Abstract
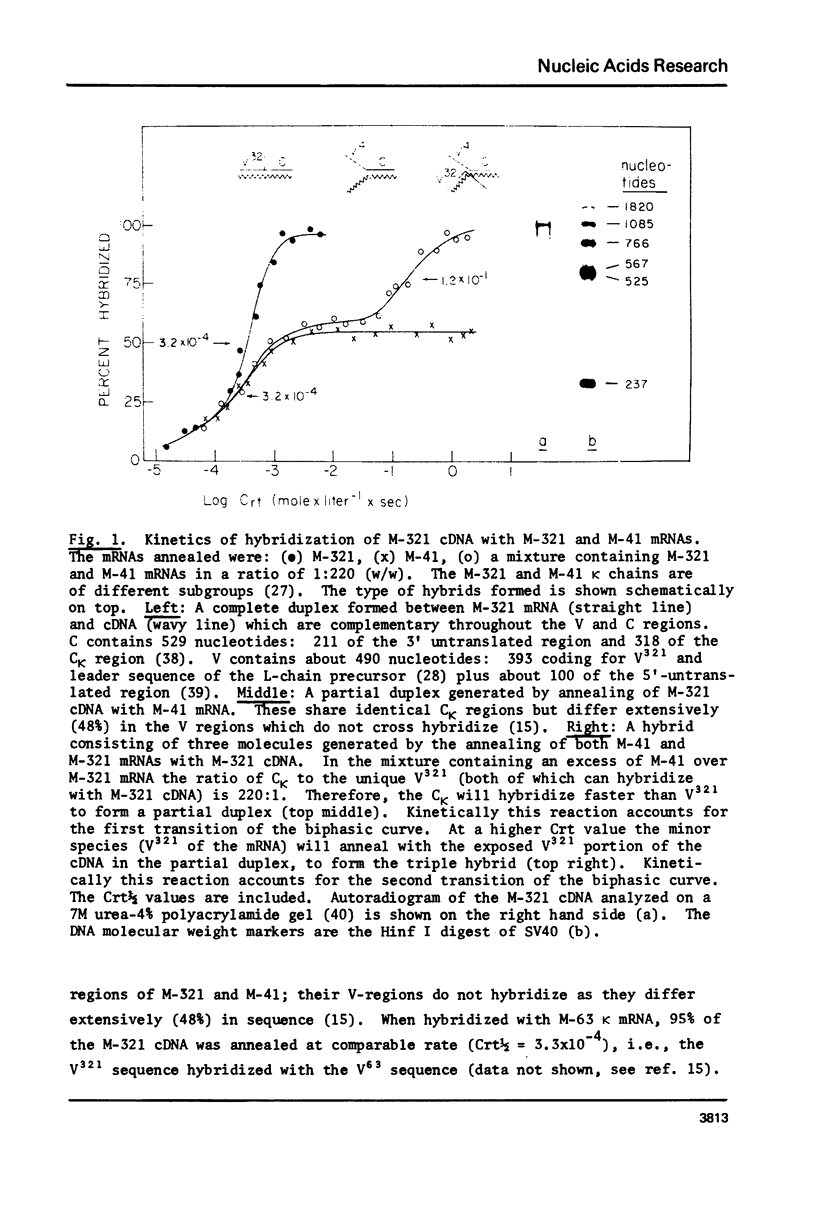
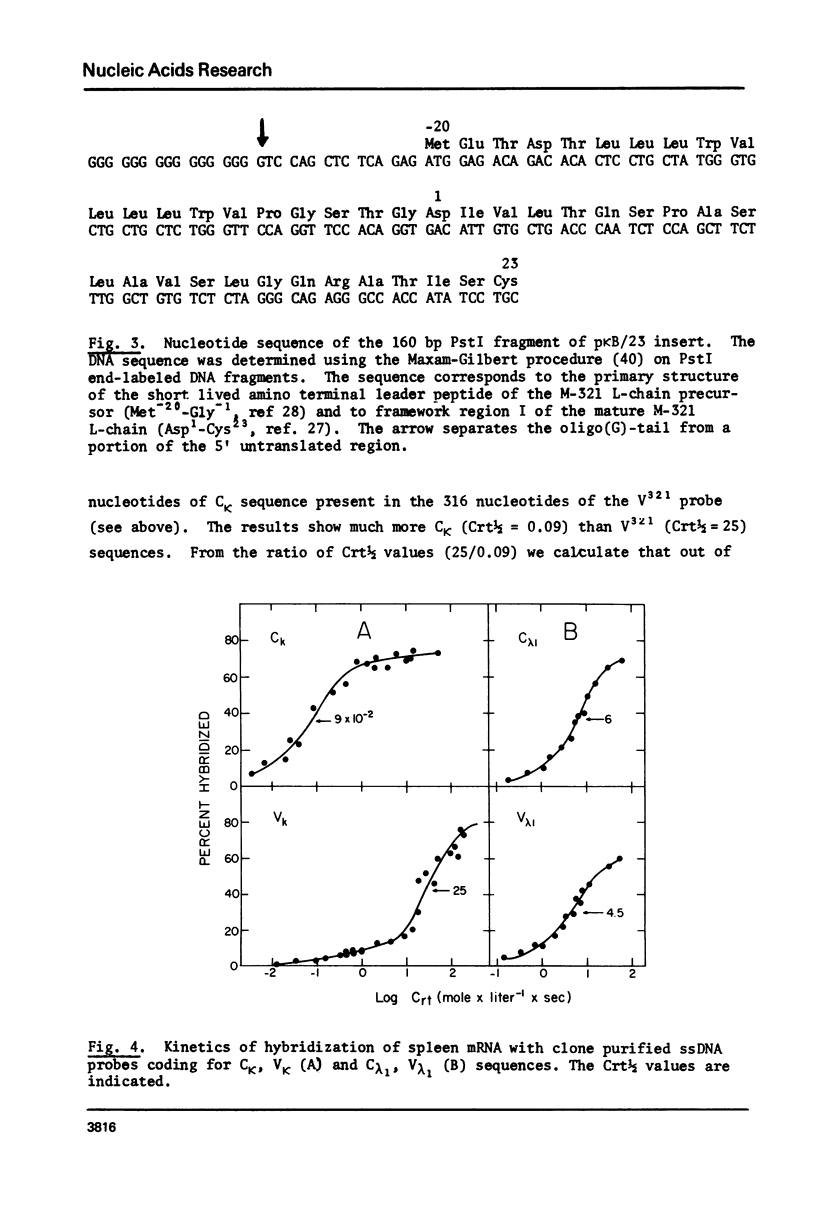
Critical to our understanding of the immune system diversity is the determination of the number of germ line V genes. The total number of V genes is given by the product: number of subgroups x number of germ line genes per subgroup. Studies of kappa chains and of embryonic DNA indicate 5-10 V genes per subgroup. Statistical analysis of the limited sequence data of mouse kappa chains suggest about 50 V kappa subgroups. We report here a general approach for direct estimation of the number of VL and VH subgroups expressed in normal spleen, and present data for V kappa. The kappa mRNA of the spleen is a heterogeneous population where different V kappa are linked to the same C kappa, i.e. C kappa equals total V kappa. The ratio C kappa/distinct V kappa approximates the number of subgroups since V kappa of the same subgroup cross hybridize while V kappa of different subgroups do not. This ratio was determined by molecular hybridization of cloned C kappa and V kappa DNA probes with spleen mRNA. The results indicate the expression of 280 V kappa subgroups in mouse. Assuming an average of 7 genes per subgroup, we estimate about 2000 V kappa germ line genes.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bentley D. L., Rabbitts T. H. Human immunoglobulin variable region genes--DNA sequences of two V kappa genes and a pseudogene. Nature. 1980 Dec 25;288(5792):730–733. doi: 10.1038/288730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Hozumi N., Tonegawa S. Sequences of mouse immunoglobulin light chain genes before and after somatic changes. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1133–1144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell A. L., Paskind M., Schwartz R. C., Sonenshein G. E., Gefter M. L., Baltimore D. Dual expression of lambda genes in the MOPC-315 plasmacytoma. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):65–67. doi: 10.1038/290065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein Y., Schechter I. Glutamine as a precursor to N-terminal pyrrolid-2-one-5-carboxylic acid in mouse immunoglobulin lambda-type light chains. Amino acid-sequence variability at the N-terminal extra piece of lambda-type light-chain precursors. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 1;165(2):347–354. doi: 10.1042/bj1650347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein Y., Schechter I. Primary structures of N-terminal extra peptide segments linked to the variable and constant regions of immunoglobulin light chain precursors: implications on the organization and controlled expression of immunoglobulin genes. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2392–2400. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesari I. M., Weigert M. Mouse lambda-chain sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2112–2116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Huang H., Davis M., Calame K., Hood L. An immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene is generated from three segments of DNA: VH, D and JH. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):981–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M., Webb E. A., Cory S., Adams J. M. Molecular cloning of seven mouse immunoglobulin kappa chain messenger ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2702–2710. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlyn P. H., Browniee G. G., Cheng C. C., Gait M. J., Milstein C. Complete sequence of constant and 3' noncoding regions of an immunoglobulin mRNA using the dideoxynucleotide method of RNA sequencing. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1067–1075. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joho R., Weissman I. L., Early P., Cole J., Hood L. Organization of kappa light chain genes in germ-line and somatic tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1106–1110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenhard-Schuller R., Hohn B., Brack C., Hirama M., Tonegawa S. DNA clones containing mouse immunoglobulin kappa chain genes isolated by in vitro packaging into phage lambda coats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4709–4713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., van deSande H. Chain length determination of small double- and single-stranded DNA molecules by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3787–3794. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Leder P. Sequences of five potential recombination sites encoded close to an immunoglobulin kappa constant region gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3450–3454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean D. J., Bell M., Potter M. Mechanisms of antibody diversity: multiple genes encode structurally related mouse kappa variable regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3913–3917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean D., Potter M., Hood L. Mouse immunoglobulin chains. Pattern of sequence variation among kappa chains with limited sequence differences. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):760–771. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M. Antigen-binding myeloma proteins of mice. Adv Immunol. 1977;25:141–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H. A molecular hybridization approach for the determination of the immunoglobulin V-gene pool size. Immunol Rev. 1977;36:29–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Hüppi K., Heinrich G., Tonegawa S. Sequences at the somatic recombination sites of immunoglobulin light-chain genes. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):288–294. doi: 10.1038/280288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Maki R., Kurosawa Y., Roeder W., Tonegawa S. Two types of somatic recombination are necessary for the generation of complete immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):676–683. doi: 10.1038/286676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Burstein Y. Identification of N-terminal methionine in the precursor of immunoglobulin light chain. Initiation of translation of messenger ribonucleic acid in plants and animals. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 1;153(3):543–550. doi: 10.1042/bj1530543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Further characterization of the mRNA coding for immunoglobulin light-chain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):228–235. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Region of immunoglobulin light-chain mRNA transcribed into complementary DNA by RNA-dependent DNA polymerase of avian myeloblastosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2511–2514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Use of antibodies for the isolation of biologically pure messenger ribonucleic acid from fully functional eukaryotic cells. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 23;13(9):1875–1885. doi: 10.1021/bi00706a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell H., Steinmetz M., Zachau H. G., Schechter I. An unusual translocation of immunoglobulin gene segments in variants of the mouse myeloma MPC11. Nature. 1980 Jul 10;286(5769):170–173. doi: 10.1038/286170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman J. G., Leder A., Edgell M. H., Polsky F., Tilghman S. M., Tiemeier D. C., Leder P. Multiple related immunoglobulin variable-region genes identified by cloning and sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3881–3885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman J. G., Leder A., Nau M., Norman B., Leder P. Antibody diversity. Science. 1978 Oct 6;202(4363):11–17. doi: 10.1126/science.99815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman J. G., Leder A., Nau M., Norman B., Leder P. Antibody diversity. Science. 1978 Oct 6;202(4363):11–17. doi: 10.1126/science.99815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman J. G., Max E. E., Leder P. A kappa-immunoglobulin gene is formed by site-specific recombination without further somatic mutation. Nature. 1979 Aug 2;280(5721):370–375. doi: 10.1038/280370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuring R. W., Sanders J. P., Borst P. A freeze-squeeze method for recovering long DNA from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 26;66(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90739-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valbuena O., Marcu K. B., Weigert M., Perry R. P. Multiplicity of germline genes specifying a group of related mouse kappa chains with implications for the generation of immunoglobulin diversity. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):780–784. doi: 10.1038/276780a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M. Purification and further properties of single-strand-specific nuclease from Aspergillus oryzae. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):192–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigert M., Gatmaitan L., Loh E., Schilling J., Hood L. Rearrangement of genetic information may produce immunoglobulin diversity. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):785–790. doi: 10.1038/276785a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigert M., Riblet R. Genetic control of antibody variable regions. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):837–846. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson A. R. The biological origin of antibody diversity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:467–500. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




