Abstract
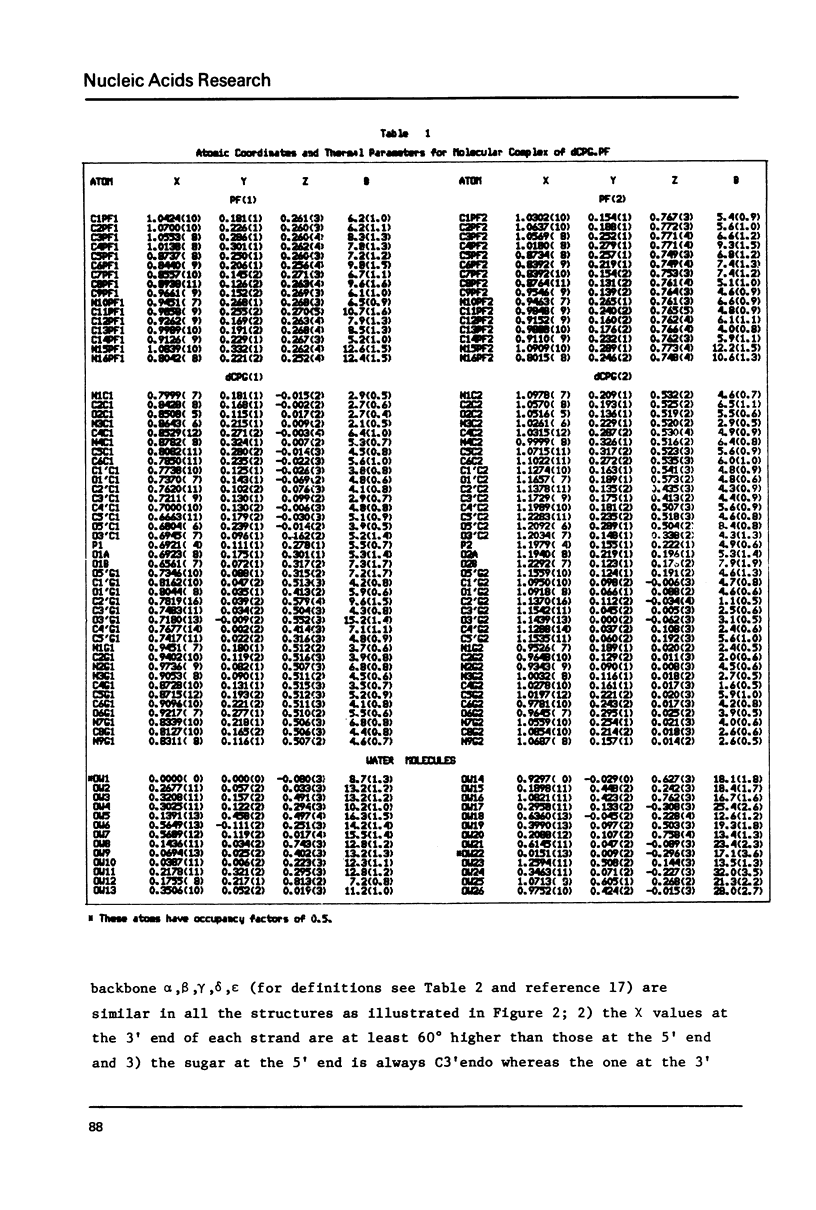
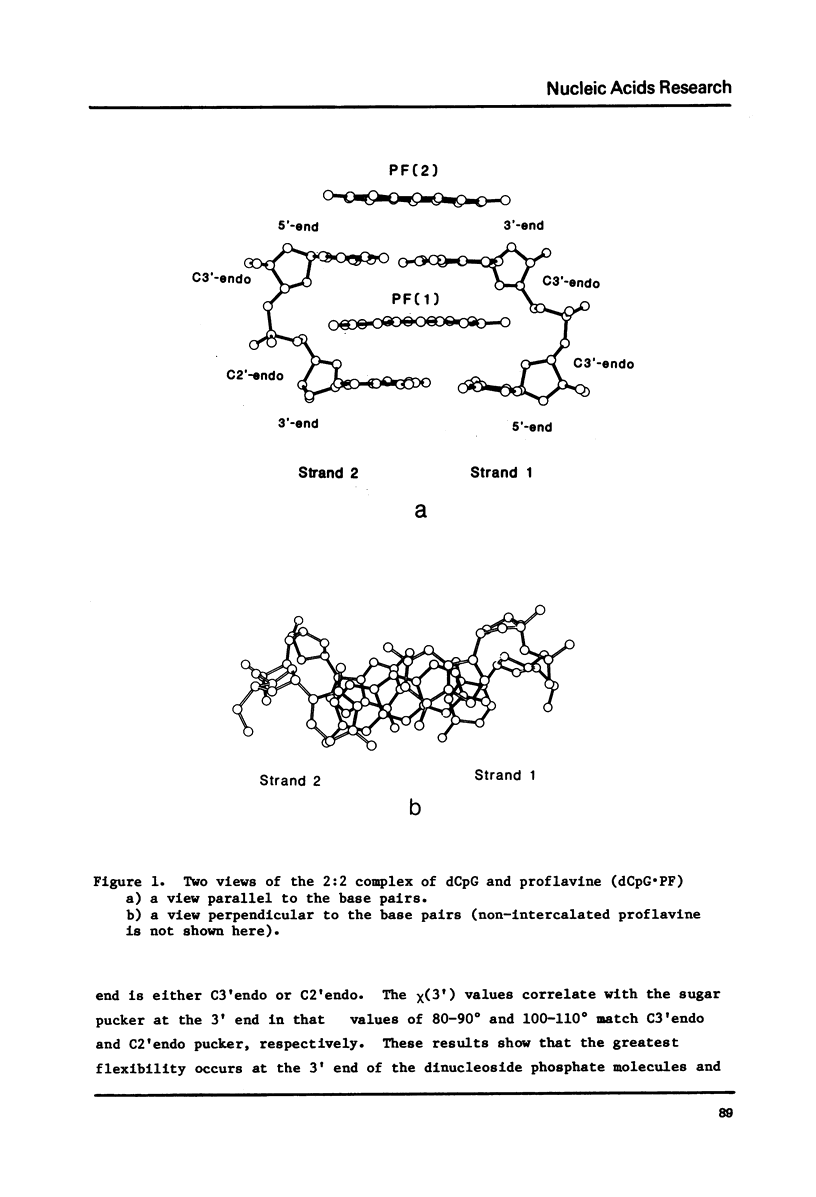
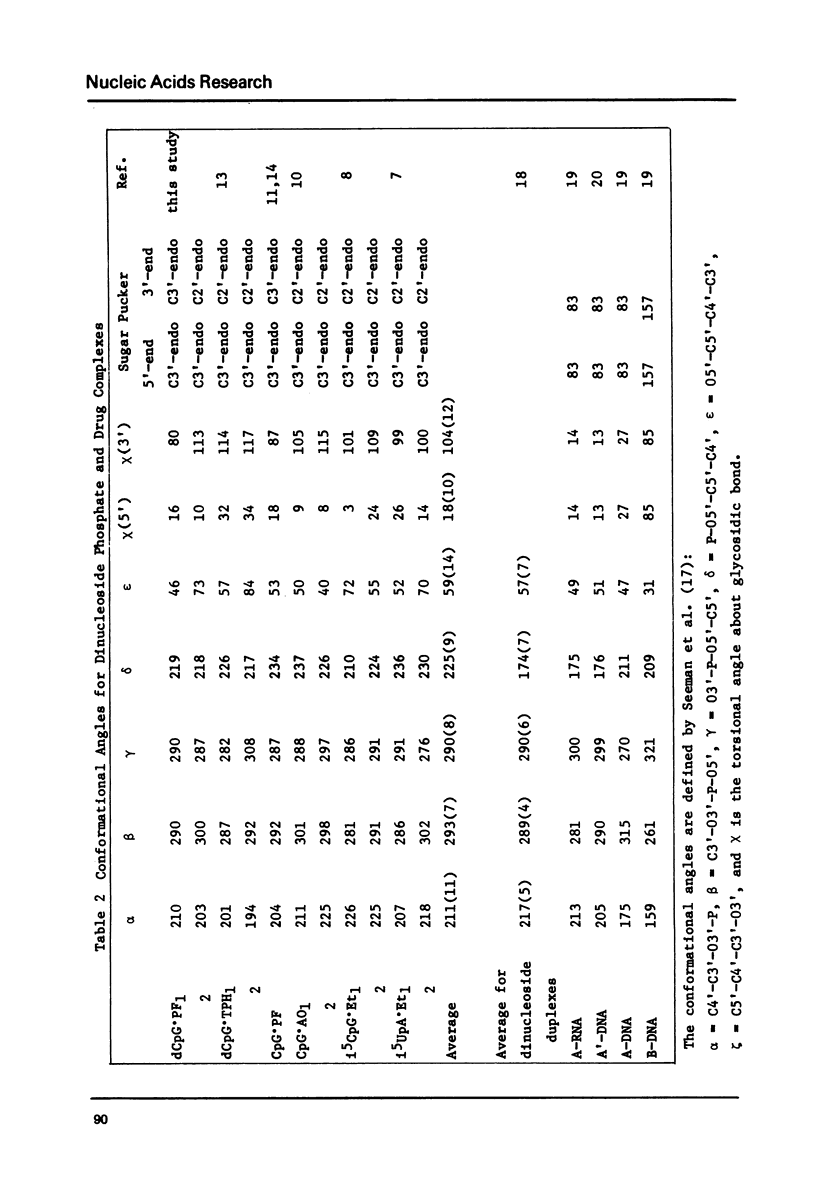
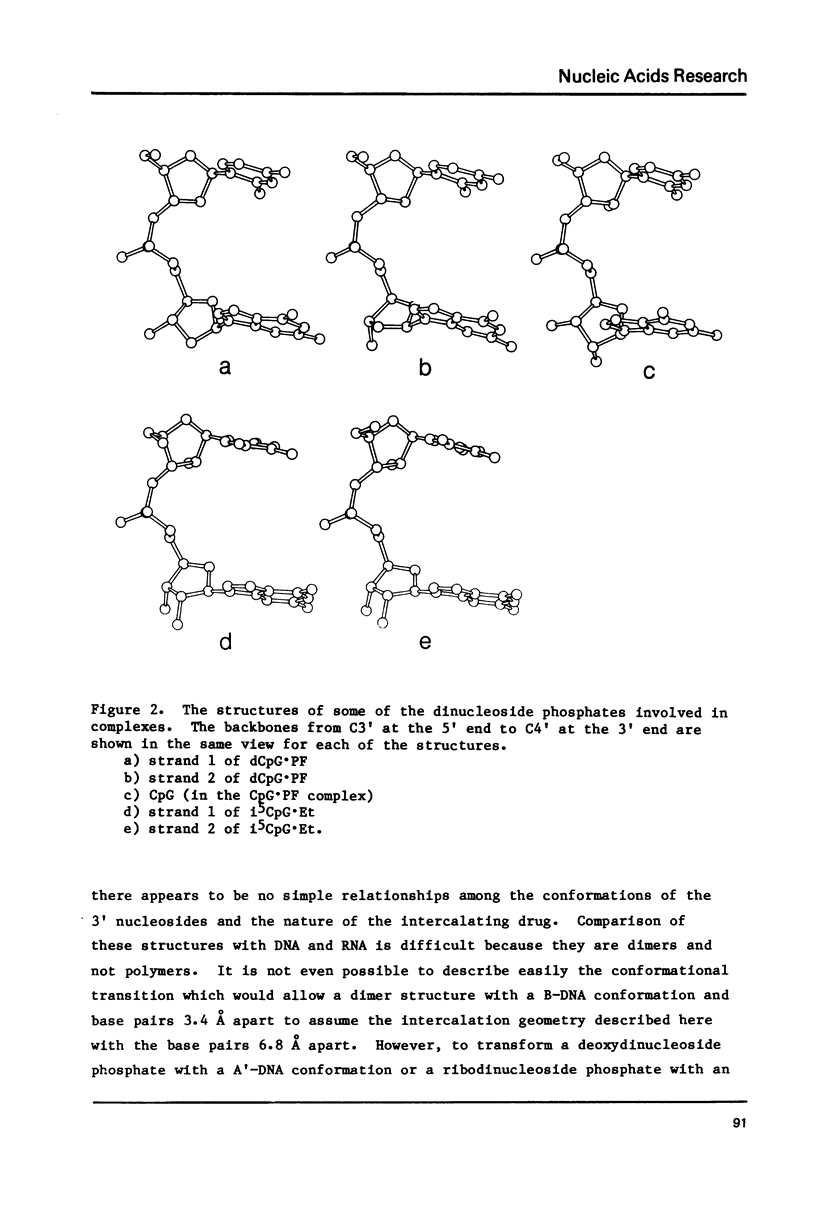
A 2:2 complex of proflavine and deoxycytidylyl-3', 5'-guanosine has been crystallized and its structure determined by x-ray crystallography. The two dinucleoside phosphate strands form self complementary duplexes with Watson Crick hydrogen bonds. One proflavin is asymmetrically intercalated between the base pairs and the other is stacked above them. The conformations of the nucleotides are unusual in that one strand has C3',C2'endomixed sugar puckering and the other has C3',C3' endo deoxyribose sugars. These results show that the conformation of the 3'sugar is of secondary importance to the intercalated geometry.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alden C. J., Arnott S. Stereochemical model for proflavin intercalation in A-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Nov;4(11):3855–3861. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.11.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alden C. J., Arnott S. Visualization of planar drug intercalations in B-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Oct;2(10):1701–1717. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.10.1701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altona C., Sundaralingam M. Conformational analysis of the sugar ring in nucleosides and nucleotides. A new description using the concept of pseudorotation. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Nov 15;94(23):8205–8212. doi: 10.1021/ja00778a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman H. M., Neidle S., Stodola R. K. Drug-nucleic acid interactions: conformational flexibility at the intercalation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):828–832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack A., Klug A., Ladner J. E. "Non-rigid" nucleotides in tRNA: a new correlation in the conformation of a ribose. Nature. 1976 May 20;261(5557):250–251. doi: 10.1038/261250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S. C., Tsai C. C., Sobell H. M. Visualization of drug-nucleic acid interactions at atomic resolution. II. Structure of an ethidium/dinucleoside monophosphate crystalline complex, ethidium:5-iodocytidylyl (3'-5') guanosine. J Mol Biol. 1977 Aug 15;114(3):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90253-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidle S., Achari A., Taylor G. L., Berman H. M., Carrell H. L., Glusker J. P., Stallings W. C. Structure of a dinucleoside phosphate--drug complex as model for nucleic acid--drug interaction. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):304–307. doi: 10.1038/269304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidle S., Taylor G., Sanderson M. A 1:2 crystalline complex of ApA:proflavine: a model for binding to single-stranded regions in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Nov;5(11):4417–4422. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.11.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidle S. The molecular basis for the action of some DNA-binding drugs. Prog Med Chem. 1979;16:151–221. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6468(08)70188-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakore T. D., Jain S. C., Tsai C. C., Sobell H. M. Mutagen-nucleic acid intercalative binding: structure of a 9-aminoacridine: 5-iodocytidylyl(3'-5')guanosine crystalline complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):188–192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Suddath F. L., Kim J. J., Rich A. RNA double-helical fragments at atomic resolution. I. The crystal and molecular structure of sodium adenylyl-3',5'-uridine hexahydrate. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 14;104(1):109–144. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobell H. M., Tsai C. C., Jain S. C., Gilbert S. G. Visualization of drug-nucleic acid interactions at atomic resolution. III. Unifying structural concepts in understanding drug-DNA interactions and their broader implications in understanding protein-DNA interactions. J Mol Biol. 1977 Aug 15;114(3):333–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90254-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. C., Jain S. C., Sobell H. M. Visualization of drug-nucleic acid interactions at atomic resolution. I. Structure of an ethidium/dinucleoside monophosphate crystalline complex, ethidium:5-iodouridylyl (3'-5') adenosine. J Mol Biol. 1977 Aug 15;114(3):301–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90252-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Nathans J., van der Marel G., van Boom J. H., Rich A. Molecular structure of a double helical DNA fragment intercalator complex between deoxy CpG and a terpyridine platinum compound. Nature. 1978 Nov 30;276(5687):471–474. doi: 10.1038/276471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., Rich A. Atomic resolution analysis of a 2:1 complex of CpG and acridine orange. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 24;6(12):3879–3890. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.12.3879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



