Abstract
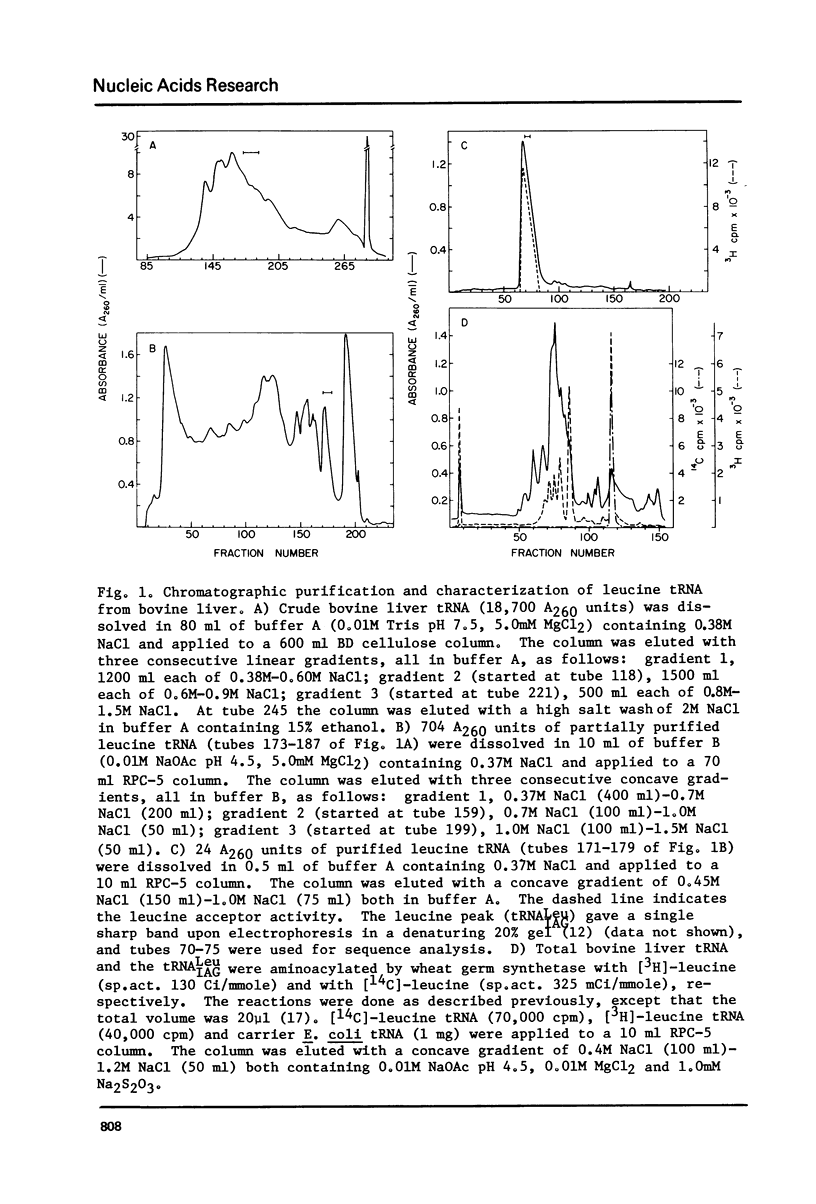
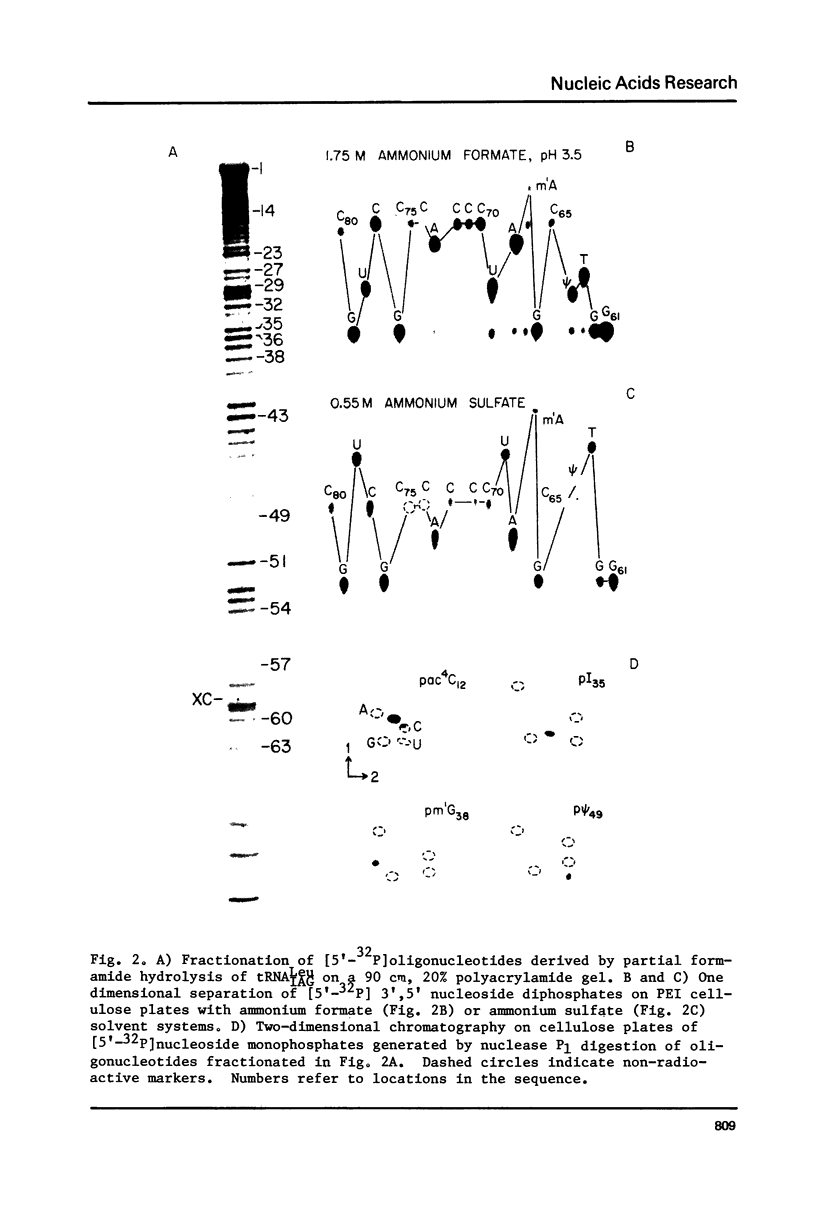
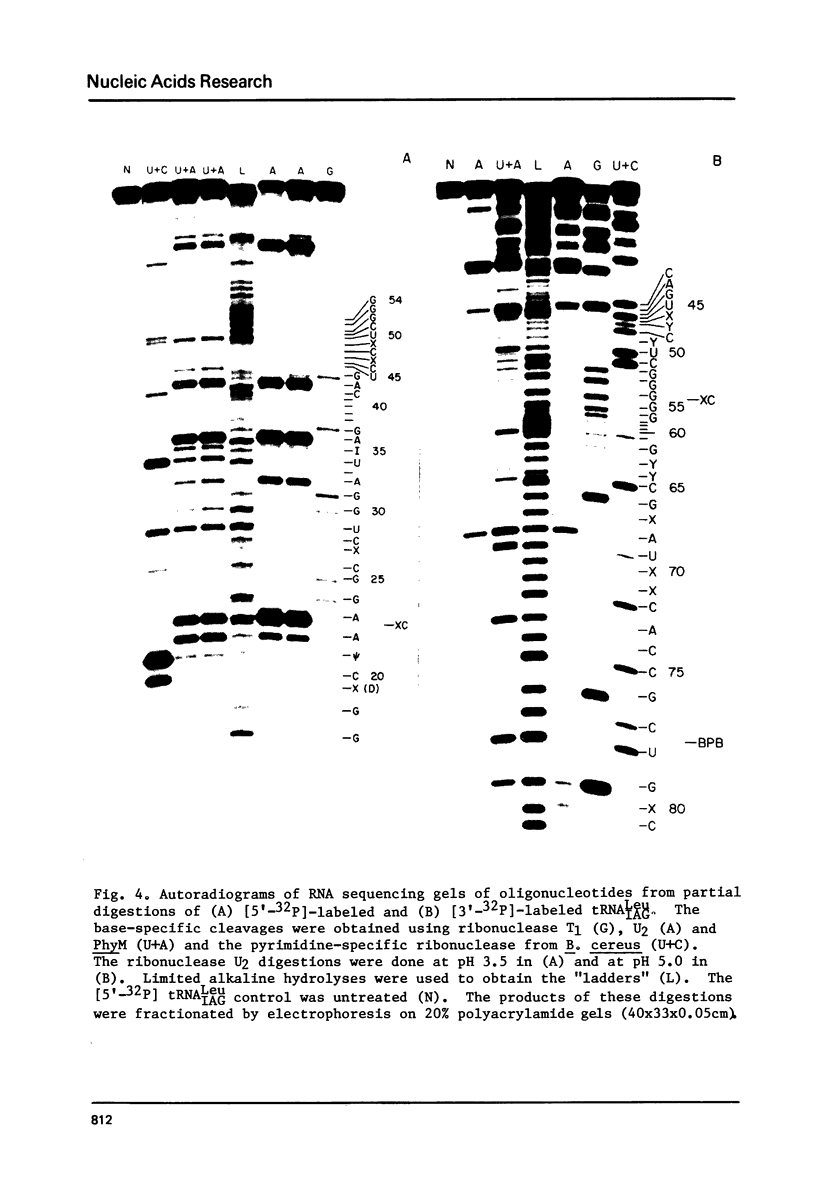
Through the use of a variety of post-labeling techniques, the nucleotide sequence of a major species of leucine tRNA from bovine liver was determined to be pG-G-U-A-G-C-G-U-G-m-G-C-ac-C-G-A-G-C-G-G-D-C-psi-A-A-G-G-C-m-G-C-U-G-G-A-psim- U-I-A-G-m-G-C-psi-C-C-A-G-U-C-psi-C-psi-U-C-G-G-G-G-G-m-C-G-U-G-G-G-T-psi-C-G-m -A-A-U-C-C-C-A-C-C-G-C-U-G-C-C-A-C-C-AOH. A comparison of known sequences of leucine tRNAs shows a consistent set of features which clearly distinguish prokaryotic and eukaryotic leucine tRNAs from each other.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruce A. G., Uhlenbeck O. C. Reactions at the termini of tRNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3665–3677. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Uhlenbeck O. C. 3'-terminal labelling of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):560–561. doi: 10.1038/275560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. C., Randerath K. Rapid print-readout technique for sequencing of RNA's containing modified nucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3443–3458. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp G., Gross H. J. Rapid RNA sequencing: nucleases from Staphylococcus aureus and Neurospora crassa discriminate between uridine and cytidine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3481–3490. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magrath D. I., Shaw D. C. The occurrence and source of beta-alanine in alkaline hydrolysates of sRNA: a sensitive method for the detection and assay of 5,6-dihydrouracil residues in RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Jan 10;26(1):32–37. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90248-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirtle R. M., Pirtle I. L., Inouye M. Homologous nucleotide sequences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic mRNAs: the 5'-end sequence of the mRNA of the lipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2190–2194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reszelbach R., Greenberg R., Pirtle R., Prasad R., Marcu K., Dudock B. Isolation and comparison of ribothymidine-lacking tRNAs of fetal, newborn and adult bovine tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 18;475(2):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., RajBhandary U. L. Transfer RNA: molecular structure, sequence, and properties. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:805–860. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe B. A. Studies on human tRNA. I. The rapid, large scale isolation and partial fractionation of placenta and liver tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Jan;2(1):21–42. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Donelson J. E., Coulson A. R., Kössel H., Fischer D. Use of DNA polymerase I primed by a synthetic oligonucleotide to determine a nucleotide sequence in phage fl DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1209–1213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. The use of nuclease P1 in sequence analysis of end group labeled RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Dec;4(12):4091–4108. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.12.4091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. Use of in vitro 32P labeling in the sequence analysis of nonradioactive tRNAs. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:58–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoncsits A., Brownlee G. G., Brown R. S., Rubin J. R., Guilley H. New rapid gel sequencing method for RNA. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):833–836. doi: 10.1038/269833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J., Vassilenko S. A different approach to RNA sequencing. Nature. 1978 Jul 6;274(5666):87–89. doi: 10.1038/274087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel R., Kohli J., Altruda F., Söll D. Identification and nucleotide sequence of the sup8-e UGA-suppressor leucine tRNA from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 May 4;172(2):221–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00268286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]