Abstract
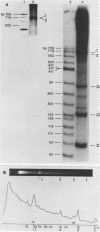
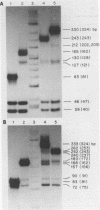
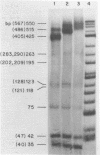
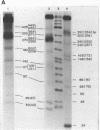
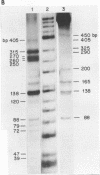
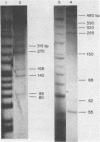
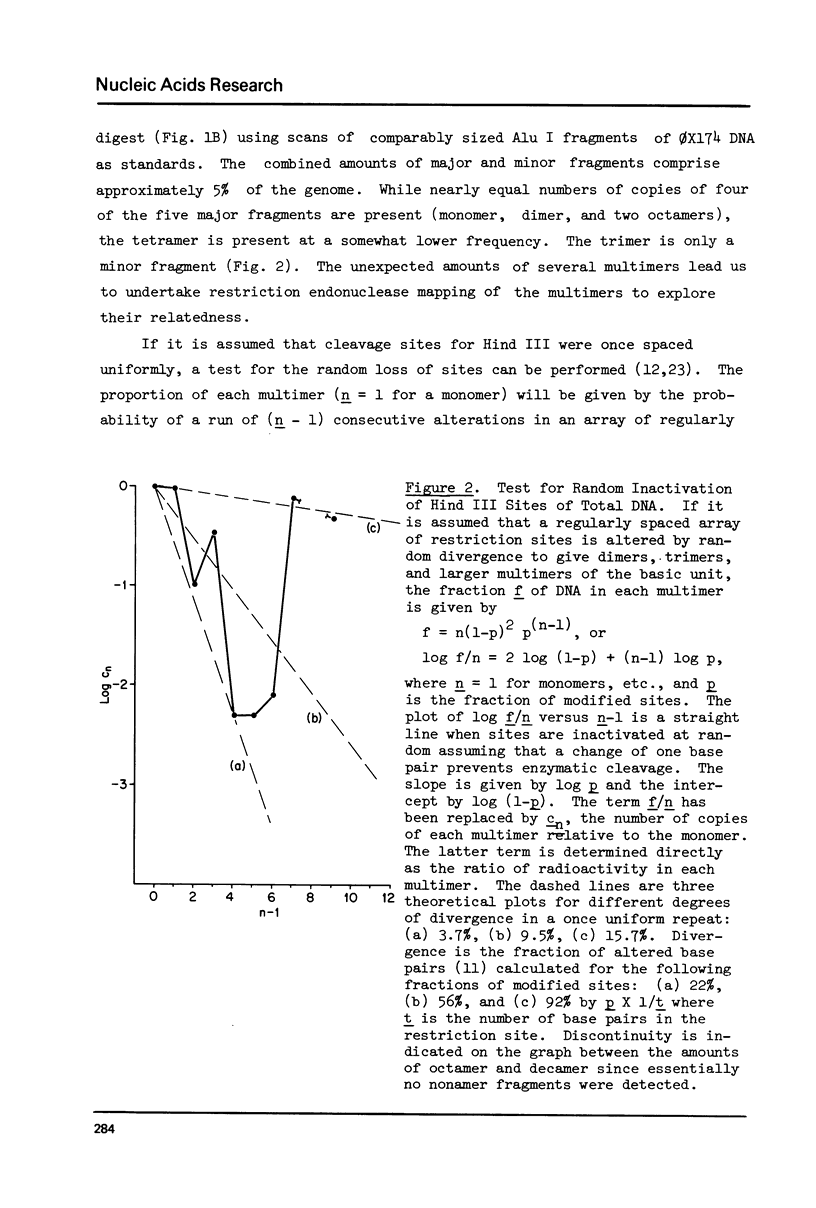
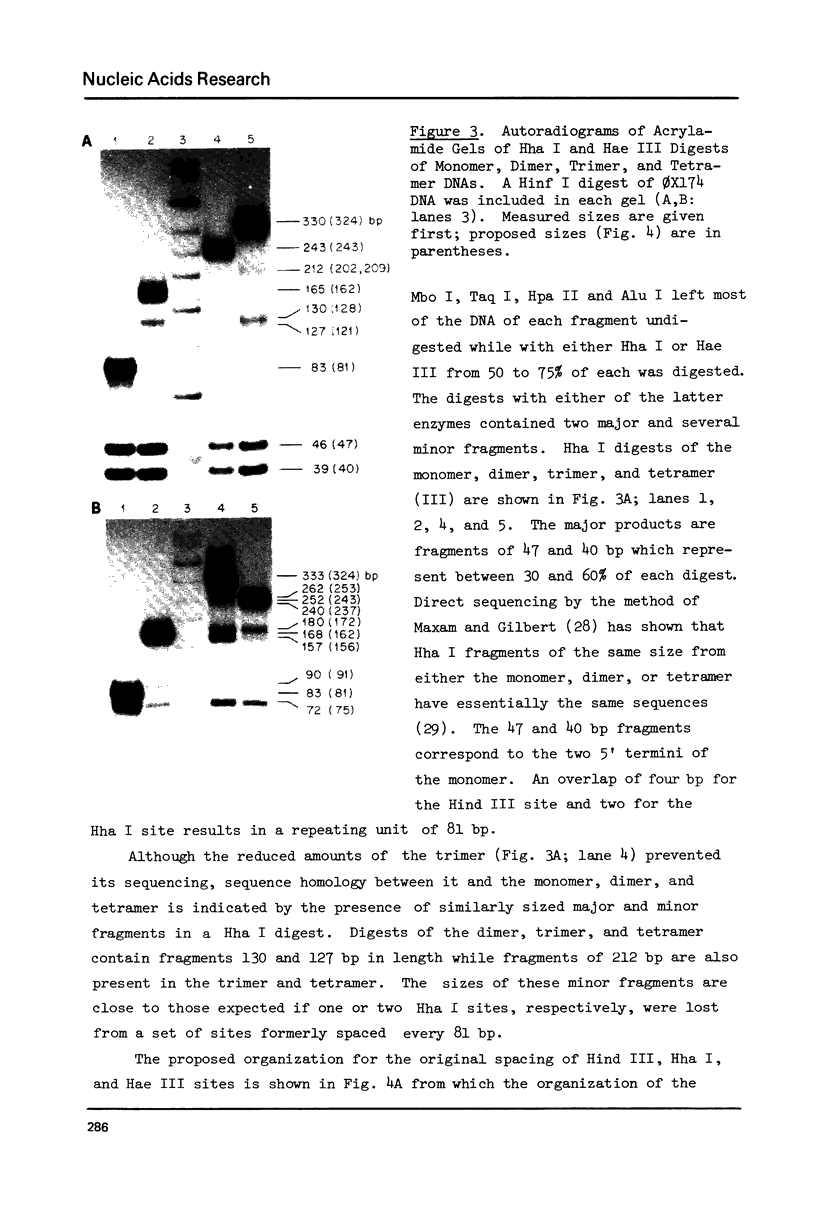
Although the DNA of the red crab Geryon quinquedens has no patent satellites, a large fraction (approximately 40%) is highly repetitive. Treatment of total DNA by Hind III produces fragments comprising 5-6% of the genome. While the sizes of some of these fragments form an arithmetic series based on an 81 bp repeating unit, the amounts of the multimers differ significantly from distributions observed for multimeric series in the DNAs of other eukaryotes. In red crab DNA, the amounts of some of the multimers suggest that they may have undergone as much as four times the divergence as the others. Other data, however, are more compatible with the conclusion that there has been selective amplification of segments of highly repeated DNA which results in the enhanced amount of specific multimers. These results indicate the presence of a nonrandom process in the evolution of the highly repetitive DNA. Selective mutation alone seems insufficient to explain these results.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenburger W., Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Comparative analysis of three guinea pig satellite DNA's by restriction nucleases. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 1;73(2):393–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11330.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes S. R., Webb D. A., Dover G. The distribution of satellite and main-band DNA components in the melanogaster species subgroup of Drosophila. I. Fractionation of DNA in actinomycin D and distamycin A density gradients. Chromosoma. 1978 Aug 14;67(4):341–363. doi: 10.1007/BF00285965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beattie W. G., Skinner D. M. The diversity of satellite DNAs of Crustacea. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Oct 11;281(2):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzer S., Freese E. INDUCTION OF SPECIFIC MUTATIONS WITH 5-BROMOURACIL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Feb;44(2):112–119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.2.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzer S. ON THE TOPOGRAPHY OF THE GENETIC FINE STRUCTURE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Mar;47(3):403–415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.3.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Repetitive and non-repetitive DNA sequences and a speculation on the origins of evolutionary novelty. Q Rev Biol. 1971 Jun;46(2):111–138. doi: 10.1086/406830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Graham D. E., Neufeld B. R. Analysis of repeating DNA sequences by reassociation. Methods Enzymol. 1974;29:363–418. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)29033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush G. L., Case S. M., Wilson A. C., Patton J. L. Rapid speciation and chromosomal evolution in mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3942–3946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Brutlag D. Cloning and characterization of a complex satellite DNA from Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):371–381. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers C. A., Schell M. P., Skinner D. M. The primary sequence of a crustacean satellite DNA containing a family of repeats. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):97–110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao M. V., Gralla J., Martinson H. G. DNA sequence directs placement of histone cores on restriction fragments during nucleosome formation. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 20;18(6):1068–1074. doi: 10.1021/bi00573a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie N. T., Skinner D. M. Interspersion of highly repetitive DNA with single copy DNA in the genome of the red crab, Geryon quinquedens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Feb;6(2):781–796. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.2.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J. Evolution of the long range structure of satellite DNAs in the genus Apodemus. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 5;94(1):87–99. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90406-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordeiro-Stone M., Lee C. S. Studies on the satellite DNAs of Drosophila nasutoides: their buoyant densities, melting temperatures, reassociation rates and localizations in polytene chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 14;104(1):1–24. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Regulation of gene expression: possible role of repetitive sequences. Science. 1979 Jun 8;204(4397):1052–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.451548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fittler F. Analysis of the alpha-satellite DNA from African green monkey cells by restriction nucleases. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Apr 1;74(2):343–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry K., Salser W. Nucleotide sequences of HS-alpha satellite DNA from kangaroo rat Dipodomys ordii and characterization of similar sequences in other rodents. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1069–1084. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch R. E. The influence of neighboring base pairs upon base-pair substitution mutation rates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):773–776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecka H., Macaya G., Cortadas J., Thiéry J. P., Bernardi G. Restriction enzyme analysis of satellite DNA components from the bovine genome. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar;84(1):189–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence C. W., Stewart J. W., Sherman F., Christensen R. Specificity and frequency of ultraviolet-induced reversion of an iso-1-cytochrome c ochre mutant in radiation-sensitive strains of yeast. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 5;85(1):137–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90134-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lejeune J., Dutrillaux B., Rethoré M. O., Prieur M. Comparaison de la structure fine des chromatides d'Homo sapiens et de Pan troglodytes. Chromosoma. 1973;43(4):423–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00406748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillehaug J. R., Kleppe K. Effect of salts and polyamines on T4 polynucleotide kinase. Biochemistry. 1975 Mar 25;14(6):1225–1229. doi: 10.1021/bi00677a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macaya G., Cortadas J., Bernardi G. An analysis of the bovine genome by density-gradient centrifugation. Preparation of the dG+dC-rich DNA components. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar;84(1):179–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12155.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maio J. J., Brown F. L., Musich P. R. Subunit structure of chromatin and the organization of eukaryotic highly repetitive DNA: recurrent periodicities and models for the evolutionary origins of repetitive DNA. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 15;117(3):637–655. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., van deSande H. Chain length determination of small double- and single-stranded DNA molecules by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3787–3794. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manteuil S., Hamer D. H., Thomas C. A., Jr Regular arrangement of restriction sites in Drosophila DNA. Cell. 1975 Aug;5(4):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Repeating restriction fragments of human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Nov;3(11):3063–3076. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.11.3063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Wu J. C. Homology between human and simian repeated DNA. Nature. 1978 Nov 2;276(5683):92–94. doi: 10.1038/276092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musich P. R., Maio J. J., Brown F. L. Subunit structure of chromatin and the organization of eukaryotic highly repetitive DNA: indications of a phase relation between restriction sites and chromatin subunits in African green monkey and calf nuclei. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 15;117(3):657–677. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prunell A., Strauss F., Leblanc B. Photographic quantitation of DNA in gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1977 Mar;78(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J., Myers P. A., Morrison A., Murray K. A specific endonuclease from Arthrobacter luteus. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 25;102(1):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90079-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Singer M., Rosenberg M. Highly reiterated sequences of SIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIAN. Science. 1978 Apr 28;200(4340):394–402. doi: 10.1126/science.205944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Air G. M., Barrell B. G., Brown N. L., Coulson A. R., Fiddes C. A., Hutchison C. A., Slocombe P. M., Smith M. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage phi X174 DNA. Nature. 1977 Feb 24;265(5596):687–695. doi: 10.1038/265687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. L., Blattner F. R. Least-squares method for restriction mapping. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F., Stewart J. W. Variation of mutagenic action on nonsense mutants at different sites in the iso-1-cytochrome c gene of yeast. Genetics. 1974 Sep;78(1):97–113. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M. The interpretation of oligonucleotide maps. A theoretical study of nucleic acid digests with special reference to repeated diverged sequences. Biopolymers. 1974 Nov;13(11):2241–2264. doi: 10.1002/bip.1974.360131107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Unequal crossover and the evolution of multigene families. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:507–513. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Base sequence and evolution of guinea-pig alpha-satellite DNA. Nature. 1970 Aug 22;227(5260):794–798. doi: 10.1038/227794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Long range periodicities in mouse satellite DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 5;94(1):51–69. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90404-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strätling W. H., Müller U., Zentgraf H. The higher order repeat structure of chromatin is built up of globular particles containing eight nucleosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Dec;117(2):301–311. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90144-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K., Van Holde K. E. Nucleosome reconstitution: effect of DNA length on nuclesome structure. Biochemistry. 1979 Jun 26;18(13):2871–2880. doi: 10.1021/bi00580a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. C. DNA reassociation kinetics and chromosome structure in the crabs Cancer borealis and Libinia emarginata. Chromosoma. 1975;50(3):243–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00283469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vereijken J. M., Van Mansfeld A. D., Baas P. D., Jansz H. S. Arthrobacter luteus restriction endonuclease cleavage map of phi chi 174 RF DNA. Virology. 1975 Nov;68(1):221–233. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90163-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Sande J. H., Kleppe K., Khorana H. G. Reversal of bacteriophage T4 induced polynucleotide kinase action. Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 4;12(25):5050–5055. doi: 10.1021/bi00749a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]