarlatzis BC. Metabolic syndrome and reproduction: I. testicular function. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2008;24:33–39. doi: 10.1080/09513590701582273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Xu YP, Chedrese PJ, Thacker PA. Growth hormone amplifies insulin-like growth factor I induced progesterone accumulation and P450scc mRNA expression. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1995;111:199–206. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(95)03569-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Spiteri-Grech J, Nieschlag E. The role of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor I in the regulation of male reproductive function. Horm Res. 1992;38:22–27. doi: 10.1159/000182566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Eden EB, Burman P, Holdstock C, Karlsson FA. Effects of growth hormone (GH) on ghrelin, leptin and adiponectin in GH-deficient patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:5193–5198. doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-030713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Randeva HS, Murray RD, Lewandowski KC, O'Callaghan CJ, Horn R, O'Hare P, et al. Differential effects of GH replacement on the components of the leptin system in GH-deficient individuals. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:798–804. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.2.8238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Gregoire Nyomba BL, Johnson M, Berard L, Murphy LJ. Relationship between serum leptin and the insulin-like growth factor-I system in humans. Metabolism. 1999;48:840–844. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(99)90215-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Luque RM, Kineman RD, Tena-Sempere M. Regulation of hypothalamic expression of KiSS-1 and GPR54 genes by metabolic factors: analyses using mouse models and a cell line. Endocrinology. 2007;148:4601–4611. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-0500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Magni P, Vettor R, Pagano C, Calcagno A, Beretta E, Messi E, et al. Expression of a leptin receptor in immortalized gonadotropin-releasing hormone-secreting neurons. Endocrinology. 1999;140:1581–1585. doi: 10.1210/endo.140.4.6622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Quennell JH, Howell CS, Roa J, Augustine RA, Grattan DR, Anderson GM. Leptin deficiency and diet-induced obesity reduce hypothalamic kisspeptin expression in mice. Endocrinology. 2011;152:1541–1550. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Jahan S, Bibi R, Ahmed S, Kafeel S. Leptin levels in infertile males. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2011;21:393–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Boberg J, Metzdorff S, Wortziger R, Axelstad M, Brokken L, Vinggaard AM, et al. Impact of diisobutyl phthalate and other PPAR agonists on steroidogenesis and plasma insulin and leptin levels in fetal rats. Toxicology. 2008;250:75–81. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2008.05.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Tena-Sempere M, Manna PR, Zhang FP, Pinilla L, Gonzalez LC, Dieguez C, et al. Molecular mechanisms of leptin action in adult rat testis: potential targets for leptin-induced inhibition of steroidogenesis and pattern of leptin receptor messenger ribonucleic acid expression. J Endocrinol. 2001;170:413–423. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1700413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Fernandez CD, Bellentani FF, Fernandes GS, Perobelli JE, Favareto AP, Nascimento AF, et al. Diet-induced obesity in rats leads to a decrease in sperm motility. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2011;9:32. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-9-32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Ishikawa T, Fujioka H, Ishimura T, Takenaka A, Fujisawa M. Expression of leptin and leptin receptor in the testis of fertile and infertile patients. Andrologia. 2007;39:22–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0272.2006.00754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Nystrom F, Ekman B, Osterlund M, Lindstrom T, Ohman KP, Arnqvist HJ. Serum leptin concentrations in a normal population and in GH deficiency: negative correlation with testosterone in men and effects of GH treatment. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1997;47:191–198. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2265.1997.2281039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Stasenko S, Bradford EM, Piasek M, Henson MC, Varnai VM, Jurasovic J, et al. Metals in human placenta: focus on the effects of cadmium on steroid hormones and leptin. J Appl Toxicol. 2010;30:242–253. doi: 10.1002/jat.1490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Kidani T, Kamei S, Miyawaki J, Aizawa J, Sakayama K, Masuno H. Bisphenol A downregulates Akt signaling and inhibits adiponectin production and secretion in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2010;17:834–843. doi: 10.5551/jat.4051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Delport R, Bornman R, MacIntyre UE, Oosthuizen NM, Becker PJ, Aneck-Hahn NH, et al. Changes in retinol-binding protein concentrations and thyroid homeostasis with nonoccupational exposure to DDT. Environ Health Perspect. 2011;119:647–651. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1002616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Hogarth CA, Griswold MD. The key role of vitamin A in spermatogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2010;120:956–962. doi: 10.1172/JCI41303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Chung SS, Wolgemuth DJ. Role of retinoid signaling in the regulation of spermatogenesis. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004;105:189–202. doi: 10.1159/000078189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Feron VJ, Cassee FR, Groten JP, van Vliet PW, van Zorge JA. International issues on human health effects of exposure to chemical mixtures. Environ Health Perspect. 2002;110:893–899. doi: 10.1289/ehp.02110s6893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Mantovani A, Maranghi F, Purificato I, Macri A. Assessment of feed additives and contaminants: an essential component of food safety. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2006;42:427–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Poppenga RH. Current environmental threats to animal health and productivity. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2000;16:545–558. doi: 10.1016/s0749-0720(15)30086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Wigle DT, Arbuckle TE, Turner MC, Berube A, Yang Q, Liu S, et al. Epidemiologic evidence of relationships between reproductive and child health outcomes and environmental chemical contaminants. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2008;11:373–517. doi: 10.1080/10937400801921320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Kang KS, Trosko JE. Stem cells in toxicology: fundamental biology and practical considerations. Toxicol Sci. 2011;120:269–289. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Hubal EA. Biologically relevant exposure science for 21st century toxicity testing. Toxicol Sci. 2009;111:226–232. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfp159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]