Abstract
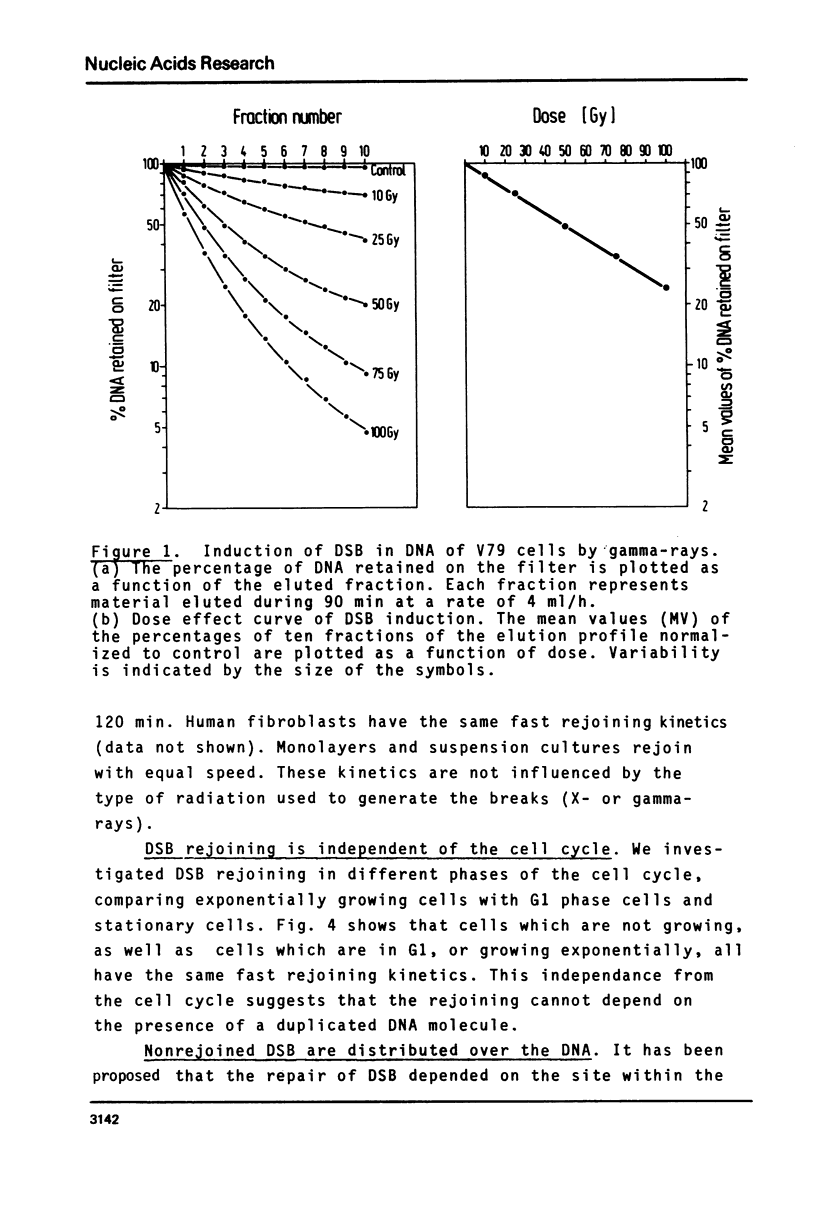
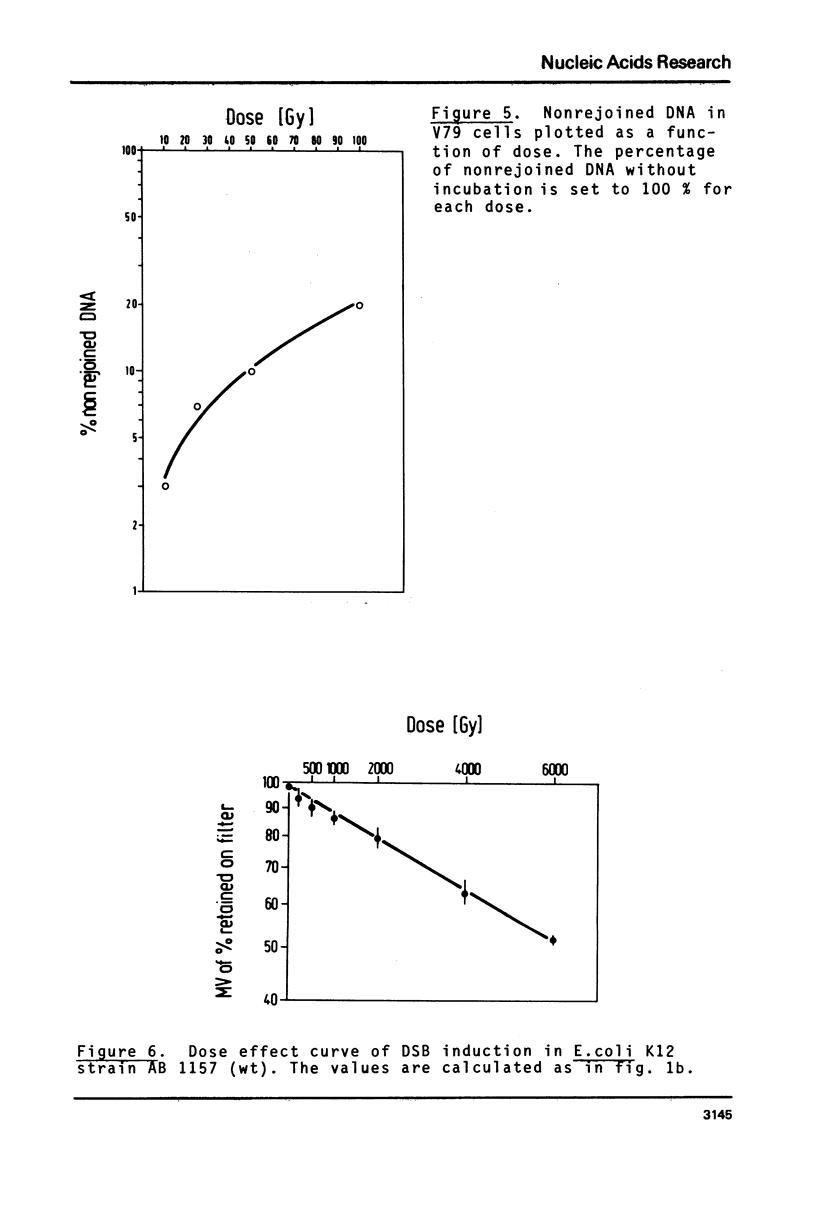
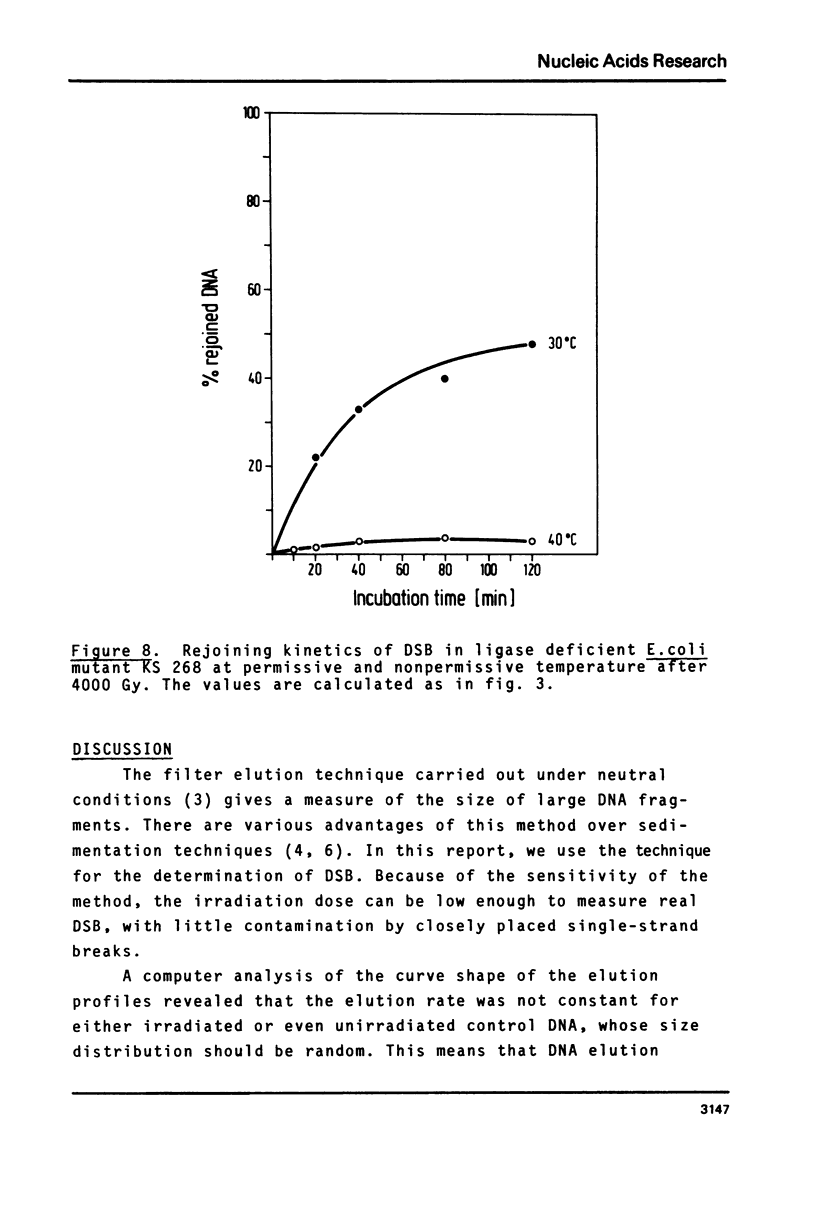
Using the method of filter elution of double stranded DNA under neutral conditions we have shown that most of gamma-ray induced double strand breaks (DSB) are rejoined in both mammalian and bacterial cells. Rejoining also occurs in the G1 phase in V79 Chinese hamster cells and under different growth conditions. Within 8 minutes at 37 C, half the breaks are rejoined. The rejoining in E. coli is equally fast and depends on the presence of DNA ligase. Some of the breaks in E. coli rejoin slowly, and these require rec+. The non-rejoined DSB are distributed over the DNA without any preference for the nucleosomal or the linker structure in the chromosome. Two kinds of DSB rejoining are discriminated, a fast process of DNA ligation and a slower process involving rec functions.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley M. O., Kohn K. W. X-ray induced DNA double strand break production and repair in mammalian cells as measured by neutral filter elution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 10;7(3):793–804. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.3.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer E. N. Repair of radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in isolated nuclei of Physarum polycephalum. Radiat Res. 1979 Aug;79(2):368–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant P. E., Blöcher D. Measurement of the kinetics of DNA double strand break repair in Ehrlich ascites tumour cells using the unwinding method. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1980 Sep;38(3):335–347. doi: 10.1080/09553008014551691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A., Shonka F., Corry P., Cooper W. G. CHO cell repair of single-strand and double-strand DNA breaks induced by gamma- and alpha-radiations. Basic Life Sci. 1975;5B:665–676. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-2898-8_40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasin F., Hutchinson F. Repair of DNA double-strand breaks in Escherichia coli, which requires recA function and the presence of a duplicate genome. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 15;116(1):81–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange C. S. The organization and repair of mammalian DNA. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 25;44(2):153–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80714-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman A. R., Stevens S. The production and repair of double strand breaks in cells from normal humans and from patients with ataxia telangiectasia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 3;474(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90213-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A., Moore P. D. Molecular recombination and the repair of DNA double-strand breaks in CHO cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):3145–3160. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.3145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A. Similar responses to ionizing radiation of fungal and vertebrate cells and the importance of DNA doublestrand breaks. J Theor Biol. 1978 Apr 6;71(3):339–346. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(78)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter M. A., Cleaver J. E., Tobias C. A. High-LET radiations induce a large proportion of non-rejoining DNA breaks. Nature. 1977 Apr 14;266(5603):653–655. doi: 10.1038/266653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibezahn K. F., Sexauer C., Coquerelle T. Negative pion irradiation of mammalian cells. III. A comparative analysis of DNA strand breakage, repair and cell survival after exposure to pi-mesons and X-rays. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1980 Oct;38(4):365–371. doi: 10.1080/09553008014551741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



